
Heat therapy is recommended for lesions caused by any species of Leishmania, and the main side effects are pain, itching, burning sensation, and even second-degree burns 2, 9, 10.
What are the treatment options for cutaneous leishmaniasis?
CUTANEOUS LEISHMANIASIS Clinical approach - Uncomplicated versus complicated infection - Whom to treat - Assessing risk for mucosal disease Overview of therapeutic approaches - Local therapy - Oral systemic therapy - Parenteral systemic therapy Specific therapeutic agents - Local therapy Cryotherapy Thermotherapy Intralesional pentavalent antimony
What are the health risks of leishmaniasis?
Another potential concern applies to some (not all) types of the parasite found in parts of Latin America: certain types might spread from the skin and cause sores in the mucous membranes of the nose (most common location), mouth, or throat ( mucosal leishmaniasis ).
Is cutaneous leishmaniasis a zoonosis?
Cutaneous leishmaniasis. This disease is considered to be a zoonosis (an infectious disease that is naturally transmissible from vertebrate animals to humans), with the exception of Leishmania tropica — which is often an anthroponotic disease (an infectious disease that is naturally transmissible from humans to vertebrate animals).
What is the prognosis of mucosal leishmaniasis?
Mucosal leishmaniasis might not be noticed until years after the original sores healed. Ensuring adequate treatment of the cutaneous infection may help prevent mucosal leishmaniasis. If not treated, severe (advanced) cases of visceral leishmaniasis typically are fatal.
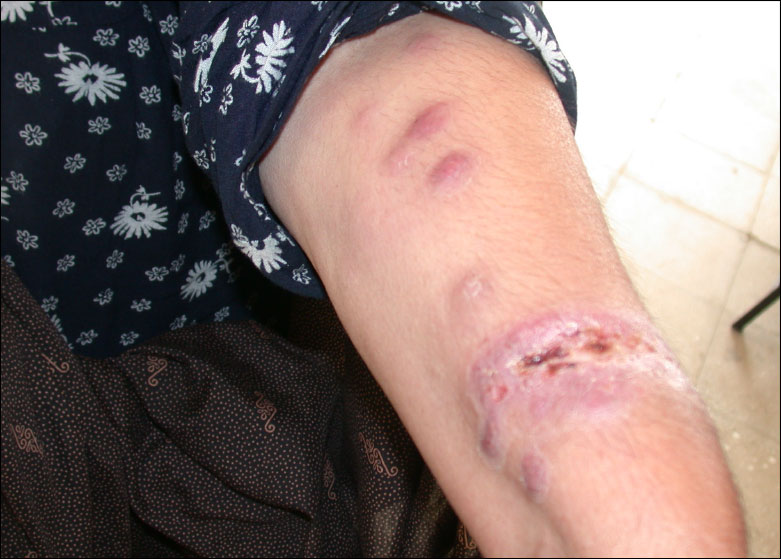
What are the long term effects of leishmaniasis?
In India, post-kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis develops several years after treatment for visceral leishmaniasis. Individuals often develop multiple, flat discolored areas of skin (macules). Eventually, these lesions turn into plaques or nodules on the face and trunk. In India, this form requires intensive treatment.
What is the treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis?
For pentavalent antimonial (SbV) therapy, the standard daily dose is 20 mg of SbV per kg, administered IV or IM. The traditional duration of therapy is 20 days for cutaneous leishmaniasis (10 days may suffice in some settings) and 28 days for mucosal (and visceral) leishmaniasis.
What are the complications of leishmaniasis?
What are the complications of leishmaniasis?Secondary bacterial infection, including pneumonia and tuberculosis.Septicemia.Disfigurement of nose, lips, and palate (eg, cancrum oris)Uncontrolled bleeding.Splenic rupture.Late stages: Edema, cachexia, and hyperpigmentation.More items...•
Can leishmaniasis come back after treatment?
After 20 days of treatment with pentavalent antimonials, there is usually evidence of healing, but lesions may not be re-epithelialized completely. They generally go on to heal. Healing is determined by a healed appearance at two months, no relapse at 12 months, and no subsequent mucosal disease.
How long does cutaneous leishmaniasis last?
major or L. tropica heal. The disease is self-curing in 2-8 months for L. major lesions and 1 year or much longer for L tropica.
