Common First-Line Treatments for COPD
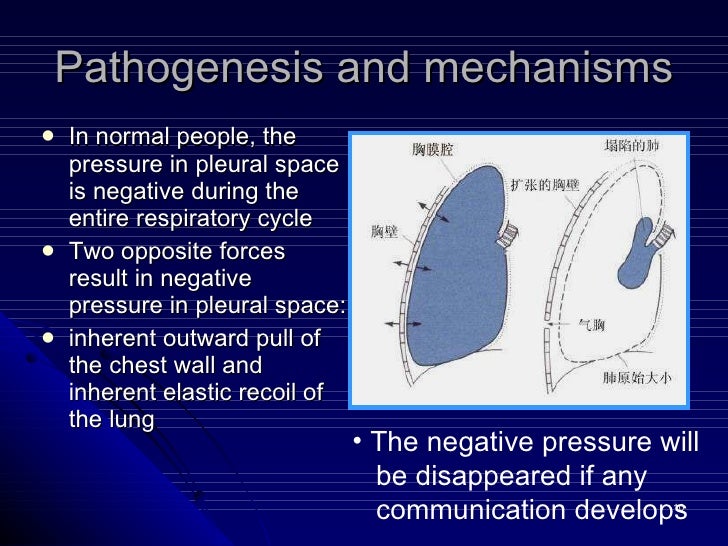
- Supplemental oxygen. Once your COPD is classified as severe, your blood oxygen levels could fall into below normal...
- Smoking cessation. It is more important than ever to quit smoking for people who are diagnosed with COPD. Smoking does...
- Proper nutrition. People with severe COPD may find it difficult to eat well because of the...
What is the best natural remedy for COPD?
Sep 01, 2017 · What Are the First-Line Treatments for COPD? Smoking cessation. If you’re still smoking when diagnosed with COPD, it’s more important than ever to stop. Quitting will help you breathe more easily ... Bronchodilators. Antibiotics. Supplemental oxygen.
What is the drug of choice for COPD?
Pulmonary rehabilitation (pull mon aire ree reha bill ii tay shun) is also a very important treatment for COPD that includes showing you exercises and activities right for you, learning about your COPD and breathing techniques as well as the correct way to use your inhalers or nebulizers. It is one of the most effective treatments we have but is not often recommended or available.
What is the latest medication for COPD?
Dec 27, 2017 · Common First-Line Treatments for COPD Supplemental oxygen. Once your COPD is classified as severe, your blood oxygen levels could fall into below normal... Smoking cessation. It is more important than ever to quit smoking for people who are diagnosed with COPD. Smoking does... Proper nutrition. ...
What is the latest treatment for COPD?
Jul 26, 2021 · The goal of therapy when treating a COPD exacerbation is to minimize the negative impact of the current exacerbation and prevent future events. The recommended initial treatment for mild exacerbations is the use of short-acting beta 2 -agonists (SABA), with or without short-acting anticholinergics.

What is the most effective treatment for COPD?
Oxygen therapy. Others use oxygen all the time. Oxygen therapy can improve quality of life and is the only COPD therapy proved to extend life.Apr 15, 2020
What is the second line of treatment for COPD?
Roflumilast is an effective oral anti-inflammatory drug that has been demonstrated to reduce exacerbation in patients with severe COPD and chronic bronchitis when used in combination with a LABD, a LABA/ICS combination, or even in addition to triple therapy [10].
What is the first line gold standard therapy for COPD?
Tiotropium is the first LAMA approved for once-daily therapy for COPD. Tiotropium has demonstrated significant and sustained bronchodilation (opening of the airways) [45] and reduction in hyperinflation (air trapping) [46, 47].Nov 26, 2012
What is the drug of choice for COPD?
The current pharmacological treatment of COPD is symptomatic and is mainly based on bronchodilators, such as selective β2-adrenergic agonists (short- and long-acting), anticholinergics, theophylline, or a combination of these drugs.
Is ipratropium short or long acting?
Background: Short-acting anticholinergic bronchodilator, ipratropium bromide has been recommended as first-line drug in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). More recently, long acting beta2-agonist (LABA) bronchodilators such as formoterol have been shown to be useful in COPD.
