How to get rid of a mole on your face?
If you have a hair growing from a mole, you might try clipping it close to the skin's surface or plucking it. Or talk with your dermatologist about permanently removing the hair and the mole.
What to do if you have a mole on your toe?
Talk to your doctor about a schedule that's appropriate for you. During a skin exam, your doctor inspects your skin from head to toe . If your doctor suspects that a mole may be cancerous, he or she may take a tissue sample (biopsy) for microscopic examination.
How long does it take for a mole to be removed?
Mole removal takes only a short time and is usually done on an outpatient basis. Your doctor numbs the area around the mole and cuts it out, along with a margin of healthy skin if necessary. The procedure may leave a permanent scar. If you notice that a mole has grown back, see your doctor promptly.
What Are Moles?
A mole is known as melanocytic naevi by its scientific name, it is a dark raised spot on the skin that is made up of skin cells grouped together instead of being individual. These cells are called melanocytes and they produce melanin, which is the natural pigment that gives your hair, and skin its natural color.
What Causes Moles?
There are many causes of moles. We have listed down the most common causes of moles down below and how to treat them using over the counter serums, tinctures, and creams.
Why do moles lighten?
In some instances, this is the result of the body's immune system attacking the mole and causing it to regress. One example of this is a " halo nevus .". The presence of this phenomenon does not necessarily signal the presence of cancer.
Where do moles appear on the skin?
Moles can occur anywhere on the skin, including the scalp, ears, eyelids, lips, palms, soles, genitals, and anal area.
What is a mole in a pencil eraser?
Moles may be tan, brown, black, reddish-brown, red, purple, or skin-colored and perfectly flat or raised. Most moles are smaller than a pencil eraser (about 1/2 inch). A dysplastic nevus may be a marker for a person at risk for melanoma, especially if there is a family history of melanoma.
What is a mole in biology?
Besides being a small burrowing mammal and a unit of chemical weight, the term mole (in reference to skin) describes a variety of skin imperfections. Many prefer the term beauty mark. The medical term for mole is melanocytic nevus. Moles may be tan, brown, black, reddish brown, red, purple, or skin-colored and perfectly flat or raised.
What is a melanocytic nevus?
A melanocytic nevus (plural nevi) is compose d of masses of melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells of the skin. However, there are a variety of other skin lesions that are also mole-like. These include seborrheic keratoses, skin tags, dermatofibromas, lentigines, and freckles.
What are the small black spots on my face?
Moles are common small flesh-colored, tan, brown, or black spots on the skin. Moles may be flat or raised. Sun exposure in childhood causes an increase in the number of moles. Most moles appear by age 30. Moles may be mistaken for freckles and other skin growths.
Why are my ear moles so common?
Ears are a particularly common site of atypical moles because of the difficulty in applying sunscreen and frequent sun exposure.
Why do moles appear on the skin?
Moles occur when cells in the skin grow in a cluster instead of being spread throughout the skin. These cells are called melanocytes, and they make the pigment that gives skin its natural color. Moles may darken after exposure to the sun, during the teen years, and during pregnancy.
What to do if you notice a mole?
If you notice changes in a mole's color, height, size, or shape, you should have a dermatologist (skin doctor) evaluate it . You also should have moles checked if they bleed, ooze, itch, or become tender or painful. Examine your skin with a mirror or ask someone to help you.
What is a mole or freckle?
A mole or freckle should be checked if it has a diameter of more than a pencil eraser or any characteristics of the ABCDEs of melanoma (see below). Dysplastic nevi are moles that are generally larger than average (larger than a pencil eraser) and irregular in shape.
How many moles are there in a person?
Most moles appear in early childhood and during the first 25 years of a person's life. It is normal to have between 10-40 moles by adulthood. As the years pass, moles usually change slowly, becoming raised and/or changing color. Sometimes, hairs develop in the mole.
What are freckles on your face?
Freckles and Your Skin. Freckles are small brown spots usually found on the face, neck, chest, and arms. Freckles are extremely common and are not a health threat. They are more often seen in the summer, especially among lighter-skinned people and people with light or red hair.