Is cutaneous leishmaniasis painful?
The sores typically progress from small bumps to open lesions with a raised border and central crater – or ulcer – which can be covered with scabs. The lesions usually are painless but can be painful, particularly if open sores become infected with bacteria.
Can cutaneous leishmaniasis turn into visceral?
Leishmania can also cause skin and mucosal lesions and/or visceral signs in animals. Most species of Leishmania are maintained in wildlife, often without clinical signs, but dogs are an important reservoir host for L.
What are the symptoms and signs of cutaneous leishmaniasis?
Symptoms of cutaneous leishmaniasis depend on where the lesions are located and may include:Breathing difficulty.Skin sores, which may become a skin ulcer that heals very slowly.Stuffy nose, runny nose, and nosebleeds.Swallowing difficulty.More items...•
What is the drug of choice for treatment of leishmaniasis?
Sodium stibogluconate (Pentostam) Sodium stibogluconate has been the drug of choice for the treatment of cutaneous and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis in the United States. This agent is also effective against visceral leishmaniasis and is often the first-line treatment outside the United States.
Does leishmaniasis go away?
The skin sores of cutaneous leishmaniasis usually heal on their own, even without treatment. But this can take months or even years, and the sores can leave ugly scars.
Is cutaneous leishmaniasis fatal?
It usually occurs two to eight months after being bitten by a sand fly. It damages internal organs, such as your spleen and liver. It also affects your bone marrow, as well as your immune system through damage to these organs. The condition is almost always fatal if it's not treated.
Is cutaneous leishmaniasis itchy?
Once an individual is infected with cutaneous leishmaniasis, it is unlikely that he or she will be re-infected by the same species. Clinical Manifestations: Begins as a red papule that later becomes itchy. Develops to o ne or more skin ulcers on exposed parts of the body, mostly the face, arms and legs.
What is the drug of choice for treatment of leishmaniasis?
Sodium stibogluconate (Pentostam) Sodium stibogluconate has been the drug of choice for the treatment of cutaneous and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis in the United States. This agent is also effective against visceral leishmaniasis and is often the first-line treatment outside the United States.
What is the treatment for leishmaniasis in dogs?
However, most dogs will require medication and this is likely to be a combination of two drugs (allopurinol and miltefosine or allopurinol and meglumine antimoniate). Allopurinol in most cases will be continued for a few months until the signs have resolved and blood tests have all returned to normal.
What is used in treatment of kala-azar?
The aim of treatment in kala-azar is killing of the parasite with effective drugs which are cheap and less toxic. Pentavalent antimonials are the first line drugs and pentamidine and amphotericin B are the second line drugs. Recently the latter are being used as first line drugs also [12].
What are Antimonial drugs?
Antimonials, in pre-modern medicine, were remedies principally containing antimony, used chiefly for emetic purposes. They might also have qualified for cathartic, diaphoretic, or simply alternative uses. Such treatments were considered unparalleled in their strength.
How many cases of cutaneous leishmaniasis are there in the world?
According to estimates, there are up to 1.2 million cases of cutaneous leishmaniasis and 400,000 cases of visceral leishmaniasis around the world.
How do you know if you have leishmaniasis?
These may include: Some cases will see the development of ulcers and a wearing away in the mouth, tongue, gums, lips, nose, and inner nose.
What are the factors that contribute to the progression of leishmaniasis?
One of the main factors for the progression of leishmaniasis to visceral leishmaniasis is the lack of nutrition: A diet that lacks protein, vitamin A, zinc, and iron increases a person’s risk, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
What are the symptoms of systemic visceral leishmaniasis?
Symptoms of systemic visceral leishmaniasis may also include: Discomfort in the abdomen. Persistent fever.
Can a phlebotomine sandfly be infected?
Humans can be infected by the condition through the bite of an infected female phlebotomine sandfly, a tiny insect vector. There are no predisposing factors for leishmaniasis. However, traveling to an area where the condition is found may increase the risk of transmission.
What were the searches and review process for leishmaniasis?
The searches and review process were performed according to a pre-established protocol restricted to the cutaneous form of leishmaniasis in the New World. Intervention studies, case series and case reports, in which patients were treated with the recommended drugs and clinical, laboratory or electrocardiographic adverse effects were recorded, were included. In the case of experimental drug studies in which the control group received the approved drugs, only this group was evaluated. Studies using miltefosine were included since this drug is currently under evaluation for the treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis in the New World. There were no restrictions in terms of patient age or language of the published articles.
What is the parasitic disease caused by sandflies?
Leishmaniases are parasitic diseases caused by different protozoan species of the genus Leishmania, including those of the subgenus Leishmania, which display dermotropism or viscerotropism in the Old World (Southern Europe, the Middle East, Asia, and Africa) and New World (Latin America), and of the subgenus Viannia, which are exclusively dermotropic (New World). The parasites are transmitted by the bite of different sandfly species ( Marzochi and Marzochi, 1994 ). Leishmaniases caused by dermotropic species are endemic in 82 countries, with an incidence of approximately 1.5 million cases per year. About 90% of cutaneous leishmaniasis cases are concentrated in Brazil and six other developing countries ( WHO, 2007 ). American tegumentary leishmaniasis, a term comprising cutaneous forms with a potential to evolve to secondary mucosal forms, is mainly caused by Leishmania ( Viannia) braziliensis and is endemic in various regions of the Americas ( Lainson, 1983, Jones et al., 1987, Brasil, 2010 ).
What is the best treatment for leishmania?
The best treatment for American cutaneous and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis (ACML) is not known. Pentavalent anti monial drugs (sodium stibogluconante [SSG] and meglumine antimonite [Glucantime, MA]) have been used since the 1940s, but they are expensive, toxic, and painful. Treatments that work for one species of Leishmania may not work for another; therefore, it is recommended that the exact species be identified prior to initiating treatment. Unfortunately, leishmaniasis is an orphan disease in developed nations, and almost all the current treatment options are toxic with significant side effects.
What is cutaneous leishmaniasis?
Diagnosis is based on the characteristic appearance of non-healing raised, scaling lesions that may ulcerate and become secondarily infected with organisms such as Staphylococcus aureus, in someone who has returned from an endemic area.
What is the most common cause of cutaneous leishmaniasis?
It is most often caused by Leishmania braziliensis, but cases caused by L. aethiopica have also been described. Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis is very difficult to treat.
How is leishmania transmitted?
Cutaneous leishmaniasis. Promastigotes of Leishmania are transmitted to human skin by the bite of a sandfly. Leishmania then invades human macrophages and replicates intracellularly. A raised, red lesion develops at the site of the bite (often weeks or sometimes years afterwards).
What is the cause of leishmania?
It is a skin infection caused by a single-celled parasite that is transmitted by the bite of a phlebotomine sand fly. There are about twenty species of Leishmania that may cause cutaneous leishmaniasis.
Where did the leishmaniasis outbreak occur in 2016?
Reports of the increase in the disease have surfaced in Turkey, Lebanon, and elsewhere.
Where is leishmaniasis endemic?
Cutaneous leishmaniasis is endemic in all tropical and subtropical areas of the world . The distribution of this disease is very tightly linked to geography, and villages even 15 miles apart can have very different rates of cutaneous leishmaniasis.

Known Risk Factors and Symptoms of Leishmaniasis
Food Items Or Nutrients That May Prevent Or Relieve Leishmaniasis
- One of the main factors for the progression of leishmaniasis to visceral leishmaniasis is the lack of nutrition: A diet that lacks protein, vitamin A, zinc, and iron increases a person’s risk, according to the World Health Organization(WHO). Eating food items that provide these nutrients, as well as those with antimicrobial properties such as garli...
Treatment and Management Options For Leishmaniasis
- An effective way to prevent leishmaniasis is to cover up exposed skin, especially when traveling to an area known for the condition. Cutaneous leishmaniasis usually heals on its own, without the need for medical treatment. However, visceral leishmaniasis, if left untreated, can prove to be fatal.
Where to Learn More
Summary
- Leishmaniasis refers to certain diseases that are caused by protozoan parasites of the Leishmaniaspecies. Humans can be infected by the condition through the bite of an infected female phlebotomine sandfly, a tiny insect vector. There are no predisposing factors for leishmaniasis. However, traveling to an area where the condition is found may increase the risk …