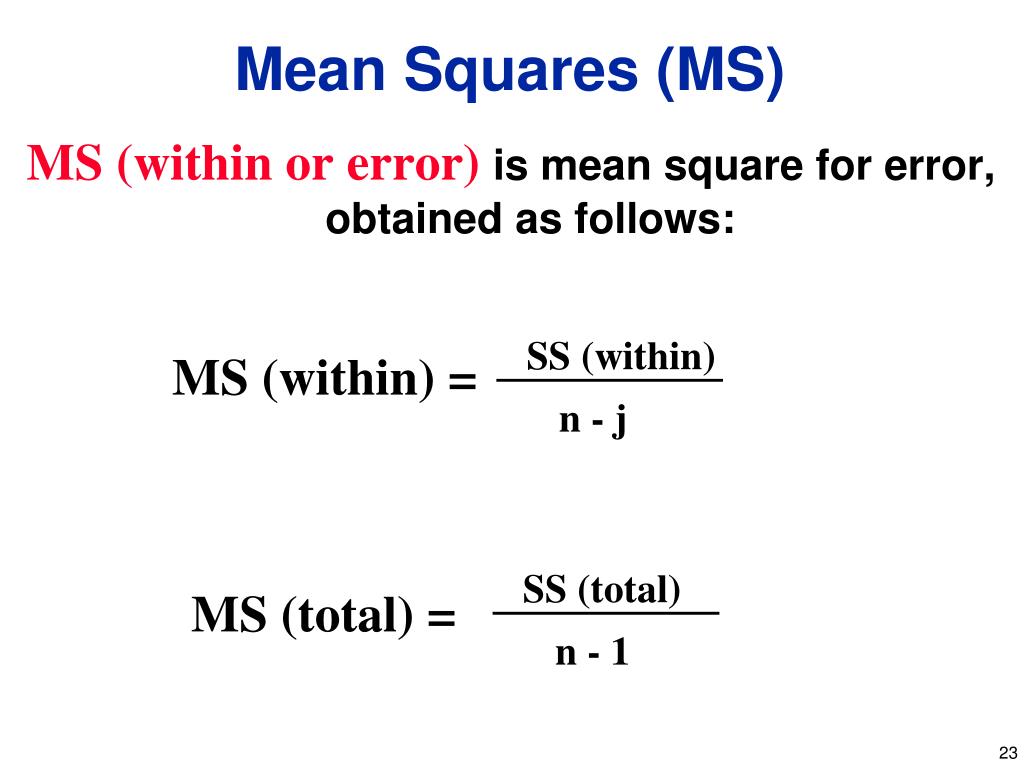
ANOVA In ANOVA, mean squares are used to determine whether factors (treatments) are significant. The treatment mean square is obtained by dividing the treatment sum of squares by the degrees of freedom. The treatment mean square represents the variation between the sample means.
When is it appropriate to use an ANOVA?
The one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) is used to determine whether there are any statistically significant differences between the means of two or more independent (unrelated) groups (although you tend to only see it used when there are a minimum of three, rather than two groups).
What does ANOVA stand for?
Analysis of variance, or ANOVA, is a technique from statistical interference that allows us to deal with several populations. To see what problems arise and why we need ANOVA, we will consider an example.
When to use one way ANOVA?
You should use a One-Way ANOVA in the following scenario:
- You want to know if many groups are different on your variable of interest
- Your variable of interest is continuous
- You have 3 or more groups
- You have independent samples
- You have a normal variable of interest
What does ANOVA test tell you?
What does two way Anova tell you?
- Determine whether the main effects and interaction effect are statistically significant.
- Assess the means.
- Determine how well the model fits your data.
- Determine whether your model meets the assumptions of the analysis.

What is treatment and block in ANOVA?
Blocks are individuals who donated a blood sample. Treatments are different methods by which portions of each of the blood samples are processed.
What is number of treatments in ANOVA?
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) for comparing means of three or more variables. Background. If we have, say, 3 treatments to compare (A, B, C) then we would need 3 separate t-tests (comparing A with B, A with C, and B with C). If we had seven treatments we would need 21 separate t-tests.
What is treatment in two way ANOVA?
Treatment Groups Treatement Groups are formed by making all possible combinations of the two factors. For example, if the first factor has 3 levels and the second factor has 2 levels, then there will be 3x2=6 different treatment groups.
What is the treatment and blocks?
The terms treatment and block are used to describe two classification factors used in analysis of variance (ANOVA). The rows often represent data from individuals who have been studied, blocks are therefore sometimes referred to as subjects instead of blocks.
What is a treatment in statistics?
