Medication
New Therapy for Partial Paralysis. In some stroke survivors with partial paralysis on one side, intensive physical therapy that restrains their good arm and hand may lead to lasting improvements in the paralyzed one.
Procedures
Preventive stroke treatments include blood-thinning and cholesterol-lowering medications (among others), and surgical procedures such as carotid endarterectomy to aid normal blood flow, and left atrial appendage closure to prevent clots in atrial fibrillation patients.
Therapy
The No. 1 reason for a hemorrhagic stroke is uncontrolled high blood pressure. If this led to yours, you'll probably need to take medicine to lower it. If an aneurysm caused your stroke, your doctor may clamp the broken vessel closed or thread a tiny coil through it that helps to keep the blood vessel from bursting again.
Nutrition
In the aftermath of a stroke, most people will undergo physical therapy and occupational therapy to help restore function and learn adaptive strategies to perform everyday tasks. Given that impaired speech and language are common consequences of a parietal lobe stroke, intensive, ongoing speech therapy may be advised.
See more
How do you treat partial paralysis after a stroke?
What are the treatments for stroke?
How do doctors treat a hemorrhagic stroke?
How is speech therapy used to treat a parietal lobe stroke?

What are 3 treatments for a stroke?
Treating ischaemic strokesThrombolysis – "clot buster" medicine. ... Thrombectomy. ... Aspirin and other antiplatelets. ... Anticoagulants. ... Blood pressure medicines. ... Statins. ... Carotid endarterectomy.
Can partial stroke be corrected?
The short answer is yes, stroke can be cured — but it occurs in two stages. First, doctors administer specific treatment to restore normal blood flow in the brain. Then, the patient participates in rehabilitation to cure the secondary effects.
How long does it take to recover from partial stroke?
Because mild strokes do not typically cause major impairments, recovery is usually fast. Sometimes recovery from a mild stroke can occur within 3-6 months. Other times it can take longer. There are many variables that affect the time it takes to recover.
What are the drugs for partial stroke?
Drugs for StrokeAspirin. Aspirin is an analgesic and antipyretic, prescribed for pain, heart attack and fever. ... Astaxanthin. ... Losartan. ... Nimodipine. ... Ticlopidine.
What is the best treatment for stroke?
An IV injection of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (TPA) — also called alteplase (Activase) or tenecteplase (TNKase) — is the gold standard treatment for ischemic stroke. An injection of TPA is usually given through a vein in the arm within the first three hours.
Can you go back to normal after a stroke?
The injury to the brain caused by a stroke can lead to widespread and long-lasting problems. Although some people may recover quickly, many people who have a stroke need long-term support to help them regain as much independence as possible. This process of rehabilitation depends on the symptoms and their severity.
How long do you stay in the hospital after a mini stroke?
The average amount of time to stay in the hospital after a TIA is 2 to 3 days.
How serious is a mini stroke?
TIAs look like strokes in terms of signs and symptoms, but they are temporary. In other words, they leave no lasting brain damage or residual symptoms. However, they serve as a warning sign that a person is at higher risk of a major stroke and should seek immediate medical attention.
How long can you live after a mild stroke?
In the 65- to 72-year age group 11% survived 15 years after stroke. In the age group <65 years 28% survived 15 years. For all age groups survival was poorer in stroke patients than in non-stroke controls. Long-term survival improved steadily over time.
What is the best drug for partial stroke?
Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) is the only stroke drug that actually breaks up a blood clot. It's used as a common emergency treatment during a stroke. For this treatment, tPA is injected into a vein so it can get to the blood clot quickly.
Which tablet is best for brain stroke?
Aspirin is the best-known example. You might have to take aspirin or other types of antiplatelets for the rest of your life if you've had an ischemic stroke or a TIA. Both types of anti-clotting drugs raise your chances of bleeding.
What causes partial stroke?
