What is the reagent treatment of chromium containing wastewater?
Mar 29, 2017 · Chemical reagent treatment is most common method of chrome and heavy metals removal. This method of treatment is based on the reactions of chemical reagents with pollutants. In case of chromium-containing wastewater, the reagents reduce hexavalent chrome to trivalent chrome followed by its precipitation. Some of the reducing agents are: copperas;
How are chemicals used in wastewater treatment?
Dec 07, 2020 · The precipitants used for chromium separation include relatively affordable chemicals, such as calcium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide, magnesium oxide, or calcium magnesium carbonate—making chemical precipitation a generally economical, simple, and popular treatment option for chromium removal.
How much chromium is in waste water?
Mar 25, 2022 · Electrochemical chromium reduction is another technology used to treat hexavalent chromimum wastewaters. It uses an electric current applied to iron electrodes that dissolve to release ferrous ions to solution. Hexavalent chromium ions are reduced as ferrous ions are oxidized to ferric ions [3]. A neutral pH is sufficient.
What is the source of hexavalent chromium in wastewater?
In industrial wastes, chromium is present primarily in the hexavalent form as chromate (Cr0 = 4 ) and dichromate (Cr 2 0 = 7 ). Keywords Chemical Oxygen Demand Wastewater Sample Hexavalent Chromium Chromium Concentration Trivalent Chromium These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors.

What is chromium in wastewater?
Chromium is such a major toxic heavy metal for both humans and the environment and often found in industrial wastewater, which is introduced into water streams from mining, tanning, electroplating, wood preservatives, paints, textile dyeing, and plants producing industrial inorganic chemicals and pigments [4,5].
Which chemical most commonly used in wastewater treatment?
Certain basic or alkaline chemicals used to raise wastewater pH are below: CaO (calcium oxide or lime), MgO (magnesium oxide), Ca (OH) (calcium hydroxide, a hydrated form of lime) or Mg (OH) (magnesium hydroxide) are the most commonly used chemicals because of availability, low cost, and high capacity.Jan 8, 2015
What chemicals are used to treat waste water?
The four main types of chemicals used in wastewater treatment are pH neutralisers, anti-foaming agents, coagulants and flocculants. The most straightforward class of chemicals is pH neutralisers, although why and how they are used varies depending on the process producing the wastewater.Sep 12, 2017
How is chromium treated in wastewater?
Several treatment procedures such as adsorption, chemical precipitation, electrocoagulation, ion exchange, electrodialysis, and membrane separation are available for removal of Cr from wastewater (Fathima et al. 2005). Among these, chemical precipitation is the common way for the removal.Aug 9, 2020
What is sodium hydroxide used for in wastewater treatment?
Sodium Hydroxide is a strong alkali which, among other facts, means that it is highly ionized and has a high pH. Thus, in wastewater treatment these products can be used to raise the pH level of the water. It is also helpful in the process of removing heavy metal particles from the water.Dec 9, 2019
What is sulfuric acid used for in water treatment?
Sulfuric Acid — sulfuric acid is the most commonly used acid in the world. It is frequently used to bring the pH level of wastewater back to normal.Jan 12, 2020
How does pH increase in waste water?
Common chemicals used to increase alkalinity and pH include:Calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide (as lime slurry)Sodium hydroxide (caustic soda)Sodium carbonate (soda ash) or sodium bicarbonate.Magnesium hydroxide or magnesium bicarbonate.
What are the types of chemical treatment on industrial waste?
Treatment methods are often specific to the material being treated. Methods include advanced oxidation processing, distillation, adsorption, ozonation, vitrification, incineration, chemical immobilisation or landfill disposal.
How does pH increase in wastewater?
Adjusting pH of wastewater & a bit about alkalinity tooTo lower pH acids such as sulfuric acid (H2SO4) can be used. A newer technology is to use carbon dioxide to adjust pH without the chance to over shoot your target. ... Raising pH is usually done using sodium hydroxide (caustic soda) (NaOH).Jul 19, 2018
How is chromium removed from water?