The term “statistical treatment” is a catch all term which means to apply any statistical method to your data. Treatments are divided into two groups: descriptive statistics, which summarize your data as a graph or summary statistic and inferential statistics, which make predictions and test hypotheses about your data.
What are treatments in one-way ANOVA?
The term one- way, also called one-factor, indicates that there is a single explanatory variable (“treatment”) with two or more levels, and only one level of treatment is applied at any time for a given subject.
How do you interpret a two-way ANOVA?
Interpret the key results for Two-way ANOVAStep 1: Determine whether the main effects and interaction effect are statistically significant.Step 2: Assess the means.Step 3: Determine how well the model fits your data.Step 4: Determine whether your model meets the assumptions of the analysis.
How do you interpret ANOVA results?
Interpret the key results for One-Way ANOVAStep 1: Determine whether the differences between group means are statistically significant.Step 2: Examine the group means.Step 3: Compare the group means.Step 4: Determine how well the model fits your data.More items...
How do I report two-way ANOVA results?
When reporting the results of a two-way ANOVA, we always use the following general structure:A brief description of the independent and dependent variables.Whether or not there was a significant interaction effect between the two independent variables.More items...•
What is a treatment factor?
In an experiment, the factor (also called an independent variable) is an explanatory variable manipulated by the experimenter. Each factor has two or more levels (i.e., different values of the factor). Combinations of factor levels are called treatments.
What is treatment in experimental design?
In terms of the experiment, we need to define the following: Treatment: is what we want to compare in the experiment. It can consist of the levels of a single factor, a combination of levels of more than one factor, or of different quantities of an explanatory variable.
What is a block and treatment in statistics?
Blocking is where you control sources of variation (“nuisance variables“) in your experimental results by creating blocks (homogeneous groups). Treatments are then assigned to different units within each block.
What is Bonferroni's method used for?
Bonferroni's Method is used to compare treatment means. It controls the family error rate (α). Both the family error and the individual error rates are given in the output as shown below.
What is Fisher's least significant difference method?
The Fisher Least Significant Difference Method is used to compare treatment means. The method compares all pairs of means. It controls the error rate (α) for each individual pairwise comparison but does not control the family error rate. Both error rates are given in the output as shown below.
What is Tukey's method?
Tukey's Method is used to compare means from multiple processes. The method compares all pairs of means. It controls the family error rate (α). Both the family error and the individual error rates are given in the output as shown below.
When is ANOVA used?
The type of ANOVA test used depends on a number of factors. It is applied when data needs to be experimental. Analysis of variance is employed if there is no access to statistical software resulting in computing ANOVA by hand. It is simple to use and best suited for small samples.
What is the ANOVA test?
The ANOVA test is the initial step in analyzing factors that affect a given data set. Once the test is finished, an analyst performs additional testing on the methodical factors that measurably contribute to the data set's inconsistency.
What is ANOVA in statistics?
What is Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)? Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is an analysis tool used in statistics that splits an observed aggregate variability found inside a data set into two parts: systematic factors and random factors.
What is the difference between a one way and a two way ANOVA?
A two-way ANOVA is an extension of the one-way ANOVA. With a one-way, you have one independent variable affecting a dependent variable.
What are the two types of ANOVA?
There are two main types of ANOVA: one-way (or unidirectional) and two-way. There also variations of ANOVA. For example, MANOVA (multivariate ANOVA) differs from ANOVA as the former tests for multiple dependent variables simultaneously while the latter assesses only one dependent variable at a time.
How does ANOVA work?
ANOVA groups differences by comparing the means of each group and includes spreading out the variance into diverse sources. It is employed with subjects, test groups, between groups and within groups .
What is the F-ratio of an ANOVA?
If no true variance exists between the groups, the ANOVA's F-ratio should equal close to 1. 1:01.
What is the purpose of ANOVA?
The analyst uses the ANOVA to determine the influence that the independent variable has on the dependent variable. With the use of Analysis of Variance (ANOVA), we test the differences between two or more means. Most of the statisticians have an opinion that it should be known as “Analysis of Means.”.
What is the ANOVA test?
In the field of business application, the marketing experts can test the two different marketing strategies of the business to see that one strategy is better than the other one in terms of cost efficiency and time efficiency. There are different types of ANOVA test. And these tests depend on the number of factors.
What is one way ANOVA?
One way ANOVA is the unidirectional ANOVA. In this ANOVA, there are sole response variables as compared with the two-way ANOVA. It evaluates the impact of a sole factor. And this factor is determined that the samples are the same or not. Besides, it is also used to determine that there is any statistically significant difference between the mean of three or more independent groups.
What is ANOVA in statistics?
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a collection of statistical models. It is one of the significant aspects of statistics. The statistics students should be aware of the analysis of variance. But most of the statistics students find it challenging to understand analysis of variance. But it is not that difficult.
What are the columns in an ANOVA table?
There are one or two ways to show the ANOVA table, depending on the various factors. The significant columns in the ANOVA table are as follows: 1. “Source” – It means the source which is responsible for the variation in the data. 2. “DF” – degree of freedom of the data. 3. “SS”- the sum of the squares of the data.
What is repeated measures ANOVA?
Analysis of repeated measures ANOVA is the equivalent of the one-way ANOVA. It is also referred to as a within-subjects ANOVA with correlated samples. It is used to detect the difference between the related means. The procedure to perform the analysis of variance designs are using the general linear models approach. It includes the three between-subject terms. The Repeated measures designs are quite popular. The reason is it allows the subject to serve as their own control. Besides, it also improves the precision of the experiment with the help of reducing the size of the error variance of the F-tests. It uses the general linear model framework to perform the calculations.
What is the purpose of the initial stage of an ANOVA?
In the initial stage of the ANOVA test, analyze factors that affect a given data set. When the initial stage finishes, then the analyst performs additional testing on the methodical factors. It helps them to contribute to the data set with consistency measurably.
What is mean in ANOVA?
As we know, a mean is defined as an arithmetic average of a given range of values. In the ANOVA test, there are two types of mean that are calculated: Grand and Sample Mean.
When to use two way ANOVA?
It is an extension of one-way ANOVA. You can use the two-way ANOVA test when your experiment has a quantitative outcome and there are two independent variables.
How many IVs are there in an ANOVA?
Sometimes the test includes one IV, sometimes it has two IVs, and sometimes the test may include multiple IVs.
When was the ANOVA test invented?
The history of the ANOVA test dates back to the year 1918. It’s a concept that Sir Ronald Fisher gave out and so it is also called the Fisher Analysis of Variance.
When do we use a MANOVA?
When we have multiple or more than two independent variables, we use MANOVA. The main purpose of the MANOVA test is to find out the effect on dependent/response variables against a change in the IV.
Why do we use ANOVA?
You would use ANOVA to help you understand how your different groups respond, with a null hypothesis for the test that the means of the different groups are equal.
What is an ANOVA test?
One-Way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) tells you if there are any statistical differences between the means of three or more independent groups. What is ANOVA? ANOVA stands for Analysis of Variance. It’s a statistical test that was developed by Ronald Fisher in 1918 and has been in use ever since.
How to run an ANOVA in Qualtrics?
You can run an ANOVA test through the Qualtrics Crosstabs featuretoo . Here’s how: Ensure your “banner” (column) variable has 3+ groups and your “stub” (rows) variable has numbers (like Age) or numeric recodes (like “Very Satisfied” = 7) Select “Overall stat test of averages”. You’ll see a basic ANOVA p-value.
What is one way ANOVA?
The one-way ANOVA tests for an overall relationship between the two variables, and the pairwise tests test each possible pair of groups to see if one group tends to have higher values than the other. How to run an ANOVA test through Stats iQ.
What is the difference between a factorial and a one way ANOVA?
Two-way ANOVA does the same thing, but with more than one independent variable, while a factorial ANOVA extends the number of independent variables even further .
Can you run ANOVA with R?
You can also run ANOVA using any number of popular stats software packages and systems, such as R, SPSS or Minitab. A more recent development is to use automated tools such as Stats iQ from Qualtrics, which make statistical analysis more accessible and straightforward than ever before. Stats iQ and ANOVA.
Can you run an ANOVA with Stats IQ?
Stats iQfrom Qualtrics can help you run an ANOVA test. When you select one categorical variable with three or more groups and one continuous or discrete variable, Stats iQ runs a one-way ANOVA (Welch’s F test) and a series of pairwise “post hoc” tests (Games-Howell tests).

Fisher's Least Significant Difference Method
Bonferroni's Method
- Bonferroni's Method is used to compare treatment means. It controls the family error rate (α). Both the family error and the individual error rates are given in the output as shown below. 1. Comparisons: treatment combinations are being compared 2. Diff in Means: the difference in the two treatment means 3. Critical Value (where t is the t value for degrees of freedom and a confid…
Tukey's Method
- Tukey's Method is used to compare means from multiple processes. The method compares all pairs of means. It controls the family error rate (α). Both the family error and the individual error rates are given in the output as shown below. 1. Comparisons: treatment combinations are being compared 2. Diff in Means: the difference in the two treatment means 3. Critical Value (where q…
Pairwise Charts
- The program will chart the confidence interval for each pairwise combination. An example of the A*B combinations using Fisher's LSD method is shown below. A zero line is included. Any confidence intervals that do not cross the zero line are considered to have significant differences in the treatment means.