A blood vessel in your brain balloons up and bursts, or a weakened one leaks. Uncontrolled high blood pressure and taking too much blood thinner medicine can lead to this kind of stroke. Some people have what's called a transient ischemic attack (TIA). This "mini stroke" is due to a temporary blockage.
What is the treatment for a stroke?
Once under the care of a medical team, and diagnosis confirmed, a patient will receive emergency stroke treatment, which may include breathing support and IV fluids; medications to break up blood clots; medications and therapies to reduce brain swelling and protect the brain; and brain surgery to remove clots, reduce pressure or repair bleeds.
What is the most important part of stroke treatment?
The most important part of stroke treatment is getting it fast. acronym “FAST” is an easy way to remember the main symptoms to be aware of in order to help someone who may be having a stroke: face drooping, arm weakness or speech difficulty.
How to treat stroke paralysis?
The most effective way to treat stroke paralysis is to activate neuroplasticity. Neuroplasticity refers to the mechanism your brain uses to reorganize nerve cells and form new neural pathways. These new neural pathways then allow healthy, undamaged portions of the brain to take over control from damaged areas.
How to recover from a stroke?
Mirror Therapy. Finally, tabletop mirror therapy is a great way to recover from hand paralysis after stroke. It involves placing a mirror over your affected hand and doing hand therapy exercises with your non-affected hand.
Why is it important to stimulate your brain after stroke?
Stimulation is important because, when post-stroke paralysis is involved, the brain has lost communication with the affected muscles. But by stimulating your brain and body with these various treatments, you may recover movement after post-stroke paralysis.
How does stroke paralysis help?
Stroke paralysis treatments can help patients improve their chances of regaining mobility in the affected limbs. Patients are encouraged to try different treatment methods because everyone responds differently. After all, every stroke is different, and every recovery will be different. To help you take charge of your recovery, ...
What is the name of the side of the brain that is affected by a stroke?
Causes and Symptoms of Stroke Paralysis. Stroke paralysis, also known as hemiplegia, usually occurs on the side of the body opposite from the side of the brain damaged by stroke. For example, if a stroke occurred in the brain’s left hemisphere, you may experience paralysis on the right side of your body. This occurs because each side of the brain ...
How to improve your movement?
As you move through passive exercises, focus intently on the movement (watch the movement with your eyes and think about the movement in your mind). Eventually, the connection between your brain and muscles will improve, and you might regain a small amount of your movement.
What are the symptoms of stroke paralysis?
Some common symptoms that often accompany stroke paralysis include: Spasticity: stiff, tight muscles. Contractures: soft tissue shortening caused by extremely stiff muscles, which can impede movement across a joint. Foot drop: inability to lift the toes up towards the shin. Dysphagia: difficulty swallowing.
What is the best treatment for stroke survivors?
Speech Therapy . Stroke survivors that are experiencing difficulties with writing, reading, speaking, comprehension, visual processing, or memory can benefit from speech therapy . A speech-language pathologist is trained to help people recover their communication skills.
How to help stroke survivors?
Visual Scanning Exercises. Visual scanning exercises (like word searches) encourage stroke survivors to make a conscious effort to focus on stimuli on the affected side. The more you practice engaging your neglected side, the better your brain will get at noticing stimuli.
What are the secondary effects of a parietal lobe stroke?
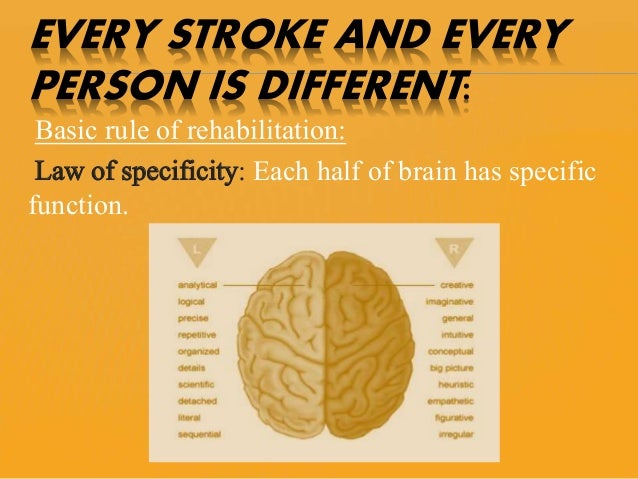
Secondary Effects Depend on the Hemisphere Affected. A parietal lobe stroke will primarily affect sensory interpretation and spatial awareness. However, effects of the stroke will greatly depend upon the side of the brain that the stroke occurs: your dominant or non-dominant side. Everyone has a dominant side of the brain.
How does a stroke affect the parietal lobe?
A stroke in the parietal lobe can affect the brain’s ability to interpret sensory information and spatial awareness. As a result, parietal lobe stroke patients often struggle with piecing together their experiences.
What happens if you have a stroke?
If you are right-handed, then the left side of your brain is dominant. When the dominant parietal lobe is affected by stroke, the following effects may occur: 1 Agnosia: when the patient cannot recognize and identify objects, people, or sounds using their senses, even when the senses are otherwise functioning normally (it’s an issue with the brain, not the senses) 2 Difficulties differentiating between left and right 3 Agraphia: difficulty communicating through writing, either from motor issues or inability to spell. 4 Alexia: partial or complete inability to read. A Speech-Language Pathologist can help diagnose this issue. 5 Acalculia: loss of ability to perform simple math problems. A problem particularly associated with parietal lobe stroke in the left side (which is usually the dominant side in most people). 6 Aphasia: difficulty communicating through speech. There are different types of aphasia, and a Speech-Language Pathologist can help diagnose. 7 Proprioception disorders: difficulties sensing where your body parts are, which can cause poor balance and uncoordinated movements
What happens to the parietal lobe when a blood vessel is clogged?
A stroke in the parietal lobe occurs when a blood vessel in the parietal lobe either gets clogged by a blood clot (an ischemic stroke) or the blood vessel bursts (a hemorrhagic stroke). Oxygen fuels cell activity. Without enough blood supply , brain cells will start to die, and the parietal lobe will begin to lose control of its function.
What happens to the parietal lobe when stroke occurs?
When the dominant parietal lobe is affected by stroke, the following effects may occur: Agnosia: when the patient cannot recognize and identify objects, people, or sounds using their senses, even when the senses are otherwise functioning normally (it’s an issue with the brain, not the senses)
What is the procedure to treat a stroke in the brain?
If an ischemic stroke in the cerebral cortex (known as a cortical stroke) is accompanied by severe edema (swelling of the brain), a surgery known as craniotomy may be performed to relieve the pressure and reduce the risk of brain damage.
What happens when you have a parietal stroke?
When brain damage occurs due to a parietal stroke, it can impair these functions and lead to a lack of spatial awareness and a loss of the perception of body's position in space, among other things. 1 . As with all strokes, a parietal lobe stroke can be diagnosed with imaging studies, a neurological exam, and other tests.
What is the most common cause of partial vision loss?
Partial vision loss may also occur after a parietal lobe stroke, making it difficult to see and recognize objects. A parietal lobe stroke is most likely to result in inferior quadrantanopia characterized by the loss of the left or right lower fields of vision of both eyes. 5
What are the signs of a parietal lobe stroke?
10 . Diagnostic signs suggestive of a parietal lobe stroke include: Problems stringing together words or syllables. Behaving as if the left side of a space is nonexistent.
What is the test for stroke?
If a stroke is suspected, the doctor will typically perform an in-office test known as a neurological exam. The test evaluates your motor, cognitive, and visual responses to various stimuli to see if there are any abnormalities suggestive of a stroke. The neurological exam is painless and can be performed with simple tools, including a penlight and reflex hammer. 10
Can a stroke be overt?
