The end of the pipe contains small holes to ensure the wastewater is evenly dispersed into the sea. This is the most cost effective option as the process uses very little energy, instead relying on gravity to transport the water. Sunlight, oxygen and ocean currents combine to continue the wastewater treatment process.
Full Answer
What sizes do our pipe launder systems come in?
Multotec’s pipe launder systems are now available in modular designs and can be successfully configured to any existing and new plant layout in the minerals processing industry. Our custom developed pipe launder systems are available in sizes of 200 mm, 250 mm, 315 mm, 355 mm and 400 mm diameters. They have been developed to cater for ...
Why choose Multotec pipe launder?
· Overview. Wastewater is used water. It includes substances such as human waste, food scraps, oils, soaps and chemicals. In homes, this includes water from sinks, showers, bathtubs, toilets, washing machines and dishwashers. Businesses and industries also contribute their share of used water that must be cleaned.
What are the features and benefits of a launder system?
· Launder covers help prevent such waste materials from ending up in your water and wastewater plant. Also, aside from preventing debris from entering the water stream, launder covers can also be helpful in containing localized odor emissions if present in the weir area (effluent trough). Choosing fiberglass launder covers helps seal water ...
How does a wastewater treatment plant work?
· Piping is an important part of modern water and wastewater treatment systems, water pumping units, desalination units, cooling water systems and others. Piping systems are like veins of modern plants. The piping is used to carry water, wastewater, chemicals and mixtures from one location to another. The design, construction, operation and ...

What is a Launder in wastewater treatment?
The launder is a slightly sloped channel that surrounds the clarifiers. The effluent water drains from the launder and flows into the main channel to the next process.
What are three types of wastewater treatment?
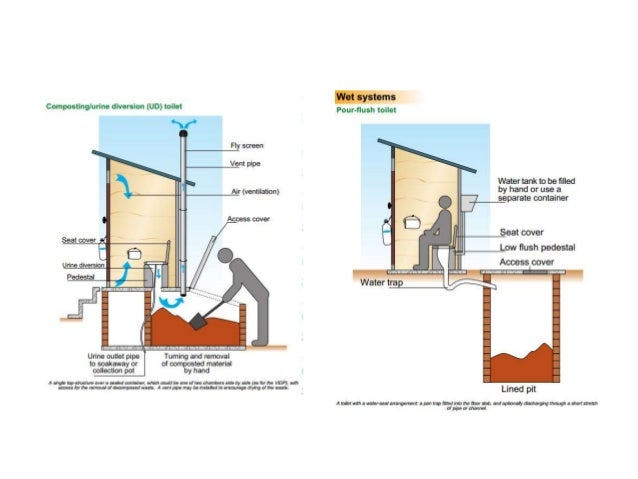
Types of wastewater treatment and application (disposal) systemsseptic tanks.aerated wastewater treatment systems (AWTS)biological filter systems.composting toilets (dry and wet)
What are the 5 stages of wastewater treatment?
Treatment StepsStep 1: Screening and Pumping. ... Step 2: Grit Removal. ... Step 3: Primary Settling. ... Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge. ... Step 5: Secondary Settling. ... Step 8: Oxygen Uptake. ... Sludge Treatment.
What are the 4 stages of wastewater treatment?
Four common ways to treat wastewater include physical water treatment, biological water treatment, chemical treatment, and sludge treatment. Let us learn about these processes in detail.
What is the best wastewater treatment system?
To give a short answer, the best system on the market is the ClearFox Nature. This is a totally non-electric plant, and it is the only non-electric treatment plant in the world that does not require replacement parts or media. So, the best non-electric sewage treatment plant is without a doubt the ClearFox Nature.
What is called sludge?
The residue that accumulates in sewage treatment plants is called sludge (or biosolids). Sewage sludge is the solid, semisolid, or slurry residual material that is produced as a by-product of wastewater treatment processes. This residue is commonly classified as primary and secondary sludge.
What is the purpose of a skimmer in primary treatment of wastewater?
An oil skimmer is designed to remove oil from both process water and wastewater. It helps a company remove oil from the surface of oily water at or near the point of origin (i.e. where oil initially contaminates water).
What is the process of wastewater treatment is commonly known?
The Correct Answer is Sewage treatment. Sewage treatment is a method for the extraction of pollutants from urban wastewater, consisting primarily of household wastewater and some industrial wastewater.
What is the first step in wastewater treatment?
The Wastewater Treatment ProcessStage One — Bar Screening. ... Stage Two — Screening. ... Stage Three — Primary Clarifier. ... Stage Four — Aeration. ... Stage Five — Secondary Clarifier. ... Stage Six — Chlorination (Disinfection) ... Stage Seven — Water Analysis & Testing. ... Stage Eight — Effluent Disposal.
How sludge is removed?
Digested sludge is put through large centrifuges that work in the same fashion as a washing machine spin cycle. The spinning centrifuge produces a force that separates the majority of the water from the sludge solid, creating a biosolid substance.
What materials Cannot be removed from wastewater?
When wastewater arrives at the treatment plant, it contains many solids that cannot be removed by the wastewater treatment process. This can include rags, paper, wood, food particles, egg shells, plastic, and even toys and money.
What are the four basic principles for water treatment?