What is lama LABA ICS?
LAMA: long-acting muscarinic antagonist; LABA: long-acting β2-agonist; ICS: inhaled corticosteroid.
Why is ipratropium used for COPD?
Ipratropium is used to control and prevent symptoms (wheezing and shortness of breath) caused by ongoing lung disease (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease-COPD which includes bronchitis and emphysema). It works by relaxing the muscles around the airways so that they open up and you can breathe more easily.
How does a LABA work in COPD?
Long acting beta agonist and LAMA are two major classes of bronchodilators and currently the principal medications for patients with COPD. LABA relax airway smooth muscle by linking with the beta2-adrenergic receptors.Apr 25, 2019
What is the GOLD ABCD classification for COPD?
Each of these studies addresses the distribution of COPD patients by the new classification and assigns them to the each of the four proposed quadrants: A: few symptoms, better lung function; B: more symptoms, better lung function; C: few symptoms, poor lung function; D: more symptoms, poor lung function.
Which antibiotic is best for COPD?
Mild to moderate exacerbations of COPD are usually treated with older broad-spectrum antibiotics such as doxycycline, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and amoxicillin-clavulanate potassium.Aug 15, 2001
What are nursing interventions for COPD?
Nursing InterventionsInspiratory muscle training. This may help improve the breathing pattern.Diaphragmatic breathing. Diaphragmatic breathing reduces respiratory rate, increases alveolar ventilation, and sometimes helps expel as much air as possible during expiration.Pursed lip breathing.Apr 22, 2021
What inhaler is used for COPD?
Advair is one of the most commonly used inhalers for the maintenance treatment of COPD. It is a combination of fluticasone, a corticosteroid, and salmeterol, a long-acting bronchodilator. Advair is used on a regular basis for the maintenance treatment of COPD and it is typically taken twice per day.Mar 24, 2022
What are the treatments for COPD?
COPD treatments include both medicines and other important therapies such as pulmonary rehabilitation, smoking/vaping cessation support and immunizations. If you were asked about COPD medicines you would probably think about your inhalers and you’d probably say, "they open up my lungs".
What is COPD360social?
The COPD Foundation offers resources such as COPD360social, an online community where you can connect with patients, caregivers and health care providers and ask questions, share your experiences and receive and provide support.
How to prevent fires in a home?
Maintenance (Controllers-Prevention): As a responsible person, you do your best to prevent fires by maintaining your home, keeping the electrical wires operating safely, turning off the stove when you’re not using it and putting hot matches in a fireproof container or in water.
What is a nebulizer?
A nebulizer is a device that changes liquid medicine into a fine mist that can be inhaled into the lungs. This mist can be breathed in through a mouthpiece or face mask. There are different types of nebulizers: jet, vibrating mesh and ultrasonic nebulizers. Sometimes the vibrating mesh and ultrasonic types are lumped together under "electronic" nebulizers.
How does the nervous system work?
This is the job of the parasympathetic nervous system. If you touch something hot, a message is sent through your nerves to pull your hand away. How does this work in the lungs? In our lungs, messages are sent to squeeze down the airways in response to things like “bad air” like smoke or cold or other pollution or in response to things that might cause an infection or irritation to the lung. You can think of this as trying to prevent unhealthy things from coming into the lungs. This squeezing down of the airways also called bronchoconstriction (brawn-co-con-stric-shun), causes feelings of chest tightness and shortness of breath. Anticholinergic medicines block these messages from being produced or getting through to the airways and helping keep your airways open. Yes, this is pretty amazing!
Can you use an inhaler with ICS?
However, some people may still use an inhaler with just the ICS. Currently approved ICS only medicines include the following commercial brand names for ciclesonide, fluticasone furoate, mometasone furoate, fluticasone furoate, budesonide and beclomethasone dipropionate. Alvesco® (I)*. Arunity Ellipta® (I)*.
What is volume reduction surgery?