A literature review revealed that coagulation–filtration (with and without prior reduction with iron(II)) is still the most commonly used and effective method of chromium removal from water. Adsorptive filtration and ion exchange are suitable for small-scale applications.Dec 1, 2008
How is hexavalent chromium treated in wastewater?
Conventional treatment of hexavalent chromium wastewaters involves the reduction of hexavalent chromium to trivalent chromium and subsequent precipitation of trivalent chromium as hydroxide. Hexavalent chromium reduction is commonly accomplished using chemical reduction.Mar 25, 2022
How do you neutralize chromium?
Neutralization. Chromium(VI) compounds can be converted to the less harmful Cr(III) using reducing agents. Ascorbic acid, sodium/potassium/ammonium sulfite/thiosulfate/bisulfite/metabisulfite, iron(II) sulfate are very effective, and being readily available and cheap, are excellent neutralization agents.Feb 21, 2019
What is the purpose of electrochemical treatment of wastewater?
Recently, the electrochemical treatment of wastewater to remove chromium and other metals using steel electrodes has become very popular. Its essence lies in the chemical reduction of chromate ions due to electrochemical processes and electrolytic decomposition of water and oxygen and hydrogen evolution reaction.
What is the best way to treat wastewater?
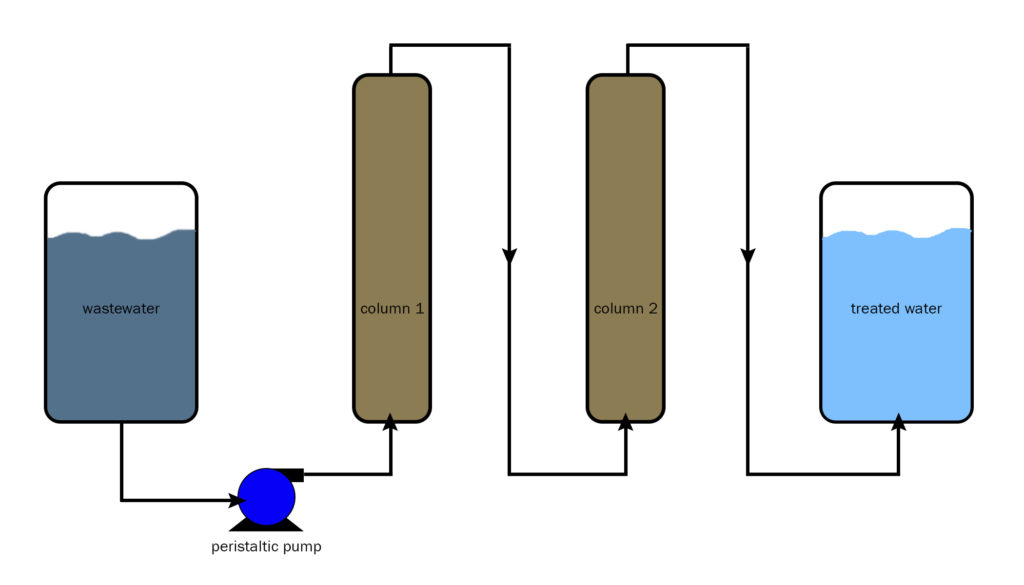
One of the promising methods of wastewater treatment is ion exchange. This method provides an almost complete removal of harmful impurities from wastewater and allows the water to be reused. But it has limitations in treating wastewater from salts of heavy metals. Ion exchange can be used for purification of wastewater with salt content ...
What is reagent treatment?
Reagent treatment of wastewater is based on the use of reducing agents for chromium purification and precipitation agents for heavy metals neutralization. The reagent treatment of chromium containing wastewater restores the hexavalent chromium to trivalent and precipitates it.
What is chromium reduction?
Batch systems may also have two pH reduction stages [3]. Electrochemical chromium reduction is another technology used to treat hexavalent chromimum wastewaters. It uses an electric current applied to iron electrodes that dissolve to release ferrous ions to solution.
What happens after a reaction is completed?
After the reaction is completed, the solution is passed to a clarifier. Ferric hydroxide and chromium hydroxide are settled generally without a need for alkali addition. The process also removes zinc, copper, and other heavy metals.
What is chromium used for?
