One goal in persistent AFib treatment is to slow down a rapid heart rate. Your doctor may prescribe medications like: beta-blockers calcium channel blockers digoxin (Lanoxin) These work by reducing electrical activities within the upper chamber of your heart to the lower chamber.
Full Answer
Why does AFIB make you feel short of breath?
Shortness of breath that comes on suddenly (called acute) has a limited number of causes, including:
- Anaphylaxis (a severe allergic reaction)
- Asthma
- Carbon monoxide poisoning
- Cardiac tamponade (excess fluid around the heart)
- COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) exacerbation — worsening of symptoms
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- Heart attack
- Heart arrhythmia (heart rhythm problems)
- Heart failure
- Pneumonia (and other pulmonary infections)
What are the early signs and symptoms of AFIB?
Those who do have atrial fibrillation symptoms may have signs and symptoms such as:
- Sensations of a fast, fluttering or pounding heartbeat (palpitations)
- Chest pain
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Lightheadedness
- Reduced ability to exercise
- Shortness of breath
- Weakness
Does atrial fibrillation make you short of breath?
However, A-fib may cause a fast, pounding heartbeat (palpitations), shortness of breath or weakness. Episodes of atrial fibrillation may come and go, or they may be persistent. Although A-fib itself usually isn't life-threatening, it's a serious medical condition that requires proper treatment to prevent stroke.
Is heart attack the biggest danger of AFIB?
No. Blood clots are a very big risk with AFib. Heart attack is not a danger of afib per se. The main danger of afib is thrombosis, which means blood clot formation, and embolism, which means that the clot plugs a vessel stopping the blood supply from that vessel. This causes strokes, pulmonary embolism, and other embolic diseases.

How do you stop shortness of breath with AFib?
Palpitations, a rapid heart beat, and a flutter in the chest might be the most common symptoms of AFib, but they aren't the only signs that your heart rhythm is off....Breathe more slowly, not more deeply.Holding your breath for 10 to 15 seconds.Breathing in and out of a paper bag.Breathing through pursed lips.
What is the most successful treatment for AFib?
Blood thinners (Aspirin and Heparin) can thin the blood and lower the risk of serious complications. Heart rate controlling medicines, such as beta-blockers that include Coreg (Carvedilol) and Lopressor and Toprol (Metoprolol), is the best way to treat AFib.
What is the immediate treatment for AFib?
Initial treatment is directed at controlling the ventricular rate, most often with a calcium channel blocker, a beta blocker, or digoxin. Medical or electrical cardioversion to restore sinus rhythm is the next step in patients who remain in atrial fibrillation.
What is the drug of choice in heart failure with atrial fibrillation?
Pharmacologic options for controlling the ventricular response to AF include β-blockers, nondihydropyridine calcium channel blockers, and digoxin. Digoxin primarily slows the ventricular rate by increasing parasympathetic tone on the atrioventricular node.
What is the first drug of choice for atrial fibrillation?
Amiodarone as a first-choice drug for restoring sinus rhythm in patients with atrial fibrillation: a randomized, controlled study. Chest.
Does atrial fibrillation cause shortness of breath?
In atrial fibrillation, the heart rate is irregular and can sometimes be very fast. In some cases, it can be considerably higher than 100 beats a minute. This can cause problems including dizziness, shortness of breath and tiredness.
What is the best beta blocker for atrial fibrillation?
Bisoprolol* or metoprolol succinate are first-choice beta-blockers for patients with atrial fibrillation as they are prescribed once-daily and do not require dose adjustment in patients with renal impairment. Bisoprolol is preferred as it is more cardioselective than metoprolol and may cause more bradycardia.
Which is better metoprolol or diltiazem?
The key finding is that diltiazem was more effective than metoprolol in achieving rate control in ED patients with AFF at all time points within 30 min and did so with no increased incidence of adverse effects.
What two treatments may help a patient with atrial fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation treatment may involve: Medications. Therapy to reset the heart rhythm (cardioversion) Surgery or catheter procedures....Medications used to treat atrial fibrillation include:Beta blockers. ... Calcium channel blockers. ... Digoxin. ... Anti-arrhythmic medications. ... Blood thinners.
Will a pacemaker correct AFib?
Treatment Overview The pacemaker does not treat atrial fibrillation itself. The pacemaker is used to treat a slow heart rate (bradycardia) that happens in some people who have atrial fibrillation.
How can I naturally reset my atrial fibrillation?
You may be able to keep your heart pumping smoothly for a long time if you:manage your blood pressure.manage your cholesterol levels.eat a heart-healthy diet.exercise for 20 minutes most days of the week.quit smoking if you smoke.maintain a healthy weight.get enough sleep.drink alcohol in moderation.More items...
Does AFib lead to congestive heart failure?
AFib can lead to heart failure, and heart failure puts you at greater risk for AFib. When you have both, which is common, symptoms tend to be worse than when you have just one or the other.
How to get out of atrial fibrillation?
There are many ways to get out of atrial fibrillation, either with medications, or with procedures, such as a cardioversion, which is an electrical shock to your heart to get out of atrial fibrillation.
Why do I have shortness of breath?
1. The Rapid Heart Rate of Atrial Fibrillation Causes Shortness of Breath. The first reason for shortness of breath is the heart rate by itself. You can imagine people who have atrial fibrillation who are not well controlled, will likely have elevated heart rates.
What is atrial flutter?
Atrial Flutter: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment. Atrial flutter is a common heart arrhythmia that can cause severe symptoms and increase risk for stroke. Learn more about atrial flutter symptoms and treatment options. Read more about the similarities between atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter here. Read More →.
What is the most common heart arrhythmia?
Atrial Fibrillation, also known as AFib, is the most common heart arrhythmia. Learn more about symptoms of atrial fibrillation and treatment options. Here I will cover a wide variety of treatment options and help you better understand this serious heart disease and improve symptoms. Read More →.
Why do I get fluid in my lungs?
That's when people start getting fluid in their lungs, this is a condition typically called congestive heart failure.
What does it feel like to have a fast heart rate?
You can imagine that if your heart rate's going very fast consistently, it's like as if you're running or exercising all the time. You can imagine when you're exercising, your heart rate gets up, and you can feel short of breath, and for patients with atrial fibrillation, they may feel this way all the time. So sometimes just the heart rate by ...
How fast is a person's heart rate when sitting?
The heart rate may be controlled when they're just sitting down, but with just a little bit of activity the heart rate may become very fast, such as, 120, 140 bpm, sometimes even faster than that. There are patients who have, even when they're just sitting and resting, their heart rate at 100, 110 bpm.
What is the cause of abnormally fast heartbeat?
There are many different types of tachycardia. They're grouped according to the part of the heart responsible for the fast heart rate and cause of the abnormally fast heartbeat. Common types of tachycardia include:
What causes a fast heart rate?
Tachycardia is caused by something that disrupts the normal electrical impulses that control the rate of your heart's pumping action. Many things can cause or contribute to a fast heart rate. These include:
What is the name of the abnormally fast heartbeat that starts somewhere above the lower chambers of the heart?
Supraventricular tachycardia is an abnormally fast heartbeat that starts somewhere above the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles). It's caused by abnormal circuitry in the heart that is usually present at birth and creates a loop of overlapping signals. Ventricular tachycardia.
What causes a flutter in the atria?
Atrial flutter is caused by irregular circuitry within the atria. Episodes of atrial flutter may go away themselves or may require treatment. People who have atrial flutter also often have atrial fibrillation at other times. Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT).
What happens if you leave tachycardia untreated?
But if left untreated, tachycardia can disrupt normal heart function and lead to serious complications, including: Heart failure. Stroke. Sudden cardiac arrest or death. Treatments, such as drugs, medical procedures or surgery, may help control a rapid heartbeat or manage other conditions contributing to tachycardia.
What happens when the heart isn't restored to normal rhythm?
Ventricular fibrillation occurs when rapid, chaotic electrical impulses cause the lower heart chambers (ventricles) to quiver instead of pumping necessary blood to the body. This can be deadly if the heart isn't restored to a normal rhythm within minutes with an electric shock to the heart (defibrillation).
How long does tachycardia last?
Ventricular tachycardia episodes may be brief and last only a couple of seconds without causing harm. But episodes lasting more than a few seconds can become a life-threatening medical emergency.
What are the symptoms of atrial fibrillation?
Those who do have atrial fibrillation symptoms may experience signs and symptoms such as: Palpitations, which are sensations of a racing, uncomfortable, irregular heartbeat or a flip-flopping in your chest. Weakness.
How fast is the heart rate in atrial fibrillation?
The result is a fast and irregular heart rhythm. The heart rate in atrial fibrillation may range from 100 to 175 beats a minute.
How long does atrial fibrillation last?
This type of atrial fibrillation is continuous and lasts longer than 12 months. Permanent. In this type of atrial fibrillation, the abnormal heart rhythm can't be restored. You'll have atrial fibrillation permanently, and you'll often require medications to control your heart rate and to prevent blood clots.
What is the electrical connection between the atria and the ventricles?
In atrial fibrillation, the signals in the upper chambers of your heart are chaotic. As a result, they quiver. The AV node — the electrical connection between the atria and the ventricles — is bombarded with impulses trying to get through to the ventricles.
What is the normal heart rate for a person with atrial fibrillation?
The heart rate in atrial fibrillation may range from 100 to 175 beats a minute. The normal range for a heart rate is 60 to 100 beats a minute. Your heart is made up of four chambers — two upper chambers (atria) and two lower chambers (ventricles).
What happens if you have a blood clot in your heart?
If a blood clot forms, it could dislodge from your heart and travel to your brain. There it might block blood flow, causing a stroke.
Is atrial fibrillation life threatening?
Although atrial fibrillation itself usually isn't life-threatening, it is a serious medical condition that sometimes requires emergency treatment. A major concern with atrial fibrillation is the potential to develop blood clots within the upper chambers of the heart.
How does AFIB affect breathing?
Loss of Atrial Contraction. When a person experiences an AFib episode, their body starts to lose the normal atrial contraction . Atrial contractions are what add pressure to the heart chambers and help with the healthy blood flow.
Why does AFIB make you lose breath?
The AFib episode is responsible for that. That’s why the condition reduces the heart’s efficiency and makes you lose breath. As a result, it puts a lot of strain on the heart and makes inhaling and exhaling very difficult to achieve. Increased Fluid Retention.
What is AFIB in a person?
AFib is an abnormal heart condition that causes rapid beating and irregular heart motions, which accelerate the heart rate. The condition can increase the odds of heart failure, stroke, or other debilitating cardiovascular conditions. Here is how AFib can impair breathing. Loss of Atrial Contraction. When a person experiences an AFib episode, their ...
How does AFIB leave you breathless?
How Can AFib Leave You Breathless? Our heart works hand-in-hand with the rest of the systems in the human body. That includes the respiratory system as well. When there is a heart complication, like AFib, it can start to impair breathing and cause a mild to severe lung discomfort.
What happens when your heart and lungs are in sync?
When our heart and lungs are in sync, the system works in harmony. But, when a serious health complication like Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) throws the body off balance, it can affect the lungs and make breathing incredibly difficult.
Why is shortness of breath so bad?
But, when it comes to shortness of breath, there are two very important factors you should know about. They are anxiety and sleep apnea. Here is how these contributors can make breathing difficult.
How many times can you get AFIB?
Sleep Apnea and AFib. According to the National Institutes of Health, sleep apnea can increase your odds of developing AFib by 2 to 4 times . Whether you are experiencing obstructive or central sleep apnea, the nervous system will start to feel the strain and increase the risk of developing several medical conditions.
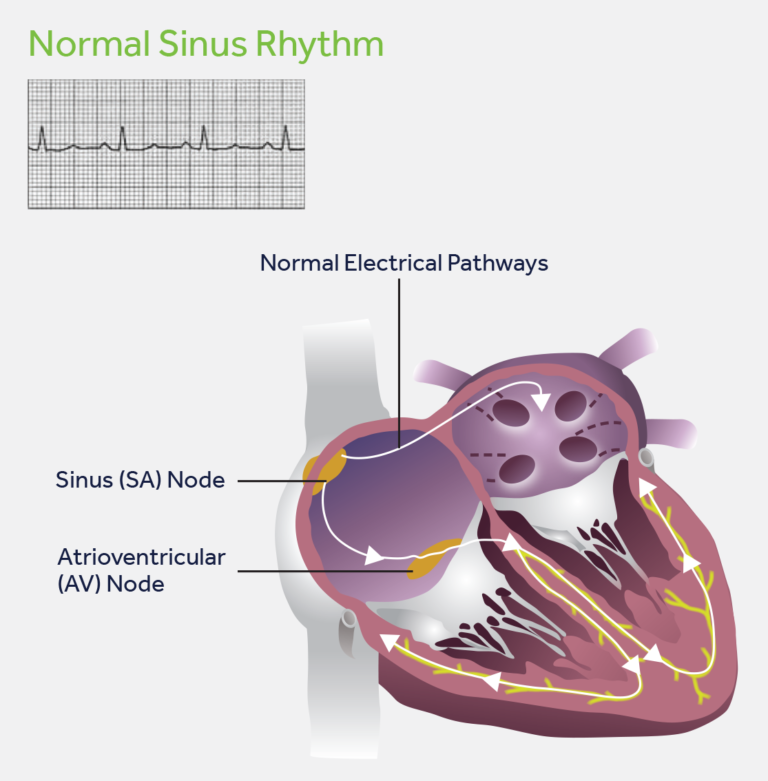
Matters of the heart
The heart is the organ that pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the body. During each heartbeat, the upper two chambers, called the atria, contract. After that, the two lower chambers, called the ventricles, contract. When the heart is working normally, the timing of the contractions is precise, making for an efficient pump.
What is atrial fibrillation?
AFib is the most common irregular heart rhythm, and it starts in the atria. The initial electrical impulse doesn’t come from the SA node; instead, many nerves fire at once, causing a fast but chaotic rhythm that doesn’t allow the atria to contract forcefully and pump blood into the ventricles.
The symptoms of atrial fibrillation
It’s possible to have AFib without any symptoms, but if they’re present, you may experience:
How to calm your breathing when you have AFIB?
If you live with Afib and are prone to panic attacks, you should learn how to calm your breathing in case you begin to hyperventilate. The key is to restore the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in your body, and a few techniques can accomplish this: Holding your breath for 10 to 15 seconds. This will help dissipate the carbon dioxide, bringing ...
What happens to the heart during AFIB?
During an AFib episode the heart begins to beat so fast that it can’t pump blood forward into the body efficiently. In turn, blood can back-up in the pulmonary veins – the pathways responsible for bringing oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the heart.
What does it mean when your lungs are full of fluid?
Not surprisingly, when the lungs are full of fluid, they can’t receive and relay oxygen very well, explaining your shortness of breath or labored breathing .
What is AFIB in the heart?
After all, AFib is an electrical malfunction within the heart, and it follows that the chambers, ventricles, and surrounding regions will bear most of the effects. But the heart doesn’t work alone: all the systems in the body can feel the strain of Afib, including the respiratory system – and the symptoms aren’t always easy to spot.
How to reset breathing pattern for AFIB?
Not everyone with AFib will prefer this method (some patients find that exercise triggers an AFib episode), but a brisk walk, short jog, or even a set of jumping jacks can reset your breathing pattern relatively quickly.
How to treat sleep apnea?
If it turns out that you are experiencing either type of sleep apnea, you can begin to treat it right away with a CPAP machine, lifestyle changes, or any other approaches that your doctor recommends.
How to get carbon dioxide out of your system?
Holding your breath for 10 to 15 seconds. This will help dissipate the carbon dioxide, bringing it back to normal levels. You may have to repeat this a few times before you can overcome the hyperventilation episode. Breathing in and out of a paper bag.
What to do if AFIB doesn't come back?
If the doctor doesn't see any clots, you'll be good to go. Someone whose AFib tends to come back may also need medication to help keep their heart beating normally. Ablation. If you still can't seem to get control of your AFib, doctors may recommend a procedure to wipe out the heart tissue that's causing the misfiring signals.
How do you know if you have atrial fibrillation?
Symptoms of atrial fibrillation can include: 1 Fatigue and lack of energy 2 Dizziness 3 Shortness of breath 4 Racing, pounding, or fluttering heart
How to check for clots in heart?
If your symptoms are too severe to wait that long, the doctor will check for clots in your heart by doing a transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE). While you're sedated, they'll put a long, flexible tube with a small device down your throat until it's behind the top of your heart.
How long do you have to take blood thinners before cardioversion?
Before you have a cardioversion, you'll probably need to take medication called a blood thinner for a month. This will give your body time to dissolve any blood clots lurking inside your heart that could come loose because of the procedure and lead to a stroke.
Can you reset your heart with an electric shock?
This is one of the first options to reset your heart. You'll be asleep under anesthesia, and the doctor will zap your chest with an electric shock. "This isn't a permanent fix," Whang says. Your heart could fall out of sync again by the time you get home.
Is it safe to have a catheter ablation?
Catheter ablation has its own risks, too. Overall, about 5% of patients have some type of complication, including bleeding where the catheter goes into your body or when it enters the heart, as well as a 1% risk of stroke.
Can you control AFIB with medication?
But when you do have symptoms, that's a different story. If your heart goes in and out of a normal beat, you may be able to control it with medication alone. If you're in AFib all of the time, your doctor may recommend something else.
What does AFIB mean?
In this Article. Atrial fibrillation, or AFib, causes an uneven and sometimes rapid heart rate. It can lead to a higher chance of a stroke, heart failure, or other heart problems. AFib usually brings symptoms like shortness of breath, weakness, fatigue, dizziness, lightheadedness, chest pain, and heart palpitations.
Why does my heart beat so fast?
Heart arrhythmias, or problems with heart rhythm, happen when the electrical impulses that manage your heartbeat don’t work the way they should. They may cause your heart to beat too fast, too slow, or unevenly.
What happens when your thyroid is overactive?
Hyperthyroidism. An overactive thyroid, also known as hyperthyroidism, happens when your thyroid gland makes too much of a hormone called thyroxine.
What are the two most common arrhythmias?
Two of the most common types of arrhythmias are: Tachycardia. This is a fast heartbeat, when your resting heart rate is more than 100 beats per minute. AFib can cause one type of tachycardia. Others include atrial flutter, supraventricular tachycardia, Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome, and ventricular tachycardia.
What does it mean when your blood pressure is too low?
This is usually when you’ll start to notice symptoms. You may feel dizzy, lightheaded, or very tired, or have rapid breathing.
Why does my heart pump backwards?
Blood can flow backward in the valve, giving you too much blood in your heart. The other problem, stenosis, is when one or more valves become narrow. This limits the flow of blood, so your heart has to use extra force to pump. Either of these problems can cause heart failure.
What is the most common type of heart disease?
Coronary Artery Disease. Coronary artery disease (CAD) happens when plaque builds up in the walls of your arteries. It’s the most common type of heart disease in the United States. The most common symptom of CAD is chest pain or discomfort, which can also happen with AFib.

Overview
Symptoms
- When the heart beats too fast, it may not pump enough blood to the rest of the body. As a result, the organs and tissues may not get enough oxygen. In general, tachycardia may lead to the following signs and symptoms: 1. Sensation of a racing, pounding heartbeat or flopping in the chest (palpitations) 2. Chest pain 3. Fainting (syncope) 4. Lightheadedness 5. Rapid pulse rate 6…
Causes
- Tachycardia is an increased heart rate for any reason. It can be a usual rise in heart rate caused by exercise or a stress response (sinus tachycardia). Sinus tachycardia is considered a symptom, not a disease. Tachycardia can also be caused by an irregular heart rhythm (arrhythmia). Things that may lead to tachycardia include: 1. Fever 2. Heavy alcohol use or alcohol withdrawal 3. Hig…
Risk Factors
- In general, growing older or having a family history of certain heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias) may increase the risk of arrhythmias that commonly cause tachycardia. Lifestyle changes or medical treatment for related heart or other health conditions may decrease the risk of tachycardia.
Complications
- Complications of tachycardia depend on: 1. The type of tachycardia 2. How fast the heart is beating 3. How long the rapid heart rate lasts 4. If there are other heart conditions Some people with tachycardia have an increased risk of developing a blood clot that could cause a stroke (risk is highest with atrial fibrillation) or heart attack. Your health care provider may prescribe a blood …
Prevention
- The best ways to prevent tachycardia are to maintain a healthy heart and prevent heart disease. If you already have heart disease, monitor it and follow your treatment plan. Be sure you understand your treatment plan, and take all medications as prescribed. Lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of heart disease may help prevent heart arrhythmias that can cause tachycardia. Take the follow…
Overview
Symptoms
- Some people with atrial fibrillation (A-fib) don't notice any symptoms. Those who do have atrial fibrillation symptoms may have signs and symptoms such as: 1. Sensations of a fast, fluttering or pounding heartbeat (palpitations) 2. Chest pain 3. Dizziness 4. Fatigue 5. Lightheadedness 6. Reduced ability to exercise 7. Shortness of breath 8. Weakness Atrial fibrillation may be: 1. Occa…
Causes
- To understand the causes of A-fib, it may be helpful to know how the heart typically beats. The typical heart has four chambers — two upper chambers (atria) and two lower chambers (ventricles). Within the upper right chamber of the heart (right atrium) is a group of cells called the sinus node. The sinus node is the heart's natural pacemaker. It produces the signal that starts e…
Risk Factors
- Things that can increase the risk of atrial fibrillation (A-fib) include: 1. Age.The older a person is, the greater the risk of developing atrial fibrillation. 2. Heart disease.Anyone with heart disease — such as heart valve problems, congenital heart disease, congestive heart failure, coronary artery disease, or a history of heart attack or heart surgery — has an increased risk of atrial fibrillation. …
Complications
- Blood clots are a dangerous complication of atrial fibrillation that can lead to stroke. In atrial fibrillation, the chaotic heart rhythm can cause blood to collect in the heart's upper chambers (atria) and form clots. If a blood clot in the left upper chamber (left atrium) breaks free from the heart area, it can travel to the brain and cause a stroke. The risk of stroke from atrial fibrillation i…
Prevention
- Healthy lifestyle choices can reduce the risk of heart disease and may prevent atrial fibrillation. Here are some basic heart-healthy tips: 1. Eat a nutritious diet 2. Get regular exercise and maintain a healthy weight 3. Don't smoke 4. Avoid or limit alcohol and caffeine 5. Manage stress, as intense stress and anger can cause heart rhythm problems
How Can Afib Leave You Breathless?
How to Recognize The Symptoms?
- The symptoms of AFib shortness of breath vary from person to person. Regardless of what kind of impact they make, they can still be terrifying. It’s normal to feel agitated when the quivering in the heart muscles keeps the blood stuck in place and leaves you short of breath. That’s why you need to know how to recognize it. To recognize the symptoms of respiratory difficulties, you sho…
Other Contributors to Shortness of Breath
- AFib is a condition with a complex nature. There are many triggers that can make the problem worse. But, when it comes to shortness of breath, there are two very important factors you should know about. They are anxiety and sleep apnea. Here is how these contributors can make breathing difficult.
When to Ask For Help?
- Many patients with AFib can manage breathing discomfort at home with calm breathing and a healthy lifestyle. This could be a clear indicator of a more serious heart complication.
Final Thoughts
- Experiencing shortness of breath with AFib is not uncommon. That’s why it’s important to understand it and recognize it so you can get proper on-time treatment. The information listed here can help you get in control of your health condition and live a healthy, stress-free life.