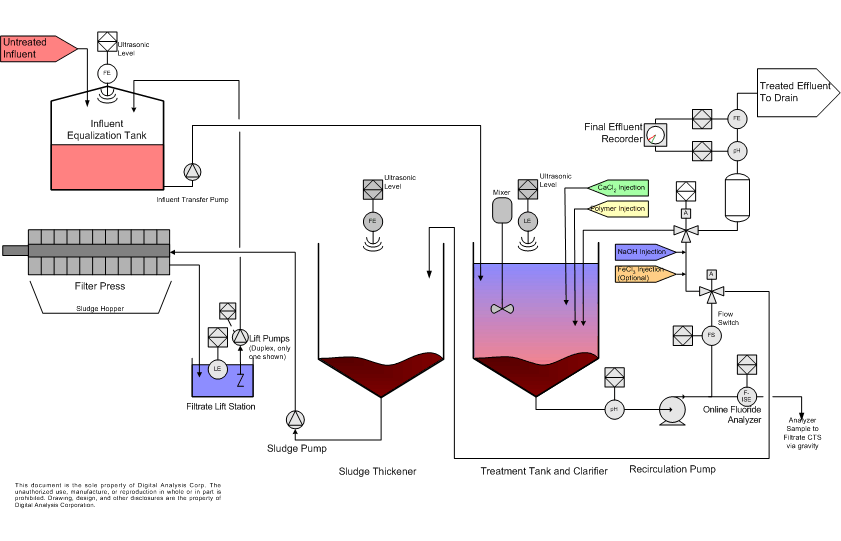
Phases of a Wastewater Treatment Plant
- Pretreatment. Pretreatment primarily uses physical processes like filtration and settling to remove larger solid particles from the wastewater.
- Primary Treatment. The next wastewater treatment plant process is the primary treatment. ...
- Secondary Treatment. Secondary wastewater treatment uses bacterial processes rather than physical ones. ...
- Tertiary Treatment. ...
What are the functions of a waste water treatment plant?
Types of treatment plants
- Sewage treatment plants. This section is an excerpt from Sewage treatment. ...
- Industrial wastewater treatment plants. This section is an excerpt from Industrial wastewater treatment. ...
- Agricultural wastewater treatment plants. This section is an excerpt from Agricultural wastewater treatment. ...
- Leachate treatment plants. ...
What are the disadvantages of a waste water treatment plant?
What Are the Dangers of Living Near a Wastewater Treatment Facility?
- Airborne Hazards. Chemicals from wastewater treatment facilities become airborne when they're air-stripped. ...
- Respiratory and Gastrointestinal Infections. If particles, organisms or pathogens that are air-stripped are inhaled, they go through the bronchial tubes and lungs, are cleared from the lungs, and then swallowed.
- Pests. ...
How do plants get rid of their waste products?
- Actually plant use their waste product for their survival or for protection. ...
- In pPlants their are two types of metabolism pathway
- Primary metabolism pathway- product of primary metabolism are such as carbohydrates, sugar, Amino acid, ATP are called as primary metabolites. ...
- Other than this there is second type of metabolism called as……
How does a sewage treatment plant actually work?
You’re basically:
- growing the organisms in a suspension and retaining them
- mixing the wastewater with the biomass
- aerating this “mixed liquor” so the bacteria can get to work
- settling out the mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSS)
- sending return activated sludge (RAS) to the reactor basin
- sending waste activated sludge (WAS) to be dewatered and treated accordingly

What is removed from waste water at water treatment plants?
The major aim of wastewater treatment is to remove as much of the suspended solids as possible before the remaining water, called effluent, is discharged back to the environment. As solid material decays, it uses up oxygen, which is needed by the plants and animals living in the water.
What do wastewater treatment plants release?
Wastewater treatment plants release large amounts of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli into the environment. Clin Infect Dis.
What does wastewater treatment not remove?
Biological stages in wastewater treatment plants are not able to remove substances such as drugs, found in the wastewater of medical centers, or halogenated compounds and cyanides from industrial wastewater.
What is removed in water treatment?
These filters remove dissolved particles and germs, such as dust, chemicals, parasites, bacteria, and viruses. Activated carbon filters also remove any bad odors. Water treatment plants can use a process called ultrafiltration in addition to or instead of traditional filtration.
What is removed during secondary wastewater treatment?
Secondary treatment is the removal of biodegradable organic matter (in solution or suspension) from sewage or similar kinds of wastewater. The aim is to achieve a certain degree of effluent quality in a sewage treatment plant suitable for the intended disposal or reuse option.
What happens to solid waste from water treatment plants?
Treating sewage produces a lot of solid matter called 'sludge'. This has to be treated before we can recycle it to farmland. We use large tanks (known as digesters) where bacteria break the sludge down and release methane gas.
What are two things that the water treatment process Cannot remove?
The Three Most Difficult Items to Remove From Wastewater#1 – Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) Both prescription and over-the-counter medications and supplements are wreaking havoc on wastewater. ... #2 – Nitrites and Nitrates. ... #3 – Polyethylene and Polypropylene Microbeads.
