Medication
Women should be cautious of the following symptoms if they persist over time 3:
- Bloating, indigestion, cramps, gas and swelling in the abdomen
- Feeling of fullness and abdominal swelling after eating even a light meal
- Diarrhea, nausea, constipation and frequent urination
- Loss of appetite
- Weight gain or loss for no known reason
- Pelvic pressure
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Constant back or leg pain
Procedures
Can you be fully cured of ovarian cancer? Around two in ten women with advanced-stage ovarian cancer are effectively cured and survive at least 12 years after the treatment as per the research. Your response to cancer therapy and chances for a cure depend on the type and the staging of ovarian cancer at the time of diagnosis.
Self-care
What if my GP thinks I have ovarian cancer?
- Talk to someone! Talking to someone about your feelings may be helpful. ...
- Councelling. When life becomes very uncertain and stressful, it can help to talk to a counsellor. ...
- Dealing with other people. Other people’s reaction to your illness can vary. ...
- Support groups. ...
- Self-help. ...
What are the best natural remedies for ovarian cancer?
- Use a soft toothbrush to take care of your dental health.
- Talk with your doctor about steroids or anti-inflammatory drugs to help manage the pain and symptoms.
- Avoid spicy foods.
- Limit acidic juices and fruits like lemons and orange juice.
- Focus on small meals and foods that are easy to chew, like yogurt, smoothies, and pureed soups.
Can you be fully cured of ovarian cancer?
What to do when you are diagnosed with ovarian cancer?
What is the best diet for ovarian cancer?
/fake-eyelashes-120337599-5ab67688a18d9e003748289f.jpg)
What happens during chemo for ovarian cancer?
Some chemotherapy side effects, such as fatigue, nausea, and numbness or tingling in the fingers and toes (neuropathy), are physical. Others, like hair loss, are more emotional because they can take a big hit on your self-esteem. "Women usually lose their hair two to three weeks after their first treatment.
What is the standard of care for ovarian cancer?
The standard treatment for ovarian cancer consists of debulking surgery followed by six rounds of chemotherapy. One recent study found that just 37 percent of women receive this standard treatment, despite evidence showing that it is the most effective.
How long does ovarian cancer treatment take?
These drugs are usually given as an IV (put into a vein) every 3 to 4 weeks. The typical course of chemo for epithelial ovarian cancer involves 3 to 6 cycles of treatment, depending on the stage and type of ovarian cancer. A cycle is a schedule of regular doses of a drug, followed by a rest period.
What happens during surgery for ovarian cancer?
During the operation, the surgeon examines the inside of your abdomen and your abdominal organs. This is to check for signs of cancer. The surgeon aims to remove as much of the cancer as possible if it has spread to other areas in your pelvis or abdomen. This is called debulking.
How many hours is ovarian cancer surgery?
If performed with chemotherapy, the debulking surgery may take six to 12 hours to complete. After surgery, you may have a tube (drain) in your abdomen to get rid of any fluid, but this is usually removed within a couple of days. The length of your hospital stay depends on the type of surgery you require.
How long after surgery do you start chemo for ovarian cancer?
Chemotherapy is usually given 2–4 weeks after the surgery (adjuvant chemotherapy) as there may be some cancer cells still in the body. For ovarian cancer, the drugs are usually given in repeating cycles spread over 4–5 months, but this can vary.
Can you be fully cured of ovarian cancer?
(When cancer returns, it is called recurrence.) This is very common if you've had cancer. For other people, ovarian cancer never goes away completely. Some women may be treated with chemotherapy on and off for years.
How long is a chemo session for ovarian cancer?
You usually have the chemotherapy drugs on day 1 followed by a rest period to allow you to recover from side effects. Each 3 week period is called a cycle of treatment. You normally have about 6 cycles in all, but you may have more. It takes 3 to 4 hours to have each treatment in the outpatients department.
What is life expectancy with ovarian cancer?
