Acute care is treatment that is necessary but only for a short period of time. It is more specialized than primary care because it may involve emergency health care workers, urgent care specialists, trauma specialists, and other health care provides that are not primary care physicians. Types of Acute Care
Full Answer
What does acute treatment mean?
Acute care is simply an active treatment for short-term needs. In contrast, long-term care is for patients who need assistance to function in their daily lives. Practitioners try to make this care fit seamlessly into a patient’s routine. Long-term care is often performed in a group home, nursing home, or in a person’s residence.
What does acute mean in medical terms?
Acute care is treatment that is necessary but only for a short period of time. It is more specialized than primary care because it may involve emergency health care workers, urgent care specialists, trauma specialists, and other health care provides that are not primary care physicians. Types of Acute Care
What is the definition of acute care?
Mar 29, 2021 · Acute often also connotes an illness that is of short duration, rapidly progressive, and in need of urgent care. "Acute" is a measure of the time scale of a disease and is in contrast to "subacute" and "chronic." "Subacute" indicates longer duration or less rapid change. "Chronic" indicates indefinite duration or virtually no change.
What is acute care in physical therapy?
acute care the level of care in the health care system that consists of emergency treatment and critical care. Called also secondary care . acute coronary syndrome a classification encompassing clinical presentations ranging from unstable angina through myocardial infarctions not characterized by alterations in Q waves ; the classification sometimes also includes …

What is considered acute treatment?
Acute care is active, short-term treatment for a severe injury or episode related to illness, an urgent medical condition or recovery from surgery.
What are examples of acute care?
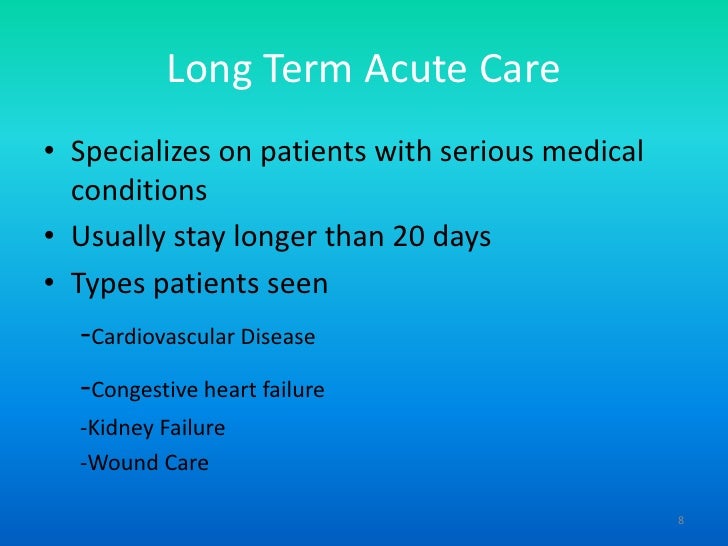
The following are considered acute care facilities:Hospital (General Acute Care as well as Psychiatric, Specialized and Rehabiltation Hospitals; and Long Term Acute Care or LTAC)Ambulatory Care Facility.Home Health Agency.End Stage Renal Disease Facility (dialysis center)Hospice.
What does acute care mean in medical terms?
DEFINITION AND DESCRIPTION. OF ACUTE CARE HOSPITALS. Acute care is a level of health care in which a patient is treated for a brief but severe episode of illness, for conditions that are the result of disease or trauma, and during recovery from surgery.
Is acute care serious?
Despite being common, there is no well accepted definition for acute care. However, most would agree that acute care encompasses a huge range of problems, from minor injuries and symptoms that may improve on their own to major trauma, patients suffering complications of chronic diseases, and life threatening illnesses.Nov 4, 2016
Is acute care the same as ICU?
It can be referred to interchangeably as the 'intensive care' and there is no difference between the two. Both specialise in the monitoring and treatment of patients who need round the clock care.Jun 9, 2021
What types of patients are treated in acute care facilities?
