How is cyanide poisoning treated?
- Oxygen will be given to help restore oxygen to your cells, and to prevent more damage.
- Cyanide antidotes will be used to bind with the cyanide so your body can remove it through your urine.
- Charcoal may be used to absorb cyanide that you have swallowed.
Full Answer
How do you treat a person for cyanide poisoning?
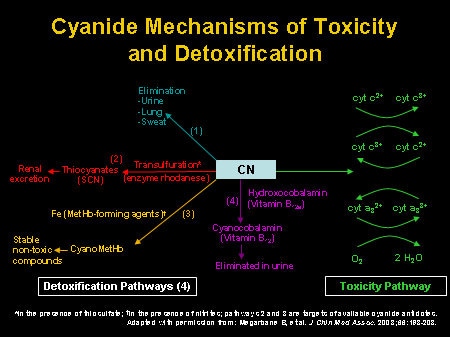
Antidotes include methaemoglobin generators, direct binding agents and sulphur donors, but there is a lack of international consensus about the treatment of choice. This article reviews the mechanisms and treatment of cyanide intoxication and emphasizes the importance of having agreed local procedures for the emergency treatment of poisoning.
How can you reverse the effects of cyanide?
Conventional treatment of cyanide poisoning includes decontamination, supportive and specific treatment. Decontamination should be adapted to the route of poisoning and never postpone supportive treatment. Basic life support includes immediate administration of high flow of oxygen, airway protection and cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
What are the signs and symptoms of cyanide poisoning?
Jan 25, 2018 · hydroxocobalamin (Cyanokit) The cyanide antidote kit consists of three medications given together: amyl nitrite, sodium nitrite, and sodium thiosulfate. The amyl nitrite is given by inhalation for...
Is atropine an antidote for cyanide?
Antidotes to cyanide include hydroxocobalamin and sodium nitrite and sodium thiosulfate. Sodium thiosulfate may be given in combination w1th sod1um mtnte or hydroxocobalamin, or may be given alone. These agents are administered intravenously. Hydroxocobalamin

Is there any treatment for cyanide?
Antidotes to cyanide include hydroxocobalamin and sodium nitrite and sodium thiosulfate. Sodium thiosulfate may be given in combination w1th sod1um mtnte or hydroxocobalamin, or may be given alone. These agents are administered intravenously.Jul 21, 2014
How do paramedics treat cyanide poisoning?
One of the treatments for cyanide poisoning is to turn some of the hemoglobin in the body into a form that will attach to cyanide. This will pull the cyanide out of the mitochondria of the cells and allow the resumption of normal energy production.May 13, 2009
Can cyanide poisoning be cured?
Cyanide poisoning is treated with specific antidotes and supportive medical care in a hospital setting. Antidotes for cyanide poisoning are most useful if given as soon as possible after exposure. Clinicians should treat suspected cases accordingly and not wait for laboratory confirmation.
Which of the following drug can be used in cyanide poisoning?
Lorazepam is the drug of choice; midazolam and phenobarbital are second-line agents. Cyanide antidotes are the key medications for hydrogen cyanide (HCN) poisoning. Hydroxocobalamin (HCO, vitamin B-12) is the first-line therapy for cyanide toxicity.Oct 20, 2021
What is the most famous poison?
Cyanide is one of the most famous poisons — from spy novels to murder mysteries, it’s developed a reputation for causing an almost immediate death. But in real life, cyanide is a little more complicated. Cyanide can refer to any chemical that contains a carbon-nitrogen (CN) bond, and it can be found in some surprising places.
Is cyanide poisoning rare?
Acute cyanide poisoning is relatively rare , and the majority of cases are from unintentional exposure. When it does occur, symptoms are sudden and severe. You may experience: If you suspect that you or a loved one is experiencing acute cyanide poisoning, seek immediate emergency medical attention.
What is cyanide in food?
Cyanide can refer to any chemical that contains a carbon-nitrogen (CN) bond, and it can be found in some surprising places. For example, it’s found in many safe-to-eat plant foods, including almonds, lima beans, soy, and spinach. like citalopram (Celexa) and cimetidine (Tagamet).
How to reduce risk of complications?
Early diagnosis and treatment are key to reducing your risk of complications. Moderate levels of acute or chronic exposure may also be resolved with quick diagnosis and treatment. In severe cases, symptoms are often sudden and life-threatening. Immediate emergency medical attention is necessary.
Who is David Jaslow?
David Jaslow, director of the Division of EMS and Disaster Medicine at the center , and his team will offer a variety of columns on fireground medical operations. Ken Lavelle is an attending physician at Albert Einstein, and previously spent 14 years working as a firefighter and EMS provider.
Is cyanide poisonous?
Cyanide is deadly. It can be encountered in either terrorism or a building fire, but the signs and symptoms are vague. What can we do about it? We need a treatment that is cheap (so it can be on all first line EMS units), safe (so it can be given by a paramedic and not hurt the victim even if they have not been exposed) and easy to give.
How to treat cyanide poisoning?
Treat the person as follows, depending on whether cyanide was inhaled, ingested, or absorbed through the skin: 1. Treat Inhalation or Ingestion.
Can you touch a person exposed to cyanide?
Avoid touching a person whose skin has been exposed to cyanide; only emergency personnel with special protective clothing should have direct contact with the victim, as secondary contamination is possible.
How long should you be in the emergency department for cyanide?
Patients who have ingested hydrogen cyanide solutions or patients who have direct skin or eye contact should be observed in the Emergency Department for at least 4 to 6 hours (Hall and Rumack 1998).
What is the effect of cyanide on the body?
In humans, cyanide combines with the ferric ion in mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase, preventing electron transport in the cytochrome system and bringing oxidative phosphorylation and ATP production to a halt. The inhibition of oxidative metabolism puts increased demands on anaerobic glycolysis, which results in lactic acid production and may produce severe acid-base imbalance. The CNS is particularly sensitive to the toxic effects of cyanide, and exposure to hydrogen cyanide generally produces symptoms within a short period of time (ATSDR 2006).
What is aqueous solution?
Aqueous solutions are referred to as hydrocyanic acid and prussic acid. Persons whose clothing or skin is contaminated with cyanide-containing solutions can secondarily contaminate response personnel by direct contact or through off-gassing vapor. Hydrogen cyanide is a colorless or pale-blue liquid at room temperature.
How is hydrogen cyanide absorbed?
Hydrogen cyanide is absorbed well by inhalation and can produce death within minutes. Substantial absorption can occur through intact skin if vapor concentration is high or with direct contact with solutions, especially at high ambient temperatures and relative humidity. Exposure by any route may cause systemic effects.
How to stabilize cervical spine?
Quickly establish a patent airway, ensure adequate respiration and pulse. Stabilize the cervical spine with a collar and a backboard if trauma is suspected. Administer supplemental oxygen as required. Assist ventilation with a bag-valve-mask device if necessary.
Can cyanide be fatal?
Ingestion of hydrogen cyanide solutions or cyanide salts can be rapidly fatal (ATSDR 2006). Treatment of ingested cyanide salts is similar to treatment of oral hydrogen cyanide poisoning because cyanide salts form hydrogen cyanide in acidic conditions.
What is an anion gap?
An anion-gap, metabolic acidosis occurs in severe poisoning from increased blood levels of lactic acid (ATSDR 2006). Because of their higher metabolic rates, children may be more vulnerable to toxicants interfering with basic metabolism.
What are the symptoms of cyanide poisoning?
Early symptoms include headache, dizziness, fast heart rate, shortness of breath, and vomiting.
What is the cause of hydrogen cyanide poisoning?
Acute hydrogen cyanide poisoning can result from inhalation of fumes from burning polymer products that use nitriles in their production, such as polyurethane, or vinyl. It can also be caused by breakdown of nitroprusside into nitric oxide and cyanide. Nitroprusside may be used during treatment of hypertensive crisis.
