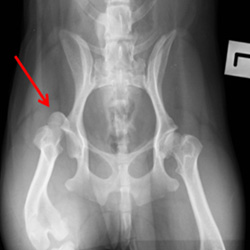
Hip dysplasia
In dogs, hip dysplasia is an abnormal formation of the hip socket that, in its more severe form, can eventually cause crippling lameness and painful arthritis of the joints. It is a genetic trait that is affected by environmental factors. It is common in many dog breeds, particularly the larger breeds, a…
How long does it take to recover from hip dysplasia?
Hip Dysplasia. Hip dysplasia is an abnormality in which the femur (thigh bone) does not fit together with the pelvis as it should. Symptoms are pain in the hip, limping and unequal leg lengths. Treatments include braces for babies, physical therapy and …
What doctor should I See to treat hip dysplasia?
Symptoms. Pain in the hip. Limping when walking. The sensation of instability in the hip. Unequal leg lengths. Loose or unstable hip joint. Treatment. Hip dysplasia treatment depends on the age of the affected person and the extent of the hip damage.
What are the treatments for hip dysplasia?
Dec 19, 2019 · Symptoms. The characteristic signs of hip dysplasia consist of the following: In babies and children: One leg being lengthier in comparison to the other; Limping while walking or running; Reduced flexibility around the hip joint towards one side; In teenagers and young adults: Osteoarthritis; Hip labral tear; Pain in the groin as in the case of prostatitis; Diagnosis And …
What exercises help hip dysplasia?
Sep 28, 2021 · Hip dysplasia occurs when the thighbone does not fit properly in the hip socket. The condition can cause a disrupted gait, pain, and …
What is the best treatment for hip dysplasia?
Does hip dysplasia always need treatment?
People with hip dysplasia don't always need surgery. If the condition is diagnosed early (in the prenatal period or during infancy) it can often be treated effectively with bracing. A mild hip dysplasia may not require any treatment, but may need to be monitored as the child grows.
What are hip dysplasia symptoms?
- Pain in the groin that increases with activity.
- Limping.
- A catching, snapping or popping sensation.
- Loss of range of motion in the hip.
- Difficulty sleeping on the hip.
How treatable is hip dysplasia?
What to avoid if you have hip dysplasia?
How painful is hip dysplasia?
When does hip dysplasia start?
Is hip dysplasia permanent?
What does hip dysplasia look like in adults?
What can hip dysplasia cause?
Can hip dysplasia cure itself?
Can you live with hip dysplasia?
What is hip dysplasia?
Overview. Hip dysplasia is the medical term for a hip socket that doesn't fully cover the ball portion of the upper thighbone. This allows the hip joint to become partially or completely dislocated. Most people with hip dysplasia are born with the condition. Doctors will check your baby for signs of hip dysplasia shortly after birth ...
Is hip dysplasia more common in girls?
Hip dysplasia tends to run in families and is more common in girls. The risk of hip dysplasia is also higher in babies born in the breech position and in babies who are swaddled tightly with the hips and knees straight.
What is the term for a hip socket that doesn't fully cover the ball portion of the upper thigh
Hip dysplasia is the medical term for a hip socket that doesn't fully cover the ball portion of the upper thighbone. This allows the hip joint to become partially or completely dislocated. Most people with hip dysplasia are born with the condition.
What is hip labral tear?
Hip dysplasia can damage the cartilage lining the joint, and it can also hurt the soft cartilage (labrum) that rims the socket portion of the hip joint. This is called a hip labral tear. In older children and young adults, surgery may be needed to move the bones into the proper positions for smooth joint movement.
How to tell if a baby has a limp?
Signs and symptoms vary by age group. In infants, you might notice that one leg is longer than the other. Once a child begins walking, a limp may develop. During diaper changes, one hip may be less flexible than the other.
How to check for hip dysplasia?
During well-baby visits, doctors typically check for hip dysplasia by moving an infant's legs into a variety of positions that help indicate whether the hip joint fits together well. Mild cases of hip dysplasia can be difficult to diagnose and might not start causing problems until you're a young adult. If your doctor suspects hip dysplasia, he ...
