Medication
Lung Nodule Treatments Treatment for lung nodules may range from a “watchful waiting” approach for benign nodules, to surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy for malignant nodules. If the nodule is benign, your physician will monitor the nodule periodically with CT scans, to determine if any changes in size or shape have occurred.
Procedures
These can include: Positron emission tomography (PET) scan – A PET scan can help your doctor determine if a lung nodule is non-cancerous or... Biopsy – During a biopsy, your doctor removes a small amount of tissue from the nodule to examine closely under a... Other tests – …
Therapy
Small, noncancerous lung nodules don’t usually require treatment. You may need treatments, such as antibiotics or antifungal medications, if you have an infection. If the nodule grows, causes problems or is cancerous, you may need surgery.
Nutrition
Nov 29, 2021 · Additional treatments for cancerous lung nodules may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and other surgical interventions. Prevention Depending on the cause, it may not be possible to prevent...
Can lung nodules be cured, or only managed?
Minimally invasive thoracic surgery, thoracotomy, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy are commonly used to treat cancerous lung nodules. The surgeon may choose the appropriate treatment depending upon the type, stage, location of the nodule, and other factors, such as the patient’s physical condition.
What are lung nodules and do they go away?
If there is a higher chance that the nodule is cancer (or if the nodule can’t be reached with a needle or bronchoscope), surgery might be done to remove the nodule and some surrounding lung tissue. Sometimes larger parts of the lung might be removed as well.
How to get rid of lung nodules?
Treatment Benign (non-cancerous) lung nodules do not need treatment. Lung cancer, if localized, is usually removed surgically. If part of the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, you may need chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, alone or in various combinations. Lung Nodules Lung Nodules: Biopsy and Treatment
What is the prognosis for lung cancer without treatment?
Mar 12, 2022 · Usually, non-cancerous pulmonary nodules do not require treatment. If you have an infection or inflammation, you may need medications, such as: Antibiotics. Antifungals. Surgical treatment is required when the pulmonary nodule turns cancerous or causes troubles.
Can nodules in the lungs be treated?
How do doctors treat lung nodules?
A doctor may request a thoracotomy to remove a cancerous nodule. This surgical procedure involves removing the nodule through an incision in the chest wall. Additional treatments for cancerous lung nodules may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and other surgical interventions.
Should a lung nodule be removed?
How serious is a nodule on the lung?
Should I be worried about lung nodules?
Should I be worried about multiple lung nodules?
Can lung nodules go away with antibiotics?
How do they biopsy a lung nodule?
What kind of infections cause lung nodules?
- Bacterial infections, such as tuberculosis and pneumonia.
- Fungal infections, such as histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis or aspergillosis.
- Lung cysts and abscesses.
- Small collections of normal cells, called hamartoma.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Sarcoidosis.
How is a nodule removed from the lung?
In general, a lung nodule can be removed very safely and using a minimally invasive surgical approach. Your surgeon may want to perform a bronchoscopy to take a closer look at your nodules and take a biopsy. A biopsy involves removing a piece of your lung to look at it under a microscope.Oct 14, 2021
What causes nodules in lungs?
Can lung nodules shrink?
What Are Pulmonary Nodules?
A pulmonary nodule is a small round or oval-shaped growth in the lung. It may also be called a “spot on the lung” or a “coin lesion.” Pulmonary nod...
How Common Are Pulmonary Nodules?
Countless pulmonary nodules are discovered each year during chest X-rays or CT scans. Most nodules are noncancerous (benign). A solitary pulmonary...
What Causes Pulmonary Nodules?
There are two main types of pulmonary nodules: malignant (cancerous) and benign (noncancerous). Over 90% of pulmonary nodules that are smaller than...
What Are The Symptoms of Pulmonary Nodules?
Usually there are no symptoms associated with pulmonary nodules. If present, symptoms would be related to the condition that led to the nodule deve...
What is a lung nodule?
A lung nodule (or pulmonary nodule) is a small, round or oval-shaped growth in the lungs that is up to 3 centimeters in diameter. A lung nodule larger than 3 centimeters is called a lung mass. Lung nodules are common, mostly in those who smoke, and are typically benign (non-cancerous) but can also be malignant (cancerous).
Can a lung nodule be left alone?
Non-cancerous nodules grow slowly, if at all, while cancerous nodules grow quickly. If the nodule hasn’t grown or changed over a period of a few years, it can be left alone. If your lung nodule is large, determined to be cancerous or causing you to have symptoms, your doctor may recommend having it removed it surgically.
What is a spot on your lung?
The good news is that these “spots” are typically small, benign (non-cancerous) lung nodules. We’re here to diagnose, monitor and guide you through treatment.
What is a nodule in the lungs called?
A lung nodule (or pulmonary nodule) is a small, round or oval-shaped growth in the lungs that is up to 3 centimeters in diameter. A lung nodule larger than 3 centimeters is called a lung mass.
Can a lung nodule be malignant?
Lung nodules are common, mostly in those who smoke, and are typically benign (non-cancerous) but can also be malignant (cancerous). You may have a single lung nodule or several.
What causes granuloma in the lungs?
Infections: When your immune system acts against an infection, it will form a granuloma. Infections can be bacterial, fungal or parasitic.
What are the risk factors for lung cancer?
However, certain risk factors can increase the likelihood that a lung nodule is malignant. These can include: Being over the age of 50. A nodule larger than 3 centimeters. Smoking. Having a family history of lung cancer. Having symptoms of lung cancer. Growth or irregular borders. Having multiple nodules.
What to do if you have a pulmonary nodule?
You may need treatments, such as antibiotics or antifungal medications, if you have an infection. If the nodule grows, causes problems or is cancerous, you may need surgery. Surgical procedures to remove noncancerous and cancerous pulmonary nodules include:
What is a lung nodule?
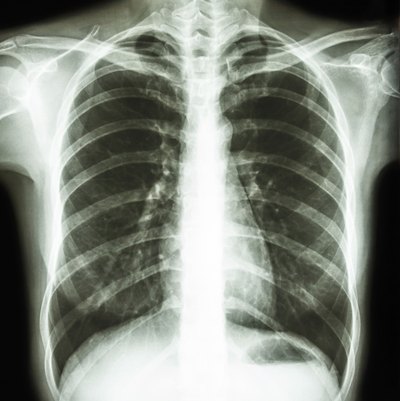
A lung (pulmonary) nodule is an abnormal growth that forms in a lung. You may have one nodule on the lung or several nodules. Nodules may develop in one lung or both. Most lung nodules are benign (not cancerous). Rarely, pulmonary nodules are a sign of lung cancer. Lung nodules show up on imaging scans like X-rays or CT scans.
Can a nodule be in one lung?
Nodules may develop in one lung or both. Most lung nodules are benign (not cancerous). Rarely, pulmonary nodules are a sign of lung cancer. Lung nodules show up on imaging scans like X-rays or CT scans. Your healthcare provider may refer to the growth as a spot on the lung, coin lesion or shadow.
Can lung nodules be cancerous?
Many people have lung nodules. These abnormal growths are rarely cancerous. Respiratory illnesses and infections can cause nodules to form in the lungs. Most lung nodules are not a sign of lung cancer and don’t require treatment.
What percentage of lung nodules are benign?
About 95% of lung nodules are benign. Many things can cause benign lung nodules, including infections and scarring. If you have a pulmonary nodule, your healthcare provider may want to perform additional tests to determine the cause and rule out lung cancer.
What is a granuloma in the lung?
When an infection or illness inflames lung tissue, a small clump of cells (granuloma) can form. Over time, a granuloma can calcify or harden in the lung, causing a noncancerous lung nodule. A neoplasm is an abnormal growth of cells in the lung. Neurofibromas are a type of noncancerous neoplasm.
What is CT scan for lung nodules?
CT scan-guided biopsy: For nodules on the outer part of the lung, your provider uses CT images to guide a thin needle through the skin and into the lung. This needle biopsy takes tissue samples from the nodule to examine for abnormal cells.
Can a lung nodule be cancer?
Although the diagnosis of any growth in the lung can be frightening, a lung nodule does not always indicate lung cancer. Lung nodules are very common. According to the American Thoracic Society, lung nodules are visible on up to 50% of chest CT scans in adults. Fewer than 5% of lung nodules end up being cancer.
What to do if nodule is low risk?
If the nodule has characteristics that suggest a low risk of cancer, the doctor may recommend watchful waiting. This approach involves monitoring the nodule with regular CT scans over time to identify any potentially malignant changes, such an increase in size.
What causes a granuloma in the lungs?
Noncancerous lung nodules can have a variety of causes, including: 1 Infection: Inflammation in the lungs might occur due to a range of infections, such as tuberculosis (TB) or fungal infections. A group of cells called a granuloma may develop around the inflamed area in the lung. Sometimes, nodules represent an area of scarring from a previous infection. 2 Noninfectious inflammation: Inflammation that does not occur due to an infection can also lead to nodules in the lung. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or sarcoidosis, for example, can contribute to noninfectious inflammation. 3 Noncancerous tumors: Other noncancerous growths may also develop in the lung. One example of this is a fibroma, which is a benign growth of connective tissue.
How to tell if a nodule is cancerous?
Symptoms of the condition that is causing the nodule may occur, however. For example, if a lung nodule is due to lung cancer, symptoms may include: 1 breathlessness 2 chest pain 3 coughing up blood 4 back pain 5 weight loss
Is a lung nodule benign or malignant?
Prevention and outlook. A lung nodule is a small growth on the lung and can be benign or malignant. The growth usually has to be smaller than 3 centimeters to qualify as a nodule. Benign nodules are noncancerous, typically not aggressive, and do not spread to other parts of the body. Malignant nodules are cancerous and can grow quickly.
What causes inflammation in the lungs?
Infection: Inflammation in the lungs might occur due to a range of infections, such as tuberculosis (TB) or fungal infections. A group of cells called a granuloma may develop around the inflamed area in the lung. Sometimes, nodules represent an area of scarring from a previous infection.
Can a lung nodule be seen on a CT scan?
When a person has symptoms of respiratory illness or infection, a doctor will usually request a chest X-ray or a CT scan. A lung nodule will often be visible on one of these scans. The nodule will show as a spot or shadow on the X-ray.
How to check for cancer in lungs?
If later scans show that the nodule has grown, or if the nodule has other concerning features, your doctor will want to get a sample of it to check it for cancer cells. This is called a biopsy. This can be done in different ways: 1 The doctor might pass a long, thin tube (called a bronchoscope) down your throat and into the airways of your lung to reach the nodule. A small tweezer on the end of the bronchoscope can be used to get a sample of the nodule. 2 If the nodule is in the outer part of the lung, the doctor might pass a thin, hollow needle through the skin of the chest wall (with the guidance of a CT scan) and into the nodule to get a sample. 3 If there is a higher chance that the nodule is cancer (or if the nodule can’t be reached with a needle or bronchoscope), surgery might be done to remove the nodule and some surrounding lung tissue. Sometimes larger parts of the lung might be removed as well.
What is the next step after a lung biopsy?
If cancer is found, then special tests will be done to find out what kind of cancer it is. If something other than cancer is found, the next step will depend on the diagnosis. Some nodules will be followed with a repeat CT scan in 6-12 months for a few years to make sure it does not change. If the lung nodule biopsy shows an infection, you might be sent to a specialist called an infectious disease doctor, for further testing. Your doctor will decide on the next step, depending on the results of the biopsy.
Can a CT scan show cancer?
Most lung nodules seen on CT scans are not cancer. They are more often the result of old infections, scar tissue, or other causes. But tests are often needed to be sure a nodule is not cancer.
Do you need surgery for a benign lung nodule?
Benign (non-cancerous) lung nodules do not need treatment. Lung cancer, if localized, is usually removed surgically. If part of the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, you may need chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, alone or in various combinations.
How to tell if a pulmonary nodule is cancerous?
If it is benign (not cancerous), your doctor will ask you to come back in the future to re-examine the spot with another X-ray. Your doctor will watch the nodule for any changes and catch it early if it becomes cancerous. If the nodule is cancerous, a few more samples ...
What is a bronchoscope?
The bronchoscope approach is an outpatient procedure without any cutting, sutures or sticking needles through the chest wall. After heavy sedation and numbing of mouth and throat, the bronchoscope is inserted into your airway and is guided to the lung nodule.
