
Medication
You can help prevent osteoporosis by leading a bone healthy lifestyle at all stages of life. In fact, osteoporosis prevention begins in childhood, when a bone-healthy diet and plenty of exercise helps children achieve their highest possible ‘peak bone mass’.
Nutrition
Primary prevention is keeping the disease of osteoporosis from getting started. The steps for primary prevention of osteoporosis are 1) getting enough calcium in your diet, 2) including vitamin D in your regime and 3) doing weight-bearing exercise. Secondary Prevention. Secondary prevention deals with the early onset of a negative health outcome.
Can I do anything to prevent osteoporosis?
You can make fractures less likely by maintaining or improving your bone density, Cosman says. That is, "you can reverse theconsequences of osteoporosis," says Robert Heaney, MD, vice president for research and professor of medicine at Creighton University in Omaha, Neb. A bone biologist, Heaney has spoken for Merck and Amgen.
What is the primary prevention of osteoporosis?
- Teriparatide (Bonsity, Forteo). This powerful drug is similar to parathyroid hormone and stimulates new bone growth. ...
- Abaloparatide (Tymlos) is another drug similar to parathyroid hormone. This drug can be taken for only two years.
- Romosozumab (Evenity). This is the newest bone-building medication to treat osteoporosis. ...
Can You reverse osteoporosis?
What is the new medication for osteoporosis?
What is the best treatment for osteoporosis?
Bisphosphonates are usually the first choice for osteoporosis treatment. These include: 1 Alendronate (Fosamax), a weekly pill 2 Risedronate (Actonel), a weekly or monthly pill 3 Ibandronate (Boniva), a monthly pill or quarterly intravenous (IV) infusion 4 Zoledronic acid (Reclast), an annual IV infusion
How does osteoporosis medication work?
Because bone rebuilding cannot keep pace, bones deteriorate and become weaker. Most osteoporosis medications work by reducing the rate at which your bones break down. Some work by speeding up the bone-building process. Either mechanism strengthens bone and reduces your risk of fractures.
What is the condition of bisphosphonates and denosumab?
A very rare complication of bisphosphonates and denosumab is a break or crack in the middle of the thighbone. This injury, known as atypical femoral fracture, can cause pain in the thigh or groin that begins subtly and may gradually worsen.
Which osteoporosis medication is usually tried first?
Which osteoporosis medications are usually tried first? Bisphosphonates are usually the first choice for osteoporosis treatment. These include: Alendronate (Fosamax), a weekly pill. Risedronate (Actonel), a weekly or monthly pill. Ibandronate (Boniva), a monthly pill or quarterly intravenous (IV) infusion.
How often is romosozumab given?
Romosozumab is given as a monthly injection at your doctor's office. It is a new drug and less is known about long-term side effects, but it is not given to people who have recently had a stroke or heart attack. Treatment stops after 12 monthly doses.
Does Raloxifene help with bone density?
Current recommendations say to use the lowest dose of hormones for the shortest period of time. Raloxifene (Evista) mimics estrogen's beneficial effects on bone density in post menopausal women, without some of the risks associated with estrogen. Taking this drug can reduce the risk of some types of breast cancer.
Can you take bisphosphonate with water?
Bisphosphonate pills aren't absorbed well by the stomach. It may help to take the medication with a tall glass of water on an empty stomach. Don't put anything else into your stomach for 30 to 60 minutes, after which you can eat, drink other liquids and take other medications.
Abstract
Approximately 10 million men and women in the U.S. have osteoporosis, 1 a metabolic bone disease characterized by low bone density and deterioration of bone architecture that increase the risk of fractures. 2 Osteoporosis-related fractures can increase pain, disability, nursing home placement, total health care costs, and mortality.
INTRODUCTION
Osteoporosis is a bone disorder that increases a person’s risk of fracture due to low bone mineral density (BMD), impaired bone microarchitecture/mineralization, and/or decreased bone strength.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Bones provide structure for the body, protection for the organs, and storage for minerals, such as calcium and phosphorus, that are essential for bone development and stability. Individuals continue to build bone and will reach peak bone mass at about 30 years of age, after which they begin to lose bone mass steadily.
ETIOLOGY
Primary osteoporosis is often associated with age and sex hormone deficiency. Age-related osteoporosis results from the continuous deterioration of the trabeculae in bone. In addition, the reduction of estrogen production in post menopausal women causes a significant increase in bone loss.
SCREENING AND DIAGNOSIS
Published osteoporosis screening guidelines vary greatly. In general, most organizations recommend that all adults older than 50 years of age with a history of fracture receive BMD screening.
SELECT GUIDELINES AND RECOMMENDATIONS
In a systematic review, Solomon et al. looked at 18 osteoporosis guidelines, among them those of the NOF, the ACR, and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology (AACE/ACE).