Acute care is a branch of medicine which actively treats patients with severe, short-term medical needs. Symptoms of acute conditions often emerge suddenly, but the treatment and recovery periods are also generally brief.Mar 30, 2021
Does acute mean short-term?
Acute illnesses generally develop suddenly and last a short time, often only a few days or weeks. Chronic conditions develop slowly and may worsen over an extended period of time—months to years.
What is the difference between acute and primary care?
Answer: Acute care nurse practitioner (NP) programs prepare registered nurses (RNs) to work with patients who are suffering from acute illnesses and health conditions, while primary care NP programs train RNs to work with patients who need routine medical care or who suffer from chronic conditions that do not need ...
What do you mean by acute?
Definition of acute 1a(1) : characterized by sharpness or severity of sudden onset acute pain. (2) : having a sudden onset, sharp rise, and short course acute illness. (3) : being, providing, or requiring short-term medical care (as for serious illness or traumatic injury) acute hospitals an acute patient.
How long does an acute illness last?
Acute illness generally develops suddenly and only lasts a short period of time, a few days or weeks. A chronic illness will develop slowly and last months or even years, even with treatment.Mar 23, 2021
What is the difference between acute and non acute care?
Acute: A patient that is on ventilator support. Non-acute/Step Down: A patient that is not on ventilator support, but requires continued nursing support.Mar 26, 2020
What is acute care?
Acute Care Definition. Acute care is simply an active treatment for short-term needs. In contrast, long-term care is for patients who need assistance to function in their daily lives. Practitioners try to make this care fit seamlessly into a patient’s routine.
Where is long term care performed?
Long-term care is often performed in a group home, nursing home, or in a person’s residence. Acute care is often performed in a hospital setting or doctor’s office for quick, urgent treatment.
What is the buzz word in medicine?
Buzz words are pretty popular in medicine. It can be difficult to know what everything means when you go to the doctor’s office. However, it is important to try to make sense of some basic medical terms so that you can understand the treatment you are receiving.
What is an emergency room?
Emergency rooms serve patients with acute needs. Often, these needs include accidents, injuries, or sudden medical needs. Emergency rooms are equipped to handle rapidly changing conditions for accurate care at all times.
Is intensive care needed in a hospital?
A patient’s needs can also change rapidly in the hospital. Therefore, intensive care units are necessary. The ICU is another example of acute care. Patients who have a sudden decline in their health can be treated quickly with the help of specialized tools and practitioners.
What is acute care?
Acute care is a type of secondary health care. Secondary care describes care that is not received from a person’s primary caregiver, or doctor. It is more specialized than primary care. Acute care is treatment that is necessary but only for a short period of time. It is more specialized than primary care because it may involve emergency health care ...
What are the different types of acute care?
Types of Acute Care. Acute care is a diverse group of medical specialties, but it can be organized into a few different types: Emergency care. Emergency care is any acute treatment that is administered for a life-threatening illness or injury. It may also be used to treat illnesses or injuries that are causing severe pain or may lead ...
Why is acute care important?
Acute care plays an important role in saving lives and preventing disability in patients. When practiced with high standards ...
What is the responsibility of a caregiver?
Your caregivers are responsible for doing all that is reasonably possible to help you and to inform you of your condition and your options for treatment so that you can give informed consent for any procedures or before being discharged or transferred to another type of care.
Why is discharge planning important?
This planning for discharge and post-acute treatment is an important part of the standard of care because it allows patients and their caregivers to make informed decisions. And, follow up after acute care is an important part of good quality health care.
What is urgent care?
Urgent care. This is a type of outpatient, or ambulatory care that is administered from a clinic rather than an emergency room and that typically does not require an appointment. Urgent care is used for pressing, but not emergency, health care needs. Trauma and acute surgery. Acute surgery is used to treat patients with immediate needs, ...
What is prehospital care?
Prehospital care. This is care provided for a patient before they arrive at the hospital. It may be emergency care administered by paramedics or EMT, or it may be evaluation by an urgent care or other doctor who then decides to transfer the patient to the hospital. Critical and intensive care.
What is sub acute care?
Sub-acute care is intensive, but to a lesser degree than acute care. This type of care is for those who are critically ill or suffer from an injury that won’t withstand the longer, daily therapy sessions of acute care. Sub-acute care is for anyone who needs treatment that involves: Intensive wound care. IV treatment.
What is ALS in medical terms?
ALS (Lou Gherig’s Disease) Any other Terminal illness in its early stages. Sub-acute care is also a great option for anyone who’s already completed acute treatment, but still needs therapy to regain full functionality. It is a less intensive therapy that includes the following:
How long does a speech therapy session last?
Therapy usually lasts three hours or more per day. Patients are given therapy at least 5 days a week. Patients receive daily face-to-face assessment and therapy plan update. Patients will receive a combination of physical, occupational, and speech therapy as needed.
What is multidisciplinary approach in healthcare?
A multidisciplinary approach is used to ensure a functional return to each patient’s daily life. Acute care gives patients a constantly moving goal that continues to improve their quality of life until they can transition to life outside of therapy, or possibly to sub-acute care, should it be needed.
What does "acute" mean?
acute. [ ah-kūt´] 1. sharp. 2. having severe symptoms and a short course. Some serious illnesses that were formerly considered acute (such as myocardial infarction) are now recognized to be acute episodes of chronic conditions.
What are the symptoms of acute illness?
Some patients continue to experience health problems caused by the acute illness, such as coughing, limited exercise tolerance, and fatigue. Anxiety, depression, and flashback memories of the critical illness may also occur and be similar to posttraumatic stress disorder. Treatment and Patient Care.
What does "exposure" mean in medical terms?
1. Referring to a health effect, usually of rapid onset, brief, not prolonged; sometimes loosely used to mean severe. 2. Referring to exposure, brief, intense, short-term; sometimes specifically referring to brief exposure of high intensity. [L. acutus, sharp] Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012.
What is appendicitis caused by?
A. Appendicitis is caused by an infection of the appendix, usually from bacterias that are already located in the abdomen. It is not a situation that can be avoided and can occur in a high prevalence in the population. More discussions about acute. This content is provided by iMedix and is subject to iMedix Terms.
Is pulmonary capillary wedge pressure normal?
Cardiac filling pressures are normal, and the pulmonary capillary wedge pressure is below 18 torr. Most authorities consider that the syndrome has three phases or stages that characterize its progression: the exudative stage, the fibroproliferative or proliferative stage, and the resolution or recovery stage.
What is sub acute care?
Sub acute level care is less intensive than acute rehabilitation. Although a combination of physical, occupational and speech therapy may be provided in the sub acute setting, the number of hours each patient receives is lower.
How long does a patient stay in a subacute facility?
Generally, patients in a sub acute facility only receive between one and two hours of therapy per day. The average length of stay at a sub acute facility is also generally longer than at an acute hospital. For patients who are not appropriate candidates for acute rehabilitation, Burke offers a network of affiliated sub acute facilities ...
What is Burke Hospital?
Burke is an acute rehabilitation hospital. Patients are admitted who have a traumatic injury, debilitating disease or following certain types of surgery. Acute rehabilitation is appropriate for patients who will benefit from an intensive, multidisciplinary rehabilitation program. Patients receive physical, occupational and speech therapy as needed ...
How many hours of therapy is a day?
Patients receive up to 3 hours of therapy a day, typically Monday through Friday, and one hour on Saturday or Sunday. Therapy is provided on both a one-to-one and group basis, depending on the needs of the individual patient.
What is a neuropsychologist?
