Stages 1, 2, and 3
- lumpectomy or mastectomy and removal of nearby lymph nodes to check for cancer
- breast reconstruction immediately or at a later date
- radiation therapy, especially if you chose lumpectomy over mastectomy
- chemotherapy
- hormone therapy for estrogen receptor-positive and progesterone receptor-positive breast cancers
Full Answer
How do you treat Stage 1 breast cancer?
Treatments
- Radiation therapy. It’s usually given after a lumpectomy. ...
- Chemotherapy. The drugs attack cancer cells. ...
- Hormone therapy. Medication can help prevent tumors from getting hormones. ...
- Targeted therapy. About 20% of women with breast cancer have too much of a protein known as HER2 that sometimes makes the cancer spread quickly.
- Clinical trials. ...
What is the life expectancy of someone with breast cancer?
While there is a significant degree of variability, according to one study, long-term survivors are:
- More likely to be younger (this is in contrast to early-stage breast cancer in which the survival rate is lower for younger people with the disease)
- More likely to have estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and/or HER2-positive tumors
- Less likely to have other medical conditions (co-morbidities)
How soon after diagnosis should breast cancer treatment begin?
Your physician may recommend receiving treatment within a month or two of the diagnosis. Before receiving treatment, though, there may be additional tests or consultations that are necessary. Some considerations before scheduling your breast cancer treatment
How should we treat Stage 0 breast cancer?
- Lumpectomy: For small, localized areas of DCIS to prevent recurrence in the same breast.
- Total mastectomy: In patients with large areas of DCIS or invasive DCIS to stop the spread of cancer to other parts of the body.
- Radiation or hormonal therapy after surgery: Radiation therapy decreases the risk of recurrence by 50 percent. ...
What is the order of treatment for breast cancer?
Usually surgery is first. For some women, surgery to remove the breast cancer and surgery to reconstruct the breast happen during the same operation. If chemotherapy is going to be part of your care, it is often given second. Radiation therapy usually follows surgery and chemotherapy (when chemotherapy is given).
What stages of breast cancer are treatable?
Most women with breast cancer in stages I, II, or III are treated with surgery, often followed by radiation therapy. Many women also get some kind of systemic drug therapy (medicine that travels to almost all areas of the body). In general, the more the breast cancer has spread, the more treatment you will likely need.
How long does breast cancer treatment take?
Each treatment session is followed by a period of recovery. Typically, if you have early-stage breast cancer, you'll undergo chemotherapy treatments for three to six months, but your doctor will adjust the timing to your circumstances. If you have advanced breast cancer, treatment may continue beyond six months.
What is the most common treatment for breast cancer?
The most common form of treatment for breast cancer is surgery. This involves removing the tumor and nearby margins. Surgical options may include a lumpectomy, partial mastectomy, radical mastectomy, and reconstruction.
Can breast cancer be cured at Stage 3?
Because stage 3 breast cancer has spread outside the breast, it can be harder to treat than earlier stage breast cancer, though that depends on a few factors. With aggressive treatment, stage 3 breast cancer is curable; however, the risk that the cancer will grow back after treatment is high.
At what stage should you have a mastectomy?
Your doctor may recommend a mastectomy instead of a lumpectomy plus radiation if: You have two or more tumors in separate areas of the breast. You have widespread or malignant-appearing calcium deposits (microcalcifications) throughout the breast that have been determined to be cancer after a breast biopsy.
How soon should you have surgery after breast cancer diagnosis?
Waiting between 31 and 90 days to first treatment after diagnosis with breast cancer may be beneficial for doctors and patients who want a more extensive diagnostic plan and additional time to make decisions, according to the results of a new study.
How soon should chemo start after diagnosis?
Cancer treatment should start very soon after diagnosis, but for most cancers, it won't hurt to wait a few weeks to begin treatment. This gives the person with cancer time to talk about all their treatment options with the cancer care team, family, and friends, and then decide what's best for them.
Does a biopsy tell you what stage cancer is?
The biopsy results help your health care provider determine whether the cells are cancerous. If the cells are cancerous, the results can tell your care provider where the cancer originated — the type of cancer. A biopsy also helps your care provider determine how aggressive your cancer is — the cancer's grade.
