
Purpose of Heat Treatment of Steel
- To improve mechanical properties such as tensile strength, hardness, ductility, shock resistance, and resistance to corrosion.
- Improve machinability.
- To relieve the internal stresses of the metal-induced during cold or hot working.
- To change or refine grain size.
- Improve magnetic and electric properties.
- Increase resistance to wear, and corrosion.
How do you heat treat 4130 steel?
Things You'll Need
- Heat treat oven
- Trough of mineral oil
- Protective equipment
Why heat treat steel?
- Nickel makes the austenitic structure more stable, adds ductility and increases high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance.
- Manganese also stabilizes the austenitic structure, and it improves hot working properties.
- Molybdenum increases resistance to corrosion from chlorides.
How to temper steel?
Things you'll need:
- Blowtorch
- Two, six inch 1040 steel rods
- Fire extinguisher
- Safety glasses and gloves
- Cold tap water in a large bucket
What is the heat treatment for high carbon steel?
What you'll need:
- Heat Treating Furnace - I've got another instructable showing you how to build this furnace.
- Source of heat - I'm using a MAPP Gas torch. ...
- Tongs/pliers - something to hold the hot metal with.
- Quenching liquid. ...
- Container for the quench. ...
- Fire extinguisher. ...
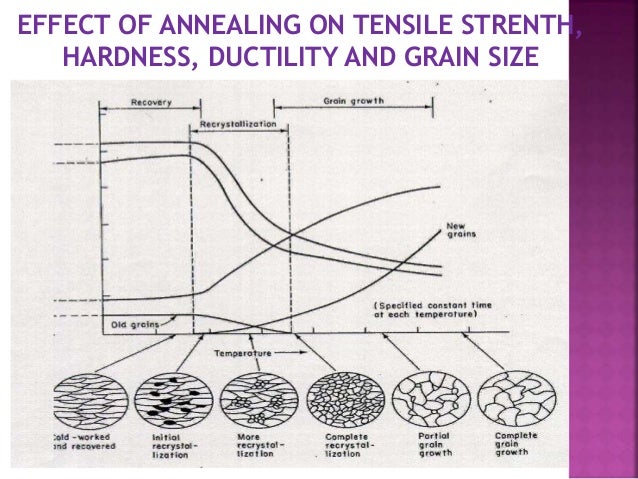
What is the purpose of heat treating steel?
Heat treating can soften metal, to improve formability. It can make parts harder, to improve strength. It can put a hard surface on relatively soft components, to increase abrasion resistance. It can create a corrosion-resistant skin, to protect parts that would otherwise corrode.
What is the purpose of heat treatment process?
What is the Purpose of Heat Treatment? Heat treatment is commonly used to alter or strengthen materials' structure through a heating and cooling process. It can be applied to both ferrous and non-ferrous metals, and there are a number of different methods of heat treatment.
How does heat treatment strengthen steel?
Hardening: When a metal is hardened, it's heated to a point where the elements in the material transform into a solution. Defects in the structure are then transformed by creating a reliable solution and strengthening the metal. This increases the hardness of the metal or alloy, making it less malleable.
What is heat treatment process for steel?
Heat treatment is the process of heating metal without letting it reach its molten, or melting, stage, and then cooling the metal in a controlled way to select desired mechanical properties. Heat treatment is used to either make metal stronger or more malleable, more resistant to abrasion or more ductile.
What is the benefits of heat treatment?
Heat treating can improve or change properties in metal, including:strength.hardness.ductility.toughness.wear resistance.elasticity.Magnetism (permeability)
What is the advantage and disadvantage of heat treatment?
Heat treatment helps to get desired mechanical and chemical properties, to reduce stresses, prevent stress relief and distortion when put to service. Whilst the disadvantages include distortion, surface oxidation or other contamination, added cost, etc.
How does heat treatment affect hardness?
The higher the cooling rate of the quenching, the smaller the size of the grain size. Hence, it will increase the hardness of the steel. When the cooling rate is very high, it will increase the strength of the steel but it will reduce the toughness and the ductility of the steel.
What does heat treating do to steel?
Heat treating is applied on steel to optimize grain structure for specific properties, relieve internal hardness, creating the hard cases and tough...
What temperature do you heat treat steel?
Mostly, heat treatment temperature lies in the region of the austenite phase. With carbon percentage, the appearance of austenite may very result i...
What are three stages of heat treatment?
What are the three stages of heat treatment in general, three stages of heat treatment are comprised of heating, soaking, and cooling of steel. Dur...
What is heat treatment process?
Heat treatment is a heating and cooling process employed on steel for achieving optimum properties and homogenized microstructure.
Does steel weaken with heat?
No, steel gets softened with heating as stresses are released and dislocations can move easily. This softening can be considered weakening but prop...
How do you harden steel after heat treat?
The heat treatment process is employed for hardening steel structures. During heat treatment, after soaking steel in the austenite region, it is qu...
What is difference between hardening and tempering?
Hardening of carbon steel improves the hardness of materials due to the formation of martensite. It is carried out by cooling the steel from the au...
Why is heat treatment important?
The casting of steel and primary metalworking processes induce various defects like coarse microstructure, segregation of impurities, softness, and...
What is normalizing heat treatment?
Normalizing heat treatment is employed for refining the grain structure. During this process, steel is heated in the austenite region then it is co...
How does steel change properties?
A third way to change the properties of steel is by adding alloying elements other than carbon that produce characteristics not achievable in plain carbon steel. Each of the approximately 20 elements used for alloying steel has a distinct influence on microstructure and on the temperature, holding time, and cooling rates at which microstructures change. They alter the transformation points between ferrite and austenite, modify solution and diffusion rates, and compete with other elements in forming intermetallic compounds such as carbides and nitrides. There is a huge amount of empirical information on how alloying affects heat-treatment conditions, microstructures, and properties. In addition, there is a good theoretical understanding of principles, which, with the help of computers, enables engineers to predict the microstructures and properties of steel when alloying, hot-rolling, heat-treating, and cold-forming in any way.
How fast does steel cool?
Cooling even faster—for instance, by quenching the steel at about 1,000° C per minute —results in a complete depression of carbide formation and forces the undercooled ferrite to hold a large amount ...
How to change the mechanical properties of steel?
Adjusting the carbon content is the simplest way to change the mechanical properties of steel. Additional changes are made possible by heat-treating—for instance, by accelerating the rate of cooling through the austenite-to-ferrite transformation point, shown by the P-S-K line in the figure. (This transformation is also called the Ar 1 transformation, r standing for refroidissement, or “cooling.”) Increasing the cooling rate of pearlitic steel (0.77 percent carbon) to about 200° C per minute generates a DPH of about 300, and cooling at 400° C per minute raises the DPH to about 400. The reason for this increasing hardness is the formation of a finer pearlite and ferrite microstructure than can be obtained during slow cooling in ambient air. In principle, when steel cools quickly, there is less time for carbon atoms to move through the lattices and form larger carbides. Cooling even faster—for instance, by quenching the steel at about 1,000° C per minute—results in a complete depression of carbide formation and forces the undercooled ferrite to hold a large amount of carbon atoms in solution for which it actually has no room. This generates a new microstructure, martensite. The DPH of martensite is about 1,000; it is the hardest and most brittle form of steel. Tempering martensitic steel — i.e., raising its temperature to a point such as 400° C and holding it for a time—decreases the hardness and brittleness and produces a strong and tough steel. Quench-and-temper heat treatments are applied at many different cooling rates, holding times, and temperatures; they constitute a very important means of controlling steel’s properties. (See also below Treating of steel: Heat-treating .)
How do alloying elements affect heat?
Alloying elements have a strong influence on heat-treating, because they tend to slow the diffusion of atoms through the iron lattices and thereby delay the allotropic transformations. This means, for example, that the extremely hard martensite, which is normally produced by fast quenching, can be produced at lower cooling rates.
What elements are used to improve hardenability?
Improved hardenability is achieved by adding such elements as manganese, molybdenum, chromium, nickel, and boron. These alloying agents also permit tempering at higher temperatures, which generates better ductility at the same hardness and strength.
How does strengthening metals work?
In principle, the strengthening of metals is accomplished by increasing the resistance of lattice structures to the motion of dislocations. Dislocations are failures in the lattices of crystals that make it possible for metals to be formed.
Can carbon be used as a weld strengthener?
This cannot be done by using only carbon as a strengthener, because carbon creates brittle zones around the weld, but it can be done by keeping carbon low and adding small amounts of other strengthening elements, such as nickel or manganese.
Why is steel heat treated?
The purpose of make steel been through heat treatment is to get the desired structure and properties.
Why do we use heat to treat steel?
It is the way of just only heat treats the steel surface, to change its mechanical properties of the surface. In order to just processing its surface without excessive heat being involved in the steel inside. Need to use the heat source with high energy density. It can give more heat energy to steel material per unit area.
How does heat treatment change the chemical composition of steel?
It is to change the chemical composition, structure, properties of steel material surface. It can change the chemical composition of the surface layer of the steel material. It is a big difference between chemical heat treatment and surface heat treatment. The way of chemical heat treatment is to heat the material in a medium (gas, liquid, solid) containing carbon, nitrogen or other alloying elements for a long time. To make the carbon, nitrogen, boron and chromium elements get into its surface layer. After that, also need other heat treatments sometimes, such as quenching and tempering. Carburizing, nitriding are the main methods of chemical heat treatment.
What are the two methods of surface heat treatment?
Make the surface of steel quickly get high temperature. The main methods of surface heat treat are flame quenching and induction heat treatment. The oxyacetylene, ethylene oxide and etc are the most useful heat sources.
What is thermomechanical treatment?
The way of thermomechanical treatment needs pressure processing deformation and heat treatment effectively combining. It will make the steel material get good hardness and toughness. The heat treatment performed in a vacuum atmosphere or in a vacuum is referred to as a vacuum heat treatment. It not only can prevent the alloy steel material ...
How does heat treatment affect steel?
Heat treatment is one of the most important processing for the production of machine fittings and mold base. It can control all kinds of properties of steel material. Such as wear resistance, corrosion resistance, magnetic properties and so on. Use the right heat treatment processing to the gear wheel, its useful life would longer than the general ones. By the way, adding some alloy elements to low-quality carbon steel would make it improve the properties. Then it can use to instead of some heat-resistant steel and stainless steel. And almost all of the alloy steel needs to be through heat treatment before the use. Heat treatment is one of the most effective technological skill to maximizing the potential properties of steel. The purpose of make steel been through heat treatment is to get the desired structure and properties. Truly understand the influence of heat treatment on the properties of steel. Then make an effective and right heat treatment way is really important.
What temperature should steel be kept at?
The steel after quenching is kept warm for a long time at a suitable temperature above room temperature and below 650 ° C and then cooled. These four steps will evolve different heat treatment according to the different temperature and the way of cooling.
What does heat treating do to steel?
Heat treating is applied on steel to optimize grain structure for specific properties, relieve internal hardness, creating the hard cases and tough core for impact applications. Depending upon the cycle given during heat treatment, steel properties can be controlled.
What is steel heat treating?
Steel Heat treating is a process which involves cooling and heating of a metal substance at usually high temperature and conditions. It is useful for softening, hardening, and changing physical properties. Moreover, you can manufacture various metal structures like glass by passing it through different thermal techniques.
What temperature do you heat treat steel?
Mostly, heat treatment temperature lies in the region of the austenite phase. With carbon percentage, the appearance of austenite may very result in variation of heat treatment temperature. To understand the importance of heat treatment temperature, follow the annealing article which can explain the importance austenite phase in achieving steel properties.
How do you harden steel after heat treat?
During heat treatment, after soaking steel in the austenite region, it is quenched in water, brine, or oil which drastically increases the hardness of steel. Details can be studies in the Effect of austenitizing temperature and Quenching media on hardening of steel.
What are three stages of heat treatment?
What are the three stages of heat treatment in general, three stages of heat treatment are comprised of heating, soaking, and cooling of steel. During soaking, the steel structure is homogenized for optimum properties throughout the microstructure.
What is difference between hardening and tempering?
On the other hand, Tempering is employed after the hardening process to induce ductility and toughness of quenched microstructure. The temperature of tempering is lower than that of the hardening process.
Why is heat treatment important?
The casting of steel and primary metalworking processes induce various defects like coarse microstructure, segregation of impurities, softness, and stresses. All these defects produced by initial manufacturing process can be recovered or removed using heat-treatment process.
Why is heat treatment important?
Heat Treatment is often associated with increasing the strength of material, but it can also be used to alter certain manufacturability objectives such as improve machining, improve formability, restore ductility after a cold working operation. Thus it is a very enabling manufacturing process that can not only help other manufacturing process, but can also improve product performance by increasing strength or other desirable characteristics.
What is the process of heating and cooling carbon steel?
Heat treating of steel is the process of heating and cooling of carbon steel to change the steel’s physical and mechanical properties without changing the original shape and size.
What is annealed hypereutectoid steel?
Annealed hypereutectoid steel with a microstructure of pearlite and cementite network generally gives poor machinability. Since cementite is hard and brittle, the cutting tool cannot cut through these plates. Instead, the plates have to be broken. Therefore, the tool is subjected to continual shock load by the cementite plates and results in a ragged surface finish. A heat-treating process which will improve the machinability is known as spheroidize annealing. This process will produce a spheroidal or globular form of carbide in a ferritic matrix as shown in the figure given below.
Why do you heat steel above the Acm line?
It may be noted that for hypereutectoid steels, it is necessary to heat it above the Acm line in order to dissolve the cementite network. The purpose of normalizing is to produce harder and stronger steel than full annealing, so that for some applications normalizing may be a final heat treatment.
How to normalize steel?
The normalizing of steel is carried out by heating approximately 100°F above the upper critical temperature line (A3 or Acm) followed by cooling in still air to room temperature. The normalizing temperatures range is shown in the figure given earlier for annealing temperature. It may be noted that for hypereutectoid steels, it is necessary to heat it above the Acm line in order to dissolve the cementite network. The purpose of normalizing is to produce harder and stronger steel than full annealing, so that for some applications normalizing may be a final heat treatment. Normalizing is also carried out to improve machinability.
Why is low carbon steel not spheroidized?
Low carbon steels are seldom spheroidized for machining, because they are excessively soft and gummy in the spheoridized conditions. The cutting tool will tend to push the material rather than cut it, causing excessive heat and wear on the cutting tip.If steel is kept too long at spheroidize-annealing temperature, the cementite particles will coalesce and become elongated, thus reducing machinability.
What is softening steel?
Softening is done to reduce strength or hardness, remove residual stresses, improve toughnesss, restore ductility, refine grain size or change the electromagnetic properties of the steel. Restoring ductility or removing residual stresses is a necessary operation when a large amount of cold working is to be performed, such as in a cold-rolling operation or wiredrawing. Annealing — full Process, spheroidizing, normalizing and tempering — austempering, martempering are the principal ways by which steel is softened.
What is heat treatment of metal?
The Heat treatment of steel is defined as the combination of the process which involves heating and cooling of metal or alloy in its solid state. The main purpose heat treatment is that to alter some physical and mechanical properties and obtain the desirable conditions without any change in chemical composition. Heat treatment is one of the main operations in the final fabrication process of many engineering components. The process of heating and cooling also occur incidentally during the manufacturing process such as welding, brazing, hot forming etc.
What is the purpose of heat treatment?
The main purpose heat treatment is that to alter some physical and mechanical properties and obtain the desirable conditions without any change in chemical composition. Heat treatment is one of the main operations in the final fabrication process of many engineering components.
Why is simple description not enough to distinguish the type of heat treatment?
While in some other cases simple description is not enough to distinguish the type of heat treatment because the same technique may be used to get different objectives. The time for which a metal keep at a certain temperature, the rate of heating and cooling, and other parameters are define the type of heat treatment.
Can metals be treated with heat?
All metals can be subjected to heat treatment but their thermal cycle may differ from one metal to another. Heat treatment has a significant impact on the properties of steel. Heat treatment is also used in many other nonmetallic materials like glass.
Why is manganese steel hot?
Because manganese-steel conducts heat extremely slowly, if it be heated suddenly its outside will become very hot and will expand greatly while its inside is still cool and has expanded but slightly. Though this unequal expansion may do no direct harm to such a tough substance as forged and toughened manganese steel, yet it may crack the relatively brittle untreated castings; and even if it does not it may defeat sudden cooling. This, to be effective, must start from a very high temperature. If either castings or forgings of manganese-steel be heated quickly, at the time when their outside is as hot as it can safely be, their inside may yet be so cool as to receive no important benefit from the sudden cooling.
How accurate is the temperature of a piece treated?
In cases where extreme accuracy is especially desirable, I believe that the error in measurement rarely exceeds 3° C. I here refer not to the error in the absolute temperature, but to the error in the difference between temperatures, the effects of exposure to which are to be compared closely, i.e., the relative error.
What is the toughening of manganese steel?
The remarkable toughening which manganese-steel undergoes when cooled suddenly is now generally known under the name of “ water-toughening.” Some attempts to learn the conditions under which this toughening occurs are recorded in Tables 5 and 6. The former treats chiefly of variations in the rate of cooling as affecting unforged cast manganese-steel; the latter treats of variations in the temperature at which cooling begins, and of the persistence of the toughness due to quick cooling, in case of forged manganese-steel.
What temperature does a bar of a sandpaper bar bend?
white heat to a moderate red heat. The interior of the bar, doubtless, had lost very little heat. These two bars bent 180° and 205° respectively before cracking, and 200° and 210° respectively, before breaking. This result is what we should anticipate. The material conducts heat so slowly that its interior is not considerably cooled during moderate exposure to cold air. These bars actually bent farther than those (E and F) which were quenched immediately and uninterruptedly ; but the latter were injured by flaws.
What temperature should reheating be?
from which we now quench; hence the injury in this case reaches a maximum with a certain degree of reheating, between 542° C. and 808° C. If the temperature to which we reheat be above that of maximum harm, the benefit caused by the re-quenching increases faster with further rise in temperature than the injury caused by the reheating itself does; and hence the higher we reheat the better.
Does increasing violence of cooling increase toughness?
In the present experiments, however, made on thin pieces of regular constant section, every increase of violence caused a further increase of toughness; in other words, no limit was found beyond which further increasing the violence of cooling failed to increase toughness further.
Does cooling cause steel to be brittle?
Such residual stress should in itself tend to make the steel brittle. Suddenness of cooling then should have two opposite effects on toughness; directly it increases toughness; indirectly, through causing stress, it should lessen toughness.
What is steel used for?
Steel is essential for the modern world and is used in commercial and residential buildings, automobiles, airplanes, and oil rigs and pipelines. It has unique properties such as strength, malleability, and durability, and is suited to many applications. This article will discuss how heat treatment changes steel’s properties.
Why is controlled heat treatment important?
Therefore, controlled heat treatment of steel is crucial to ensure that it has the desired properties necessary for its intended use, and heating and cooling in different ways cause different structural changes that can fine-tune the desired structure.
What are the limitations of carbon steel?
Carbon steel is an incredibly versatile material, and its properties can be altered. The material does have its limitations, including: 1 Limited hardness, tensile strength, and hardness in its untreated form 2 Poor oxidation resistance 3 Cracking and distortion caused by drastic quenching 4 Can undergo softening at high temperatures 5 Large sections are difficult to harden
How does annealing change metals?
Annealing. Annealing changes a metal's properties by altering and realigning the grain structure using heat, making the metal softer and more ductile. In this process, the steel is heated to just above its re-crystallization point, allowing it to cool slowly. A full anneal involves leaving the metal to cool in the furnace itself.
How hot can steel be?
Depending on steel’s carbon content, they can be heated to specific temperatures (780 o C to 850 o C) and then quenched in oil or water to cool them quickly. The higher the carbon content, the lower the temperature needed to harden the metal.
What is cast iron?
Known as cast iron, this material laid the groundwork for much of the modern world. To increase the iron content again to make steel, the iron was subjected to a carburization process. Over the next few centuries, much progress was made in the steel-making industry to refine the process and manufacture the material we are all familiar with today.
How was iron made?
Early iron was produced in small shaft furnaces, forming as solid lumps or blooms, which were then forged into wrought iron. When steel has a carbon content of over 0.3%, it becomes brittle. By 900 BC, Egyptians were starting to use heat to reduce this. There is evidence that they could produce heat-treated steel in China by ...
What is the purpose of heat treating metals?
grain size and composition) is one of the most effective factors that can determine the overall mechanical behavior of the metal. Heat treatment provides an efficient way to manipulate the properties of the metal by controlling the rate of diffusion and the rate of cooling within the microstructure. Heat treating is often used to alter the mechanical properties of a metallic alloy, manipulating properties such as the hardness, strength, toughness, ductility, and elasticity .
How does heat treatment work?
These tend to consist of either cooling different areas of an alloy at different rates, by quickly heating in a localized area and then quenching, by thermochemical diffusion, or by tempering different areas of an object at different temperatures, such as in differential tempering.
How is annealing done?
In ferrous alloys, annealing is usually accomplished by heating the metal beyond the upper critical temperature and then cooling very slowly, resulting in the formation of pearlite. In both pure metals and many alloys that cannot be heat treated, annealing is used to remove the hardness caused by cold working. The metal is heated to a temperature where recrystallization can occur, thereby repairing the defects caused by plastic deformation. In these metals, the rate of cooling will usually have little effect. Most non-ferrous alloys that are heat-treatable are also annealed to relieve the hardness of cold working. These may be slowly cooled to allow full precipitation of the constituents and produce a refined microstructure.
What color is tempered steel?
Very hard tools are often tempered in the light to the dark straw range, whereas springs are often tempered to the blue. However, the final hardness of the tempered steel will vary, depending on the composition of the steel. Higher-carbon tool steel will remain much harder after tempering than spring steel (of slightly less carbon) when tempered at the same temperature. The oxide film will also increase in thickness over time. Therefore, steel that has been held at 400˚F for a very long time may turn brown or purple, even though the temperature never exceeded that needed to produce a light straw color. Other factors affecting the final outcome are oil films on the surface and the type of heat source used.
How does salt heat up?
Parts are loaded into a pot of molten salt where they are heated by conduction, giving a very readily available source of heat. The core temperature of a part rises in temperature at approximately the same rate as its surface in a salt bath.
What is a heat treating schedule?
Complex heat treating schedules, or " cycles," are often devised by metallurgists to optimize an alloy's mechanical properties. In the aerospace industry, a superalloy may undergo five or more different heat treating operations to develop the desired properties. This can lead to quality problems depending on the accuracy of the furnace's temperature controls and timer. These operations can usually be divided into several basic techniques.
Why are nonferrous alloys annealed?
Most non-ferrous alloys that are heat-treatable are also annealed to relieve the hardness of cold working. These may be slowly cooled to allow full precipitation of the constituents and produce a refined microstructure. Ferrous alloys are usually either " full annealed" or " process annealed.".
Why do we heat treat steel?
This is another heat treatment process that helps to increase the resilience of steel. Iron-based alloys are usually hard but often too brittle for certain applications. Tempering helps to alter the hardness, brittleness, and ductility of the metal. This is in a bid to make the machining process easier.
Why use heat treated metal?
Using effectively heat-treated metal parts ensures the effective and cost-effective running of machines. Furthermore, the product will be a lot more efficient, even for the toughest applications. Also, there may be the need for extremely hard metals for some applications.
How Does Heat Treatment of Metals Work?
Although there are many types of heat treatment, they follow similar processes. The first step involves the heating of the metal or alloy to the required temperature. Sometimes, the temperature goes up to 2400°F. It is held at the temperature for a specified amount of time before cooling.
What is the process of making metal harder?
This usually made the metal a lot harder and less brittle. This is a basic process called heat treatment of metals. Modern machining and metalworking processes are now more precise and sophisticated. Many different techniques help shape metals for various purposes.
What would happen if metals were not heat treated?
Without the heat treatment of metals, there may be nothing like metal parts for devices and equipment. Even if they existed, they wouldn’t function in the right manner. For example, non-ferrous metal parts would be too weak for several applications.
Why does cooling occur?
Then, cooling occurs to harden the heated material. The process aims towards changing the microstructure of the metal. Also, it helps to bring out desired mechanical, chemical, and physical characteristics. The alteration of these properties benefits the working life of the component involved.
What happens to the microstructure of a metal when it is hot?
While the metal is hot, the microstructure changes . This is the physical structure of the metal. The change in the structure ultimately results in a change in the physical properties of the metal. The ‘soak time’ is the amount of time used to heat the metal.
Overall Steel Heat Treatment
- Heat treat the hole steel, then cooling it at the right temperature. It can change the whole mechanical property. It includes annealing, normalizing, quenching, tempering. And the quenching and tempering are closely related. People always used together. Each part of them is indispensable.
Annealing
- Heat the material to make it get the appropriate temperature. According to the size and material of it to choose the right time of heat preservation. Then make it cool slowly. The purpose is to make the material get ready for quenching. Make the material internal structure get equilibrium state. Then it will get great technological properties.
Normalizing
- The steel sample is heated to a suitable temperature and then cooling it in the air. Its influence on the material is the same as annealing. But the resulting tissue is finer. People usually use it to improve the free cutting performance of mild steel. And sometimes use it to do finally heat treatment for the material of lower request.
Quenching
- Heat the steel material to get the right temperature and keep it. Then make it fast cooling in the transmitter substance of water, oil, inorganic salts and etc. After quenching, steel material will become harder. But at the same time, it becomes brittle.
Tempering
- In order to make steel get lower brittleness. The steel after quenching is kept warm for a long time at a suitable temperature above room temperature and below 650 ° C and then cooled. These four steps will evolve different heat treatment according to the different temperature and the way of cooling. In order to get great strength and toughness, need to do the processing of combining q…
Surface Heat Treatment
- It is the way of just only heat treats the steel surface, to change its mechanical properties of the surface. In order to just processing its surface without excessive heat being involved in the steel inside. Need to use the heat source with high energy density. It can give more heat energy to steel material per unit area. Make the surface of steel quickly get high temperature. The main method…
Chemical Heat Treatment
- It is to change the chemical composition, structure, properties of steel material surface. It can change the chemical composition of the surface layer of the steel material. It is a big difference between chemical heat treatment and surface heat treatment. The way of chemical heat treatment is to heat the material in a medium (gas, liquid, solid) containing carbon, nitrogen or ot…