
DESCRIPTION The sequencing batch reactor (SBR) is a fill-and- draw activated sludge system for wastewater treatment. In this system, wastewater is added to a single “batch” reactor, treated to remove undesirable components, and then discharged. Equali zation, aeration, and clarification can all be achieved using a single batch reactor.
What is a sequencing reactor in wastewater treatment?
Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) A sequencing batch reactor is an activated sludge type wastewater treatment system that can carry out various treatment operations in one tank. A specific volume of wastewater, called a batch, is first screened to remove larger particles within the water.
What is sequencing batch reactor (SBR)?
The sequencing batch reactor (SBR) process is one of the most popular aerobic treatment technologies employed to treat municipal wastewater and wastewater from a variety of industries including refineries and petrochemical plants. This technology offers several operational and performance advantages over the conventional ASP.
What is a batch reactor in wastewater treatment?
A specific volume of wastewater, called a batch, is first screened to remove larger particles within the water. The reactor is a tank into which air is pumped to ensure that a sufficient supply of oxygen is present for aerobic biochemical processes to occur.
What is a SBR in wastewater treatment?
Sequencing Batch Reactors DESCRIPTION The sequencing batch reactor (SBR) is a fill-and-draw activated sludge system for wastewater treatment. In this system, wastewater is added to a single “batch” reactor, treated to remove undesirable components, and then discharged. Equali zation, aeration, and clarification can all be
What are the advantages of SBR?
An SBR reduces both the mechanical and manual resources used. Since it uses one tank which does all three tasks, equalize, aerate and clarify the water, it does not require separate tanks for each of these. Therefore, reduces the resources required. It is mostly automated and hence, does not require supervision.
How do you create a sequencing batch reactor?
0:233:10Sequencing Batch Reactor - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipStep one is the filling process for this example the SPR is treating mostly municipal waste withMoreStep one is the filling process for this example the SPR is treating mostly municipal waste with about 10 percent of the flow coming from industrial discharges.
Which reactors are used for waste water treatment?
Types of Reactors in Wastewater TreatmentThe Activated Sludge Process. ... The Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) Process. ... The Biodiscs Sewage Treatment. ... Wastewater Treatment Biofilters. ... Trickling Filters in Wastewater Treatment. ... Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR)
What type of reactor is used for SBR?
The SBR process utilizes a fill-and-draw reactor in which cBOD oxidation, nitrification, denitrification, and settling are accomplished in a single reactor (Figure 12). The reactor is operated in six or more stages, which accomplish in time what an MLE process does in space.
How does a batch reactor work?
Batch reactors are used for most of the reactions carried out in a laboratory. The reactants are placed in a test-tube, flask or beaker. They are mixed together, often heated for the reaction to take place and are then cooled. The products are poured out and, if necessary, purified.
What is Mbbr in wastewater treatment?
The Ecologix MBBR is a highly effective biological treatment process based on a combination of conventional activated sludge process and biofilm media. The MBBR process utilizes floating High Capacity MicroOrganism BioChips media within the aeration and anoxic tanks.
What is reactor in environmental engineering?
Chemical, biological, and physical processes in nature and in engineered systems usually take place in what we call “reactors.” Reactors are defined by a real or imaginary boundary that physically confines the processes. Lakes, segments of a river, and settling tanks in treatment plants are examples of reactors.
What is meant by activated sludge?
The activated sludge is a process with high concentration of microorganisms, basically bacteria, protozoa and fungi, which are present as loose clumped mass of fine particles that are kept in suspension by stirring, with the aim of removing organic matter from wastewater.
Which of the following principle types of reactors is related to trickling filter?
13. Which type of bacteria are used in trickling filters? Explanation: Facultative bacteria are used in trickling filters.
What is anaerobic sequencing batch reactor?
Anaerobic sequencing batch reactors (ASBR) operate in four cyclic steps: feed, reaction, settling and discharge. ASBRs allow typical biological anaerobic metabolism from substrate consumption to methane and carbon dioxide production.
What does SBR stand for?
styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), a general-purpose synthetic rubber, produced from a copolymer of styrene and butadiene.
In which stage of the SBR is aeration performed?
second stage aeration6. In which stage of the SBR is aeration performed? Explanation: The fixed or floating mechanical pumps are used or air is transferred into fine bubble diffusers fixed to the floor of the tank during the second stage aeration of the mixed liquor. 7.
What is sequencing batch reactor?
A sequencing batch reactor is an activated sludge type wastewater treatment system that can carry out various treatment operations in one tank . A specific volume of wastewater, called a batch, is first screened to remove larger particles within the water. The reactor is a tank into which air is pumped to ensure that a sufficient supply of oxygen is present for aerobic biochemical processes to occur. The addition of oxygen allows microorganisms to consume dissolved organic matter in the wastewater that are not removed by a screening or settling process. After a specified period of aeration, the wastewater in the reactor is allowed to settle. The sludge that settles on the bottom now primarily consists of the microorganisms that have fed on the organics in the wastewater. Sequencing batch reactors utilize an activated sludge treatment process. After the treated effluent is discharged, all but a small portion of the sludge, which is rich in microorganisms, is removed from the reactor. This helps quickly reestablish a population of microorganisms within the next batch of wastewater delivered to the reactor, reducing the amount of time necessary for treating each batch. Usually more than one reactor is needed so that while one batch of wastewater is being treated, additional flow can be directed elsewhere. The number of reactors ultimately depends on the expected volume of wastewater flow and the amount of time allowed for treatment of each batch in the reactor. A longer retention period produces less sludge and cleaner effluent.
Why do we need more than one reactor?
Usually more than one reactor is needed so that while one batch of wastewater is being treated, additional flow can be directed elsewhere. The number of reactors ultimately depends on the expected volume of wastewater flow and the amount of time allowed for treatment of each batch in the reactor.
How does SBR work?
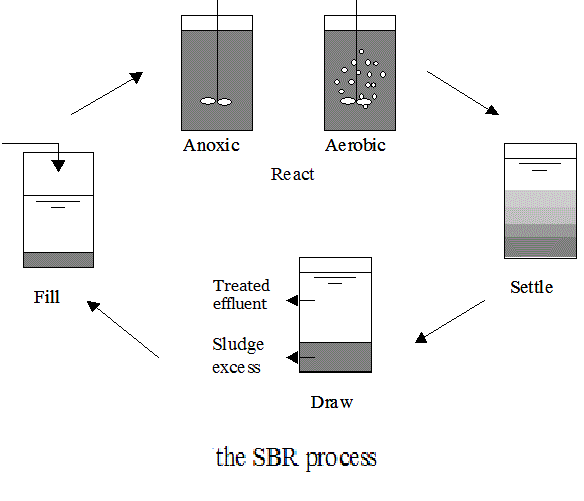
The SBR process utilizes a fill-and-draw reactor in which cBOD oxidation, nitrification, denitrification, and settling are accomplished in a single reactor ( Figure 12 ). The reactor is operated in six or more stages, which accomplish in time what an MLE process does in space. During Stage 1, influent wastewater is added to the nitrified MLSS, which remains in the reactor from the previous cycle. In Stage 2, anoxic mixing is applied to allow the nitrified wastewater to be denitrified under anoxic conditions. The first two stages can be combined so that anoxic mixing is applied during the fill stage. In Stage 3, the reactor is aerated to oxidize the remaining cBOD and nitrify TKN from the influent wastewater. In Stage 4, both aeration and mixing are turned off to allow the sludge to settle to the bottom of the reactor. During Stage 5, a portion of the reactor contents are decanted from the reactor above the level of the settled sludge. The last stage is a variable length ‘idle’ stage to allow for variations in the flow. Additional nitrogen removal can be accomplished in a similar manner as the four-stage Bardenpho process by cycling the air off after the aerobic reaction stage to drive denitrification through endogenous respiration or using an external electron donor. The aeration is cycled back for a short period to nitrify NH 4+ released because of endogenous decay and to improve sludge settling. There is no set time during the cycle for biomass wasting; however, it is normally accomplished during one of the reaction stages. SBRs are very flexible systems that can be operated continuously by having multiple reactors so that when one reactor finishes the fill stage the next one is ready to begin filling. They are particularly well suited to areas with large variations in flows, such as universities or resort communities, as the reactors can be taken offline and put back online during different seasons of the year.
Why are SBR processes so popular?
Major steps in the SBR operation cycle. These processes are popular because entire process uses one reactor basin. In areas where there is a limited amount of space, treatment takes place in a single basin instead of multiple basins, allowing for a smaller footprint.
What is SBR in sludge?
The sequencing batch reactor (SBR) is a fill and draw type modified activated sludge process, where four basic steps of filling, aeration, settling and decantation take place sequentially in a batch reactor.
Why is oxygen added to a reactor?
The addition of oxygen allows microorganisms to consume dissolved organic matter in the wastewater that are not removed by a screening or settling process.
Is soft drink wastewater biodegradable?
Because there are no nonbiodegradable substances used at soft drink bottling facilities, all wastewaters are amenable to biological treatment. As a general rule, no pretreatment other than screening and pH adjustment is required before secondary treatment by either an on-site biological treatment system or a POTW. Adjustment of pH is required because of the caustic used for cleaning bottles, pipes, tanks, floors, and mixing and bottling machinery.
What is sequencing batch reactor?
The sequencing batch reactor process ( SBR ) involves a single complete mix type reactor in which aeration takes place followed by clarification, when ce the designation “sequential”. Sludge settles when aeration is shut down and a drainage mechanism used to draw off the supernatant liquor. The various treatment stages take place at predetermined and programmable intervals, all the stage constituting a cycle.
How many tanks are needed for continuous infeed?
In order to achieve continuous infeed, a second tank has to be added, offset by half a cycle in the case of the example selected. However, at least four tanks will be required in order to ensure a constant outflow.
What is a sequential batch reactor?
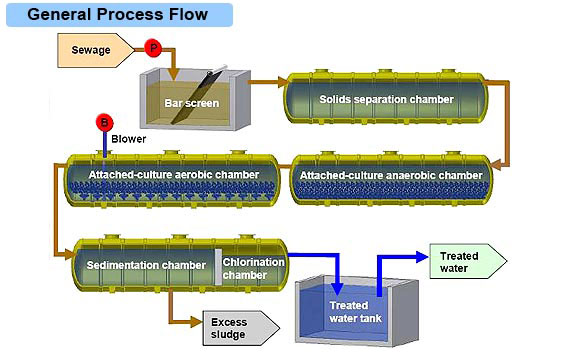
Sequencing batch reactors (SBR) or sequential batch reactors are industrial processing tanks for the treatment of wastewater. SBR reactors treat waste water such as sewage or output from anaerobic digesters or mechanical biological treatment facilities in batches. Oxygen is bubbled through the waste water to reduce biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand (COD) to make suitable for discharge into sewers or for use on land. While there are several configurations of SBRs the basic process is similar. The installation consists of at least two identically equipped tanks with a common inlet, which can be switched between them. The tanks have a “flow through” system, with raw wastewater (influent) coming in at one end and treated water (effluent) flowing out the other. While one tank is in settle/decant mode the other is aerating and filling. At the inlet is a section of the tank known as the bio-selector. This consists of a series of walls or baffles which direct the flow either from side to side of the tank or under and over consecutive baffles. This helps to mix the incoming Influent and the returned activated sludge, beginning the biological digestion process before the liquor enters the main part of the tank.
How is treated effluent removed from a SBR tank?
For large scale SBR facilities, treated effluent is removed from the SBR tank after the settle period by a moving weir decanter. The weir trough of the decanter is situated above top water level for both aeration and settling phases to prevent the accidental discharge of mixed liquor suspended solids. When operated during the decant phase of the cycle, the decanter is driven by an electro-mechanical actuator mechanism into the liquid at a uniform rate and a constant flow of clarified effluent is discharged from the tank. Upon reaching the pre-set designated bottom water level, the decanter then returns to its out-of-liquid rest position. The decanter is fitted with a scum guard that positively excludes surface scum and other floating material.
What is SBR technology?
SBR technology has the advantage of being much more flexible than conventional activated sludge processes in terms of matching reaction times to the concentration and degree of treatment required for a particular wastewater. For example, the SBR process allows for the following adjustments to be made in addition to those (such as sludge age and operating mixed liquor solids concentration) that can be made in an equivalent conventional process: total cycle duration duration of each phase within the process cycle pattern of inflow dissolved oxygen profile during aeration operating top water level operating bottom water level.
How is activated sludge treated?
Waste activated sludge can be further treated by aerobic or anaerobic processes, or thickened and dewatered before disposal. Most SBR processes use air blowers to provide aeration air to biologically degrade the organic components in the wastewater.
What is SBR treatment?
Basic treatment process. In its most basic form, the SBR system is a set of tanks that operate on a fill-and draw basis. Each tank in the SBR system is filled during a discrete period of time and then operated as a batch reactor. After desired treatment, the mixed liquor is allowed to settle and the clarified supernatant is then drawn from the tank.
When does sludge wasting occur?
Sludge wasting may take place near the end of React, or during Settle, Draw or Idle. Central to SBR design is the use of a single tank for multiple aspects of wastewater treatment.
What is the flow through system in a wastewater tank?
The tanks have a “flow through” system, with raw wastewater (influent) coming in at one end and treated water (effluent) flowing out the other. While one tank is in settle/decant mode the other is aerating and filling. At the inlet is a section of the tank known as the bio-selector.
Introduction
Background
- During the early 1900’s, the basic principles of biological degradation processes using activated sludge were established by Ardern, Lockett and Fowler amongst others. These researchers operated “fill-and draw” processes on crude sewage at Manchester in the UK and established the concept of sequencing batch reactors (SBR’s) operating a single biological reactor basin using r…
SBR Operating Principles
- Basic treatment process
In its most basic form, the SBR system is a set of tanks that operate on a fill-and draw basis. Each tank in the SBR system is filled during a discrete period of time and then operated as a batch reactor. After desired treatment, the mixed liquor is allowed to settle and the clarified supernata… - SBR Process Configuration
The essential components of SBR’s are: · reactor basin · waste sludge draw-off mechanism · aeration equipment · effluent decanter · process control system To accommodate continuous inflow of wastewater, the SBR system generally comprises either a storage / equalization tank a…
Modifications of The Sequencing Batch Reactor
- Large scale applications of SBR’s are generally based on the Cyclic Activated Sludge System (CASS™), or Intermittent Cycle Aerated Extended System (ICEAS®). These systems have been used on municipal wastewater treatment plants treating populations over 1 million. For example, the Dublin Bay WWTP in Ireland utilizes the ICEAS® process in 24 SBR basins stacked in two lev…
Further Reading
- Enrique Cabrera Jr., Peter Dane, Scott Haskins, Heimo Theuretzbacher-Fritz (2011) Benchmarking Water Services: Guiding water utilities to excellence , IWA Publishing.