How much cyanide is in blood?
Blood levels of cyanide can be measured but take time. Levels of 0.5–1 mg/L are mild, 1–2 mg/L are moderate, 2–3 mg/L are severe, and greater than 3 mg/L generally result in death. If exposure is suspected, the person should be removed from the source of exposure and decontaminated.
Which is better, cobinamide or cyanide?
Cobinamide is the final compound in the biosynthesis of cobalamin. It has greater affinity for the cyanide than cobalamin itself, which suggests that it could be a better option for emergency treatment.
What happens if you eat cassava roots?
Exposure to lower levels of cyanide over a long period (e.g., after use of improperly processed cassava roots, which are a primary food source in tropical Africa) results in increased blood cyanide levels, which can result in weakness and a variety of symptoms, including permanent paralysis, nervous lesions, hypothyroidism, and miscarriages. Other effects include mild liver and kidney damage.
How does hydrogen cyanide affect the body?
If hydrogen cyanide is inhaled it can cause a coma with seizures, apnea, and cardiac arrest, with death following in a matter of seconds. At lower doses, loss of consciousness may be preceded by general weakness, dizziness, headaches, vertigo, confusion, and perceived difficulty in breathing. At the first stages of unconsciousness, breathing is often sufficient or even rapid, although the state of the person progresses towards a deep coma, sometimes accompanied by pulmonary edema, and finally cardiac arrest. A cherry red skin color that changes to dark may be present as the result of increased venous hemoglobin oxygen saturation. Despite the similar name, cyanide does not directly cause cyanosis. A fatal dose for humans can be as low as 1.5 mg/kg body weight. Other sources say a lethal dose is 1–3 mg per kg body weight for vertebrates.
Does hydrogen cyanide require decontamination?
Decontamination of people exposed to hydrogen cyanide gas only requires removal of the outer clothing and the washing of their hair. Those exposed to liquids or powders generally require full decontamination.
Why is cyanide harmful to the heart?
When this happens, the cells die. Cyanide is more harmful to the heart and brain than to other organs because the heart and brain use a lot of oxygen.
What are combustion products?
Combustion products are substances given off when things burn. In manufacturing, cyanide is used to make paper, textiles, and plastics. It is present in the chemicals used to develop photographs. Cyanide salts are used in metallurgy for electroplating, metal cleaning, and removing gold from its ore.
How do you get cyanide?
You could be exposed to cyanide by breathing air, drinking water, eating food, or touching soil that contains cyanide. Cyanide enters water, soil, or air as a result of both natural processes and industrial activities. When present in air, it is usually in the form of gaseous hydrogen cyanide.
Where does cyanide come from?
Cyanide is released from natural substances in some foods and in certain plants such as cassava, lima beans and almonds. Pits and seeds of common fruits, such as apricots, apples, and peaches, may have substantial amounts of chemicals which are metabolized to cyanide.
Is cyanide a gas?
Cyanide can be a colorless gas, such as hydrogen cyanide (HCN) or cyanogen chloride (CNCl), or a crystal form such as sodium cyanide (NaCN) or potassium cyanide (KCN). Cyanide sometimes is described as having a “bitter almond” smell, but it does not always give off an odor, and not everyone can detect this odor.
How do you know if you are exposed to cyanide?
Immediate signs and symptoms of exposure to cyanide. People exposed to a small amount of cyanide by breathing it , absorbing it through their skin, or eating foods that contain it may have some or all of the following signs and symptoms within minutes: Dizziness . Headache. Nausea and vomiting. Rapid breathing.
Is cyanide gas dangerous?
Cyanide gas is most dangerous in enclosed places where the gas will be trapped. Cyanide gas evaporates and disperses quickly in open spaces, making it less harmful outdoors. Cyanide gas is less dense than air; so it will rise. Cyanide prevents the cells of the body from using oxygen. When this happens, the cells die.
