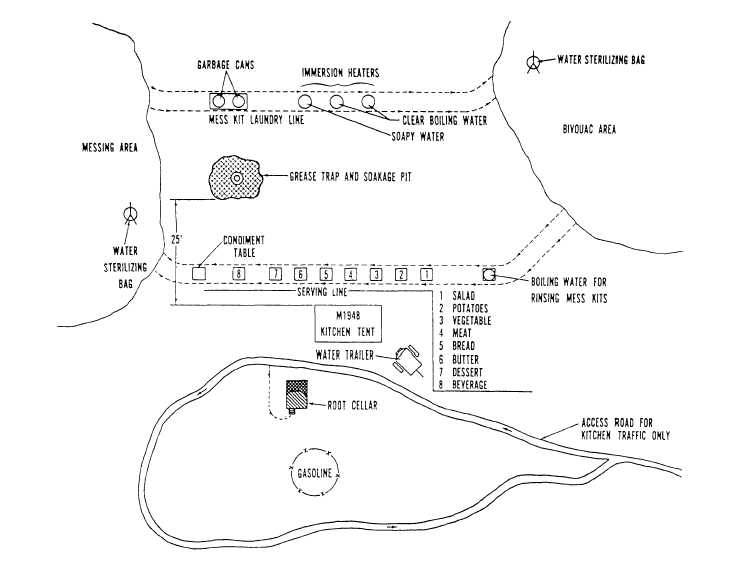
What is side water depth (SWD)?
Side Water Depth (SWD) is critical when the design engineer is planning new clarification equipment or evaluating existing units. Side water depth/sidewall depth is the depth of the water at the wall of the basin. The application of the clarifier/settling tank has a lot to do with the selection of the side water depth.
Do I need to use disinfection with the swtrs?
The SWTRs requires water systems to filter and disinfect surface water sources. Some water systems are allowed to use disinfection only for surface water sources that meet criteria for water quality and watershed protection.
What is smart water discharge (SWD)?
Control Logic Flow Chart Smart Water Discharge Definition (SWD): Constantly maintain the output (overboard water quality) at a predetermined set point by means of monitoring and controlling the vital process parameters (such as chemical injection rate and excursion skid).
How is the side water depth of a waste treatment unit determined?
With waste treatment primary units, the side water depth is determined by holding solids inventory. In chemical clarifiers, solids inventory and detention time for flocculation and separation might be the basis of determining the side water depth. For water treatment units, the same parameters as chemical clarifiers/settling tanks are used.
What is SWD in water?
Side Water Depth (SWD) is critical when the design engineer is planning new clarification equipment or evaluating existing units. Side water depth/sidewall depth is the depth of the water at the wall of the basin. The application of the clarifier/settling tank has a lot to do with the selection of the side water depth.
What is sidewater depth?
Side water depth refers to the measurement of the depth of the water contained in a basin. That depth measurement will be taken near the wall of a unit.
What does STP stands for in water?
Environmental Solutions, Sewage Treatment Plants (STP), Efflaent Treatment Plant(ETP) & Water Treatment Plant(WTP) | NT AGNI.
What does WTP mean in water?
Water Treatment PlantRelated to Water Treatment Plant (WTP. Water treatment plant means a process, device, or structure used to improve the physical, chemical, or biological quality of the water in a public water system.
How much BOD does a primary clarifier remove?
A typical primary clarifier removes 60 percent of suspended solids and 30 to 40 percent of Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD).
What is weir in clarifier?
A weir is an overflow structure that is used to alter flow characteristics. In the example below, the water is flowing from left to right. The black triangular-shaped structure is the weir. It is impeding the flow of water causing the water to flow over the weir structure.
What is ETP & STP?
Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) – The mechanism or process used to treat the wastewater prior to release into the environment or its reuse. Sewage Treatment Plant (STP) -It is the process of removing contaminants from wastewater and household / industrial sewage, both runoffs (effluents)
What is ETP and WTP?