How soon after breast cancer diagnosis does chemo start?
The NICE guideline on early and locally advanced breast cancer recommends: “Start adjuvant chemotherapy or radiotherapy as soon as clinically possible within 31 days of completion of surgery in patients with early breast cancer having these treatments”. This is in line with the findings of the study.
What are the 5 different types of treatments for breast cancer?
How Is Breast Cancer Treated?Surgery. An operation where doctors cut out cancer tissue.Chemotherapy. Using special medicines to shrink or kill the cancer cells. ... Hormonal therapy. Blocks cancer cells from getting the hormones they need to grow.Biological therapy. ... Radiation therapy.
What is the easiest breast cancer to treat?
Ductal carcinoma in situ or DCIS The cancer cells have not spread through the walls of the ducts into the nearby breast tissue. Nearly all women with DCIS can be cured.
What is stage 0 breast cancer?
At stage 0, the breast mass is noninvasive. At this stage, there is no indication that the tumor cells have spread to other parts of the breast or...
What is stage I (stage 1) breast cancer?
This breast cancer is the earliest stage of invasive breast cancer. In stage I, the tumor measures up to 2 cm and no lymph nodes are involved. At t...
What is stage II (stage 2) breast cancer?
Also known as invasive breast cancer, the tumor in this stage measures between 2 cm to 5 cm, or the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the...
What is stage III (stage 3) breast cancer?
Also known as locally advanced breast cancer, the tumor in this stage of breast cancer is more than 2 inches in diameter across and the cancer is e...
What is stage IV (stage 4) breast cancer?
Also known as metastatic breast cancer, the cancer in this stage has spread beyond the breast, underarm and internal mammary lymph nodes to other p...
What are the stages of breast cancer?
Most women with breast cancer in stages I to III will get some kind of drug therapy as part of their treatment. This may include: 1 Chemotherapy 2 Hormone therapy (tamoxifen, an aromatase inhibitor, or one followed by the other) 3 HER2 targeted drugs, such as trastuzumab (Herceptin) and pertuzumab (Perjeta) 4 Some combination of these
What is the treatment for stage 1 breast cancer?
Local therapy (surgery and radiation therapy) Surgery is the main treatment for stage I breast cancer. These cancers can be treated with either breast-conserving surgery (BCS; sometimes called lumpectomy or partial mastectomy) or mastectomy.
What is the treatment for BCS?
Women who have BCS are treated with radiation therapy after surgery. Women who have a mastectomy are typically treated with radiation if the cancer is found in the lymph nodes.
How big is a stage 3 breast tumor?
In stage III breast cancer, the tumor is large (more than 5 cm or about 2 inches across) or growing into nearby tissues (the skin over the breast or the muscle underneath), or the cancer has spread to many nearby lymph nodes.
Can you get radiation therapy before mastectomy?
If you were initially diagnosed with stage II breast cancer and were given treatment such as chemotherapy or hormone therapy before surgery, radiation therapy might be recommended if cancer is found in the lymph nodes at the time of the mastectomy.
Can you get a mastectomy with a large breast?
For women with fairly large breasts, BCS may be an option if the cancer hasn’t grown into nearby tissues. SLNB may be an option for some patients, but most will need an ALND.
Can breast reconstruction be done at the same time as breast surgery?
In some cases, breast reconstruction can be done at the same time as the surgery to remove the cancer.
How many stages of breast cancer are there?
Ultimately, your specific combination of TNM and these other markers will determine your cancer’s stage. Breast cancer has five general stages under the TNM system: 0 through 4.
What is the earliest stage of breast cancer?
Also called carcinoma in situ, stage 0 is the earliest breast cancer stage. At stage 0, the breast mass is noninvasive, and there is no indication that the tumor cells have spread to other parts of the breast or other parts of the body.
What does the R mean in breast cancer?
These markers, along with the TNM measurements, define your stage. A cancer recurrence refers to cancer that returns in the same breast, and it requires new staging. This new stage is marked by an “R” at the end to indicate “restaging.”. If it develops in the other breast, it’s considered a new cancer.
How big is a stage 2B breast tumor?