For all types of ovarian cancer taken together, about 3 in 4 (72.4%) women with ovarian cancer live for at least 1 year after diagnosis. Almost half (46.2%) of women with ovarian cancer are still alive at least 5 years after diagnosis. Women diagnosed when they are younger than 65 do better than older women.
How long are you in the hospital after ovarian cancer surgery?
Recovery. You'll stay in the hospital for 3 to 7 days after your surgery. You'll be in some pain, but your doctor will give you medicine to control it.
Is removing an ovary major surgery?
Salpingo-oophorectomy is a procedure to remove the fallopian tube (salpingectomy) and ovaries (oophorectomy), which are the female organs of reproduction. Since it requires anesthesia, overnight hospital stay, and removal of body parts, it is classified as major surgery. It requires 3-6 weeks to heal completely.
Is ovarian cancer a terminal?
Ovarian cancer can be terminal. About 45% of people with any stage of ovarian cancer survive for 5 years or longer from the date a doctor diagnoses them. For stage 4 ovarian cancer, the 5-year survival rate is 30.3% .
Which Treatments Are Used For Ovarian Cancer?
There are several ways to treat ovarian cancer, depending on its type and stage.Local treatments: Some treatments are local, meaning they treat the...
How Is Ovarian Cancer Typically Treated?
Most women with ovarian cancer will have some type of surgery to remove the tumor. Depending on the type of ovarian cancer and how advanced it is,...
Who Treats Ovarian Cancer?
Doctors on your cancer treatment team might include: 1. A gynecologic oncologist: a gynecology doctor who is specially trained to use surgery to tr...
Making Treatment Decisions
It’s important to discuss all of your treatment options, including their goals and possible side effects, with your doctors to help make the decisi...
Help Getting Through Cancer Treatment
Your cancer care team will be your first source of information and support, but there are other resources for help when you need it. Hospital- or c...
How to test for ovarian cancer?
Genetic testing. Your doctor may recommend testing a sample of your blood to look for gene changes that increase the risk of ovarian cancer. Knowing you have an inherited change in your DNA helps your doctor make decisions about your treatment plan. You may wish to share the information with your blood relatives, such as your siblings and your children, since they also may have a risk of having those same gene changes.
How does estrogen therapy help ovarian cancer?
Hormone therapy uses drugs to block the effects of the hormone estrogen on ovarian cancer cells. Some ovarian cancer cells use estrogen to help them grow, so blocking estrogen may help control the cancer.
What is the name of the doctor who treats ovarian cancer?
A gynecological oncologist is an obstetrician-gynecologist (OB-GYN) who has additional training in the diagnosis and treatment of ovarian cancer and other gynecological cancers.
What test can detect ovarian cancer?
Your doctor might also test your blood for tumor markers that indicate ovarian cancer. For example, a cancer antigen (CA) 125 test can detect a protein that's often found on the surface of ovarian cancer cells. These tests can't tell your doctor whether you have cancer, but may give clues about your diagnosis and prognosis.
How to help with cancer?
Take time for yourself. Eating well, relaxing and getting enough rest can help combat the stress and fatigue of cancer.
When is chemotherapy used?
Chemotherapy is often used after surgery to kill any cancer cells that might remain. It can also be used before surgery.
Where is chemo injected?
Chemotherapy drugs can be injected into a vein or taken by mouth. Sometimes the drugs are injected directly into the abdomen (intraperitoneal chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is often used after surgery to kill any cancer cells that might remain. It can also be used before surgery.
What is the procedure for ovarian cancer?
In early-stage ovarian cancer, less-invasive laparoscopic surgery may be an option. This is done with a video camera and long, thin instruments inserted through tiny incisions.
What are the factors that help guide treatment for ovarian cancer?
This is usually combined with chemotherapy, hormone therapy, or targeted treatments. Some factors that help guide treatment are: your specific type of ovarian cancer. your stage at diagnosis. whether you’re pre- or postmenopausal. whether you plan to have children.