Basically, there are three types of treatment plants for water – water treatment plant (WTP), effluent treatment plant (ETP), and sewage treatment plant (STP). All of them have the sole purpose of treating wastewater.
What are the 3 stages of wastewater treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment.
What are the 3 types of water treatment plant?
Types of water treatment plants:Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs) Sewage treatment refers to the procedure of getting rid of contaminants from wastewater. ... Effluent Treatment Plants (ETPs) ... Activated sludge plants. ... Common and combined effluent treatment plants.
Why is ETP important?
Effluent treatment plant cleans industrial effluents, contaminated water from outlet pipes, reservoir, rivers, lakes etc and reclaim the water resource for using in different purposes. ETP are mostly installed in industries like textile industry, Medicine manufacturing, leather industry, and chemicals industry.
What is OWC in plumbing?
Elevation. EWC. Electrical Water Cooler (Drinking Fountain)
Meanings of SWD in English
As mentioned above, SWD is used as an acronym in text messages to represent Side Water Depth. This page is all about the acronym of SWD and its meanings as Side Water Depth. Please note that Side Water Depth is not the only meaning of SWD.
Other Meanings of SWD
Besides Side Water Depth, SWD has other meanings. They are listed on the left below. Please scroll down and click to see each of them. For all meanings of SWD, please click "More". If you are visiting our English version, and want to see definitions of Side Water Depth in other languages, please click the language menu on the right bottom.
Why did Zhang focus on SWD and BMSB?
Zhang focused first on SWD and BMSB because they are fast becoming important agricultural and household pests, even though they are relatively new invasive species. The fragrance of a new pesticide. SWD revenue totaled $664,000 last year, which included $146,081 in recycling revenue that would go away.
Can SWD use resources?
Not only can SWD use a broad range of resources, but they also develop relatively rapidly. Phenology of spotted wing drosophila in the San Joaquin Valley varies by season, crop and nearby vegetation. These new SWD wells should be turned on to commercial operations prior to year-end, concluded the company.
Where are the SWD facilities located?
Geographic Distribution. A large portion of the U.S. SWD facilities are located in Texas due to the disproportionate amount of shale acreage in the state and the SWD conducive geology in Texas . Far fewer SWD facilities are located in other shale areas, such as the Marcellus and the Bakken, due to less favorable geological formations in those areas.
What factors come into play when securing a SWD?
When siting a SWD facility, a number of factors come into play, including demand, proximity, and geology.
Why are salt water disposal wells built?
Salt water disposal wells have very specific construction requirements in order to ensure that there will be no contamination of the area USDW or the environment in general. For example, in Texas, salt water disposal wells are constructed with three layers of casing to ensure that groundwaters are not impacted.
How has the oilfield waste water industry grown?
This growth has been largely driven by the increased volumes of waste water generated in the production of oil from shale plays. This post discusses the basics of salt water disposal which has become so important given the rise of hydraulic fracturing.
How important is proximity to waste water disposal?
Proximity can be viewed both as distance and as the availability of the appropriate infrastructure (roads) to efficiently transport the waste water from the production site to the disposal site. Transporting oilfield waste water is a significant expense and for obvious reasons is tied directly to the transport distance. Many oil and gas wells are located in remote areas where the existence of roads, or lack thereof, plays into the SWD location decision.
Why is shale oil a form of water?
Because shale hydrocarbon deposits are located in tight-rock formations, the naturally occurring produced water (water that is naturally present in oil and gas formations, referred to as “formation water”) to oil ratio is lower than in conventional reservoirs that have increased pore space and connectivity. To economically produce oil/gas from unconventional reservoirs composed of shale or tight (low permeability) rock, the reservoir must be stimulated by a process such as fracking.
What is salt water?
Even after treatment to extract some of the impurities, the resulting water (referred to as “salt water”) contains significant contaminants and must be handled carefully and disposed of properly. The method of salt water disposal depends on a number of factors: geology, technology, area infrastructure, and the prevailing climate in the area.
What is a salt water disposal well?