Does wastewater treatment remove chemicals?
New research shows that wastewater treatment plants that employ a combination of purifying techniques followed by reverse osmosis – a process by which water is forced through a barrier that only water can pass – do a good job of removing chemicals that may elicit health effects.
What does wastewater contain?
Wastewater contains nitrogen and phosphorus from human waste, food and certain soaps and detergents. Once the water is cleaned to standards set and monitored by state and federal officials, it is typically released into a local water body, where it can become a source of nitrogen and phosphorus pollution.
What is removed when water is filtered?
What are Water Filters? Water Filters remove unwanted impurities from water such as sediment, taste and odour, hardness and bacteria to result in better quality water.
What impurities are removed from water by filtration?
There are hundreds of physical, chemical, biological, and radiological elements removed by water filters, including lead, chlorine, bacteria, calcium, minerals, salt, and carcinogens. Most drinking water purification methods look to remove the majority of those contaminants.
How do water treatment plants remove soap?
Local water treatment plants often remove environmentally harmful impurities, such as soap, from waste water before returning it to the environment. One way to remove soap from water is to have it react with other substances. When these reactions occur, a solid called a precipitate is sometimes formed.
What is reverse osmosis in wastewater treatment?
New research shows that wastewater treatment plants that employ a combination of purifying techniques followed by reverse osmosis – a process by which water is forced through a barrier that only water can pass – do a good job of removing chemicals that may elicit health effects.
Does reverse osmosis remove contaminants?
The research shows that water-reclamation plants employing reverse osmosis do in fact remove more contaminants. For example, the conventional treatment plant, which after initial treatment still contained detectable levels of 13 of the different contaminants under study, eliminated only five of them from the discharged water.
Does wastewater contain hormones?
As Pedersen explains, wastewater typically contains any number of pharmaceuticals and hormones that people have either excreted or flushed away for easy disposal. Many times, these chemical compounds remain biologically active, he says, adding that some of them, especially hormones such as estrogen, appear to significantly alter aquatic organisms.
Do treatment plants remove drugs from wastewater?
Do treatment plants effectively remove drugs, hormones from wastewater? Given the number of human pharmaceuticals and hormones that make their way into wastewater, some people are concerned about how well treatment plants that turn sewage into reusable water remove these chemical s.
Does well water reclamation remove hormones?
While this treatment process has the promise to save an evaporating natural resource, Pedersen points out that little is known about just how well water-reclamation plants remove the pharmaceuticals and hormones that typically are found in sewage.
What is wastewater treatment plant?
February 11, 2021 Blog. admin-seo. Wastewater treatment plants are there to clean and purify water that arrives through sewer lines, septage haulers, etc. The process removes bacteria, solids, and other impurities until the water is clean enough to go back into the district’s water supply or get released into area bodies of water.
How do medications get into wastewater?
The reality is that the medications people take also find their way into your wastewater. They’re excreted through fecal matter and urine or expired or unneeded pills are flushed down drains or toilets. The wastewater treatment process does what it can to remove them.
Which is the best treatment for a soil aquifer?
Diazepam (Sedative) – Reverse osmosis was the most effective with ultrafiltration using powdered activated carbon as a second-best choice. Diclofenac and Ibuprofen (NSAID) – Reverse osmosis and soil aquifer treatments were the best options, and granular activated carbon filters also worked well on.
Does wastewater remove everything?
Wastewater Treatment May Not Remove Everything. In a month’s time, it’s estimated that close to 46% of Americans have taken at least one prescription drug. As you get older, chronic health conditions are more likely. Around 85% of American’s aging adults (60 or older) take medications daily. Adults aren’t alone.
Does modernizing wastewater equipment help?
If you’re looking to clean wastewater effectively and efficiently, modernizing some equipment can help improve your plant’s performance while lowering electricity costs. Your district saves money, which makes everyone happy. Lakeside Equipment has been a leader in water purification for close to a century.
Does wastewater treatment cover pharmaceuticals?
Federal Regulations on Wastewater Treatment Don’t Cover Pharmaceuticals. The Federal Government maintains a list of chemicals, metals, and other contaminants that must be removed from wastewater before it’s released. Pharmaceuticals are not on that list.
Why upgrade wastewater treatment system?
Enhanced treatment systems enable some wastewater plants to produce discharges that contain less nitrogen than plants using conventional treatment methods . Upgrading wastewater treatment systems is often expensive for municipalities and rate payers, but upgrades can pay for themselves or end up saving a plant money.
What is the source of nitrogen and phosphorus in wastewater?
Wastewater contains nitrogen and phosphorus from human waste, food and certain soaps and detergents. Once the water is cleaned to standards set and monitored by state and federal officials, it is typically released into a local water body, where it can become a source of nitrogen and phosphorus pollution. Some wastewater treatment plants are able ...
How to maintain a septic system?