Things can move quickly when a stroke is suspected. In some cases, the symptoms will be overt, and you may be rushed to emergency for imaging tests and other urgent evaluations. In other cases, the symptoms may be less characteristic and require a combination of tests to determine the cause.
Can a parietal lobe stroke cause sensory loss?
It can be challenging to care for someone who has had a parietal lobe stroke. Sensory loss can cause injuries if a loved one is suddenly unable to coordinate movements or judge distances when reaching or walking. Moreover, people with spatial neglect, hemiagnosia, or asomatognosia are often less aware of their surroundings ...
Patients Worked Hard
Three to nine months after their strokes, 106 of the patients were assigned to receive constraint-induced movement therapy (CIMT).
Big Improvements
Both the CIMT group and the usual-care group were studied over the year to see how quickly and effectively they could perform the tasks they had chosen.
Improvements May Be Permanent
"One of the most convincing things about this trial is that it showed the durability of CIMT," Marler says. "The effects of a relatively short intervention could still be seen a year later. This is solid evidence that there is a benefit."
Future Looks Promising
Researchers are now evaluating whether CIMT might be even more effective if it's started earlier -- one to three months after a stroke stroke -- or if it continues longer than two weeks.
What is a cryptogenic stroke?
Cryptogenic Stroke. In most cases, a stroke is caused by a blood clot that blocks the flow of blood to the brain. In some instances, despite testing, the cause of a stroke can’t be determined. This is called a cryptogenic stroke. Learn more about cryptogenic stroke.
What happens when a stroke occurs in the brain stem?
When stroke occurs in the brain stem, it can affect both sides of the body and may leave someone in a ‘locked-in’ state. When a locked-in state occurs, the patient is generally unable to speak or move below the neck.
What causes a hemorrhagic stroke?
Occurs when a weakened blood vessel ruptures. The two types of weakened blood vessels that usually cause hemorrhagic stroke are aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations (AVMs ). The most common cause of hemorrhagic stroke is uncontrolled high blood pressure.
How long does it take for a stroke to go away?
Ischemic stroke (part of the brain loses blood flow) Hemorrhagic stroke (bleeding occurs within the brain) Transient ischemic attack, TIA, or mini-stroke (The stroke symptoms resolve within minutes, but may take up to 24 hours on their own without treatment.
What is a stroke called?
A stroke occurs when part of the brain loses its blood supply and stops working. This causes the part of the body that the injured brain controls to stop working. A stroke also is called a cerebrovascular accident, CVA, or "brain attack.". ...
Why does the artery in the brain narrow?
In a thrombotic stroke, an artery can narrow over time because of cholesterol buildup, called plaque. If that plaque ruptures, a clot is formed at the site and prevents blood from passing to brain cells downstream, which are then deprived of oxygen.
What is the term for a stroke that is caused by a lack of blood flow?
A stroke, also known as a cerebrovascular accident or CVA is when part of the brain loses its blood supply and the part of the body that the blood-deprived brain cells control stops working. This loss of blood supply can be ischemic because of lack of blood flow, or hemorrhagic because of bleeding into brain tissue.
What type of stroke is a clot?
Embolic stroke. Another type of stroke may occur when a blood clot or a piece of atherosclerotic plaque (cholesterol and calcium deposits on the wall of the inside of the heart or artery) breaks loose, travels through the bloodstream, and lodges in an artery in the brain.
What is the most common cause of stroke?
The blockage of an artery in the brain by a clot (thrombosis) is the most common cause of a stroke. The part of the brain that is supplied by the clotted blood vessel is then deprived of blood and oxygen.
Why does the artery narrow in a stroke?
The artery can be blocked in a couple of ways. In a thrombotic stroke, an artery can narrow over time because of cholesterol buildup, called plaque. If that plaque ruptures, a clot is formed at the site and prevents blood from passing to brain cells downstream, which are then deprived of oxygen.