Wastewater usually contains about 5 ppm of chromium. Chromium may be applied as a catalyser, in wood impregnation, in audio and video production and in lasers.
How much chromium is in stainless steel?
It is applied for example for metal surface refinery and in alloys. Stainless steel consists of 12-15% chromium. Chromium metal is applied worldwide in amounts of approximately 20,000 tons per year. It may be polished and it does not oxidize when it comes in contact with air.
How much Chromium is in the human body?
The human body contains approximately 0.03 ppm of chromium. Daily intake strongly depends upon feed levels, and is usually approximately 15-200 μg, but may be as high as 1 mg. Chromium uptake is 0.5-1%, in other words very small. The placenta is the organ with the highest chromium amounts.
Is chromium found in water?
The main chromium mineral is chromite. As was mentioned earlier, chromium compounds can be found in waters only in trace amounts. The element and its compounds can be discharged in surface water through various industries.
Is chromium a hazard?
The LC50value for chromium in sea fish lies between 7 and 400 ppm, for daphnia at 0.01-0.26 ppm, and for algae at 0.032-6.4 ppm. Chromium ( VI) compounds are divided up in water hazard class 3, and are considered very toxic. Chromium phytotoxicity is undetermined.
Is hexavalent chromium carcinogenic?
It causes allergic and asthmatic reactions, is carcinogenic and is 1000 times as toxic as trivalent chromium. Health effects related to hexavalent chromium exposure include diarrhoea, stomach and intestinal bleedings, cramps, and liver and kidney damage. Hexavalent chromium is mutagenic.
Does chromium react with water?
Elementary chromium does not react with water at room temperature. Solubility of chromium and chromium compounds. Many chromium compounds are relatively water insoluble. Chromium (III) compounds are water insoluble because these are largely bound to floating particles in water.
What are the different types of chromium?
The most common forms of chromium that occur in natural waters in the environment are: 1 Trivalent chromium (chromium-3) 2 Hexavalent chromium (chromium-6)
Where is chromium found?
Chromium is an odorless and tasteless metallic element. Chromium is found naturally in rocks, plants, soil and volcanic dust, and animals. The most common forms of chromium that occur in natural waters in the environment are:
What is SDWA in drinking water?
The Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) requires EPA to determine the level of contaminants in drinking water at which no adverse health effects are likely to occur . These non-enforceable health goals, based on possible health risks from exposure over a lifetime, are called maximum contaminant level goals (MCLGs). ...
What is the EPA's IRIS?
EPA is actively working on the development of an Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS) assessment , which will include a comprehensive evaluation of potential health effects associated with both inhalation and ingestion of hexavalent chromium.
Why is chromium oxide important?
Chromium oxide is important to the refractory industry for production of fire-resistant and anti-corrosive bricks, tiles, and surface coverings. Additionally, many chromium compounds have intense coloring, making them useful in the production of paints and pigments.
What is chromium metal?
Chromium is a heavy metal that offers several distinctive properties, such as hardness, high polish, a high melting point, and resistance to tarnish and corrosion. Native chromium metal is not generally found in nature, but is instead found in the form of ore deposits consisting mostly of a compound known as chromite (iron chromium oxide).
Is Cr VI toxic?
Cr VI, on the other hand, is highly toxic to humans when inhaled or ingested in food or drinking water. Even tiny amounts of Cr VI can present a number of health hazards for humans, including gastrointestinal and respiratory inflammation, organ damage, cancer, and birth defects. As such, the most important reason to treat wastewater ...
Where is chromium mined?
Chromite ore is mined from deposits scattered around the world, with the highest production occurring in South Africa, Kazakhstan, India, and Turkey. In industry, metallurgy accounts for the highest demand for chromium, as the metal is used extensively in the production of stainless steel and other metal alloys and in chrome plating applications.
Is chromium a heavy metal?
Chromium (Cr) is a heavy metal that is used extensively within the mining and metal s , leather tanning, paint and pigments, electronics, and chemical industries, among others, and it can exist in various forms and compounds—some of which are toxic to plant and animal life. As such, it is sometimes necessary for industrial facilities ...
Is chromium a hazard?
Improper discharge and disposal of chromium-contaminated wastewater poses a hazard to human, plant, and animal life. As with other heavy metals like copper or lead, chromium can enter waterways and drinking water supplies when industrial wastewater is not discharged responsibly, potentially resulting in harm to aquatic plant and animal life, ...
What are the functions of wastewater treatment?
These functions include: Removal of solid particles, pH Adjustment, Odor Control, Disinfection, Foam Prevention & Removal, and Sludge Removal .
What is bleach used for?
Bleach is used for disinfection and production processes in all kinds of industrial applications including coatings, food processing, paper & packaging, pharmaceuticals, and more. Often foam can develop in the wastewater treatment process, which can cause many problems. In fact, the foam can stand in the way of measuring instruments getting ...
What are the effects of wastewater?
Unpleasant odors produced by the wastewater can impact employee morale, invite complaints from neighbors including other businesses, and even be a health hazard. It is a major issue that must be solved. For most industrial plants something more must be done than just “covering up” the problem to contain the odors.
What acid is used to adjust pH?
The most used acid is Sulfuric Acid. This is due to its cost, abundance, and effectiveness in adjusting the pH level. Other acids that are used include Hydrochloric Acid and Phosphoric Acid . As far as bases, some common chemicals that are effective are Sodium Hydroxide, Calcium Hydroxide (Lime), among others.
What is the chemical used in wastewater treatment?
A chemical that is also present in wastewater treatment plant is ferric chloride. Ferric chloride is a corrosive chemical used in water purification and sewage treatment. The function of ferric chloride is to remove metal substance from the waste that highly possible will harm environment as well as living being.
What is wastewater treatment plant?
Wastewater treatment plant itself is a process of removing waste and dirts. This also works as a system to offer soluble and environmentally result of industrial waste. The contaminants in the sewage are removed and in turn produced safer wastewater for the environment. In order to do so, this treatment needs some chemicals as listed in the list ...
What is aluminum sulfate?
Aluminum sulfate in wastewater plant acts as purifier of the wastewater. The chemical itself is soluble and easily reacts to the chemicals in wastewater. As a result, it produces protein antigens that break insoluble and hazardous chemicals. Moreover, it also helps to regulate the ph level of the chemical, making the wastewater less dangerous ...
What chemicals are harmful to the environment?
Also read: Harmful Effects of Oxidizing Chemicals for Environmental Health. Sodium Aluminate. The next chemical used in wastewater treatment plant is sodium aluminate. Sodium aluminate is a chemical belongs to inorganic compound. The liquid form of it works well as phosphorus remover.
What is the function of polymer?
The function of polymer is to coagulate any solids dirts and work in diluted water in order to free these materials from suspension.
What is the function of hydrochloric acid?
While the chemical has many uses in industry, it also works for wastewater treatment. Its function is to lower the ph of the wastewater. Since wastewater often includes many waste of industrial chemicals, the ph tend to be in extreme level either higher or lower than normal.
Is sodium aluminate soluble in water?
However, sodium aluminate is inorganic insoluble chemical and it is only soluble with some chemicals.

Wastewater Treatment with Reagents
- Reagent treatment of wastewater is based on the use of reducing agents for chromium purification and precipitation agents for heavy metals neutralization. The reagent treatment of chromium containing wastewater restores the hexavalent chromium to trivalent and precipitates it. The reducing agents are sulfur (sodium sulfite, sodium bisulfite) copper...
Ion Exchange Methods For Wastewater Treatment
- One of the promising methods of wastewater treatment is ion exchange. This method provides an almost complete removal of harmful impurities from wastewater and allows the water to be reused. But it has limitations in treating wastewater from salts of heavy metals. Ion exchange can be used for purification of wastewater with salt content of up to 2.3 g / dm3 and small amounts …
Electrochemical Methods of Wastewater Treatment
- Recently, the electrochemical treatment of wastewater to remove chromium and other metals using steel electrodes has become very popular. Its essence lies in the chemical reduction of chromate ions due to electrochemical processes and electrolytic decomposition of water and oxygen and hydrogen evolution reaction. Simultaneously hydroxide and iron hydroxide, chromiu…