What is the procedure to remove ovaries?
A procedure called debulking cytoreductive surgery is used to treat stage 4 ovarian cancer. It involves removal of your ovaries and fallopian tubes, along with any other affected organs. This can include: uterus and cervix. pelvic lymph nodes. tissue that covers your intestines and lower abdominal organs.
What is a clinical trial for ovarian cancer?
Clinical trials for ovarian cancer. Clinical trials compare standard treatment with innovative new therapies not yet approved for general use. Clinical trials can involve people with any stage of cancer. Ask your oncologist whether a clinical trial is a good option for you.
What is targeted therapy for ovarian cancer?
Targeted therapy for ovarian cancer. Targeted drugs find and change specific traits of cancer cells that aren’t found in healthy cells. They do less damage to healthy tissue than chemotherapy or external radiation treatments. Tumors need blood vessels to grow and spread.
How many times can you give ovarian cancer?
Epithelial ovarian cancer starts in cells on the outer lining of your ovaries. Treatment typically involves at least two IV drugs. They’re given three to six times, usually three to four weeks apart. The standard drug combination is cisplatin or carboplatin plus paclitaxel (Taxol) or docetaxel (Taxotere).
What hormones are used to lower estrogen production in premenopausal women?
It’s more often used for stromal cancer. Luteinizing-hormone-releasing hormone agonists are used to lower estrogen production in premenopausal women. Two of these are goserelin (Zoladex) and leuprolide (Lupron). They’re given by injection every one to three months.
How do doctors treat ovarian cancer?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), doctors usually treat ovarian cancer with a combination of surgery and chemotherapy.
How often do they give ovarian cancer drugs?
They usually give these intravenously every 3–4 weeks for three to six cycles, depending on the stage of the ovarian cancer.
What is stage cancer?
Staging usually involves a surgeon performing a hysterectomy, which removes the uterus, and a bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (BSO), which removes both ovaries and the fallopian tubes.
What is the number to call for ovarian cancer?
People who are looking for ovarian cancer support can call the American Cancer Society’s cancer helpline on 800-227-2345, chat with a representative online, or find programs or services in their area.
What are the stages of ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer stages range from 1–4. The lower the stage, the less the cancer has spread. Higher stages mean that the cancer has spread farther.
What is hormone therapy?
Hormone therapy involves a doctor using hormones or hormone-blocking drugs. Doctors do not often use this type of treatment for the most common type of ovarian cancer, epithelial ovarian cancer. However, they are likely to use this treatment for ovarian stromal tumors, which grow in the connective tissue of the ovaries.
How does targeted therapy work?
Targeted therapy uses drugs to identify and attack cancer cells without significantly damaging normal healthy cells. Each type of targeted therapy works differently, but they all affect how cancer cells:
What is the treatment for ovarian cancer?
Types of Treatment. Treatment for ovarian cancer usually involves a combination of surgery and chemotherapy. Surgery: Doctors remove cancer tissue in an operation. Chemotherapy: Using special medicines to shrink or kill the cancer.
How to choose the right cancer treatment?
Choosing the treatment that is right for you may be hard. Talk to your cancer doctor about the treatment options available for your type and stage of cancer. Your doctor can explain the risks and benefits of each treatment and their side effects . Side effects are how your body reacts to drugs or other treatments.
What is the name of the doctor who treats cancer?
Different treatments may be provided by different doctors on your medical team. Gynecologic oncologists are doctors who have been trained to treat cancers of a woman’s reproductive system. They perform surgery and give chemotherapy (medicine). Surgeons are doctors who perform operations.
What kind of doctor treats peritoneal cancer?
If your doctor says that you have ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancers, ask to be referred to a gynecologic oncologist —a doctor who was trained to treat cancers of a woman’s reproductive system. Gynecologic oncologists can perform surgery on and give chemotherapy (medicine) to women with ovarian cancer.