A salt water disposal well (SWD) operator was injecting produced water that was both trucked in from various local operations and also delivered by pipelines from two water- collection facilities. As a result, the water quality varied substantially and treatment was historically challenging. Water quality issues that faced the site included high bacteria levels, H
What biocide reduced the dissolved H?
Figure 3 – The figure above shows that BIOC16734A bio cide reduced the dissolved H
How to determine water clarity?
Water clarity was determined by comparing turbidity, frequency of sock filter changes, and volume of throughput using a Millipore filter. The goal was to reduce all of these levels and to determine optimal location and rate for the treatment.
What are the issues with dissolved solids?
These issues caused concerns related to safety, corrosion, and well plugging, and additional costs were incurred for maintenance, pumping energy and chemicals for managing the risks.
What is SWD in medical terms?
Shortwave diathermy (SWD) is a modality that produces heat by converting electromagnetic energy into thermal energy.
What is SWD thermal?
Short wave diathermy (SWD) is another deep-heating thermal modality, and it is probably the best thermal modality available to the practitioner.148 It is also a modality about which many practitioners have significant reservations, some of which are well founded and others are not. SWD uses short wave (10 to 100 MHz) electromagnetic energy to cause an increase in tissue temperature. To avoid radiofrequency interference with communications frequencies, the Federal Communications Commission regulates the frequencies of SWD available and has allocated three frequencies for medical use (13.56, 27.12, and 40.68 MHz).
How does diathermy work?
As with ultrasound, short-wave diathermy is thought to exert its therapeutic effects by both thermal and nonthermal mechanisms. The primary nonthermal mechanism associated with the use of therapeutic short-wave diathermy is via vibration induction of tissue molecules when exposed to radio waves. By changing the characteristics of the short-wave applicator, the clinician can target the specific type of tissue he or she wants to heat. By using an inductive applicator that generates a magnetically induced eddy of radio wave currents in the tissues, selective heating of water-rich tissues, such as muscle, can be obtained ( Fig. 124-8). By using a capacity-coupled applicator that generates heat via generation of an electrical field, selective heating of water-poor tissues, such as subcutaneous fat and adjacent soft tissues, can be accomplished.12 With either type of short-wave diathermy, metal must be avoided; the patient must remove all jewelry and treatment must be carried out on a nonconductive (e.g., wooden) treatment table. Implanted pacemakers, spinal cord stimulators, surgical implants, and copper-containing IUDs should never be exposed to short-wave diathermy to avoid excessive heating and thermal injury. Indications for short-wave diathermy mirror those listed for ultrasound, although the ability to heat subcutaneous fat and adjacent soft tissues not reached by superficial heat modalities and less well heated by ultrasound may lead the clinician to choose short-wave diathermy to treat painful conditions and other pathologic processes that are thought to find their nidus in more superficial tissues.13
Why is it important to follow the instruction manuals of shortwave diathermy devices?
Therefore, it is of utmost importance to strictly follow the instruction manuals of various shortwave diathermy devices in order to obtain optimal therapeutic results and to avoid any unwanted side effects.
How does pulsed SWD work?
Although several application systems are available for pulsed SWD, the most common is the induction method . In this setup, an electromagnetic field is generated by passing an electrical current through a coiled cable electrode, and the patient is placed into this field. Unlike the conductance method of diathermy, the patient is not actually part of the electrical circuit. A tissue's resistance to the passage of this electromagnetic field causes the increase in temperature. The inductance method has two main configurations. One uses a cable electrode that is coiled on top of or around the body part. The other has the cable precoiled into a "drum" that is usually on a swing arm attached to the unit. The drum setup is very popular because it is the easiest and safest to use.
How does short wave diathermy work?
Short wave diathermy uses electromagnetic radio waves to deliver heat down to 3 to 5 cm below the skin without overheating the skin and subcutaneous tissue.
Does shortwave diathermy produce endogenic heat?
Contrary to various thermotherapeutic methods which apply so-called egzogenic heat from outside, short wave diathermy produces an endogenic heat inside the tissues. A therapeutic dosage of shortwave diathermy can be estimated according to the following criteria:
