Tertiary treatment of wastewater
Wastewater
Wastewater, also written as waste water, is any water that has been adversely affected in quality by anthropogenic influence. Wastewater can originate from a combination of domestic, industrial, commercial or agricultural activities, surface runoff or stormwater, and from sewer inf…
What is tertiary water treatment?
Tertiary water treatment is the final stage of the multi-stage wastewater cleaning process. This third stage of treatment removes inorganic compounds, bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Removing these harmful substances makes the treated water safe to reuse, recycle, or release into the environment.
What is advanced water treatment and why does it matter?
One area of focus is advanced water treatment processes, which help streamline how water is obtained and used. The planet is made up of 71 percent water, but what does it consist of, and why does it matter? Water makes the world go round and is a critical part of life as we know it. Without water, very little could survive.
What is the final stage of the tertiary wastewater treatment process?
The final stage of the tertiary wastewater treatment process involves removing the chlorine that was used to disinfect the water. This step is very important because chlorine is harmful to aquatic life. Chlorine also reduces biological water quality when it is present in high concentrations.
What are the characteristics of tertiary treatment?
Tertiary Treatment 1 Dirty water unit operation design. Tertiary treatment processes are more commonly proprietary than secondary treatment processes, usually being newer (or at least new variants on old processes). 2 Sewage. ... 3 Environmental Impact. ... 4 Water and wastewater treatment: chemical processes. ...
What is the purpose of tertiary treatment?
The purpose of tertiary treatment is to provide a final polishing treatment stage prior to discharge or reuse of the wastewater. Chlorination – A water treatment method that destroys harmful bacteria, parasites, and other organisms. Chlorination also removes soluble iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide from the water.
What is the main role of tertiary treatment of wastewater?
Tertiary treatment is the next wastewater treatment process after secondary treatment. This step removes stubborn contaminants that secondary treatment was not able to clean up. Wastewater effluent becomes even cleaner in this treatment process through the use of stronger and more advanced treatment systems.
What does tertiary water treatment remove?
Tertiary water treatment is the final stage of the multi-stage wastewater cleaning process. This third stage of treatment removes inorganic compounds, bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Removing these harmful substances makes the treated water safe to reuse, recycle, or release into the environment.
What is the purpose of advanced wastewater treatment?
Any process which reduces the level of impurities in a wastewater below that attainable through conventional secondary or biological treatment. Includes the removal of nutrients such as phosphorus and nitrogen and a high percentage of suspended solids.
Is there a difference between advanced and tertiary treatment system?
Tertiary treatment, also called advanced waste treatment, provides contaminant removal beyond that achieved in primary (physical settling) or secondary (biological) treatment.
Which process is used in tertiary treatment?
Several tertiary treatment processes can be employed depending on the purpose, with some of the most used being the following: membrane separation processes (microfiltration, ultrafiltration, and reverse osmosis), adsorption (activated carbon), ion exchange, disinfection (chlorination), advanced oxidative processes ( ...
Can you drink water after tertiary treatment?
And this gets done through UV-based purification and clinical treatment. There's also a sand filtration system to purify water at this stage. So, after this stage, the water becomes completely clean and safe for drinking.
What is tertiary system?
Tertiary systems carry the same treatment process as a secondary system with an additional filtration or "polishing" process often in the form of UV treatment. This process will further remove the remaining organic matter and bacteria. Tertiary systems are required in very sensitive receiving environments.
What is a tertiary septic system?
The tertiary system treats the wastewater to a higher level than a septic tank. The treated effluents are discharged into a much smaller area, and it uses aeration to accelerate the time to break down solids.
What are advanced wastewater treatment methods?
The processes behind advanced water treatmentReverse osmosis. Reverse osmosis involves taking water from the ground and putting it through a process that removes all of the water's minerals and deionizes it so that it is safe for people to drink. ... Membrane filtration. ... Water oxidation. ... Recommended Reading. ... Sources.
What are the 3 stages of wastewater treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment. In some applications, more advanced treatment is required, known as quaternary water treatment.
Which of the following is advanced wastewater treatment?
Three methods which are finding wide application in advanced waste treatment are ion-exchange, electro dialysis and reverse osmosis. For the removal of soluble organics from waste water the most commonly used method is adsorption on activated carbon.
What is tertiary treatment?
Tertiary treatment includes the removal of the remaining inorganic compounds (phosphate, sulfate, ammonium) and other refractory organic compounds by one or more physical separation methods, such as carbon adsorption, deep-bed filtr ation, and in some cases, membrane-based techniques, such as reverse osmosis or electrodialysis.
What is the main tertiary treatment process?
The main tertiary treatment process is then filtration, using either a sand bed or a membrane process, usually microfiltration, possibly followed by ultrafiltration. There may also be too high a content of nitrogen and phosphorus, and this will require additional biological processes, with some more sludge to be separated.
What is the most used filtration material in wastewater treatment?
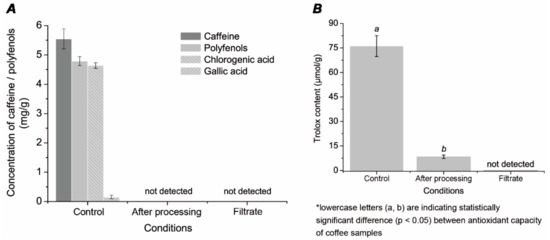
Sand, activated carbon, and zeolite are the most employed filtering materials in wastewater tertiary treatment. Sand filtration is a conventional wastewater treatment process characterized by its simplicity, low energy inputs, and easy maintenance. In this system, chemical reagents are not required, resulting in lower costs in comparison with other methods. In addition, the use of sand as wastewater filtering material has shown to be effective as tertiary treatment stage achieving high turbidity removal rates. Its use in combination with activated carbon is an effective alternative to the conventional method [20].
What is used to reduce solids?
If the solids need to be reduced, sand filters or other clarifiers may be used. The collected materials are then usually bulked with the other sludges on site for further treatment and disposal.
When is tertiary treatment necessary?
Usually tertiary treatment of wastewater is only regarded as necessary when the nutrient concentrations in the effluent have to be reduced i.e., if the mill discharges to very sensitive recipients. View chapter Purchase book. Read full chapter.
What are the drawbacks of biological treatment?
Although chemical treatment shows good results, the treatment has associated drawbacks such as dewatering and disposal of the generated sludge.
Is tertiary treatment more proprietary than secondary treatment?
Tertiary treatment processes are more commonly proprietary than secondary treatment processes, usually being newer (or at least new variants on old processes). Secondary treatment was developed in large part to deal with the 1912 Reports of the UK Royal Commission.
What Is Tertiary Wastewater Treatment?
What is tertiary treatment in wastewater? To answer this question, let’s look into how treatment plants generally work and how the main stages of wastewater treatment progress.
What happens to wastewater after tertiary treatment?
Once the wastewater has undergone tertiary treatment, it is ready for discharge back into the environment. Many municipalities have specific requirements about the discharge of treated water, and tertiary treatment should be sufficient to meet those standards, keep the environment clean, and preserve human health.
What are tertiary filtration components?
Tertiary filtration components can contain a few different materials. Sand and activated carbon filters are common, and filters can also contain fine woven cloth. The filters also come in a few different types, including bag filters, drum filters and disc filters: Bag filters: Bag filters are ideal for wastewater treatment plants ...
Why is chlorine used in wastewater treatment?
Wastewater treatment plants can dump chlorine into the wastewater to kill harmful microorganisms like bacteria and viruses.
How does tertiary treatment work?
Tertiary wastewater treatment often works by using a combination of physical and chemical processes to remove harmful microbiological contaminants from wastewater. The process usually involves filtration followed by additional disinfecting treatment. In some cases, tertiary treatment may also use other specialized treatments like lagoon storage, biological nutrient removal, and nitrogen and phosphorus removal.
What is secondary treatment?
Secondary treatment applies additional biological processes like aeration and activated sludge treatment to break down dissolved and suspended biosolids using good bacteria. Tertiary treatment adds a third, more advanced and rigorous level of treatment.
Why do plants use tertiary treatment?
Many treatment plants use tertiary treatment specifically to make the water safe for human ingestion. After tertiary treatment, the water has undergone sufficient purification to be as clean and healthy as drinking water.
What is secondary treatment?
Secondary treatment removes 85 to 90% of BOD, TSS, and the small portion of nitrogen, phosphorus, and heavy metals from wastewater. Tertiary treatment of wastewater is the third stage of the wastewater treatment and is also known as an advanced treatment.
What is membrane technology?
Membrane technology is used to treat a variety of wastes including sewage, organic and inorganic matter and water-soluble oil wastes. The membrane processes are classified on the basis of driving force and separation mechanism such as Multi Filtration (MF), Ultrafiltration (UF), Nano filtration (NF), Reverse Osmosis (RO), and Forward Osmosis (FO)
What is the process of removing particulate matter?
Filtration Process. Filtration process removes the particulate matter by passing water through the porous media. The filtration process consists of different types of media which are usually made up of sand, gravel, and charcoal. There are two types of sand filtration , slow sand filtration , and rapid sand filtration .
What is secondary treatment of wastewater?
Secondary treatment of wastewater makes use of oxidation to further purify wastewater. This can be done in one of three ways:
How is wastewater treated?
Primary treatment of wastewater involves sedimentation of solid waste within the water. This is done after filtering out larger contaminants within the water. Wastewater is passed through several tanks and filters that separate water from contaminants. The resulting “sludge” is then fed into a digester, in which further processing takes place. This primary batch of sludge contains nearly 50% of suspended solids within wastewater.
What is the third step in wastewater management?
This third and last step in the basic wastewater management system is mostly comprised of removing phosphates and nitrates from the water supply. Substances like activates carbon and sand are among the most commonly used materials that assist in this process.
How long does it take for a wastewater solution to be aerated?
The resulting mixture is then aerated for up to 30 hours at a time to ensure results.
What is advanced water treatment?
One area of focus is advanced water treatment processes, which help streamline how water is obtained and used. ...
How does water oxidation work?
Water oxidation is used to break down water into two elements- hydrogen and oxygen. The process separates the water back into its original elements so that it can be used for other things. People and other living organisms need oxygen to live, so this process can be used anywhere where oxygen is readily needed, such as filling up oxygen tanks. Given that climate change and air pollution are currently harming the environment, people are looking for other sources of fuel, one of which is hydrogen. This treatment process helps provide water and hydrogen where it’s needed to improve the environment as a whole.
How does reverse osmosis work?
Reverse osmosis involves taking water from the ground and putting it through a process that removes all of the water’s minerals and deionizes it so that it is safe for people to drink. Without this critical process, people would not be able to extract the harmful materials found in natural water and could become sick or die as a result. This process is used in desalinization, which is when ocean water is turned into clean, fresh water. Reverse osmosis helps remove the salt from ocean water leaving behind clean water. The world is running out of fresh and natural resources to use, and 97 percent of the water on the planet is salt water. Reverse osmosis can also help recycle water to make it clean and safe again, and also is used in wastewater treatments.
Why is water filtration important?
Though water filtration is used for a variety of reasons, one is to help create beverages and dairy products in the food industry. This process helps concentrate and purify a variety of foods, from beverages such as beer and vegetable juice to dairy products such as yogurt and cheese.
Why is water important to life?
Water helps all living things grow and survive in their natural environments. From serving up a pitcher of water at a restaurant to watering crops on a massive farm, water is used constantly. However, not all areas of the world are abundant in clean water. Some places even face droughts.
Why is hydrogen used in the treatment process?
This treatment process helps provide water and hydrogen where it’s needed to improve the environment as a whole.
Why do we need clean water?
All people need access to clean water in order to survive. Dirty water can kill plants, animals and make people very sick. People in this field determine the best water treatments for safe water. They also establish best processes for handling waste water.
What is tertiary treatment?
In the case of water treated by municipalities, tertiary treatment also involves the removal of pathogens, which ensures that water is safe for drinking purposes.
Why is secondary wastewater treatment important?
Completing secondary wastewater treatment allows for safer release into the local environment, reducing common biodegradable contaminants down to safe levels.
What are the stages of wastewater treatment?
What Are the Three Stages of Wastewater Treatment? There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment. In some applications, more advanced treatment is required, known as quaternary water treatment.
Where is wastewater held?
During primary treatment, wastewater is temporarily held in a settling tank where heavier solids sink to the bottom while lighter solids float to the surface. Once settled, these materials are held back while the remaining liquid is discharged or moved through to the more rigorous secondary phase of wastewater treatment.
What is biofiltration?
Biofiltration uses sand filters, contact filters or trickling filters to ensure that any additional sediment is removed from the wastewater.
What is wastewater treatment?
The wastewater treatment processes are basically concentrating or thickening processes on which the suspended solids are removed as sludge’s. The impurities in the wastewater are concentrated into solid form and are then separated from the bulk liquid. This concentrated form is referred to as sludge. Whereas the dissolved solids are first ...
Can wastewater be reused?
The treated wastewater can be reused for several purposes, for instance: (a) Treated water can be reused for recreation purposes like fishing and boating. (b) Treated water can be reused as industrial water supply. (c) Reclaimed wastewater can be used for irrigation or municipal purposes.
What is advanced wastewater treatment?
In a way, advanced wastewater treatment can be defined broadly as any process designed to produce an effluent of higher quality than normally achieved by secondary treatment processes or containing unit operations not normally found in the secondary wastewater treatment.
Why is wastewater treated with nitrogen?
The pollution problems arising from excessive amounts of certain nutrients in wastewater are the most common reason for advanced waste-water treatment and mainly caused by nitrogen-rich and phosphorus-rich compounds. The nitrogen-rich substances, such as proteins, are biologically converted into ammonia through a process called ammonification.
What is the pollution problem associated with wastewater treatment?
Another area of pollution problem associated with wastewaters, which is not addressed adequately by the conventional wastewater treatment, is the category of priority pollutants and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) identified by the regulatory agencies since the early 1980s.
What is biological treatment?
Biological treatment processes, in combination with primary sedimentation, typically remove 85% of the BOD5 and soluble solids originally present in the raw wastewater and some of the heavy metals. Activated sludge generally produces an effluent of slightly higher quality, in terms of these constituents, than trickling filters or RBCs.
Is VOC resistant to biological treatment?
VOCs are found to be quite resistant to biological treatment , and physic-ochemical processes such as air stripping have their own limitations in terms of VOC removal from wastewater and may turn a water pollution problem into an air pollution quandary.