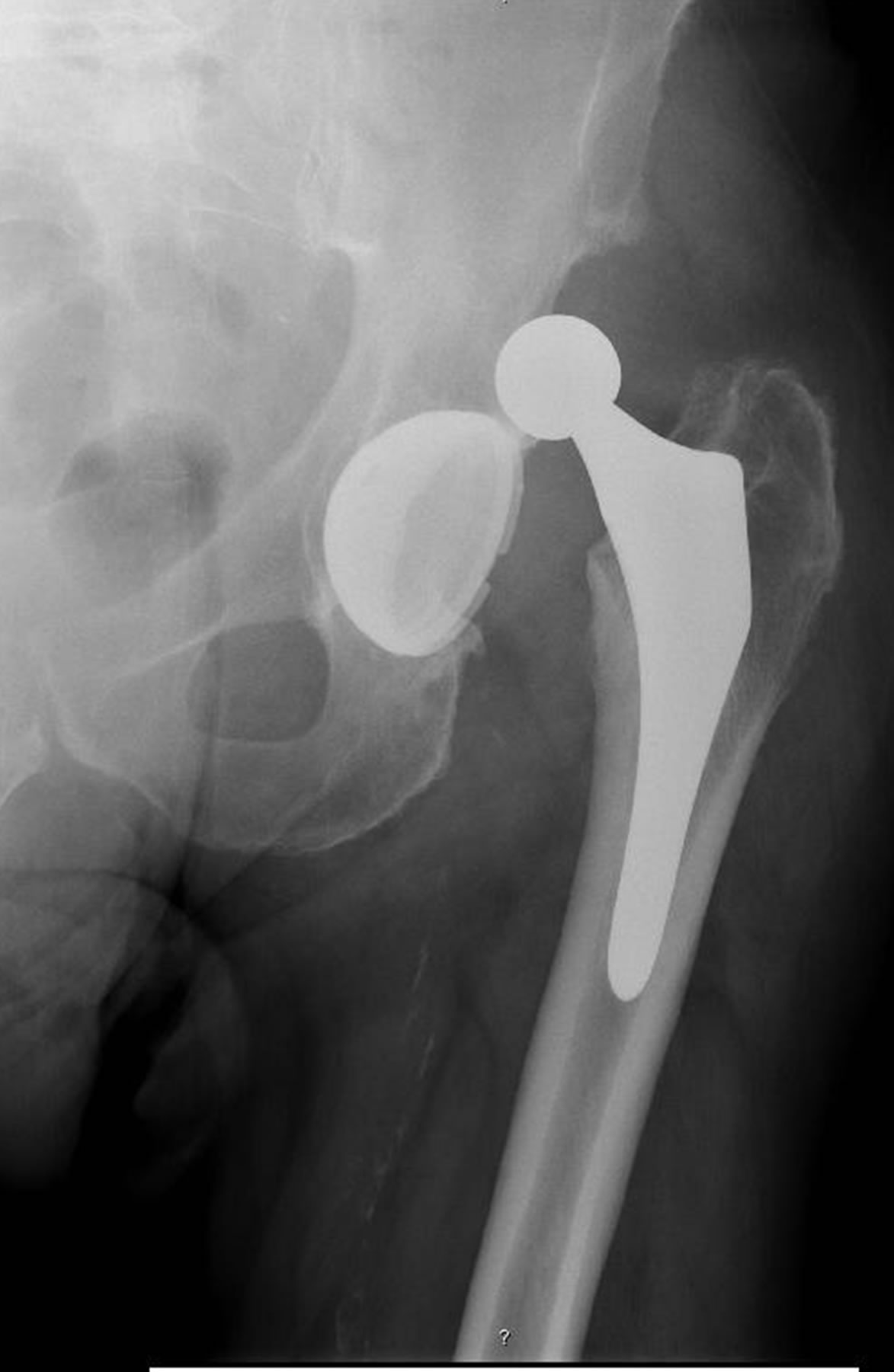
Can hip dysplasia be corrected?
Sometimes surgery is needed to fit the joint together properly. If the dysplasia is more severe, the position of the hip socket can also be corrected. In a periacetabular (per-e-as-uh-TAB-yoo-lur) osteotomy, the socket is cut free from the pelvis and then repositioned so that it matches up better with the ball.
What is the term for a hip socket that doesn't fully cover the ball portion of the upper thigh
Periacetabular osteotomy. Hip dysplasia is the medical term for a hip socket that doesn't fully cover the ball portion of the upper thighbone. In periacetabular (per-e-as-uh-TAB-yoo-lur) osteotomy, the socket is cut free from the pelvis and then repositioned so that it matches up better with the ball.
What is a Pavlik harness?
Pavlik harness. Infants are usually treated with a soft brace, called a Pavlik harness, that holds the ball portion of the joint firmly in its socket for several months. This helps the socket mold to the shape of the ball. Spica cast.
What to do before a doctor appointment?