4 Steps of Community Water TreatmentCoagulation and Flocculation. ... Sedimentation. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection.
Why are launder covers used in wastewater treatment?
Once launder covers are installed, they provide an attractive and extremely low maintenance structure to help eliminate algae growth problems.
What is a laundering cover?
Launder covers provide great protection against debris, harsh weather conditions, and direct sunlight. They further help protect weir structures, prevent algae growth, and are handy in avoiding the potential damage that algae can do to UV bulbs in treatment facilities using UV disinfection technology.
Why are launder covers important?
Launder covers are useful in providing a continuous protective environment above the effluent stream. They can contain odor and gas to prevent environmental pollution and protect the health of workers in the area.
What does it mean to choose a good launder cover?
Choosing high-quality launder covers would mean having long-term peace of mind that your water quality is preserved and wastewater treatment operations can function smoothly.
What is a custom launder cover?
Custom designed launder covers can be placed in rectangular and round tanks, providing essential value for different water and wastewater operations. This page will teach you everything about wastewater treatment.
Why use fiberglass launder covers?
Choosing fiberglass launder covers helps seal water environments in order to control odor.
Why do we need launder covers?
Strong winds, storms, snow, or heavy rainfall may introduce debris to water environments. Installing launder covers helps protect them against debris and damage caused by natural disasters. Choosing high-quality launder covers will ensure that they can withstand harsh weather conditions while protecting water and wastewater treatment plants.
Pressure drop through piping
Pressure drop or head loss occurs in all piping systems because of friction within the pipe and fittings and elevation changes. There are pressure drops because of turbulence caused by abrupt changes in direction, which is usually included in the overall frictional pressure drop.
Piping of tanks, drums and vessels
Fixed equipment such as tanks, filters, pressure vessels, drums and others have been widely used in water and wastewater treatment plants and water-related facilities. Low-pressure or atmospheric tanks and drums usually have relatively thin shells, and the loads transmitted from piping to shell nozzles of tanks and drums can be a concern.
Vents and drains
Provisions for low-point drains and high-point vents are typically needed for pressure testing, startup, cleaning (such as chemical cleaning), decommissioning and some other operational situations for piping systems of water-related facilities.
Conclusion
It is important to identify the various facets of piping in water and wastewater treatment plants and water-related facilities and consider these aspects and parameters in the process of piping design, engineering, installation and operation.
What stop is wastewater running through?
There is wastewater running though the room from various channels that move through the strainers before exiting toward the #2 stop in the process: the clarifiers.
What are the two types of wastewater?
Two categories of wastewater are directed to the facility in two different pipes: sanitary sewer wastewater and storm sewer wastewater. Stormwater, although it can carry with it debris, requires less treatment than sanitary wastewater, so the process for treatment is shorter. The process, once you flush your toilet, drain the washing machine, ...
Where is Fairhaven Wastewater Treatment Facility?
We start with the Fairhaven Wastewater Treatment Facility on Arsene Street in Fairhaven, which services some 1,780 Mattapoisett homes accounting for about 10-percent of the facility’s wastewater doodies. (We meant duties).
How long does it take for a clarifier to separate human waste?
It takes two to four hours in the clarifier to separate about 40 percent of the “sludge” (solid human waste) from the water.
How long does it take to drain a toilet?
The process, once you flush your toilet, drain the washing machine, take a shower or drain the bath, takes from a half day to one day to complete. From your house, the wastewater travels underground and is pulled by gravity through a pipe sized from 8 to 24 inches laid at a pitch, moving at a speed of 2 to 10 feet per second.
What stuff do people flush?
The stuff that some people flush – plastic objects, plastic bags, diapers, sometimes figurines and toys – gets collected, raked up with a pitchfork, and thrown into large plastic bins for disposal into the landfill.
What is the sound of gray water in the aeration basin?
In the aeration basins, the grayish water is bubbled and makes a sizzling noise as it is oxygenated and introduced to anaerobic bacteria that, as Furtado put it, literally eat [crap] and die. “You just let nature take over,” said Furtado.
What is the most commonly used pond in domestic wastewater treatment?
The most often used ponds in domestic wastewater treatment are the stabilization pond and facultative lagoon . The stabilization pond is designed to be aerobic throughout its depth and the facultative lagoon will be anaerobic at the bottom and aerobic at the top.
How much BOD can a pond eliminate?
The pond system can eliminate 80% to 90% of the BOD and reduce bacteria to levels comparable to other accepted oxidation types of treatment. This type of treatment system meets the needs of many small or rural communities due to low construction costs as well minimal operation and maintenance requirements.
How does a pond system stabilize organic matter?
Pond systems stabilize organic material through natural processes involving sunlight, water, nutrients, algae, atmospheric oxygen and bacterial action. Organic matter in the wastewater is broken down by aerobic bacteria and oxygen found in the pond.
What causes DO levels to decline in ponds?
Surface levels will have higher DO levels and as the depth increases it becomes more difficult for sunlight to penetrate therefore DO levels decline. Ponds use a multitude of organisms in the treatment process. Bacteria, algae, protozoa, and insects all have a part of the treatment in a pond system.
What is the purpose of stabilization ponds?
Stabilization ponds provide secondary biological treatment and are the most commonly used wastewater pond.
