One of the first steps that a water treatment facility can do is to just shake up the sewage and expose it to air. This causes some of the dissolved gases (such as hydrogen sulfide, which smells like rotten eggs) that taste and smell bad to be released from the water. Wastewater
Wastewater
Wastewater, also written as waste water, is any water that has been adversely affected in quality by anthropogenic influence. Wastewater can originate from a combination of domestic, industrial, commercial or agricultural activities, surface runoff or stormwater, and from sewer inf…
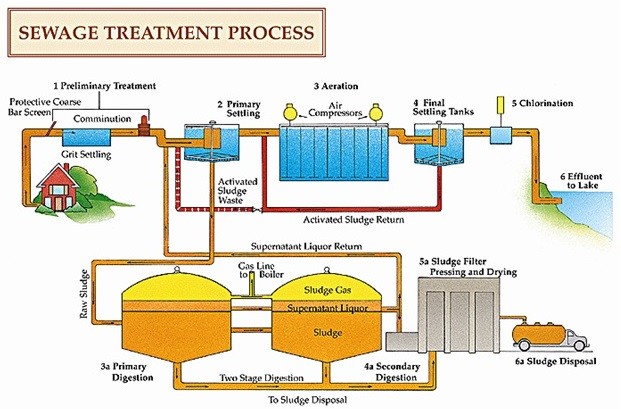
- Stage One — Bar Screening. ...
- Stage Two — Screening. ...
- Stage Three — Primary Clarifier. ...
- Stage Four — Aeration. ...
- Stage Five — Secondary Clarifier. ...
- Stage Six — Chlorination (Disinfection) ...
- Stage Seven — Water Analysis & Testing. ...
- Stage Eight — Effluent Disposal.
What are the three stages of wastewater treatment?
What are the main treatment steps in a water treatment plant to treat river water?
- Coagulation.
- Coagulation-Flocculation.
- Flocculation.
How to start reducing waste?
Reducing your waste is a practice that happens gradually. Start with one change at a time. Once you feel settled in that new habit, then maybe add one more. Resist the urge to throw out everything that doesn’t fit your reducing waste mindset.
How to reduce your water waste?
- Collect rainwater to water your gardens and even indoor houseplants!
- Don’t leave the water running. Brushing your teeth, washing your hands, washing dishes? ...
- Only wash dishes and laundry when you have a full load. Running them before that is just wasteful. ...
- Eat locally and seasonally. ...
- Eat more produce, in general. ...
What is the three step water treatment process?
What are the 7 stages of water filtration?
- ION EXCHANGE AND COAGULATION. This is the first step of water purification process. …
- SEDIMENTATION. …
- FILTRATION AND GRANULAR ACTIVATED CARBON. …
- DISINFECTION. …
- CARBON FILTERS. …
- REVERSE OSMOSIS. …
- STORE PURIFIED WATER.

What are the 3 steps to wastewater treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment. In some applications, more advanced treatment is required, known as quaternary water treatment.
Are there four steps in wastewater treatment?
Four common ways to treat wastewater include physical water treatment, biological water treatment, chemical treatment, and sludge treatment. Let us learn about these processes in detail.
What are the 4 steps of water treatment?
Water treatment stepsCoagulation. Coagulation is often the first step in water treatment. ... Flocculation. Flocculation follows the coagulation step. ... Sedimentation. Sedimentation is one of the steps water treatment plants use to separate out solids from the water. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection.
What are the 8 steps in the water treatment process?
These include: (1) Collection ; (2) Screening and Straining ; (3) Chemical Addition ; (4) Coagulation and Flocculation ; (5) Sedimentation and Clarification ; (6) Filtration ; (7) Disinfection ; (8) Storage ; (9) and finally Distribution.
What is the first step of the water treatment process?
The first step is coagulation, which involves adding chemicals to the water. That causes small particles to adhere to one another, or coagulate. The second step is called flocculation, in which larger particles called flocc form after coagulation.
What are the four main stages of waste water treatment GCSE?
Sewage TreatmentScreening & Grit Removal. The first stage of treatment removes large materials such as plastic bags and twigs and grit by screening.Sedimentation. Sedimentation comes next which occurs in a settlement tank. ... Aerobic Digestion. ... Anaerobic Digestion.
What are the 7 steps in wastewater treatment?
The Wastewater Treatment ProcessStage One — Bar Screening. ... Stage Two — Screening. ... Stage Three — Primary Clarifier. ... Stage Four — Aeration. ... Stage Five — Secondary Clarifier. ... Stage Six — Chlorination (Disinfection) ... Stage Seven — Water Analysis & Testing. ... Stage Eight — Effluent Disposal.
What are the 7 methods of water treatment?
Top 7 Methods of Water TreatmentCoagulation / Flocculation. Coagulation is adding liquid aluminum sulfate or alum and/or polymer to raw or untreated water. ... Sedimentation. When water and flocs undergo the treatment process, they go into sedimentation basins. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection. ... Sludge Drying. ... Fluoridation. ... pH Correction.
What are the 5 stages of sewage treatment?
Treatment StepsStep 1: Screening and Pumping. ... Step 2: Grit Removal. ... Step 3: Primary Settling. ... Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge. ... Step 5: Secondary Settling. ... Step 8: Oxygen Uptake. ... Sludge Treatment.
What are the 4 steps of water treatment PDF?
So, the groundwater required chemical treatment more than the physical one.Collection of Water. The water is collected from the sources like a lake, river, or reservoir. ... Screening. ... Sedimentation. ... Clarification or Sedimentation with Coagulation. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection. ... Water Softening. ... Other Treatment Methods.
Importance of Wastewater Treatment Process
Wastewater contains a large number of toxins that might harm the environment; thus, treatment is essential.
Stages of Wastewater Treatment Process
Unit Operation: It is a process in which wastewater treated by Physical Method
Flow Diagram for Wastewater Treatment Process
Note: – All treatment plants have different equipment depending upon what they want to achieve or other several factors.
What is the first stage of wastewater treatment?
The first mechanical stage is called preliminary treatment or rather pre-treatment. Water flows through gravel chamber for settling out the grit from water. Afterwards, gravel is disposed of at the dump. Water further reaches the bar screens used to remove large objects from the wastewater.
How is wastewater drained to the WWTP?
1. Firstly, wastewater is drained to the WWTP by gravity through the main sewer system of the size of a car. Having such size, objects you could hardly imagine reach the WWTPs, ranging from mattresses, fridges, tree branches to wallets disposed of by thieves in order to get rid of the evidence. 2.
How long does it take for sludge to dry out?
9. Sludge, digested and dewatered to the optimal degree, is finally disposed of at the dump. In about a month, sludge is adequately dried out and ripe. If it complies with agricultural standards, it can be reused for fertilisation of industrial crops.
What is wastewater water?
Wastewater can be divided into two major groups: Sewage water is all wastewater used in domestic dwellings (e. g. originating from toilets, showers or sinks). Industrial wastewater originates from production, industrial and commercial activities, and has a different chemical composition to sewage water.
What is wastewater in agriculture?
What is wastewater? It is used water originating from domestic, industrial, agricultural, and medical or transport activities. Used water becomes wastewater upon the change of its quality, composition and/or temperature. However, wastewater does not include water released from ponds or reservoirs for fish farming.
What is the purpose of bar screens in wastewater treatment?
Water further reaches the bar screens used to remove large objects from the wastewater. At first come the coarse screens and then the fine screens which remove smaller objects such as matches, cigarette butts or undigested foods. 3. After the removal of large objects, grit is to be removed from the wastewater.
What is secondary treatment?
The secondary treatment, also called biological stage, is based on natural processes. WWTPs use bacteria which consume the contaminants, in particular biodegradable organics, carbon and phosphorus. Dead bacteria and organic residues subsequently transform into sludge. 6.
What is wastewater treatment?
Wastewater treatment is a process to treat sewage or wastewater to remove suspended solid contaminants and convert it into an effluent that can be discharged back to the environment with acceptable impact. The plants where the wastewater treatment process takes place are popularly known as Wastewater treatment plants, ...
What is a sewage treatment plant?
Sewage treatment plants eliminate contaminants from wastewater and household sewage. It uses physical, chemical, and biological processes to remove physical, chemical and biological contaminants to make the water and solid waste reusable. Combined Effluent Treatment Plants are established where a cluster of small scale industries are present.
How is suspended solid removed from wastewater?
Suspended solid materials from the wastewater are removed by the sedimentation primary treatment. Other floatable materials like oils, fats, etc are removed using dissolved air floatation treatment. Primary wastewater treatment, in general, removes about 60% of suspended solids from wastewater.
Why is industrial wastewater considered domestic wastewater?
Industrial wastewater results because of chemical and manufacturing industry discharges. So, wastewater is essentially the used water that has been affected by domestic, commercial, or industrial use. Domestic wastewater is relatively easy to treat as compared to industrial wastewater due to its high-strength nature.
Why is domestic wastewater generated?
Domestic wastewater is generated because of activities like bathing, washing, using the toilet, etc in residences, restaurants, and businesses. Surface rainwater runoff is generated due to the mixing of debris, grit, nutrients, and various chemicals. Industrial wastewater results because of chemical and manufacturing industry discharges.
Why is wastewater treatment important?
So, Wastewater treatment plants plays a major role in keeping environment clean and saving numerous lives.
What are the pollutants that are normally present in wastewater?
Typical pollutants that are normally present in wastewater are: Bacteria, viruses, and disease-causing pathogens. helminths (intestinal worms and worm-like parasites) Toxic Chlorine compounds and inorganic chloramines.
Stage Two — Screening
- Removal of grit by flowing the influent over/through a grit chamber. Fine grit that finds its way into the influent needs to be removed to prevent the damage of pumps and equipment downstream (or impact water flow). Too small to be screened out, this grit needs to be removed from the grit …
Stage Three — Primary Clarifier
- Initial separation of solid organic matter from wastewater. Solids known as organics/sludge sink to the bottom of the tank and are pumped to a sludge digestor or sludge processing area, dried and hauled away. Proper settling rates are a key indicator for how well the clarifier is operating. Adjusting flow rate into the clarifier can help the operator adjust the settling rates and efficiency…
Stage Four — Aeration
- Air is pumped into the aeration tank/basin to encourage conversion of NH3 to NO3 and provide oxygen for bacteria to continue to propagate and grow. Once converted to NO3, the bacteria remove/strip oxygen molecules from the nitrate molecules and the nitrogen (N) is given off as N2↑ (nitrogen gas). At the heart of the wastewater treatment process is the encouragement and …
Stage Five — Secondary Clarifier
- Treated wastewater is pumped into a secondary clarifier to allow any remaining organic sediment to settle out of treated water flow. As the influent exits the aeration process, it flows into a secondary clarifier where, like the primary clarifier, any very small solids (or fines) sink to the bottom of the tank. These small solids are called activated sludge and consist mostly of active …
Stage Six — Chlorination
- Chlorine is added to kill any remaining bacteria in the contact chamber. With the enhanced concentration of bacteria as part of the aeration stage, there is a need to test the outgoing effluent for bacteria presence or absence and to disinfect the water. This ensures that higher than specified concentrations of bacteria are not released into the environment. Chlorinationis the m…
Stage Seven — Water Analysis & Testing
- Testing for proper pH level, ammonia, nitrates, phosphates, dissolved oxygen, and residual chlorine levels to conform to the plant’s NPDES permit are critical to the plant’s performance. Although testingis continuous throughout the wastewater treatment process to ensure optimal water flow, clarification and aeration, final testing is done to make sure the effluent leaving the p…
Stage Eight — Effluent Disposal
- After meeting all permit specifications, clean water is reintroduced into the environment. Although testingis continuous throughout the wastewater treatment process to ensure optimal water flow, clarification and aeration, final testing is done to make sure the effluent leaving the plant meets permit specifications. Plants that don`t meet permit discharge levels are subject to fines and po…
Understanding The Waste Treatment Process
- Thoroughly treating and reclaiming water from wastewater is vital to preventing the spread of diseases and other environmental hazards. Wastewater is any water that was used within homes or businesses for: 1. Bathing 2. Washing dishes 3. Flushing toilets 4. Storm sewers Wastewater treatment is the process of removing pollutants from disposed water ...
Waste Treatment Facility Limitations
- The sanitation industry continues to deal with the ever-growing amount of human waste. Economic expansion and urbanization have increased the need for more wastewater-related operations. Waste facilities have imposed greater restrictions and guidelineson which chemicals can be used in the portable restroom industry. This is an attempt to simplify the treatment proce…
Septic Truck Disposal Process Required Permits
- All PROs and Waste Disposal Technicians need to use septic tanks to transport and properly dispose of wastewater. Updated permits are required in any professionals working in the following fields. 1. Cesspools 2. Grease traps 3. Pumping septic tanks 4. Holding tanks 5. Stocking or cleaning toilets It’s also worth noting that vacuum truck operators, portable restroo…
The Future of Waste Management
- To effectively remove harmful pollutants from our wastewater, waste treatment facilities continue to evolve their process. We know it’s stressful to worry about the increasing cost of some chemicals and deodorizers. However, it’s equally stressful to pay fines for using non-eco-friendly/EPA-approved products. It’s a good idea to reduce waste disposal expenses by utilizing …