Precautions
Some side effects of daptomycin may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects.
Do the side effects of daptomycin go away?
Daptomycin will not treat a viral infection such as the flu or a common cold. Store daptomycin in the refrigerator. Do not freeze. After mixing daptomycin with a diluent, store in the refrigerator and use it within 48 hours.
Does daptomycin need to be refrigerated?
Daptomycin Dosing and Use Guidelines Dosing: Soft tissue infection = 4 mg/kg every 24 hours Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia, other deep-seated infections = 6 mg/kg every 24 hours VRE bacteremia, other deep-seated infections = 8-10 mg/kg every 24 hours TBW Morbidly Obese patients-
How often should I take daptomycin for bacteremia?
However, recent consensus guidelines recommend that clinicians consider using alternative agents such as daptomycin when the vancomycin minimum inhibitory concentration is greater than 1 ug/ml.
When should we use daptomycin instead of vancomycin?
How long should you take daptomycin?
Hide table of contentsAge GroupIndicationDosage RegimenDuration of Therapy12 to 17 years5 mg/kg once every 24 hours infused over 30 minutesUp to 14 Days7 to 11 years7 mg/kg once every 24 hours infused over 30 minutes2 to 6 years9 mg/kg once every 24 hours infused over 60 minutes2 more rows
What should I monitor while on daptomycin?
Patients should also receive monitoring for muscle pain or weakness, new-onset or worsening peripheral neuropathy, and signs or symptoms of eosinophilic pneumonia. [14][18] Furthermore, patients who develop diarrhea should have testing for C. difficile infection.
How do you know if daptomycin is working?
Your doctor will check your progress closely while you are receiving this medicine. This will allow your doctor to see if the medicine is working properly and to decide if you should continue to receive it. Blood and urine tests may be needed to check for unwanted effects.
Does daptomycin cause renal failure?
Statistical analysis. In a previous study [17], the incidence of renal dysfunction was estimated at 12% with daptomycin and 35% with standard therapy. However, a higher incidence of renal failure was expected in ICU population, as much as twice the incidence observed in the reference study [10, 19].
Does daptomycin need renal adjustment?
Renal Dosing Daptomycin is eliminated primarily by the kidneys; therefore, a modification of CUBICIN dosage is recommended for patients with CLCR <30 mL/min, including patients receiving hemodialysis or continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD).
What are the most common side effects of daptomycin?
More commonBleeding, blistering, burning, coldness, discoloration of the skin, feeling of pressure, hives, infection, inflammation, itching, lumps, numbness, pain, rash, redness, scarring, soreness, stinging, swelling, tenderness, tingling, ulceration, or warmth at the injection site.difficulty having a bowel movement.
Before Taking This Medicine
You should not use daptomycin if you are allergic to it.To make sure daptomycin is safe for you, tell your doctor if you have: 1. kidney disease; o...
How Should I Use Daptomycin?
Follow all directions on your prescription label. Do not use this medicine in larger or smaller amounts or for longer than recommended.Daptomycin i...
What Should I Avoid While Using Daptomycin?
Antibiotic medicines can cause diarrhea, which may be a sign of a new infection. If you have diarrhea that is watery or bloody, call your doctor. D...
What Other Drugs Will Affect Daptomycin?
Tell your doctor about all your current medicines and any you start or stop using, especially a "statin" cholesterol medicine such as: 1. atorvasta...
What is daptomycin (Cubicin) used to treat?
Daptomycin (Cubicin) is an injectable antibiotic used to treat serious bacterial infections of the skin and underlying tissues and infections that...
Is daptomycin (Cubicin) the same as vancomycin?
Daptomycin (Cubicin) and vancomycin are similar in that they both treat very serious bacterial infections. Daptomycin (Cubicin) can be an alternati...
What are the side effects of daptomycin (Cubicin)?
Common side effects of daptomycin (Cubicin) include chest pain, trouble breathing, headache, dizziness, stomach pain, vomiting, rash, itching, and...
How often is daptomycin (Cubicin) given?
Daptomycin (Cubicin) is given by a healthcare provider in a hospital or a clinic. It is usually administered via IV in 0.9% sodium chloride, either...
Can daptomycin (Cubicin) cause C. diff?
Extended use of daptomycin (Cubicin) can lead to the development of a super infection, such as Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) or...
How long does it take to review daptomycin?
A single dose only of daptomycin (6 mg/kg for bacteremia, endocarditis, or osteomyelitis) will be dispensed pending ID response; therefore, the review must be initiated within 24 hours of the original order.
Why are there antimicrobial restrictions?