For patients with neurological diagnoses, a neuropsychologist is on staff to determine if they are in need of additional psychological or psychiatric treatment. In an acute rehabilitation hospital, the patient is expected to make significant functional gains and medical improvement within a reasonable time frame.
What is chronic health?
With the HHS, chronic is used to describe a public health concern for surveillance purposes. With the CMMS, the term broadly describes a disease for healthcare utilization purposes. There is currently no one consistent definition of either acute or chronic that fits all purposes.
What are the phases of illness?
General Definitions. Phases of Illness. Flaws in Definitions. Clearing Up Confusion. Broadly speaking, acute conditions occur suddenly, have immediate or rapidly developing symptoms, and are limited in their duration (e.g., the flu). Chronic conditions, on the other hand, are long-lasting.
How long does it take for a chronic illness to resolve?
Acute. Symptoms develop quickly. Expected to be brief; typically resolves in less than six months. Chronic.
Can psoriasis be cured?
The same can occur with non-infectious disorders like rheumatoid arthritis or psoriasis. Both are considered chronic in that they cannot be cured but can be managed with proper care and treatment. Even so, the diseases can have episodic flares in which acute symptoms spontaneously develop and disappear.
Can HIV be a chronic disease?
Neither does HIV (a chronic infection that can be controlled over a lifetime with antiretroviral drugs) compare to multiple sclerosis (a chronic illness that invariably progresses despite treatment). In the end, labeling an illness as a cute or chronic cannot describe the nature of a disease, nor predict outcomes.
How long does it take for a disease to persist?
Persists beyond six months. Acute does not mean new, although many newly diagnosed diseases present with acute symptoms. Nor does it mean that symptoms are severe. It simply means that symptoms have developed quickly and that some sort of medical intervention is needed.
Is chronic disease curable?
Similarly, chronic should not be construed to mean fatal or something that will inherently shorten your life. It simply indicates that the condition is not curable. Chronic conditions can often be managed (like diabetes or high blood pressure ).
What is the best treatment for inflammation?
Topical – Topical hemp treatments are a good way to get relief from acute inflammation without some of the side-effects that may be present in NSAIDs and narcotic pain relievers. Hemp topicals can be found in creams, massage oil, or serum form.
How to treat inflammation in the body?
Cannabis may provide relief in ingested or topical forms: 1 Ingested – Hemp or marijuana may be smoked, eaten in edibles, or used in teas and tinctures. 2 Topical – Topical hemp treatments are a good way to get relief from acute inflammation without some of the side-effects that may be present in NSAIDs and narcotic pain relievers. Hemp topicals can be found in creams, massage oil, or serum form. Hemp topicals made from the root of the hemp plant are especially effective at treating inflammatory pain, with the use of hemp root dating back to ancient China. It is important to note that hemp oil or any essential oil should not be placed directly on the skin. Products are typically combined with carrier oils or other base ingredients.
What are the signs of inflammation?
The five cardinal signs of inflammation are: 1. Rubor – Rubor or a redness of the injured or infected area is caused by increased blood flow. 2.
How to treat swelling and inflammation?
One of these natural ways you can treat inflammation pain and swelling is to elevate the area and apply an ice pack. It is also a good idea to drink plenty of water to help the healing progress. Diet also plays a role in natural inflammation pain relief.
What is the body's response to injury?
Acute inflammation is the body’s normal tissue response to injuries, foreign bodies and other outside factors. It is the defense mechanism of body tissue reacting to kick start the healing process. 1. Physical – Some of the physical causes of inflammation include frostbite, burns and injuries. 2.
How long does it take for inflammation to subside?
Products are typically combined with carrier oils or other base ingredients. If inflammation symptoms don’t subside within 48 hours, it is wise to check with a healthcare professional to see if further treatment is needed. If untreated, acute inflammation may develop into chronic inflammation.
What causes redness and inflammation?
4. Psychological – Blushing is a form of inflammation. It is usually caused by embarrassment, but other types of nervousness or emotional responses may also cause redness and inflammation.