Suggested Approach
| Medication Type | Indications | Contraindications, Side Effects |
| Adrenergic Agonists Epinephrine compound ... | Rarely used, limited effectiveness. | Systemic effects: hypertension, tachycar ... |
| Alpha Agonists Apraclonidine 0.5%; Brimo ... | Apraclonidine helps during and after ang ... | Apraclonidine is systemically safe; effe ... |
| Beta Blockers Nonselective: timolol, lev ... | 1st-line therapy for many, 2nd‑line for ... | Systemic effects: bronchospasm, bradycar ... |
| Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Topical: . ... | 1st- or 2nd-line in young children; add ... | Topical systemically safe. In children w ... |
Why is levodopa contraindicated in glaucoma?
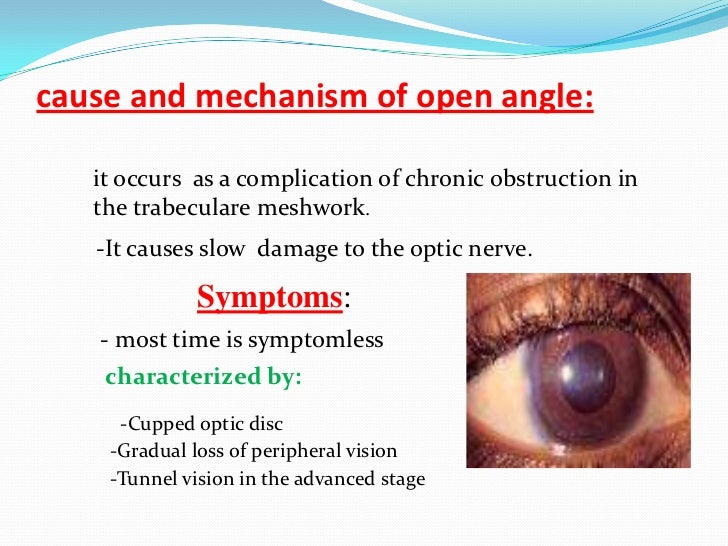
Glaucoma and Parkinson’s medication Glaucoma is a type of eye disease that damages the optic nerve, which, if untreated, can lead to loss of sight. If you have glaucoma you may have problems with some Parkinson’s medications, such as anticholinergic drugs and levodopa. ‘Open-angle’ glaucoma is the most common type of glaucoma.
What are common glaucoma contraindications?
You may be at higher risk for normal-tension glaucoma if you:
- Are of Japanese ancestry
- Have a family history of normal-tension glaucoma
- Have had certain heart problems, like an irregular heartbeat
- Have low blood pressure
Can I take guaifenesin with glaucoma?
No decongestants: Avoid mucinex-d if you have glaucoma, but standard Mucinex (guaifenesin) should be fine. Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers — it's anonymous and free! Doctors typically provide answers within 24 hours.
Is Claritin safe if you have glaucoma?
People with "narrow angle glaucoma" may have risk of acute angle closure glaucoma wit these medications. Common examples of these medication include Claritin (Loratadine), Sudafed, Allegra (fexofenadine), Singulair, Benadryl (Diphenhydramine), and Zyrtec.
What medications should be avoided with glaucoma?
Closed-Angle Glaucoma: Medicines to AvoidAntihistamines and decongestants.Asthma medicines.Motion sickness medicines.Some medicines used to treat depression (tricyclic antidepressants).
What drugs interact with glaucoma?
Conditions Contraindicated With Glaucoma Meds Calcium channel blockers such as Norvasc (amlodipine, Pfizer), Cardizem CD (diltiazem, Biovail) and Calan (verapamil, Searle) may interact with topical beta-blockers and can cause irregular heart beat.
What medication worsens glaucoma?
Several types of drugs have the potential to precipitate acute angle closure glaucoma. These include adrenergic, cholinergic and anticholinergic, antidepressants, anticoagulants and sulfa-based agents.
Is Atropine is contraindicated in glaucoma?
The product should not be used in patients with closed angle glaucoma. It is also contraindicated in patients with narrow angle between the iris and the cornea since it may raise intra-ocular pressure and precipitate an acute attack of closed angle glaucoma.
Which antiemetic is contraindicated for a patient with glaucoma?
Antihistamines are contraindicated in patients with glaucoma or an enlarged prostate gland.
Is propranolol contraindicated in glaucoma?
The effect of propranolol (Inderal) on the intraocular pressure (IOP) in glaucoma has been measured. Twenty-two patients completed the clinical trial. Propranolol in doses of 160 mg/d effectively lowered IOP in eyes with various types of open angle glaucoma.
Why are anticholinergics contraindicated in glaucoma?
Anticholinergics inhibit parasympathetic nerve impulses by selectively blocking the binding of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine to its receptor in nerve cells. This can cause glaucoma in individuals with narrow anterior chamber angles by dilating the pupil and causing pupillary block.
Can certain medications cause glaucoma?
Asthma and COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) medications include drugs such as Atrovent (ipratroprium bromide) or Spiriva (tiotropium bromide), and may be associated with angle-closure glaucoma attacks.
Can you take NSAIDs with glaucoma?
In conclusion, this meta-analysis suggests that topical NSAIDs may enhance the IOP lowering effect of topical PG analogues in glaucoma patients. Therefore, the short-term usage of topical NSAIDs may not be contraindicated in glaucoma patients receiving PG analogues to control IOP.
What is a contraindication of atropine?
Atropine generally is contraindicated in patients with glaucoma, pyloric stenosis, thyrotoxicosis, fever, urinary tract obstruction and ileus.
Is pilocarpine used for glaucoma?
Pilocarpine is used to treat glaucoma and other eye conditions. Vuity™ eye drops are used to treat presbyopia (age-related eye or vision problem). This medicine is available only with your doctor's prescription.
Why is pilocarpine contraindicated in inflammatory glaucoma?
Pilocarpine is also contraindicated in uveitis and secondary glaucoma because its miotic effect may predispose to posterior synechiae and pupillary occlusion. A frequently observed side effect after prolonged use is conjunctival hypersensitivity which warrants dilution of the pilocarpine or discontinuance of this drug.
What is angle closure glaucoma?
What is Angle-Closure Glaucoma? Angle-closure glaucoma, the second most common type, is a largely inherited disorder caused by a too-narrow angle in the passageway where aqueous fluid would normally drain. This type of glaucoma may occur in two ways:
Which medications can cause angle closure?
Medications such as Tagamet (cimetidine) and Zantac (ranitidine) are weak anticholinergics that may lead to angle-closure. Medications such as Norflex (orphenadrine) and Artane (trihexyphenidyl) have been associated with angle closure.
What are anticholinergic drugs?
Medications that have anticholinergic properties are used to treat the following medical conditions: Asthma and COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) medications include drugs such as Atrovent (ipratroprium bromide) or Spiriva (tiotropium bromide), and may be associated with angle-closure glaucoma attacks.
What is the effect of anticholinergic drugs on narrow angles?
Medications that have anticholinergic properties can adversely affect patients with narrow angles. Anticholenergic means that these drugs block the action of acetylcholine, a chemical messenger that transmits signals from one nerve cell to another nerve cell, muscle cell, or gland cell, for example.
What percentage of glaucoma cases are open?
Primary open-angle glaucoma is the most common type and accounts for 70-90 percent of all cases. Often there are no noticeable symptoms at early stages, and high intraocular pressure (IOP) is the most significant risk factor or indication that you are developing glaucoma.
How does glaucoma affect the optic nerve?
This type of glaucoma may occur in two ways: The chronic type progresses slowly and, like open-angle glaucoma, can result in optic nerve damage. There are no symptoms until there is an apparent loss off peripheral vision. Treatment includes medication and laser therapy.
How long does it take to get blind from glaucoma?
Without treatment, blindness can result in one or two days. Most medications that could adversely affect glaucoma, or increase the chance of developing glaucoma, have the potential to narrow the drainage angle of your eye, called the trabecular meshwork. This would prevent eye fluid from exiting properly resulting in high eye pressure.
Glaucoma Medication Side Effects & Contraindications
By: Paul M. Karpecki, OD, FAAO Clinical Director – PECAA Glaucoma affects millions of patients and is a very important part of optometry practice. We know there are inherent risks with almost all pharmaceutical agents and glaucoma medications are no exception.