Stage 2B: One of the following is true: The tumor measures 2 cm to 5 cm and cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes, or. The tumor is larger than 5 cm but cancer has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes. The survival rate for stage 2A breast cancer may be slightly higher than for stage 2B.
How is breast cancer classified?
Your cancer will always retain that label, regardless of its progress. Breast cancer staging is classified by: The size and location of the tumor. Whether the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes or other parts of the body. The grade of the tumor—or how likely it is to grow and spread.
What are the different types of breast cancer?
There are three types of recurrent breast cancer: Local recurrence is when the cancer has returned to the same location as the original cancer. Regional recurrence is when the cancer has been found in or near the original location.
How long does it take for breast cancer to recur?
Most recurrent cancers appear within the first two or three years after treatment, but, in some cases, the cancer may recur many years later . According to the Susan G. Komen ® organization, women with early breast cancer most often develop local recurrence within the first five years after treatment. On average, 7 percent to 11 percent of women with early breast cancer experience a local recurrence during this time.
What is the earliest stage of breast cancer?
Doctors also use a cancer's stage when talking about survival statistics. The earliest stage breast cancers are stage 0 (carcinoma in situ). It then ranges from stage I (1) through IV (4). As a rule, the lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. A higher number, such as stage IV, means cancer has spread more.
How is lymph node staging based on breast cancer?
Lymph node staging for breast cancer is based on how the nodes look under the microscope, and has changed as technology has improved. Newer methods have made it possible to find smaller and smaller collections of cancer cells, but experts haven't been sure how much these tiny deposits of cancer cells affect outlook.
How far does cancer spread in the lymph nodes?
The areas of cancer spread in the lymph nodes are at least 0.2mm across, but not larger than 2mm. N1a: Cancer has spread to 1 to 3 lymph nodes under the arm with at least one area of cancer spread greater than 2 mm across.
Where does cancer spread?
Cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the collarbone (infraclavicular nodes), with at least one area of cancer spread greater than 2 mm. N3b: either: Cancer is found in at least one axillary lymph node (with at least one area of cancer spread greater than 2 mm) and has enlarged the internal mammary lymph nodes, OR.
How many cells are needed to change the N stage?
This is still being studied, but for now, a deposit of cancer cells must contain at least 200 cells or be at least 0.2 mm across (less than 1/100 of an inch) for it to change the N stage.
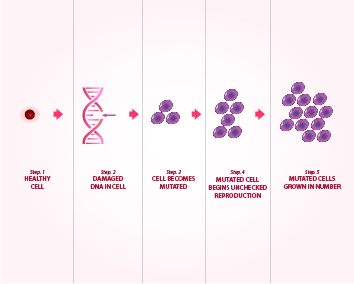
What is the process of determining how far a cancer has spread?
After someone is diagnosed with breast cancer, doctors will try to figure out if it has spread, and if so, how far. This process is called staging. The stage of a cancer describes how much cancer is in the body. It helps determine how serious the cancer is and how best to treat it. Doctors also use a cancer's stage when talking about survival statistics.
Can you describe every combination of breast cancer?
Because there are so many factors that go into stage grouping for breast cancer, it's not possible to describe here every combination that might be included in each stage. The many different possible combinations mean that two women who have the same stage of breast cancer might have different factors that make up their stage.
What is stage IV breast cancer?
By stage IV breast cancer, also called metastatic breast cancer, the cancer has spread to other areas of the body. The cancer staging system continues to evolve and is becoming more complex as doctors improve cancer diagnosis and treatment.
Why is it important to classify breast cancer?
Classifying your breast cancer by stage helps predict your chance of cure and helps identify the best treatment options for your particular cancer. After discovering that you have breast cancer, your doctor will decide what additional tests may be helpful to find out if the disease has spread outside the breast.
What tests are used to check for breast cancer?
Breast-imaging tests. Mammogram, ultrasound and breast MRI give your doctor more information about your cancer and help determine if additional imaging tests may be necessary. Additional imaging tests. Additional imaging can be used to look for breast cancer cells that have spread to other areas of your body.
Where does stage IV breast cancer go?
When breast cancer spreads, it most commonly goes to the bones, liver, and lungs. It may also spread to the brain or other organs.
What is the immunotherapy for triple negative breast cancer?