The Antimicrobial Restrictions are in place due to concerns regarding a variety of issues: off-label use; the need for increased dosage for patients with bacteremia/endocarditis or other serious infections due to gram-positive pathogens; contraindication for daptomycin use in patients with pneumonia. In order to make this medication available as ...
Is daptomycin safe for pneumonia?
Daptomycin is NOT indicated for the treatment of pneumonia. Phase III trials of community acquired pneumonia (CAP) treated with daptomycin resulted in a higher incidence of death and serious cardiorespiratory adverse events versus CAP treated with comparator agents.
Is daptomycin a formulary agent?
In order to make this medication available as a formulary agent for the general medical staff, to ensure appropriate usage, and to protect the medical staff from medical/legal considerations, the Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee has approved the following requirements for daptomycin use:
Can you stop Daptomycin?
Daptomycin should be discontinued in patients with symptoms of muscle pain or weakness whose CPK levels exceed 1000 U/L (~ 5x ULN), or in patients without symptoms whose CPK exceeds 10x ULN.
Can daptomycin cause muscle weakness?
Daptomycin can cause skeletal muscle myopathy with elevations in CPK. The percentage of patients treated with daptomycin in phase III trials who experienced muscle pain or weakness associated with CPK elevations > 4x ULN was 0.2%. Myopathy is fully reversible when therapy is withdrawn.
Before Using
In deciding to use a medicine, the risks of taking the medicine must be weighed against the good it will do. This is a decision you and your doctor will make. For this medicine, the following should be considered:
Proper Use
A nurse or other trained health professional will give you this medicine. This medicine is given through a needle placed into one of your veins. This medicine may be injected for 2 minutes (in adults only) or it may be given slowly, so the needle will have to remain in place for up to 60 minutes.
Precautions
Your doctor will check your progress closely while you are receiving this medicine. This will allow your doctor to see if the medicine is working properly and to decide if you should continue to receive it. Blood and urine tests may be needed to check for unwanted effects.
Side Effects
Along with its needed effects, a medicine may cause some unwanted effects. Although not all of these side effects may occur, if they do occur they may need medical attention.
Where is daptomycin given?
Daptomycin (Cubicin) is given through the intravenous (IV) route, usually in a hospital setting or at an infusion center by a nurse.
How long after taking cubicin can you use daptomycin?
It usually happens 2 to 4 weeks after starting daptomycin (Cubicin), and means you can't use this antibiotic anymore. Talk to your healthcare provider right away if you have a high fever, chest pain, cough, or trouble breathing.
What is the purpose of daptomycin?
Daptomycin (Cubicin) is an injectable antibiotic used to treat serious bacterial infections of the skin and underlying tissues and infections that have entered the bloodstream. Daptomycin (Cubicin) is usually used for complicated and serious infections since it is a strong antibiotic.
What is the name of the drug that kills bacteria?
Daptomycin ( Cubicin) is an antibacterial medication. It kills bacteria by preventing them from making their own DNA, RNA, and proteins they need to survive.
What to do if you have allergies to antibiotics?
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any allergies to antibiotics. If you get a rash, itchy skin, hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling of your face or mouth while taking daptomycin (Cubicin), talk to your healthcare provider or go to the emergency room right away.
Does daptomycin interact with other medications?
Daptomycin (Cubicin) may interact with certain medications or supplements. Always let your doctor and pharmacist know about any other medications or supplements (including prescribed and over-the-counter medications, vitamins, and dietary or herbal supplements) that you are currently taking. The list below does not include all possible drug interactions with daptomycin (Cubicin). Please note that only the generic name of each medication is listed below.
Can daptomycin cause hives?
In rare cases, daptomycin (Cubicin) can cause a severe and life-threatening allergic reaction. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any allergies to antibiotics. If you get a rash, itchy skin, hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling of your face or mouth while taking daptomycin (Cubicin), talk to your healthcare provider or go to the emergency room right away.
What are the issues related to pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic considerations?
Issues related to pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic considerations, challenges with susceptibility testing and emergence of resistance, dosing, monitoring, adverse effects, and drug interactions will be reviewed here .
Is UpToDate a substitute for medical advice?
The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your own physician or other qualified health care professional regarding any medical questions or conditions. The use of UpToDate content is governed by the UpToDate Terms of Use. ©2021 UpToDate, Inc. All rights reserved.
What is the name of the drug that is used to treat gram positive bacteria?