Prostaglandin Analogs
There are no absolute contraindications for this class except patients with a known hypersensitivity to the ingredients. However a relative contraindication would include patients with ocular inflammatory conditions such as uveitis, CME or chronic inflammatory eye disease.
Beta Blockers
Contraindications to this class are generally patients with pulmonary or heart disease. This class of drugs can cause bradycardia or a lowered heart rate, lower blood pressure and can induce arrhythmia in susceptible patients. There are even reports that beta-blockers can raise serum triglyceride levels.
Selective Alpha Agonists
Although this class is generally well tolerated, there is a high incidence of allergy to certain brands within the class and many experts advise against the use of this class in children because of the potential CNS side effects.
Carbonic Anyhdrase Inhibitors
In this class we use both the topical and the oral forms (e.g. use or oral diamox in acute angle closure cases) and contraindications/side effects can vary between the two. For the topical form, there are few if any contraindications.
Download Our Ultimate Checklist for Running a Successful Optometry Practice
Carl Zeiss Vision is an industry leader in lenses and coatings, delivered through a nationwide network of Rx Laboratories.
What is the best treatment for glaucoma?
There are four prostaglandin analogs available in the United States as topical therapy for glaucoma: latanoprost, bimatoprost, travoprost, and tafluprost.
What is the goal of glaucoma treatment?
Goals of medication use in children with glaucoma include simplifying the schedule, minimizing side effects, and maximizing adherence.
What is the IOP for glaucoma?
The indication for intraocular pressure (IOP)-lowering medications in childhood glaucoma can vary with the context of diagnosis and disease course. When primary surgical intervention is advantageous (e.g., in primary congenital glaucoma, in which angle surgery has a high likelihood of success) or urgently necessary (e.g., angle-closure glaucoma, in which intervention can open the angle and allow it to regain function), medical therapy is adjunctive. In these cases, medications (topical and sometimes systemic) are used as a temporizing measure and often to help clear corneal edema ahead of surgery. Medications can also be used postoperatively if surgery has incompletely controlled the IOP.
What is the most widely used non-selective beta blocker?
The most widely used nonselective beta blocker in children is timolol, whereas betaxolol is the most widely used relatively beta‑1 selective beta blocker; both of these are most often available as 0.25% and 0.5% solutions, with viscous gel-forming versions also sold.
Is timolol a preservative?
Several commonly used glaucoma drops are available in the Unit ed States in preservative-free form including timolol (Ocudose 0.25% and 0.50% packets), Cosopt PF (dorzolamide 2%/timolol 0.5%), and Zioptan PF. Some patients might benefit from using preservative-free formulations of long-term glaucoma drugs including those with aniridia, allergic tendencies, and corneal pathology. Cost often makes these drugs difficult for patients to use in place of more affordable preservative-containing formulations.
How does carbonic anhydrase inhibitor work?
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (CAIs) work by reducing aqueous production; both oral and topical formulations are available and have been widely used in children with glaucoma. The topical CAIs are generally second-line medication for children, but might be preferred in small infants and in those with contraindications to beta blockers, alpha agonists, and prostaglandin analogs. CAIs lack the convenience of once-daily drugs, but add well to all other drug classes.
Is glaucoma a long term condition?
As in adult-onset glaucoma, long-term medication use in the management of pediatric glaucoma can be life-long, and each agent exposes the child to potentially undesirable side effects and incurs cost. The greater life expectancy in these young patients also means greater medication exposure and higher cumulative risk of potential side effects.
Does Promethazine cause glaucoma?
Promethazine has been reported to cause swelling of the lens that can in turn result in pupillary block. Ranitidine and cimetidine used in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux and peptic ulcers have also been shown to increase intraocular pressure in individuals known to have glaucoma.2,6. Botulinum toxin.
Does botulinum toxin cause glaucoma?
Botulinum toxin is thought to induce acute angle closure glaucoma due to its anticholinergic effect on the sympathetic ganglia, preganglionic and postganglionic nerve terminals of the parasympathetic nervous system.
Is it safe to take ipratropium bromide and salbutamol together?
They concluded that whilst it is relatively safe to use nebulized ipratropium bromide and salbutamol separately in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma, a combination of the two drugs carries a higher risk of inducing an attack of acute angle closure glaucoma in susceptible patients.
