Some factors that lead to thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia
A condition where abnormally low level of platelets are observed.
Purpura
Hemorrhages in the skin and mucous membranes that result in the appearance of purplish spots or patches.
What are the causes of purpura?
There are a couple of varieties of this type of purpura, and there can be a range of causes. Congenital disorders and infections that cause abnormalities in blood vessels or blood production (rubella, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome) This form of purpura is essentially due to the fragility of blood vessels in old age.
How is purpura treated?
Purpura itself is a symptom rather than a condition. To determine the cause, doctors must run a range of tests. These tests will assess the patient’s nutrition, platelet levels, inflammation, potential for infection, and blood vessel health. Treatment for purpura usually requires treating the rash’s underlying cause.
What are the causes of Nonthrombocytopenic purpura and senile purpura?
Causes of nonthrombocytopenic purpura can include blood vessel changes, inflammation, viruses, and medications. Senile purpura is caused by a thinning and weakening of the skin and blood vessels. These changes are usually related to damage from the sun’s UV rays, as well as aging and drugs like warfarin or aspirin.
Why is thrombocytopenic purpura dangerous?
This is a very rare form of thrombocytopenic purpura where blood clots form in small blood vessels throughout the body. It can be quite dangerous because of the potential to cut off oxygen-rich blood from vital organs like your brain, kidneys, and heart.
What type of cancer causes purpura?
some forms of cancer, such as leukemia and myeloma. inflammatory conditions and disorders, such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. advanced age. poor blood vessel health.
Why do cancer patients bleed out?
Hemorrhage, referred to as a “Bleed-out” is a rare event and most often occurs due to tumor invasion and erosion of vessels. Any tumor that involves the vascular tissue or is near a major vessel can result in a bleed out.
What is the most common cause of bleeding in cancer patients?
The most common reason for cancer patients to experience excessive bruising or bleeding is a low platelet count, a condition also referred to as thrombocytopenia. Platelets are necessary for blood clotting.
Which complication will likely cause thrombocytopenia in a patient with cancer?
The most common cause of thrombocytopenia in people with cancer is bone marrow suppression related to chemotherapy. Chemotherapy destroys rapidly dividing cells, such as those in the bone marrow which become platelets.
What are signs of end of life with cancer?
Signs that death has occurredBreathing stops.Blood pressure cannot be heard.Pulse stops.Eyes stop moving and may stay open.Pupils of the eyes stay large, even in bright light.Control of bowels or bladder may be lost as the muscles relax.
What are the final stages of cancer like?
The following are signs and symptoms that suggest a person with cancer may be entering the final weeks of life: Worsening weakness and exhaustion. A need to sleep much of the time, often spending most of the day in bed or resting. Weight loss and muscle thinning or loss.
Can chemotherapy cause bleeding?
Some cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy and targeted therapy, can increase your risk of bleeding and bruising. These treatments can lower the number of platelets in the blood. Platelets are the cells that help your blood to clot and stop bleeding.
How do you know if chemo is killing you?
Here are some signs that chemotherapy may not be working as well as expected: tumors aren't shrinking. new tumors keep forming. cancer is spreading to new areas....Along the way, the timeline may have to be adjusted due to:low blood counts.adverse effects to major organs.severe side effects.
What is the most common cause of death in cancer patients?
What were the leading causes of cancer death in 2020? Lung cancer was the leading cause of cancer death, accounting for 23% of all cancer deaths. Other common causes of cancer death were cancers of the colon and rectum (9%), pancreas (8%), female breast (7%), prostate (5%), and liver and intrahepatic bile duct (5%).
What happens if your platelets are too low for chemo?
Low platelets can lead to easy bruising and bleeding and are a consequence of certain chemotherapy drugs and radiation. Low platelets can lead to easy bruising and bleeding and are a consequence of certain chemotherapy drugs and radiation.
Can chemotherapy cause thrombocytopenia?
Chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia (CIT) is a potentially serious complication that can lead to chemotherapy dose delays, dose reductions, or discontinuation, and increases the risk of serious bleeding events.
How do chemo patients keep their platelets up?
Having low platelets (the medical term is thrombocytopenia) during chemotherapy is reasonably common and the most common way to increase platelet count during chemotherapy is to either delay the next dose of chemotherapy or to have a platelet transfusion administered by your healthcare provider.
What is non thrombocytopenic purpura?
Non-Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Non-thrombocytopenic purpura is when blood platelet levels remain normal but rashes still occur. There are a couple of varieties of this type of purpura, and there can be a range of causes. Some of the causes include:
What is a TPP?
1.1 Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TPP) This is a very rare form of thrombocytopenic purpura where blood clots form in small blood vessels throughout the body. It can be quite dangerous because of the potential to cut off oxygen-rich blood from vital organs like your brain, kidneys, and heart.
What is purpura thrombocytopenic?
One type of purpura is a thrombocytopenic purpura, which means it results from low blood platelet counts. This type of purpura diagnosis indicates there is a more severe health issue at play.
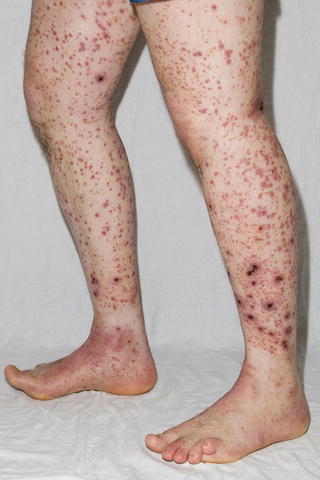
What is purpura rash?
Purpura is a skin rash usually characterized by small, purplish-red spots on skin. There are different types of purpura, and they can be signified by slight differences in color, location, and longevity. Generally speaking, spots are four to 10 millimeters in diameter—like a pinpoint—and cluster in a concentrated area.
How big are purpura spots?
Generally speaking, spots are four to 10 millimeters in diameter—like a pinpoint—and cluster in a concentrated area. Purpura rashes are unique in a few ways. The first is that, while they can appear as a rash, they don’t always itch or cause irritation. Secondly, when touched, they may not change colors.
What is the name of the rash caused by a small blood vessel that leaks blood?
This form of purpura is more commonly known as Henoch-Schonlein purpura (HSP) and predominantly affects children. It occurs when small blood vessels become inflamed and leak blood to cause rashes.
Why is purpura not a risk factor?
Purpura itself does not possess any risk factors because it is a symptom of another issue. Conditions that cause purpura generally are not related to lifestyle, so there aren’t really any preventative measures available. Factors that can influence the likelihood of types or purpura are: Genetics.
What are purpura rash patches?
Some people develop larger patches of 1 centimeter or greater. These are called ecchymoses. Sometimes the spots can appear on mucous membranes, for instance, inside the mouth.
What are the symptoms of purpura?
Patients who experience purpura with any of the following symptoms should seek medical treatment: Low platelet count, which may lead to increased bleeding after an injury, bleeding gums or nose, or blood in urine or bowel movements. Sore, swollen joints, particularly in the ankles and knees.
How to treat purpura?
This can include options such as chemotherapy, antiviral drugs, steroid medications, antibiotics, and surgery. Corticosteroids – these can help increase platelet count by reducing the activity of the immune system.
What is purpura in medical terms?
Purpura, also known as skin hemorrhages or blood spots, can signal a number of medical problems, ranging from minor injuries to life-threatening infections. Purpura is a symptom rather than a disease in itself, and there are a number of potential causes.
What is the cause of a lack of vitamin C?
A lack of vitamin C, also known as scurvy. Infectious or inflammatory diseases that affect the blood vessels. Some drugs, such as steroids and sulfonamides. Purpura with a lowered platelet count (thrombocytopenia) has a number of potential causes: drugs that reduce platelet count. recent blood transfusions.
What causes purpura?
Purpura that does not lower platelet levels (nonthrombocytopenia) has a range of causes and risk factors, including: Disorders and infections present from birth that cause abnormalities in blood vessels or blood production, such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and rubella.
How to treat Henoch-Schönlein purpura?
Treatment for Henoch-Schönlein purpura focuses on improving the symptoms. Doctors may recommend non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) to reduce inflammation and pain. Steroid treatment can reduce kidney damage and abdominal pain. If kidney damage is severe, doctors may prescribe drugs to suppress the immune system.
A. What is the differential diagnosis for this problem?
The differential diagnosis to purpura can be divided into platelet disorders, vascular factors and coagulation factor deficiencies.
B. Common Pitfalls and Side-Effects of Management of this Clinical Problem
Copyright © 2017, 2013 Decision Support in Medicine, LLC. All rights reserved.
What causes purpura in the body?
Amyloidosis is a rare medical condition that causes abnormal proteins to build up in the body’s organs and tissues. This buildup of proteins leads to inflammation, which can cause purpura.
Where does purpura occur?
It can occur on the skin and mucous membranes, including the lining of the mouth . Purpura has a wide array of possible causes that range from a temporary drug side effect to a sign of a serious underlying medical condition. 1. RapidEye / Getty Images.
What are the symptoms of nonthrombocytopenic purpura?
Senile purpura is characterized by ecchymoses on the hands and forearms, while symptoms of IgA vasculitis include a skin rash and joint pain.
How are purpura and thrombocytopenic purpura classified?
They are classified by whether platelets are involved. Platelets are cells in the bloodstream that work to clot blood and prevent bleeding. Thrombocytopenic purpura is caused by low platelet counts, while nonthrombocytopenic purpura is not related to the number of platelets in your blood.
How to treat thrombocytopenic purpura?
In children with ITP, the disease usually goes away on its own without treatment, but some may require medical interventions. Adults are usually started on a steroid medicine, prednisone or dexamethasone, and may need to have their spleens removed through a splenectomy to increase platelet levels. If your platelet count is dangerously low, your healthcare provider may recommend a platelet or blood transfusion as well.
Why does IgA cause purpura?
IgA vasculitis leads to purpura because of inflammation. When blood vessels experience inflammation, they become damaged and red blood cells leak out, causing the fine rash. IgA vasculitis usually occurs after a respiratory illness, such as strep throat, but the exact cause is still unknown.
What is the name of the condition that causes inflammation of the blood vessels in the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and kidney?
Vasculitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels in the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and kidneys. 3 IgA vasculitis, previously known as Henoch-Schönlein purpura, and leukocytoclastic vasculitis are among the subsets of this condition that can cause purpura.
What are purpura?
Purpura are purple or red spots on the skin or mucus membranes. Purpura happen when blood leaks from blood vessels and collects under the skin or mucus membrane.
What increases my risk for purpura?
Any condition or medicine that causes low platelet levels can increase your risk for purpur a. Your risk is also increased if you have a condition, or take medicine, that prevents platelets from working correctly.
How is the cause of purpura diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will examine you and ask about your symptoms. Tell him about any health condition you have that causes bleeding. Also tell him what medicines or supplements you take. You may need blood tests to count your platelets or time how fast your blood clots. You may also need blood tests to check for infection or other conditions that cause purpura.
How is purpura treated?
If you have a large amount of bleeding, you may need a blood transfusion, medicines, or surgery to stop the bleeding.
What can I do to manage my symptoms?
Do not take NSAIDs, aspirin, or blood thinner medicine. These medicines can make purpura worse. Ask your healthcare provider how long you need to stop these medicines.
When should I seek immediate care?
You have bleeding that does not stop or a bruise that suddenly gets bigger.
How to stop bleeding from nose?
Apply firm, steady pressure to cuts or scrapes. If possible, elevate the area above the level of your heart. If your nose bleeds, pinch the upper part of your nose and hold a tissue at the opening. Do this until the bleeding stops.
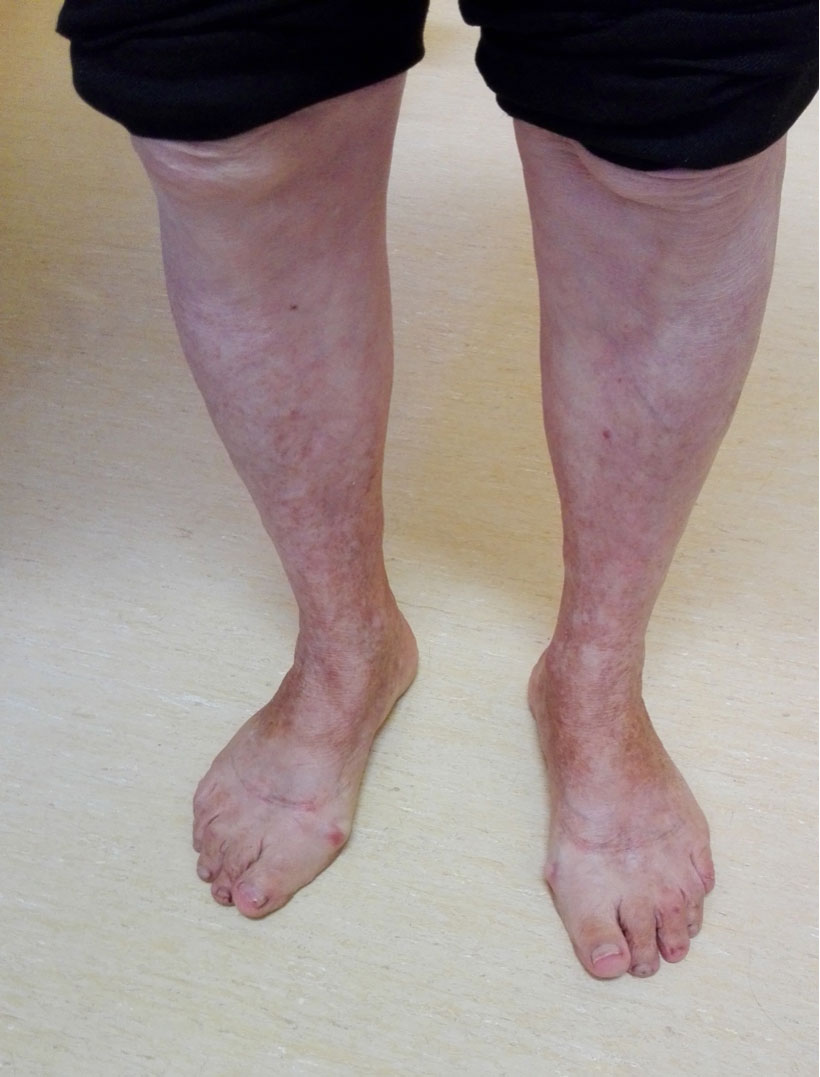
What Causes Purpura?
Although there are numerous potential causes of purpura, the most common type is called senile or actinic purpura and is due to changes in the skin secondary to aging and UV damage. As we age the tissues in our skin become thinner and the blood vessels in our skin become more fragile. Normally tissues in our skin act like pillows and support blood vessels, protecting them from trauma. When these tissues thin you lose the support surrounding the blood vessels so that even very minor trauma, such as lightly hitting your arm, can disrupt the blood vessel integrity and cause bleeding into the skin.
Who Gets It?
Risk factors include chronic sun damage and fair complexion. People on blood thinners or aspirin are also more prone to developing it.
How to treat senile purpura?
Unfortunately, due to the changes in the skin structure described above, new lesions will continue to appear. Sun protection and moisturizing the skin may help to prevent further damage to skin tissues and lead to less purpura in the future. Topical retinoids have been reported to decrease signs of aging on the skin and may also prevent senile purpura. Some studies have reported that oral supplementation of citrus bioflavonoids may help prevent its development due to their antioxidant effects. Studies have also shown that vitamin C supplementation improved purpura in patients who had a prior vitamin C deficiency.
Is senile purpura benign?
Although senile purpura is completely benign, if you notice that you are developing large areas of involvement, have numerous lesions developing all at once, or a sudden development of lesions that you never had before, it might be a sign of an underlying medical problem.
Does citrus help purpura?
Studies have also shown that vitamin C supplementation improved purpura in patients who had a prior vitamin C deficiency.
Is purpura bad for you?
Purpura is often frustrating and often cosmetically bothersome, but luckily it is usually not worrisome to your health. Please schedule a skin check with one of our board-certified dermatologists at Siperstein Dermatology Group to learn more or have your skin evaluated.
What is the side effect of Sorafenib?
Side effects include: Hand/foot skin reactions (tender, thickened areas sometimes with blisters on palms and soles) Redness and flaking on scalp and eyebrows.
What is immunotherapy for cancer?
Immunotherapy is also called biologic therapy. It is a type of cancer treatment that boosts the body's natural defenses to fight cancer. It uses materials made either by the body or in a laboratory to improve, target, or restore immune system function. Many side effects are similar to those of an allergic reaction.
How do you know if you have a rash?
You may notice redness or a warm sensation like a sunburn before the rash begins. After several days, pimples and pus bumps appear, and the surrounding skin feels slightly tender. Rashes are usually mild to moderate. But some people have severe rashes that cause major physical and cosmetic discomfort.
What is the molecule that targets EGFR?
Drugs that target EGFR. This common type of targeted therapy focuses on a molecule known as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). EGFR fuels the growth of cancer cells. It also plays a role in the normal growth of the skin, hair, and nails.
What is the drug used for melanoma?
Pembrolizumab (Keytruda). This drug may be used to treat NSCLC and melanoma. Skin-related side effects include:
What is nivolumab used for?
Nivolumab (Opdivo). This medicine may be prescribed for renal cell cancer, NSCLC, and melanoma. Possible skin reactions include:
What drugs cause skin problems?
Below is a list of common targeted therapy drugs that can cause skin related problems. Afatinib (Gilotrif), cetuximab (Erbitux), erlotinib (Tarceva), gefitinib (Iressa), osimertinib (Tagrisso), and panitumumab (Vectibix). These drugs may be prescribed for colorectal cancer, head and neck cancer, lung cancer, and pancreatic cancer.
How to get rid of a rash on the side of the head from cancer?
In certain cases, your doctor may prescribe medication to help with the rash. Clean the skin gently with warm water, gentle soap, and a soft cloth. Rinse the rash area carefully and pat dry. Keep your skin moisturized.
What is a rash that develops in patients receiving radiation therapy?
It is common in patients who receive certain treatment drugs. Radiation dermatitis: This is a rash that develops in patients receiving radiation therapy. It usually occurs in the area of the skin getting radiation. It may be mild or severe depending on the location of the radiation, how much skin was affected, total radiation dose, ...
How long does it take for a cancer rash to develop?
They usually develop within a few weeks of receiving the treatment, but can develop at any time during your cancer treatment. It's important to know that a skin rash that is an expected side effect of treatment is not considered an allergy or allergic reaction.
What is the most common rash that is itchy and painful?
It is common in patients who receive certain treatment drugs. Radiation dermatitis: This is a rash that develops in patients receiving radiation ...
What are the different types of rash?
Some common types of rashes experienced by patients receiving treatment include: 1 Papulopustular eruption: This is a rash that may be itchy and painful and commonly occurs on the chest, upper back, or face. It is common in patients who receive certain treatment drugs. 2 Radiation dermatitis: This is a rash that develops in patients receiving radiation therapy. It usually occurs in the area of the skin getting radiation. It may be mild or severe depending on the location of the radiation, how much skin was affected, total radiation dose, and how long the radiation is given. 3 Radiation recall: This is a rash that develops in an area of the body that has previously had radiation therapy. It sometimes happens when a person receives chemotherapy or targeted therapy drugs after completing radiation therapy. 4 Hand-foot syndrome :Certain patients may develop this condition, which causes redness, swelling, pain, and sometimes tingling in the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
What does it mean when you have a rash?
Has a rash that is uncomfortable and keeps them up at night . Has blisters, bright red skin, or crusts on the skin. Has foul-smelling drainage or pus coming from the skin. Develops yellowish skin or has urine the color of tea. Written by.
Why do my hands feel tingly?
Hand-foot syndrome :Certain patients may develop this condition, which causes redness, swelling, pain, and sometimes tingling in the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