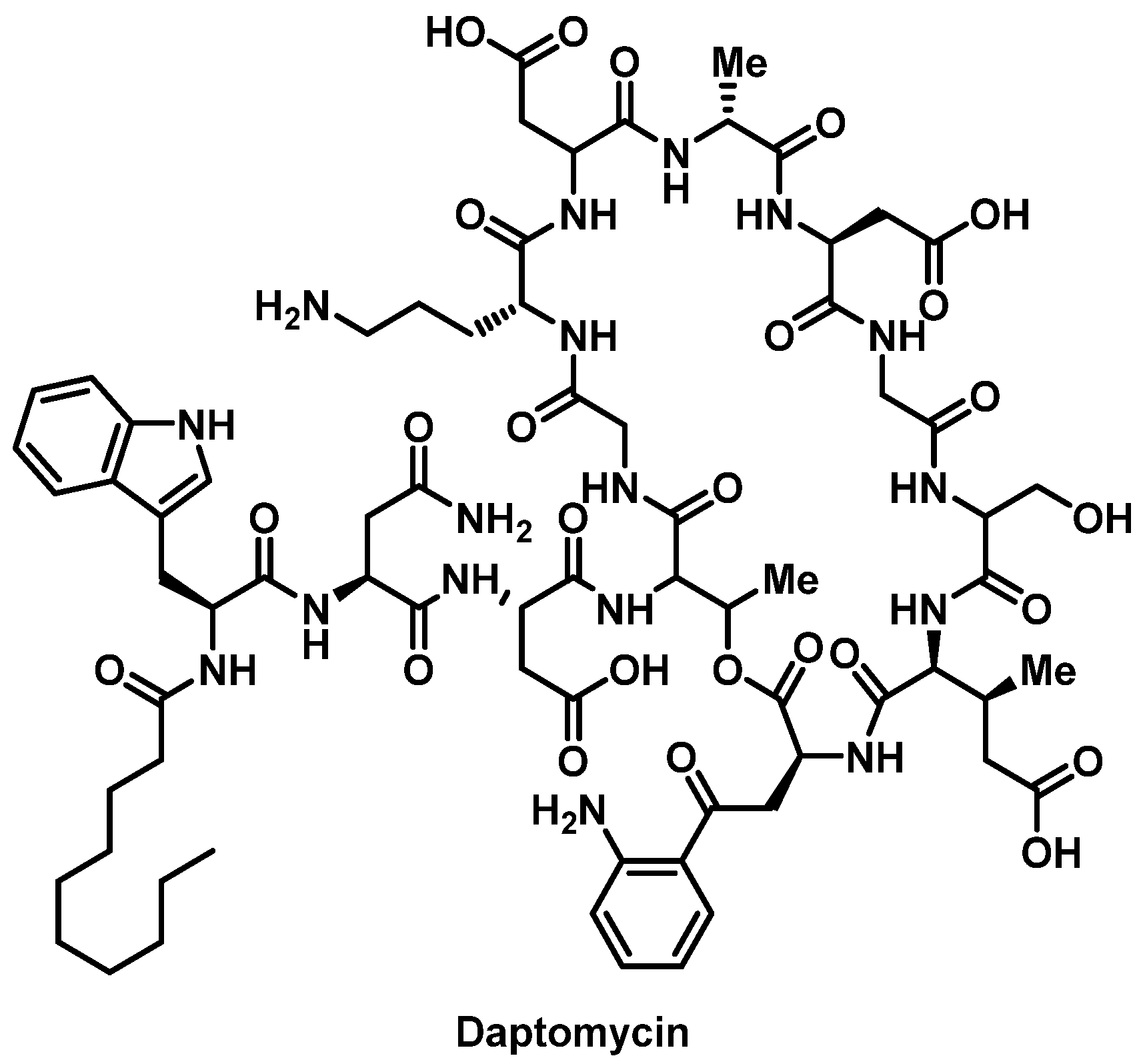
Daptomycin (Cubicin; Cubist Pharmaceuticals) is a member of a new class of antibiotics, called the cyclic lipopeptides, which was approved on 12 September 2003 for the treatment of complicated skin and skin-structure infections [ 1 ]. Daptomycin exhibits in vitro activity against gram-positive bacteria, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis, vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus species, and penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae [ 1 ]. We present a case of vancomycin- and linezolid-resistant Enterococcus faecium bacteremia treated with daptomycin. The patient subsequently developed rhabdomyolysis during therapy. A Naranjo score was calculated and correlated to a probable classification for daptomycin as a cause of rhabdomyolysis.
Does daptomycin affect skeletal muscle?
Once-daily dosing with daptomycin has been shown to have fewer effects on skeletal muscle in dogs, compared with twice-daily dosing [ 5 ]. These investigative studies have shown that skeletal muscle effects were related to dosing frequency rather than to peak plasma concentrations.
Does daptomycin cause rhabdomyolysis?