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) The immunotherapy dug atezolizumab (Tecentriq) can be used along with albumin-bound paclitaxel (Abraxane) in people with advanced triple-negative breast cancer whose tumor makes the PD-L1 protein. (The PD-L1 protein is found is about 20% of triple-negative breast cancers.)
What hormones are used for cancer?
For hormone receptor-positive (ER-positive or PR-positive) cancers that were being treated with hormone therapy, switching to another type of hormone therapy sometimes helps. For example, if either letrozole (Femara) or anastrozole (Arimidex) were given, using exemestane, possibly with everolimus (Afinitor), may be an option. Another option might be using fulvestrant (Faslodex) or an aromatase inhibitor (such as letrozole), along with a CDK inhibitor. If the cancer has a PIK3CA mutation and has grown while on an aromatase inhibitor, fulvestrant with alpelisib might be considered. If the cancer is no longer responding to any hormone drugs, chemotherapy is usually the next step.
What is the treatment for HER2 negative cancer?
HER2-negative cancers in women with a BRCA gene mutation. These women are typically treated with chemotherapy (and hormone therapy, if the cancer is hormone receptor-positive). An option after getting chemo is treatment with a targeted drug called a PARP inhibitor, such as olaparib or talazoparib.
What is the treatment for estrogen receptor positive cancer?
Women with hormone receptor-positive (estrogen receptor-positive or progesterone receptor-positive) cancers are often treated first with hormone therapy (tamoxifen or an aromatase inhibitor). This may be combined with a targeted drug such as a CDK4/6 inhibitor, everolimus or a PI3K inhibitor.
What is the best treatment for bone metastases?
Treatment to relieve symptoms depends on where the cancer has spread. For example, pain from bone metastases may be treated with radiation therapy, drugs called bisphosphonates such as pamidronate (Aredia) or zoledronic acid (Zometa), or the drug denosumab (Xgeva).
What is radiation therapy?
Radiation therapy and/or surgery may also be used in certain situations, such as: When the breast tumor is causing an open wound in the breast (or chest) To treat a small number of metastases in a certain area, such as the brain. To help prevent bone fractures. When an area of cancer spread is pressing on the spinal cord.
What is the treatment for stage IV breast cancer?
Systemic (drug) therapy is the main treatment for stage IV breast cancer in men. Depending on many factors, this may be hormone therapy , chemo , targeted therapy, immunotherapy, or some combination of these treatments. Radiation therapy and/or surgery may also be used in certain situations, such as:
How do I get rid of stage 1 breast cancer?
The main treatment for stage I breast cancer is to remove it with surgery. This is usually done by mastectomy, but breast-conserving surgery (BCS) might occasionally be an option. If breast-conserving surgery is done, it is usually followed by radiation therapy.
What is the name of the biopsy done on lymph nodes?
The lymph nodes under the arm will be checked for cancer spread, either with an axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) or sentinel node biopsy (SLNB). If the sentinel lymph node contains cancer, a full ALND may be needed, depending on the size of the cancer in the lymph node as well as what other treatment is planned.
What happens if cancer cells have HER2?
If the cancer cells contain hormone receptors (that is, if the cancer is ER-positive or PR-positive) If the cancer cells have large amounts of the HER2 protein (that is, if the cancer is HER2-positive) Your overall health and personal preferences. How fast the cancer is growing (measured by grade or other measures)
What is radiation therapy?
Radiation therapy and/or surgery may also be used in certain situations, such as: When the breast tumor is causing an open wound in the breast (or chest) To treat a small number of metastases in a certain area, such as the brain. To help prevent bone fractures.
How is DCIS treated?
It is treated with surgery to remove the cancer. Most often in males, a mastectomy is done. If breast-conserving surgery is done, it is followed by radiation therapy to the remaining breast tissue. Sometimes DCIS can contain an area of invasive cancer.
How to treat breast cancer with radiation?
Radiation therapy and/or surgery may also be used in certain situations, such as: 1 When the breast tumor is causing an open wound in the breast (or chest) 2 To treat a small number of metastases in a certain area, such as the brain 3 To help prevent bone fractures 4 When an area of cancer spread is pressing on the spinal cord 5 To treat a blood vessel blockage in the liver 6 To relieve pain or other symptoms