Lung Volume Reduction Surgery is surgical procedure for carefully selected patients with severe emphysema struggling despite maximal medical therapy. Currently, the surgery is almost always done with a minimally invasive approach called VATs, video assisted thoracoscopy. During the operation, the surgeon removes the worst area of emphysema. By doing this, the healthier portions of the lung are able to work more efficiently. This surgery also reduces pressure on the diaphragm, making it easier to breathe.
What is the best treatment for COPD?
Bronchodilators. Once you have been diagnosed with COPD, your doctor will discuss with you the best treatment options available considering the severity of your disease. A common medication that should be prescribed are bronchodilators, which work by allowing your bronchial muscles to relax, thereby opening them wider.
Why is it so hard to eat with COPD?
People with severe COPD may find it difficult to eat well because of the symptoms of their condition. This could lead to unintended weight loss, especially in those with a more advanced stage of the lung disease. When one is not eating enough, he is not only heading for malnutrition but also for a worsening of COPD symptoms and even a likelihood of infection.
Is breathing a function of the body?
Breathing is a certain function of our body that just comes naturally for everyone—except those with COPD. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is a breathing disorder that affects 11 million people in the United States. COPD is a common lung condition that makes it difficult to get air in and out of the lungs.
Can COPD be reversed?
But while the disease cannot be reversed, it can be treated and controlled to increase one’s comfort.
Does smoking cause COPD?
Smoking does not only trigger COPD flare-ups, but it is also the leading cause of the condition. COPD patients already find it hard to breathe with injured lungs, and smoking makes breathing worse by damaging the airways up to the air sacs of the lungs. If you are a chronic smoker, quitting can be a difficult feat.
What are the two types of bronchodilators?
While there are two types of bronchodilators—the short-acting and the long-acting —they fall into different categories depending on how they function. These categories include anticholinergic, beta2-agonist, steroid or glucocorticosteroid, theophylline, and mucolytic.
Can COPD be treated with oxygen?
Supplemental oxygen. Once your COPD is classified as severe, your blood oxygen levels could fall into below normal levels, which would then require a prescription for supplemental oxygen from your doctor.
Diagnosis, Assessment, and Classification
COPD is diagnosed through a combination of spirometry and medical history, including symptom history and presence of risk factors. Spirometry is a noninvasive, readily available, objective measure of airflow limitation.
Nonpharmacologic and Preventative Therapy
Nonpharmacologic therapy for COPD includes smoking cessation, physical activity, and vaccination. Smoking cessation is important to prevent disease progression. Patients with COPD who are current smokers should be assessed for willingness to quit smoking and be provided with education on how to quit.
Maintenance Treatment of COPD
GOLD classifications are used to determine initial treatment options for patients with COPD. FIGURE 2 shows the initial pharmacologic treatment for each GOLD group classification. Refer to TABLE 1 and FIGURE 2 for classifications.
COPD Exacerbations
Exacerbations may be triggered by several factors, most commonly infections of the respiratory tract. Conditions with nonspecific symptoms similar to a COPD exacerbation include pneumonia, pneumothorax, pleural effusion, pulmonary embolism, pulmonary edema, and/or cardiac arrhythmias.
Conclusions
First-line management of COPD is dependent upon patient-specific factors such as GOLD classification and patient preference; however, nonpharmacologic and preventative methods should always be considered. Preventative methods include vaccination, including the new recommendation for a Tdap booster in patients with COPD.
What is the best treatment for COPD?
For most people with COPD, short-acting bronchodilator inhalers are the first treatment used. Bronchodilators are medicines that make breathing easier by relaxing and widening your airways. There are 2 types of short-ac ting bronchodilator inhaler : beta-2 agonist inhalers – such as salbutamol and terbutaline.
What to do if you have COPD?
stopping smoking – if you have COPD and you smoke, this is the most important thing you can do. inhalers and tablets – to help make breathing easier. pulmonary rehabilitation – a specialised programme of exercise and education. surgery or a lung transplant – although this is only an option for a very small number of people.
How long does pulmonary rehabilitation last?
Pulmonary rehabilitation programmes usually involve 2 or more group sessions a week for at least 6 weeks. The programmes are provided by a number of different healthcare professionals, including physiotherapists, nurse specialists and dietitians.
What is lung rehabilitation?
Pulmonary rehabilitation is a specialised programme of exercise and education designed to help people with lung problems such as COPD. It can help improve how much exercise you're able to do before you feel out of breath, as well as your symptoms, self-confidence and emotional wellbeing.
What is an inhaler for COPD?
If COPD is affecting your breathing, you'll usually be given an inhaler. This is a device that delivers medicine directly into your lungs as you breathe in. A doctor or nurse will advise you on how to use an inhaler correctly and how often to use it. There are several different types of inhaler for COPD.
How to stop COPD from getting worse?
Long-term oxygen therapy. If COPD causes a low level of oxygen in your blood, you may be advised to have oxygen at home through nasal tubes or a mask. This can help stop the level of oxygen in your blood becoming dangerously low, although it's not a treatment for the main symptoms of COPD, such as breathlessness.
How long should you use oxygen?
Long-term oxygen treatment should be used for at least 16 hours a day. The tubes from the machine are long, so you will be able to move around your home while you're connected. Portable oxygen tanks are available if you need to use oxygen away from home. Do not smoke when using oxygen.
What is the best treatment for COPD?
Pharmacologic therapy for COPD is used to decrease symptoms, reduce the frequency and severity of exacerbations, and improve exercise intolerance. Common classes of medications used in treatment of COPD include beta 2 agonists, antimuscarinics, inhaled corticosteroids (ICS), and combination therapy. Identification and reduction of exposure ...
What is the gold classification for COPD?
According to the GOLD 2019 Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of COPD guideline update, first-line pharmacologic therapy depends on the patient’s GOLD classification ( FIGURE 1 .) Short-acting bronchodilators (short-acting muscarinic antagonist [SAMA] or short-acting inhaled beta 2 agonist [SABA]) should be prescribed to all patients for immediate symptom relief, regardless of their GOLD classification. 1
What is an inhaler used for?
ABSTRACT: Inhalers used in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) come in a variety of novel mono-, dual-, and triple-therapies. These inhalers may contain short-acting beta2 agonists, long-acting beta2 agonists, short-acting muscarinic antagonists, long-acting muscarinic antagonists, or inhaled corticosteroids.
How old do you have to be to get a PPSV23?
The yearly influenza vaccine and the PPSV23 and PCV13 pneumococcal vaccines are recommended in all patients with COPD. 2 PPSV23 is recommended for patients aged 19 to 64 years, and PCV13 is recommended for patients aged 65 years and older, administered at least 1 year after PPSV23.
Can beta 2 agonists cause hypokalemia?
Beta 2 agonists (SABAs, LABAs) can produce sinus tachycardia and precipitate cardiac-rhythm disturbances in susceptible patients. Hypokalemia can occur, especially when beta 2 agonists are combined with thiazide diuretics, as can increased oxygen consumption in patients with heart failure, but these effects decrease over time. 8,9
Can you use inhalers for COPD?
These provide patients with more options to treat their COPD based on individual preferences. Inhalers used in the treatment of COPD are generally well tolerated. It is important for the pharmacist to assess inhaler technique and understand how each inhaler is used with each follow-up or encounter with patients.
What is a short acting bronchodilator?
Short-acting bronchodilators (short-acting muscarinic antagonist [SAMA] or short-acting inhaled beta 2 agonist [SABA]) should be prescribed to all patients for immediate symptom relief, regardless of their GOLD classification. 1.
What is the best treatment for COPD?
Monotherapy with a long-acting beta 2 agonist or long-acting anticholinergic is recommended for symptomatic patients with COPD whose FEV 1 is less than 60% of predicted. A. 3. Initial monotherapy with a long-acting beta 2 agonist or long-acting anticholiner gic is recommended for patients with COPD.
What are the risk factors for COPD?
Risk factors include age older than 35 years with significant smoking history, α 1 -antitrypsin deficiency, and a history of significant exposure to indoor or outdoor air pollution, occupational dusts, or chemicals. Other findings from the history and physical examination that increase the likelihood of COPD include a smoking history of more than 40 pack-years (positive likelihood ratio [LR+] = 7.3; negative likelihood ratio [LR–] = 0.5), self-reported history of COPD (LR+ = 8.3; LR– = 0.8), maximal laryngeal height of 4 cm or less (from top of thyroid cartilage to suprasternal notch; LR+ = 1.3; LR– = 0.4), and age older than 45 years regardless of smoking history (LR+ = 2.8; LR– = 0.8). 8 The presence or absence of all four of these features can rule COPD in (LR+ = 220.5) or out (LR– = 0.13). 8 Another good clinical predictor of COPD is the combination of three clinical variables: peak flow rate less than 350 L per minute, diminished breath sounds, and a smoking history of 30 pack-years or more. 9 The presence of any one of these clinical variables predicts airflow obstruction with 98% sensitivity and 46% specificity, whereas the absence of all three essentially rules out airflow obstruction (3% false-negative rate). 9
What is pulmonary rehabilitation?
Pulmonary rehabilitation consists of structured programs with multidisciplinary health care teams to provide exercise training, education, nutritional counseling, and behavioral modification. A meta-analysis of 20 RCTs showed that pulmonary rehabilitation reduced dyspnea and increased exercise ability and health-related quality of life, but required at least six months to achieve benefits. 27 Patients most likely to benefit are those with severe COPD who have impaired quality of life and dyspnea that limits activity; however, patients with moderate COPD may also benefit. 3, 4, 28 Clinicians should prescribe pulmonary rehabilitation for symptomatic patients whose FEV 1 is less than 50% of predicted. Pulmonary rehabilitation should be considered for symptomatic or exercise-limited patients whose FEV 1 is greater than 50% of predicted.
What is the BODE index?
Whereas spirometry is used to determine lung function or decline in patients with COPD, the BODE ( b ody mass index, degree of airflow o bstruction and d yspnea, and e xercise capacity) index can be used to determine overall disease severity and risk of death ( Table 7 ). 33
Can methylxanthines be used for COPD?
The adverse effects, narrow therapeutic window, and modest benefits of methylxanthines (primarily theophylline [ Table 5]) limit their use in the treatment of patients with COPD, as does the need to monitor patients receiving these medications. Therefore, they are generally not recommended. Their use is supported by GOLD guidelines for patients with severe refractory symptoms; however, they should be discontinued if the patient does not respond after several weeks of therapy. 4 Oral corticosteroids are not recommended for long-term treatment of COPD. 3, 4
What are the two classes of bronchodilators?
There are two classes of inhaled bronchodilators: beta 2 agonists and anticholinergics ( Table 5 ). Both classes improve quality of life and decrease the annual rate of FEV 1 decline (the anticholinergic tiotropium [Spiriva], 40 mL per year; long-acting beta 2 agonists [LABAs], 42 mL per year) and number of exacerbations (relative risk [RR] for tiotropium = 0.84; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.78 to 0.90; RR for LABAs = 0.87; 95% CI, 0.82 to 0.93). 3, 10, 15, 16 Studies have shown that tiotropium reduces hospitalizations for COPD exacerbations (absolute risk difference = −2%; 95% CI, –4% to –1%), and that salmeterol (Serevent) reduces annual hospitalizations by 18%. 11, 17 In two large clinical trials, no combination of bronchodilators has been found superior to monotherapy in decreasing COPD symptoms or preventing exacerbations. 10, 15 The consensus among the guidelines is to initiate COPD treatment with a single bronchodilator (LABA or anticholinergic), then step up to combination bronchodilators (LABA plus anticholinergic or LABA plus corticosteroid) if symptoms are not controlled. 3 – 5 The ACP recommends monotherapy with a LABA or long-acting anticholinergic for symptomatic patients whose FEV 1 is less than 60% of predicted. 3 The choice of initial bronchodilator should be based on patient preference, adverse effects, and cost.
Can spirometry be used for COPD?
Spirometry should not be used to screen for airflow obstruction in patients without respiratory symptoms. (Grade: strong.) Inhaled bronchodilators may be used for patients with stable COPD who have respiratory symptoms and FEV 1 of 60% to 80% of predicted. (Grade: weak.)