What areas of the body are most likely to be exposed to the sun?
Pay special attention to areas of the skin that are often exposed to the sun, such as the hands, arms, chest, neck, face, ears, legs, and back. If a mole does not change over time, there is little reason for concern.
Where is melanoma most common?
Melanoma is a form of skin cancer. The most common location for melanoma in men is the chest and back and in women, it is the lower leg. Melanoma is the most common cancer in young women.
Why do moles appear in my body?
Moles usually emerge in childhood and adolescence, and change in size and color as you grow. New moles commonly appear at times when your hormone levels change, such as during pregnancy.
What are moles on the skin called?
Acquired moles (also called common moles) Acquired moles are those that appear on your skin after you’re born. They’re also known as common moles. They can appear anywhere on your skin. People with fair skin can normally have between 10 and 40 of these moles. Common moles are usually:
What is the risk of a mole becoming malignant?
Risk. Larger congenital moles have a greater risk of becoming malignant in adulthood ( 4 to 6 percent lifetime risk ). Changes in growth, color, shape, or pain of a birthmark should be evaluated by a doctor.
How big are moles?
Most moles are less than 1/4 inch in diameter. Mole color ranges from pink to dark brown or black. They can be anywhere on your body, alone or in groups. Almost all moles are benign (noncancerous). But new moles in an adult are more likely to become cancerous than old moles.
Where do atypical moles appear?
Atypical moles can appear anywhere on your body. Atypical moles are often on the trunk, but you can also get them on your neck, head, or scalp. They rarely appear on the face. Benign atypical moles may have some of the same characteristics as melanoma (a type of skin cancer).
What is the name of the cell that produces moles?
Moles are concentrations of pigment-producing cells (melanocytes) in your skin. People with light skin tend to have more moles. The technical name for a mole is nevus (plural: nevi). It comes from the Latin word for birthmark. The cause of moles isn’t well understood.
Can a new mole become cancerous?
New moles are more likely to become cancerous. A 2017 review of case studies found that 70.9 percent of melanomas arose from a new mole. If you’re an adult with a new mole, it’s important to have it checked by your doctor or a dermatologist.
What are moles on the skin?
Moles are characterized by color (tan, black, pink, skin-tone, no color, blue) and shape ( round, slightly raised, flat on the skin) and if they change in appearance over time. Moles in children are normal and may just appear.
What are moles called?
Some moles appear at birth and these are called congenital nevi. These common moles may be more likely to develop into cancer (melanoma) than those that appear after birth. Regular moles have symmetrical shapes, regular borders, uniform in color, and are small (no bigger than the size of a pencil eraser). They may be flat or raised, and may have hair on them.
What is the classification of moles?
Moles are classified based on their evolution. Junctional Melanocytic (NMN) Moles that start at the epidermal-dermal junction which is beneath the top skin layer. Moles are flat and dark (tan, brown, dark brown, black) with a uniform appearance.
What is an irregular mole?
Irregular or atypical moles are called dysplastic nevi and are usually asymmetrical (oddly shaped), having irregular borders, with multiple colors. They tend to be bigger than the size of a regular pencil eraser, often flat or nearly flat. People who have more than 20-25 atypical moles have a greater likelihood of developing skin cancer or melanoma. However, the irregular moles themselves are not likely to become cancerous.
How many people are born with moles?
Approximately 1 in 100 individuals are born with a congenital (at birth) mole. People born with moles are considered at higher risk for melanoma (skin cancer). Skin moles are not contagious and may regrow after removal. Excessive sun exposure and pregnancy can result in the development of additional moles later in life.
Why do my spots get darker?
These spots may become darker after constant exposure to the sun , during adolescence, and during pregnancy. If the melanocytes proliferate deeper into the skin it causes the mole to rise above the skin's surface creating what is called a compound naevus.
When do you have to check for moles?
Only moles that look different from existing moles, those that appear after age 30, and those that change in color, size, and shape must checked especially if they ooze, bleed, or become painful . A dermatologist may request for a biopsy of the suspicious mole to determine if it is cancerous.
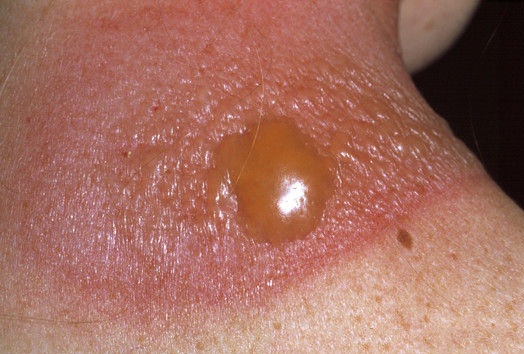
What is a cyst on the face?
Cyst : A raised, circumscribed area of the skin, filled with fluid or semi-solid fluid. Macule: A non-palpable, flat lesion that is different in color, and less than 0.5cm in size. Papule (also maculopapular): An elevated solid lesion, up to 0.5 cm in size, circumscribed and firm. It can appear in various colors.
Why is my skin lighter?
Maceration: This is when skin becomes wet, wrinkly, and lighter in color due to being in contact with water or fluid for too long. This can occur due to leaking wounds due to improper wound care. Phyma: A thickening of the skin, often seen in advanced rosacea 2.
What are secondary skin lesions?
Secondary Lesions. Secondary skin lesions are caused when a primary skin lesion is disturbed, irritated, or changes over time. For example, if eczema is scratched and causes a crust to form, the crust is a secondary lesion. Examples of secondary skin lesions include: 1.
What is a blister that pops?
See a doctor if any signs of infection such as pus, fever, or red hot skin around the blister occur. When a blister is less than 0.5 cm, it is known as a vesicle , and when greater than 0.5 cm, it is known as a bulla. 4.
What is scale in dermatology?
Scale: A build-up of keratinized cells that form patches and then flake off the skin. Ulcer: A wound deeper than the epidermis, damaging the dermis, concave, variable in size, and graded depending on depth. Umbilication: A dip inside a skin lesion that looks similar to a navel. 1.
What is a primary lesion?
Skin lesions that are solid, palpable masses, such as nodules or tumors. Flat, non-palpable skin lesions like patches and macules. Types of primary lesion include: 1. Bulla : A vesicle that is greater than 0.5 centimeters (cm) or 1/5 of an inch and filled with fluid.
What are the physical characteristics of a skin lesion?
A skin lesion's physical characteristics—including color, size, texture, and location —can be used to help establish if there is an underlying cause.
How to treat skin disorders?
Eat a healthy diet. Protect your skin from excessive cold, heat, and wind. Learning about proper skin care and treatment for skin disorders can be very important for skin health. Some conditions require the attention of a doctor, while you can address others safely at home.
Why do people with diabetes have skin problems?
Others occur more frequently in people with diabetes because the disease increases the risk for infection and blood circulation problems.
What are the bumps on my arms?
Keratosis pilaris is a minor condition that causes small, rough bumps on the skin. These bumps usually form on the upper arms, thighs, or cheeks. They’re typically red or white and don’t hurt or itch. Treatment isn’t necessary, but medicated creams can improve skin appearance.
Why does my skin get red and itchy?
Contact dermatitis. Contact dermatitis is one of the most common occupational illnesses. The condition is often the result of contact with chemicals or other irritating materials. These substances can trigger a reaction that causes the skin to become itchy, red, and inflamed.
What are the symptoms of skin disorders?
Symptoms on your skin that appear due to common problems aren’t always the result of a skin disorder. Such symptoms can include blisters from new shoes or chafing from tight pants.
How to prevent non-infectious skin?
Here are some tips for preventing some noninfectious skin disorders: Wash your face with a gentle cleanser and water every day. Use moisturizer.
What is a pink patch on the face?
Thick, scaly, or crusty skin patch. Appears on parts of the body that receive a lot of sun exposure (hands, arms, face, scalp, and neck) Usually pink in color but can have a brown, tan, or gray base. Read full article on actinic keratosis.