What you can do. Before your appointment, you might want to: Write down any signs and symptoms you are experiencing, including any that may seem unrelated to the reason for which you scheduled the appointment. Make a list of any medications, vitamins or supplements that you're taking.
How to make an appointment for a syringe?
Before your appointment, you might want to: 1 Write down any signs and symptoms you are experiencing, including any that may seem unrelated to the reason for which you scheduled the appointment. 2 Make a list of any medications, vitamins or supplements that you're taking. 3 Consider taking a family member or friend along. Sometimes it can be difficult to remember all the information provided during an appointment. Someone who accompanies you may remember something that you missed or forgot. 4 Request that a copy of previous medical records be forwarded to your current doctor, if you're changing doctors. 5 Write down questions to ask the doctor.
What is hip dysplasia?
Hip dysplasia refers to the condition where the hip socket does not entirely encompass the area of the upper thighbone. This leads to either a partial or a complete dislocation of the hip joint.
How to tell if you have hip dysplasia?
The characteristic signs of hip dysplasia consist of the following: In babies and children: One leg being lengthier in comparison to the other. Limping while walking or running. Reduced flexibility around the hip joint towards one side. In teenagers and young adults: Osteoarthritis. Hip labral tear.
When does hip dysplasia develop?
Hip dysplasia often develops right from the time the baby is born and is more common in girls than in boys. In minor instances, symptoms are not prominently displayed until the teenage years or early twenties.
What is the ball and socket of the hip?
In a healthy individual, the ball and socket portions of the hip joint develop fully, from cartilage tissues to hardened bones, to enable proper movement around the hips and thighs. However, in case of hip dysplasia, the ball is not accurately fitted into the socket, resulting in the incomplete formation of the latter and causing difficulty in ...
What is the treatment for hip dysplasia?
Treatment measures for infants with hip dysplasia are soft braces called a Pavlik harness , which balances the ball segment of the joint intact in the socket for many months, until the position is corrected.
What are the symptoms of a swollen groin?
In teenagers and young adults: 1 Osteoarthritis 2 Hip labral tear 3 Pain in the groin as in the case of prostatitis
What is hip dysplasia?
Hip Dysplasia in Children: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment. For parents, a diagnosis of Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) brings a wide range of emotions and responses. Parents want to understand not only the condition, but what the future holds for their child after diagnosis.
How to tell if a child has a dislocated hip?
However, common symptoms of DDH include the leg on the side of the dislocated hip appearing shorter or turning outward, uneven folds in the skin of the thigh or buttocks and the space between the legs seeming wider than normal .
How many babies have hip instability?
Each year, approximately one in six newborns will have some type of hip instability and two to three out of every 1,000 infants will require treatment. Several mechanical, hormonal, genetic and environmental factors can lead to DDH.
What to do if your child has DDH?
If DDH is detected, your child will be referred to a pediatric orthopedist for treatment . As DDH presents differently for every child, treatment looks different as well. Stable hips that become normal do not need treatment. However, close follow-up and routine exams are required through the child’s development.
What are the symptoms of hip dysplasia?
If there are any symptoms, they can include: ♦ Limited range of motion. ♦ Uneven folds on the legs when legs are extended. ♦ Legs that turn outward.
What is hip dysplasia?
Hip dysplasia is an unstable hip. When the hip socket does not fully cover the ball portion of the thighbone, the hip joint becomes unstable and can become completely dislocated.
What is it called when your hip is unstable?
An unstable hip is known as dysplasia. Oftentimes a hip can become completely dislocated, which can be increasingly painful if left untreated. Lifestyle changes can help recovery and improve quality of life. Here’s what you need to know.
What age does hip dysplasia occur?
Hip dysplasia in adults is common after the age of 50 and can be caused by injury, weakened bone strength, or complications from having hip dysplasia as a child.
Can hip dysplasia be diagnosed at birth?
Hip Dysplasia Symptoms. There are not always going to be symptoms for hip dysplasia, so doctors will routinely check for this condition. If there are any symptoms, they can include: Screening for hip dysplasia happens at birth and regularly over the first year of life.
Can hip dysplasia be cured?
Hip dysplasia cannot be cured by dietary changes, but balanced nutrition can benefit your healing process and promote bone strength and health. Excess weight is also a contributing problem to hip dysplasia, so following a healthy diet reduces weight and can help prevent unnecessary stress to your joints.
What is the best diet for hip dysplasia?
The ideal diet to promote bone health and reduce the risk of bone disorders such as hip dysplasia includes plenty of proteins, fresh fruits and vegetables, healthy fats, and foods high in vitamin D and calcium.