NONPHARMACOLOGICAL MANAGEMENT
Nonpharmacological management of osteoporosis includes adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, weight-bearing exercise, smoking cessation, limitation of alcohol/caffeine consumption, and fall-prevention techniques. 2 – 6, 9, 18, 34
How to prevent osteoporosis?
It describes how you can prevent and treat osteoporosis through diet, exercise, and medications. You'll also find advice on the right amount of calcium and vitamin D, tips on fall-proofing your home, and help with putting together a personalized plan to preserve or boost your bone strength. Other Product Information.
What is the Harvard Medical School guide to osteoporosis?
In Osteoporosis: A guide to prevention and treatment, Harvard Medical School doctors will show you the positive, proactive, and practical steps you can take to protect your bones now and in the years ahead. You will be alerted to red flags that signal you’re at greater risk for a broken bone. You'll be warned about medications that hasten bone loss.
What is the T score for bone turnover?
Lab tests for bone turnover. Developing a plan of action. If you have osteopenia (T-score between –1 and –2.5) If you have osteoporosis (T-score –2.5 and below) If your bone density is normal. Protecting your bone: Nutrition. Calcium and Vitamin D. Vitamin K. Potential dietary dangers.
How many bone fractures are caused by osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis: A guide to prevention and treatment. Each year, osteoporosis contributes to more than 2 million bone fractures in the United States. This Special Health Report, Osteoporosis: A guide to prevention and treatment, can help you keep your bones strong and healthy, and avoid fractures. It describes how you can prevent ...
Can osteoporosis erode your bones?
Don’t let osteoporosis erode your bones! Learn what you can do now to keep your bones strong and lower your risk of osteoporosis-related fractures. Osteoporosis can be intimidating and inhibiting. The prospect that a simple fall could break your hip or wrist can make you watch every step you take.
Is osteoporosis inevitable?
You’ll learn about other bone-protective strategies, too, including specific exercise routines, and discover some surprising foods that help weaken bones. Osteoporosis is not inevitable. The good news is there’s a lot you can do to shield your bones from this disease.
What is the best treatment for osteoporosis?
If you can't tolerate the more common treatments for osteoporosis — or if they don't work well enough — your doctor might suggest trying: Teriparatide (Forteo). This powerful drug is similar to parathyroid hormone and stimulates new bone growth. It's given by daily injection under the skin.
How to reduce the risk of osteoporosis?
Smoking increases rates of bone loss and the chance of fracture. Avoid excessive alcohol. Consuming more than two alcoholic drinks a day might decrease bone formation.
How long can you take teriparatide for osteoporosis?
After two years of treatment with teriparatide, another osteoporosis drug is taken to maintain the new bone growth. Abaloparatide (Tymlos) is another drug similar to parathyroid hormone. You can take it for only two years, which will be followed by another osteoporosis medication. Romosozumab (Evenity).
What is the newest bone building medication?
Romosozumab (Evenity). This is the newest bone-building medication to treat osteoporosis. It is given as an injection every month at your doctor's office. It is limited to one year of treatment, followed by other osteoporosis medications.
How often is denosumab shot?
Denosumab is delivered via a shot under the skin every six months. If you take denosumab, you might have to continue to do so indefinitely.
How to prevent falling?
Prevent falls. Wear low-heeled shoes with nonslip soles and check your house for electrical cords, area rugs and slippery surfaces that might cause you to fall.
How to determine bone density?
Diagnosis. Your bone density can be measured by a machine that uses low levels of X-rays to determine the proportion of mineral in your bones. During this painless test, you lie on a padded table as a scanner passes over your body. In most cases, only a few bones are checked — usually in the hip and spine.
What is the best treatment for osteoporosis?
Antiresorptive drugs. Bisphosphonates — Bisphosphonates are medications that slow the breakdown and removal of bone (ie, resorption). They are widely used for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Some of the commonly prescribed bisphosphonates include:
Why do women have osteoporosis?
Women are at a higher risk for osteoporosis after menopause due to lower levels of estrogen, a female hormone that helps to maintain bone mass. Fortunately, preventive treatments are available that can help to maintain ...
What is the name of the drug that is given under the skin to reduce bone fractures?
Denosumab — Denosumab (brand name: Prolia) is an antibody directed against a specific protein involved in the formation of cells that break down bone. Denosumab improves bone mineral density and reduces fracture in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. It is given as an injection under the skin once every six months.
What is menopausal hormone therapy?
Menopausal hormone therapy in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Screening for osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and men. Treatment of osteoporosis in men. Use of biochemical markers of bone turnover in osteoporosis. The following organizations also provide reliable health information.
How old do you have to be to get osteoporosis?
Experts suggest screening for osteoporosis for women 65 years and older and for women under 65 who have gone through menopause and have risk factors (such as past fracture, certain medical conditions or medications, or cigarette or alcohol use).
Does raloxifene help with osteoporosis?
In addition, SERMs decrease the risk of breast cancer in women who are at high risk. Raloxifene can be used for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis in post menopausal women, although it may be less effective in preventing bone loss than bisphosphonates or estrogen (see 'Hormone therapy' below).
Is calcitonin safe for osteoporosis?
Calcitonin is no longer used to treat osteoporosis, because other available options (eg, bisphosphonates) are more effective for the prevention of bone loss and reduction of fracture risk. In addition, there is concern about the long-term use of calcitonin for osteoporosis and an increase in cancer rates.
What is the FDA approved treatment for osteoporosis?
Denosumab, brand name Prolia® . Denosumab is approved by the FDA for the treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women at high risk of fracture. Denosumab reduces the incidence of vertebral fractures by about 68 %, hip fractures by about 40 %, and nonvertebral fractures by about 20 % over 3 years [56].
Who developed the Clinician's Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis?
The Clinician’s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis was developed by an expert committee of the National Osteoporosis Foundation (NOF) in collaboration with a multispecialty council of medical experts in the field of bone health convened by NOF.
How much does zoledronic acid reduce hip fractures?
Zoledronic acid reduces the incidence of vertebral fractures by 70 % (with significant reduction at 1 year), hip fractures by 41 % , and nonvertebral fractures by 25 % over 3 years in patients with osteoporosis defined by prevalent vertebral fractures and osteoporosis by BMD of the hip [66]. Drug administration .
Why is calcium important for bone health?
Lifelong adequate calcium intake is necessary for the acquisition of peak bone mass and subsequent maintenance of bone health. The skeleton contains 99 % of the body’s calcium stores; when the exogenous supply is inadequate, bone tissue is resorbed from the skeleton to maintain serum calcium at a constant level.
Is raloxifene safe for postmenopausal women?
Raloxifene is approved by the FDA for both prevention and treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Raloxifene reduces the risk of vertebral fractures by about 30 % in patients with a prior vertebral fracture and by about 55 % in patients without a prior vertebral fracture over 3 years [55].
How many fractures are attributed to osteoporosis?
Economic toll. Annually, two million fractures are attributed to osteoporosis, causing more than 432,000 hospital admissions, almost 2.5 million medical office visits, and about 180,000 nursing home admissions in the USA [1].
Is osteoporosis a silent disease?
Osteoporosis is a silent disease until it is complicated by fractures—fractures that occur following minimal trauma or, in some cases, with no trauma. Fractures are common and place an enormous medical and personal burden on the aging individuals who suffer them and take a major economic toll on the nation.
How many people have osteoporosis?
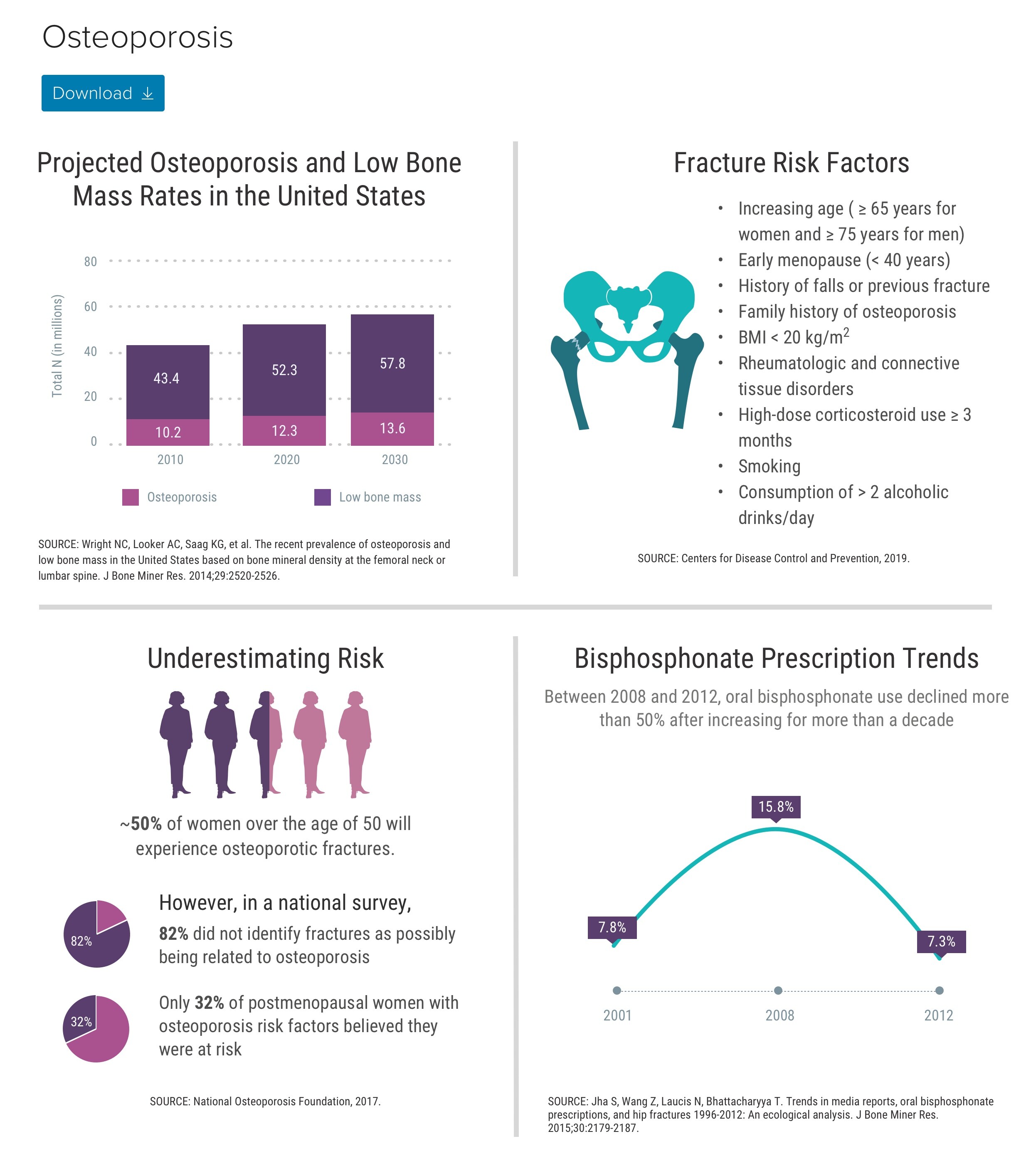
According to the National Osteoporosis Foundation, 10.2 million American adults have osteoporosis and another 43.3 million have low bone mass.
What foods are good for bone health?
Eat foods that are good for bone health. Dairy products, dark leafy greens and fortified juices and cereals are excellent sources of calcium. Fatty fish like salmon, tuna and sardines are a great source of vitamin D. And sweet potatoes, tomato products and artichokes are a great source of magnesium. 4.
What is the best way to get calcium?
Calcium is important for building bone strength, but most Americans don’t get the required daily amount. Eating calcium-rich food is the best way to get calcium, or you can take calcium supplements . Vitamin D is important for protecting bones, and your body also requires it to absorb calcium.
Is smoking bad for osteoporosis?
Smoking has been identified as a risk factor for osteoporosis. Some studies have shown a relationship between tobacco use and decreased bone density. You should also limit your alcohol intake to no more than 2 to 3 drinks a day, because drinking heavily can lead to bone loss. 5.
How can osteoporosis be prevented?
Osteoporosis can be prevented. Exercise, especially lifting weights, helps to maintain healthy bone mass. Healthy lifestyle choices, such as not smoking or misusing substances, also decrease your risk for developing osteoporosis.
Can osteoporosis be treated with alternative medicine?
The goal of any alternative treatment is to manage or heal the condition without the use of medication. Some alternative therapies can be used for osteoporosis. While there’s little scientific or clinical evidence to suggest that they’re truly effective, many people report success. Always inform your doctor before beginning any alternative medicine ...
Does black cohosh help with bone loss?
It contains phytoestrogens (estrogen-like substances) that may help prevent bone loss. A 2008 study. Trusted Source. found that black cohosh promoted bone formation in mice. More scientific research is needed to determine if these results can be extended to treatment in humans with osteoporosis.
Can you lose bone mass with osteoporosis?
When a person is diagnosed with osteoporosis, they’re advised to change their diet to incorporate more calcium. Though bone mass can’t be instantly corrected, dietary changes may stop you from losing more bone mass. Hormone replacement drugs, particularly ones that contain estrogen, are often prescribed.
Can soy be used for osteoporosis?
Isoflavones are estrogen-like compounds that may help protect bones and stop bone loss. It’s generally recommended that you talk to your doctor before using soy for osteoporosis, especially if you have an increased risk of estrogen-dependent breast cancer .
Does red clover help with osteoporosis?
Red clover is thought to contain estrogen-like compounds. Since natural estrogen can help protect bone, some alternative care practitioners may recommend its use to treat osteoporosis. However, there’s no scientific evidence to show that red clover is effective in slowing down bone loss. The estrogen-like compounds in red clover may interfere ...

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment