What is the best treatment for bronchitis?
How do you know when you have bronchitis?
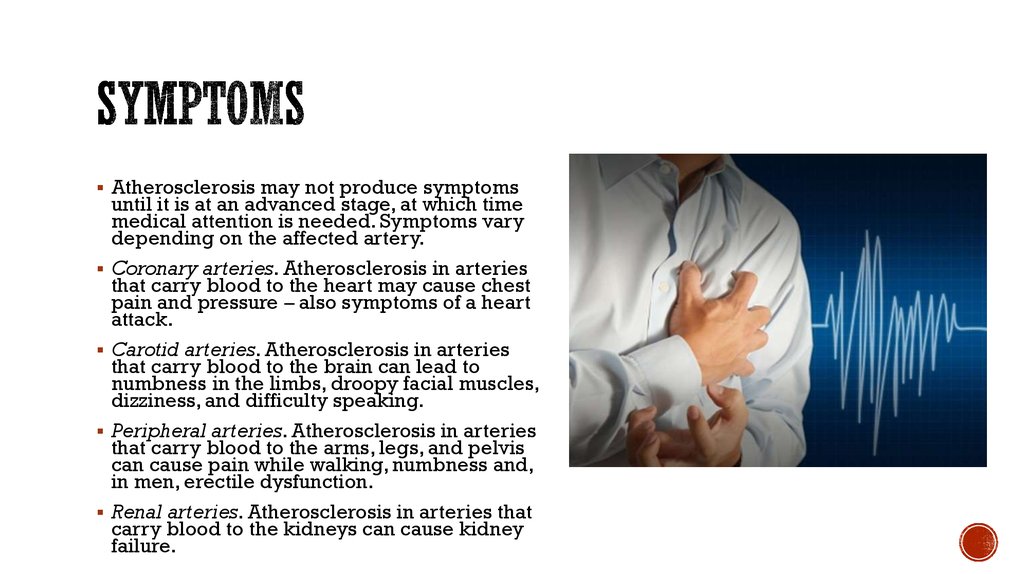
- Cough.
- Production of mucus (sputum), which can be clear, white, yellowish-gray or green in color — rarely, it may be streaked with blood.
- Fatigue.
- Shortness of breath.
- Slight fever and chills.
- Chest discomfort.
What are 3 symptoms of bronchitis?
Chest congestion, when your chest feels full or clogged. A cough that may bring up mucus that's clear, white, yellow, or green. Shortness of breath. Wheezing or a whistling sound when you breathe.
Does Covid feel like bronchitis?
What antibiotics treat bronchitis?
- Extended macrolides like Zithromax (azithromycin)
- Fluoroquinolones like Cipro (ciprofloxacin) and Levaquin (levofloxacin)
- Aminopenicillins like Principen (ampicillin), Moxatag (amoxicillin), and Hetacin (hetacillin)
- Cephalosporins.
Does bronchitis go away?
Should I take antibiotics for bronchitis?
Is bronchitis serious?
Chronic bronchitis is a serious condition that makes your lungs a breeding ground for bacterial infections and may require ongoing medical treatment. It's one form of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), a lung disease that makes it hard to breathe.Jan 15, 2022
How do I know if bronchitis is viral or bacterial?
What does bronchitis sound like?
How long does Covid bronchitis last?
What are the symptoms of bronchitis?
Symptoms. For either acute bronchitis or chronic bronchitis, signs and symptoms may include: Cough. Production of mucus (sputum), which can be clear, white, yellowish-gray or green in color — rarely, it may be streaked with blood. Fatigue.
How long does bronchitis last?
Chronic bronchitis is defined as a productive cough that lasts at least three months, with recurring bouts occurring for at least two consecutive years. If you have chronic bronchitis, you're likely to have periods when your cough or other symptoms worsen.
Can bronchitis be chronic?
People who have bronchitis often cough up thickened mucus, which can be discolored. Bronchitis may be either acute or chronic. Often developing from a cold or other respiratory infection, acute bronchitis is very common. Chronic bronchitis, a more serious condition, is a constant irritation or inflammation of the lining of the bronchial tubes, ...
How long does it take for bronchitis to go away?
Acute bronchitis, also called a chest cold, usually improves within a week to 10 days without lasting effects, although the cough may linger for weeks. However, if you have repeated bouts of bronchitis, you may have chronic bronchitis, which requires medical attention.
Can antibiotics kill bronchitis?
Antibiotics don't kill viruses, so this type of medication isn't useful in most cases of bronchitis. The most common cause of chronic bronchitis is cigarette smoking. Air pollution and dust or toxic gases in the environment or workplace also can contribute to the condition.
Can smoking cause bronchitis?
Cigarette smoke. People who smoke or who live with a smoker are at higher risk of both acute bronchitis and chronic bronchitis. Low resistance. This may result from another acute illness, such as a cold, or from a chronic condition that compromises your immune system.
Can bronchitis cause pneumonia?
Although a single episode of bronchitis usually isn't cause for concern, it can lead to pneumonia in some people. Repeated bouts of bronchitis, however, may mean that you have chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
What is the best treatment for bronchitis?
If you have chronic bronchitis, you may benefit from pulmonary rehabilitation — a breathing exercise program in which a respiratory therapist teaches you how to breathe more easily and increase your ability to exercise.
Can antibiotics help with bronchitis?
Because most cases of bronchitis are caused by viral infections, antibiotics aren't effective. However, if your doctor suspects that you have a bacterial infection, he or she may prescribe an antibiotic. In some circumstances, your doctor may recommend other medications, including: Cough medicine.
What tests can help you know if you have pneumonia?
In some cases, your doctor may suggest the following tests: Chest X-ray. A chest X-ray can help determine if you have pneumonia or another condition that may explain your cough. This is especially important if you ever were or currently are a smoker. Sputum tests. Sputum is the mucus that you cough up from your lungs.
How to get rid of a swollen lung?
Lifestyle and home remedies. To help you feel better, you may want to try the following self-care measures: Avoid lung irritants. Don't smoke. Wear a mask when the air is polluted or if you're exposed to irritants, such as paint or household cleaners with strong fumes. Use a humidifier.
How to get rid of a cough that is causing a cough?
Avoid lung irritants. Don't smoke. Wear a mask when the air is polluted or if you're exposed to irritants, such as paint or household cleaners with strong fumes. Use a humidifier. Warm, moist air helps relieve coughs and loosens mucus in your airways.
How to get rid of mucus in your airways?
Wear a mask when the air is polluted or if you're exposed to irritants, such as paint or household cleaners with strong fumes. Use a humidifier. Warm, moist air helps relieve coughs and loosens mucus in your airways.
How to get rid of coughing and sneezing?
Use a humidifier. Warm, moist air helps relieve coughs and loosens mucus in your airways. But be sure to clean the humidifier according to the manufacturer's recommendations to avoid the growth of bacteria and fungi in the water container. Consider a face mask outside.
How do you diagnose bronchitis?
Healthcare providers diagnose bronchitis by asking patients questions about symptoms and doing a physical examination. Though they rarely order additional tests, if you have a fever, your physician may order a chest X-ray to rule out pneumonia.
How to prevent bronchitis?
Preventing Bronchitis. Avoiding lung irritants, including smoking, is important for preventing bronchitis. To help protect your lungs, wear a mask over your mouth and nose when using lung irritants such as paint, paint remover or varnish. Wash your hands often, and receive a flu shot every year.
How long does bronchitis last?
On average, the symptoms of acute bronchitis last only a couple of weeks. However, if you have a cough that won't go away, or if you get sick with bronchitis frequently, it may be the sign of a more serious disease and you should visit your doctor. Here are some questions to ask your doctor about bronchitis.
How to treat a swollen chest?
Treatment options your doctor may suggest are: Resting and getting plenty of fluids. Drinking lots of water, which helps loosen chest congestion. A cough suppressant and/or pain reliever. A humidifier or steam.
How long does bronchitis last?
Acute bronchitis typically lasts less than 10 days, but the coughing can continue for several weeks. Chronic bronchitis, on the other hand, can last for several weeks and usually comes back. This condition is more common in people with asthma or emphysema. Read on to learn more about symptoms, causes, and treatment of acute bronchitis.
Can you prevent bronchitis?
There’s no way to completely prevent acute bronchitis because it has a variety of causes. However, you can decrease your risk by following the tips listed here. If you have a weakened immune system due to a health condition or older age, you should take special care to avoid getting acute bronchitis.
Can bronchitis go away without treatment?
In many cases, acute bronchitis will go away without treatment. But if you see your doctor because of symptoms of acute bronchitis, they will start with a physical exam. During the exam, your doctor will listen to your lungs as you breathe, checking for symptoms such as wheezing.
Can antibiotics help with bronchitis?
When you feel sick, you may really hope your doctor will prescribe medication to make you feel better. It’s important to know, though, that antibiotics aren’t recommended for people with acute bronchitis.
Can you take antibiotics for bronchitis?
It’s important to know, though, that antibiotics aren’t recommended for people with acute bronchitis. Most cases of the condition are caused by viruses, and antibiotics don’t work on viruses, so the drugs wouldn’t help you.
What causes acute bronchitis?
Causes of acute bronchitis include viral and bacterial infections, environmental factors, and other lung conditions. Viral infection: Viruses cause 85 to 95 percent. Trusted Source. of acute bronchitis cases in adults. The same viruses that cause the common cold or flu can cause acute bronchitis.
Can bronchitis be caused by a viral infection?
Bacterial infection: In rare cases, bacterial bronchitis can develop after a viral infection of bronchitis. This can result from infections by bacteria such as Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydia pneumoniae, and Bordetella pertussis (which causes whooping cough ).
How to get rid of bronchitis?
Below are some ways you can feel better while your body fights off acute bronchitis: Get plenty of rest. Drink plenty of fluids. Use a clean humidifier or cool mist vaporizer. Use saline nasal spray or drops to relieve a stuffy nose. For young children, use a rubber suction bulb to clear mucus.
Can antibiotics help with bronchitis?
Transcript. txt icon. [TXT – 294 B] Acute bronchitis usually gets better on its own—without antibiotics. Antibiotics won’t help you get better if you have acute bronchitis. When antibiotics aren’t needed, they won’t help you, and their side effects could still cause harm.
Can antibiotics help with chest cold?
You could have a chest cold. Antibiotics will not help you get better if you have a chest cold (acute bronchitis). If you’re healthy without heart or lung problems or a weakened immune system, this information is for you.
How long does a chest cold last?
That’s what makes you cough. A chest cold, often called acute bronchitis, lasts less than 3 weeks and is the most common type of bronchitis.
Can you take cough and cold medicine at 4?
Cough and cold medicines: Children younger than 4 years old: do not use unless a doctor specifically tells you to. Use of over-the-counter cough and cold medicines in young children can result in serious and potentially life-threatening side effects.
Can you give a child over the counter cough medicine?
Use of over-the-counter cough and cold medicines in young children can result in serious and potentially life-threatening side effects. Children 4 years or older: discuss with your child’s doctor if over-the-counter cough and cold medicines are safe to give to your child for temporary symptom relief.
How old do you have to be to give a child cough medicine?
Children 4 years or older: discuss with your child’s doctor if over-the-counter cough and cold medicines are safe to give to your child for temporary symptom relief. Be sure to ask your doctor or pharmacist about the right dosage of over-the-counter medicines for your child’s age and size.
How do you know if you have bronchitis?
Symptoms. Most cases of bronchitis start out as a simple cold with a runny nose and sore throat. After several days, your symptoms may seem to move down into the chest. This shows up as: A persistent cough that produces mucus or sputum, which may be white, green or yellow.
What are the risks of getting bronchitis?
There are a few risk factors that can increase your chances of getting sick with bronchitis, including: Environmental factors . Air pollution, chemical fumes, pesticides, dust and smoke can all irritate the lungs and create a more hospitable environment for bacteria or viruses to cause infection.
How does bronchitis start?
Most cases of bronchitis start out as a simple cold with a runny nose and sore throat. After several days, your symptoms may seem to move down into the chest. This shows up as: A persistent cough that produces mucus or sputum, which may be white, green or yellow.
How long does it take for bronchitis to move down?
Most cases of bronchitis start out as a simple cold with a runny nose and sore throat. After several days, your symptoms may seem to move down into the chest. This shows up as:
What is the most common type of bronchitis?
Acute bronchitis is the most common type, and is “most often caused by a virus,” says Dr. Avraham Cooper, a pulmonologist with the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center. One study noted that about 5% of adults self report having had an episode of acute bronchitis each year.
What causes bronchitis?
Acute bronchitis can arise for a number of reasons, but by far the most common is a viral infection. A bacterial infection or exposure to inhaled irritants such as tobacco or wildfire smoke, dust, fumes and air pollution can also lead to bronchitis.
Can a child have bronchitis?
Because children are still building their immune systems, they may develop colds and subsequently bronchitis more frequently than adults, but some adults also frequently develop bronchitis, especially after having had a cold or the flu.
What is bronchitis?
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that connect your mouth and nose to your lungs. Viruses, like those that cause colds or the flu, are responsible for most cases of bronchitis. As your body fights the infection, the bronchial tubes become swollen and inflamed.
Symptoms of bronchitis
Bronchitis often starts with a dry cough and progresses to coughing that brings up thick mucus. Typical bronchitis symptoms include:
Causes of bronchitis
Viruses cause most cases of bronchitis. But several factors increase your risk for both acute and chronic bronchitis.
How long does bronchitis last?
If you have acute bronchitis, most of your symptoms should improve within a week. Coughing may hang on for several weeks. In most cases, you will be contagious for a few days and possibly as long as a week.
How to treat bronchitis
Most people recover from acute bronchitis on their own. See a health care provider if you:
Five things to do when Daylight Saving Time ends
This weekend, most of us will be savoring that extra hour of sleep as we turn back our clocks with the end of Daylight Saving Time. Besides a little more shut-eye now is a good time to do a few seasonal safety tasks throughout your home.
How long does bronchitis last?
The condition typically starts with common cold-like symptoms like sore throat and cough, and it can be either acute or chronic that usually affects just one part or both parts of the respiratory system. Acute bronchitis lasts up to three weeks, while chronic bronchitis lasts for months or more. With chronic bronchitis, symptoms might continue to come back or linger forever. In addition to that, bronchitis can also be developed into pneumonia when there’s excessive inflammation that blocks airflow through the lung tissue, preventing oxygen from reaching the bloodstream and resulting in fever and difficulty breathing. This article will help you understand the causes of bronchitis, symptoms, treatments for this condition, and how will a pulmonary doctor helps you.
Is bronchitis a chronic disease?
While acute bronchitis is typically a short-term condition that can be treated with antibiotics, chronic bronchitis is a long-term respiratory complication. Chronic means the symptoms are prolonged and persistent in nature rather than being temporary. It also usually involves two or more consecutive flare-ups of coughing spells at least three times per year for over one year.
What causes bronchitis in humans?
Bronchitis can be caused by bacterial infections (most often strep), viruses, environmental irritants such as smoke from fires, pollution or chemicals in paint fumes, etc., dander from animals with fur who sleep in beds with humans, allergies that cause an overactive response to otherwise harmless substances like pollen particles, fungi that live on food and sometimes within the body itself – not usually harmful but may trigger asthma-like reactions in susceptible people.
What is the most common symptom of bronchitis?
(Chronic bronchitis is a different subject altogether.) The most common symptoms of bronchitis include: Coughing with clear, yellow or green sputum (the gunk you cough up) Fatigue.
How do you know if you have bronchitis?
The most common symptoms of bronchitis include: Coughing with clear, yellow or green sputum (the gunk you cough up) Fatigue. Wheezing. Runny, stuffy nose occurring before chest congestion begins. Shortness of breath, usually following a coughing jag. Discomfort in the center of the chest due to cough. Mild fever.
What are the symptoms of pneumonia?
An inflammation of the lungs, pneumonia has many of the same symptoms as bronchitis, including: Persistent fever (often high) Cough, often with yellow or green mucus. Chills, which sometimes cause shaking. Shortness of breath. Sharp chest pain.
Is pneumonia the same as bronchitis?
Pneumonia. An inflammation of the lungs, pneumonia has many of the same symptoms as bronchitis, including: Though many of the signs may be similar, pneumonia is much more serious than acute bronchitis. It's more often caused by bacteria than by a virus, which means that antibiotics can be used to treat it.
Is bronchitis a respiratory disease?
Respiratory conditions like bron chitis and pneumonia symptoms are often hard to differentiate, but this guide can help. Bronchitis and pneumonia both affect the lungs and share some common symptoms, but they are different diseases that require different treatment. Here's how you can tell the difference.
How long does it take for bronchitis to go away?
Acute bronchitis will most often go away on its own within a week to 10 days, though your mucus-y cough will likely persist for several more weeks. "It's just a matter of the body cleaning up the mess," says pulmonologist Len Horovitz, M.D., of Lenox Hill Hospital in New York.
How to reduce the chances of bronchitis?
You can reduce your chances of getting acute bronchitis by practicing good hygiene. "That means handwashing, especially around kids with colds," says Boushey. "We love our grandchildren, but they do spread viruses. Get them to wash their hands frequently and to sneeze and cough into their elbows, not their hands.

Overview
Symptoms
- For either acute bronchitis or chronic bronchitis, signs and symptoms may include: 1. Cough 2. Production of mucus (sputum), which can be clear, white, yellowish-gray or green in color — rarely, it may be streaked with blood 3. Fatigue 4. Shortness of breath 5. Slight fever and chills 6. Chest discomfort If you have acute bronchitis, you might have...
Causes
- Acute bronchitis is usually caused by viruses, typically the same viruses that cause colds and flu (influenza). Antibiotics don't kill viruses, so this type of medication isn't useful in most cases of bronchitis. The most common cause of chronic bronchitis is cigarette smoking. Air pollution and dust or toxic gases in the environment or workplace also can contribute to the condition.
Risk Factors
- Factors that increase your risk of bronchitis include: 1. Cigarette smoke.People who smoke or who live with a smoker are at higher risk of both acute bronchitis and chronic bronchitis. 2. Low resistance.This may result from another acute illness, such as a cold, or from a chronic condition that compromises your immune system. Older adults, infants and young children have greater v…
Complications
- Although a single episode of bronchitis usually isn't cause for concern, it can lead to pneumonia in some people. Repeated bouts of bronchitis, however, may mean that you have chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Prevention
- To reduce your risk of bronchitis, follow these tips: 1. Avoid cigarette smoke.Cigarette smoke increases your risk of chronic bronchitis. 2. Get vaccinated.Many cases of acute bronchitis result from influenza, a virus. Getting a yearly flu vaccine can help protect you from getting the flu. You may also want to consider vaccination that protects against some types of pneumonia. 3. Wash …
Diagnosis
- During the first few days of illness, it can be difficult to distinguish the signs and symptoms of bronchitis from those of a common cold. During the physical exam, your doctor will use a stethoscope to listen closely to your lungs as you breathe. In some cases, your doctor may suggest the following tests: 1. Chest X-ray.A chest X-ray can help dete...
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- To help you feel better, you may want to try the following self-care measures: 1. Avoid lung irritants.Don't smoke. Wear a mask when the air is polluted or if you're exposed to irritants, such as paint or household cleaners with strong fumes. 2. Use a humidifier.Warm, moist air helps relieve coughs and loosens mucus in your airways. But be sure to clean the humidifier accordin…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- You're likely to start by seeing your family doctor or a general practitioner. If you have chronic bronchitis, you may be referred to a doctor who specializes in lung diseases (pulmonologist).