The use of daptomycin has been associated with an elevation in creatine phosphokinase level, with a reported incidence of 2.8% in phase III clinical trials. Published case reports have documented the presence of myopathy in patients who received daptomycin; however, there have been no previously reported cases of rhabdomyolysis in animals ...
When can a patient withdraw from a study?
A patient will be withdrawn from the study if the patient or legally acceptable representative withdraws consent at any time or if the investigator deems it is in the best interest of the patient due to safety concerns .
How long does it take for bacteremia to clear?
Participants with uncomplicated bacteremia will receive a minimum of 14 days antibiotics and those with complicated bacteremia or infective endocarditis will receive a minimum of 28 to 42 days antibiotics from the date that microbiological clearance is achieved. Microbiological clearance is defined as two consecutive MRSA negative blood cultures. Uncomplicated bacteremia is defined as the isolation of MRSA from enrolment blood cultures in patients without endocarditis and without evidence of spread to other organs. Complicated bacteremia without endocarditis is defined as the persistence of MRSA in blood cultures beyond four days from initial positive culture, the presence of spread of infection, or infection of a vascular catheter, implantable cardiac device, or orthopedic/joint prosthetic implant not removed within four days. Right-sided endocarditis (complicated bacteremia) is defined as definite or possible endocarditis involving the tricuspid or pulmonary valve in patients without predisposing abnormalities or active infection of the mitral or aortic valves. Left-sided endocarditis (complicated bacteremia) is defined as definite or possible endocarditis involving the mitral or aortic valve. In order to make the above diagnoses, participants will be required to undergo an echocardiogram within the first 10 days of randomization. The definition of ‘definite’ or ‘possible’ endocarditis will be determined using the modified Duke criteria [19]. The diagnosis of the type of bacteremia may change during the course of study and treatment duration will be changed accordingly. This decision will be made by the managing physician.
What is the best treatment for methicillin resistant staph?
Vancomycin is the standard first-line treatment for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureusbacteremia. However, recent consensus guidelines recommend that clinicians consider using alternative agents such as daptomycin when the vancomycin minimum inhibitory concentration is greater than 1 ug/ml. To date however, there have been no head-to-head randomized trials comparing the safety and efficacy of daptomycin and vancomycin in the treatment of such infections. The primary aim of our study is to compare the efficacy of daptomycin versus vancomycin in the treatment of bloodstream infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureusisolates with high vancomycin minimum inhibitory concentrations (greater than or equal to 1.5 ug/ml) in terms of reducing all-cause 60-day mortality.
Is daptomycin a good substitute for vancomycin?
aureusbacteremia and is considered a reasonable alternative to vancomycin. The efficacy of daptomycin has been demonstrated in an open-label randomized clinical trial by Fowler et al.[14]. In a subgroup analysis this trial showed that the success rate for daptomycin was marginally greater (although not statistically significant) than the standard treatment among patients with MRSA bacteraemia (44% for daptomycin versus 31.8% for standard treatment; P = 0.28). Daptomycin, however, showed a worse outcome than standard treatment in patients with left-sided endocarditis due to S. aureus. A subsequent report evaluating the MRSA isolates from this study found that all strains in the vancomycin arm had an MIC of less than or equal to 1 ug/ml [15], hence it is difficult to state conclusively whether daptomycin is superior to vancomycin in the treatment of MRSA infections. Three recent cohort studies comparing daptomycin and vancomycin for bloodstream infections (BSIs) due to MRSA with a high vancomycin MIC demonstrated that daptomycin was associated with a better outcome, both in terms of rates of clinical success and mortality, compared to vancomycin [16-18]. However, being retrospective non-randomized studies, these results need to be interpreted with caution.
Does vancomycin cause bacteremia?
In recent years, there has been an increase in the number of MRSA isolates with high vancomycin minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) [5]. Higher vancomycin MICs have been associated with prolonged bacteremia and increased mortality [6,7]. Vancomycin, a tricyclic glycopeptide, is the standard first-line treatment for patients with MRSA bacteremia. However, studies have linked vancomycin treatment failure in MRSA with higher vancomycin MICs even at MICs below the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) susceptibility breakpoints for S. aureus(≤2 ug/ml) [8-11]. Recent consensus guidelines recommend that clinicians consider using alternative agents for MRSA infection when the vancomycin MIC is greater than 1 ug/ml [12,13], especially if there is evidence of clinical failure with regards to vancomycin treatment.
Does daptomycin help with bloodstream infections?
This would help guide clinicians and inform practice guidelines on the optimal treatment for such infections.
Can you withdraw from a study without giving a reason?
However, all patients are free to withdraw completely from the study at any time without giving a reason. If patients withdraw completely from study participation no further information will be collected for study purposes.