What is a medical oncologist?
Medical oncologists are doctors who treat cancer with medicine (chemotherapy).
What is the treatment for ovarian cancer?
Surgery is one of the main treatments for ovarian cancer. In most cases, one of the first big decisions is whether to start with surgery or chemotherapy. “The initial course of treatment is primarily determined by the extent of disease,” Boyd explained. Imaging tests, such as CT scans, and other diagnostic procedures help your doctor determine ...
What is the best treatment for cancer?
Radiation therapy: High-energy X-rays or particles are used to kill cancer cells. Hormone therapy: Hormones or hormone-blocking drugs are used to shift the balance of hormones in your body, which affects how some types of cancer grow. Targeted therapy: Drugs or other substances are used to target the inner workings of cancer cells.
Where does ovarian cancer start?
Ovarian cancer starts in the ovaries or far end of the fallopian tubes. Screening options are limited. By the time the cancer is diagnosed, it may have spread to the pelvis, abdomen, or other parts of the body. Surgery is one of the main treatments for ovarian cancer. In most cases, one of the first big decisions is whether to start with surgery ...
Can you retrieve eggs from your ovaries?
In some cases, they might suggest a procedure to retrieve eggs from your ovaries before you start treatment. In general, for most people, the best treatment plan for ovarian cancer depends in part on: the specific type of ovarian cancer. the location and extent of the cancer, including whether or not it has spread.
Can you remove the ovaries and fallopian tubes?
Surgery may involve removing only one ovary and fallopian tube. In some cases, it might involve removing both ovaries and fallopian tubes. In more advanced cases, surgery may mean removing both ovaries, fallopian tubes, the uterus, nearby lymph nodes, and a fold of fatty tissue known as the omentum.
Is ovarian cancer hard to treat?
Ovarian cancer has a reputation for being difficult to treat, but years of research have started to bring change. If you’ve been diagnosed with ovarian cancer, you may have a wider range of treatment options than you realize.
Can complementary medicine help with side effects of chemotherapy?
Understanding the potential side effects of treatment can help you be prepared. If side effects develop, your doctor can recommend medications and complementary therapies to help you manage them. “A lot of complementary therapies can be particularly helpful for side effects of standard chemotherapy,” said Boyd.
What is the goal of ovarian surgery?
The goals of surgery are to see how far the ovarian cancer has spread and to take out as much of the cancer as the doctor can. How much and what type of surgery you have depends on how far the cancer has spread, your health (other than the cancer), and if you still hope to have children.
What is the name of the cancer that starts in the ovary?
Cancer that starts in the ovary is called ovarian cancer. It starts when cells in the ovary grow out of control. Some ovarian cancers can also start in the fallopian tubes - tubes that connect the ovary to the uterus. Women have 2 ovaries. They are where eggs are made, and also where most of women’s hormones are made.
What is it called when ovarian cancer spreads to the liver?
When cancer cells do this, it’s called metastasis. To doctors, the cancer cells in the new place look just like the ones from the ovary. Cancer is always named for the place where it starts. So when ovarian cancer spreads to the liver (or any other place), it’s still called ovarian cancer. It’s not called liver cancer.
How do you know if you have cancer?
In a biopsy, the doctor takes out a little bit of tissue to check it for cancer cells. A biopsy is the only way to tell for sure if you have cancer. For ovarian cancer, the biopsy is most often done when you have surgery to take out the cancer.
How many ovaries do women have?
Women have 2 ovaries. They are where eggs are made, and also where most of women’s hormones are made. Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body. Cancer cells in the ovary can sometimes travel to the liver and grow there. When cancer cells do this, it’s called metastasis. To doctors, the cancer cells in the new place look just like ...
What does it mean when your ovary is stage 4?
The lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. A higher number, like stage 4, means a worse cancer that has spread to areas of the body farther from the ovary. Ask the doctor about the cancer stage and what it means for you.
What is the name of the X-ray that shows the ovaries?
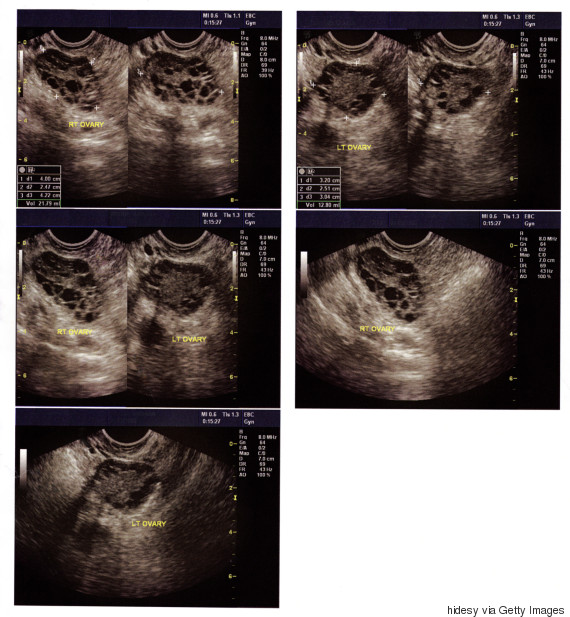
The sound waves make a picture of the ovaries on a video screen. CT (comput ed tomography) scans: This is also called a “CAT scan.”. It’s a kind of x-ray that takes clear pictures of the ovaries and other body parts to see if the cancer has spread.
What to do if you have ovarian cancer?
If you have (or have had) ovarian cancer, you probably want to know if there are things you can do that might lower your risk of the cancer growing or coming back, such as exercising, eating a certain type of diet, or taking nutritional supplements.
What is the follow up for ovarian cancer?
Follow-up for ovarian cancer usually includes blood tests for tumor markers or hormones that help recognize recurrence. The choice of which blood tests to do depends on the type of cancer a woman has.
What blood test is used to detect ovarian cancer?
Blood tests for tumor markers 1 For epithelial ovarian cancer, CA-125 is the tumor marker used most often to check for recurrence. But it is not clear if checking for CA-125 levels and treating you before you have symptoms will help you live longer. Treatment based only on CA-125 levels and not symptoms can increase side effects, so it is important to discuss the pros and cons of CA-125 monitoring and quality of life with your doctor. Tests for other tumor markers, such as CA 19-9, CEA, and HE-4, are used most often for women whose CA-125 levels never went up. 2 For germ cell tumors, blood is tested for alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and/or human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG). 3 For stromal cancers, checking levels of hormones like estrogen, testosterone, and inhibin is sometimes helpful.
What happens if cancer comes back?
If the cancer does recur at some point, your treatment options will depend on where the cancer is located, what treatments you’ve had before, and your health. For more general information on recurrence, you may also want to see Understanding Recurrence.
What is the importance of follow up appointments?
During these visits, your doctors will ask questions about any problems you may have and may do exams and lab tests or x-rays and scans to look for signs of cancer or treatment side effects.
How long do side effects of cancer last?
Some cancer treatment side effects may last a long time or might not even show up until years after you have finished treatment. Your doctor visits are a good time to ask questions and talk about any changes or problems you notice or concerns you have. To some extent, the frequency of follow up visits and tests will depend on the stage ...
What is a survivorship plan?
This plan might include: A schedule for other tests you might need in the future, such as early detection (screening) tests for other types of cancer, or tests to look for long-term health effects from your cancer or its treatment.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Tests and procedures used to diagnose ovarian cancer include: 1. Pelvic exam.During a pelvic exam, your doctor inserts gloved fingers into your vagina and simultaneously presses a hand on your abdomen in order to feel (palpate) your pelvic organs. The doctor also visually examines your external genitalia, vagina and cervix. 2. Imaging tests.Tests, such as ultrasound or CT scans of y…