Homeowners are responsible for maintaining their septic systems in most cases. To protect and maintain their system, homeowners should: 1 Have their system inspected regularly and pump their tank as necessary 2 Use water efficiently 3 Not dispose of household hazardous waste in sinks or toilets 4 Avoid driving vehicles or placing heavy objects on their drainfield 5 Visit EPA's decentralized wastewater (septic) systems webpage to learn more about septic systems and EPA's SepticSmart Week Program 6 Consult EPA's guide on maintaining septic systems for more information: Homeowner's Guide to Septic Systems (PDF) (9 pp, 3 MB, About PDF)
How does a septic system contribute to nutrient pollution?
Septic systems can easily become a source of nutrient pollution if not properly maintained. Most homes and businesses send their wastewater to a treatment plant where many pollutants are removed from the water. Wastewater treatment facilities in the United States process approximately 34 billion gallons of wastewater every day.
Who is responsible for septic system maintenance?
Homeowners are responsible for maintaining their septic systems in most cases. To protect and maintain their system, homeowners should: Have their system inspected regularly and pump their tank as necessary. Use water efficiently. Not dispose of household hazardous waste in sinks or toilets.
What is wastewater treatment?
It’s the water from toilet flushes, showers, washing machines, sinks, and dishwashers. As wastewater is filled with fecal matter, urine, household or commercial cleaners, soaps/shampoos, etc., it has to be treated before it can return to water sources or public water supplies. While this is something wastewater treatment plants do every hour ...
How often do wastewater treatment plants work?
While this is something wastewater treatment plants do every hour of the day , there are things that homeowners may not think of. Wastewater treatment can only do so much. Three items come from homes and businesses that are very difficult to fully remove from water.
What is the removal rate of microbeads in wastewater treatment plants?
Wastewater treatment plants that use primary clarification have better success rates at removing microbeads, but the removal rate is still only an average of 87% .
How much estrogen is removed from wastewater?
It’s found that a secondary wastewater treatment process is still only able to remove a maximum of 95% of the estrogen. Antibacterial soaps that contain triclocarban are even worse. Scientists found that only 25% of the triclocarban in wastewater was removed by the end of the process.
Where does urine end up in a water treatment plant?
That urine ends up in a water treatment plant where the medications do not fully get removed. One study found that antibiotics and synthetic hormones (birth control) were being found in water sources and the fish living in those rivers and lakes. It’s found that a secondary wastewater treatment process is still only able to remove a maximum ...
What are the most difficult items to remove from a septic system?
The Three Most Difficult Items to Remove From Wastewater. Wastewater is the water that comes from homes and businesses through sewer lines or after a septic tank is pumped. It’s the water from toilet flushes, showers, washing machines, sinks, and dishwashers.
What are nitrates used for?
Nitrates are used as a food additive in many cured meats. People consume them regularly in deli meats, bacon, sausage, and hot dogs. As the body’s bacteria break down those foods, they convert to nitrite. Nitrites are incredibly harmful to bodies of water as they deplete oxygen and increase algae growth. A wastewater treatment plant has ...
What is Ozonation in Wastewater Treatment?
Ozonation uses ozone (O3 molecules). People use an electric field or ultraviolet light to make ozone because O3 molecules aren’t stable. Then, the ozone is pulled into water. In this way, we use ozone to increase purification efficiency in water treatment. Simply put, ozonation breaks down most organic micropollutants.
What is Granular Activated Carbon (GAC) in Wastewater Treatment?
Granular activated carbon is carbon that is processed to be like a sponge. As a result, this process greatly increases the carbon’s surface area. Also, this process makes it easier for molecules to pass through carbon.
Three Ways You Can Stop Pharmaceutical Pollution in Water
Drop off medicine you don’t use, either prescribed or over the counter, a drug take back site, location, or program.
The myth: Wastewater treatment plants smell
Do wastewater treatment plants smell? A common belief regarding wastewater treatment plants is that they produce bad odors that travel into the atmosphere and the surrounding environment. This makes sense — after all, the reason for treating wastewater in the first place is to remove unpleasant chemicals and compounds.
The myth: Wastewater treatment poses a risk to public health
If a wastewater treatment plant is located in or close to a community, it is not unusual for local residents to become alarmed. Again, because these wastewater treatment plants are dealing with hazardous chemicals and substances, there is a worry that this could put the local populace at risk.
The myth: Wastewater treatment is environmentally unsafe
It is not just public safety that is sometimes considered to be at risk due to wastewater treatment technology — the environment is also a major cause for concern.
The myth: Wastewater treatment facilities are dangerous places to work
In America, everyone has the right to go about their work in a safe and secure manner, free from undue risk or threat to personal well-being. Due to the negative associations of wastewater treatment plants, employment practices in this industry have come under significant scrutiny.
Ongoing improvement for wastewater plants
As society becomes more engaged with environmental issues, wastewater treatments plants will continue to play a role in eliminating toxic chemicals and hazardous materials from waste. What’s more, they will become better — cleaner, safer, and more efficient, with increasingly effective odor control.