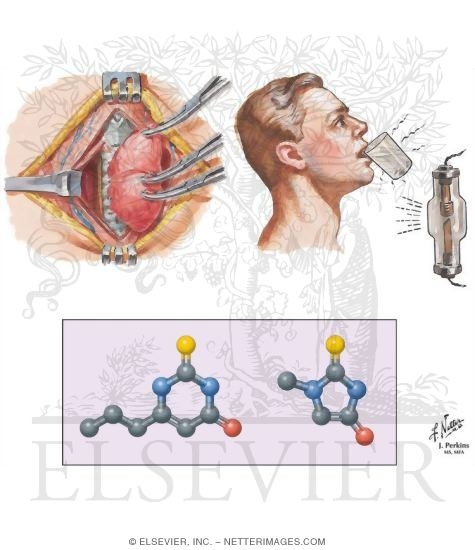
Medication
What Happens if Hypothyroidism Is Left Untreated?
- Goiter. A goiter is simply an enlarged thyroid gland, and it happens when the organ is trying extra hard to make thyroid hormone.
- Heart disease. There are at least two ways that hypothyroidism can contribute to heart disease, according to Tylee.
- Kidney disease. ...
- Peripheral neuropathy. ...
- Cognitive issues. ...
- Fertility issues. ...
Procedures
What is Hypothyroidism? If hypothyroidism is left untreated or not adequately treated, the disease can progress and lead to profound coma or even death. Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) is an endocrine disorder that occurs when a person’s body does not make enough thyroid hormone.
Therapy
fruits and starchy plants: sweet potatoes, cassava, peaches, strawberries, etc. nuts and seeds: millet, pine nuts, peanuts, etc. In theory, people with hypothyroidism should avoid goitrogens.9 Foods to Avoid if You’re Diagnosed With Hypothyroidism. Foods With Soy, Including Edamame, Tofu, and Miso. Shutterstock.
Self-care
What Can Happen If Hyperthyroidism Goes Untreated. Untreated hyperthyroidism can lead to serious complications, mainly related to the heart. When you have hyperthyroidism, your body is, in a way, running on overdrive all the time, and that can greatly affect your heart.
Nutrition
What are the dangers of not treating hypothyroidism?
What happens if hypothyroidism is not treated?
What to eat and not to eat for hypothyroidism?
Can hypothyroidism be dangerous if not treated?
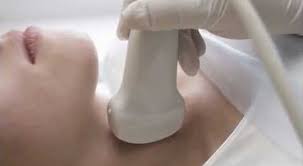
What are 3 treatments for hyperthyroidism?
Possible treatments include:Radioactive iodine. Taken by mouth, radioactive iodine is absorbed by your thyroid gland, where it causes the gland to shrink. ... Anti-thyroid medications. ... Beta blockers. ... Surgery (thyroidectomy).
Which is used in treatment of hyperthyroidism?
Medicines called thionamides are commonly used to treat an overactive thyroid. They stop your thyroid producing excess hormones. The main types used are carbimazole and propylthiouracil.
What if hyperthyroidism is not treated?
Over time, severe, untreated hyperthyroidism can lead to an irregular heartbeat, which in turn can cause problems such as blood clots, heart failure, and stroke. Once again, treatment for hyperthyroidism is essential to preventing heart problems in people with Graves' disease, says Mikhael.
Does hyperthyroidism need to be treated?
Hyperthyroidism is a manageable and treatable condition, and most people do well with treatment. While some forms of treatment require you to take medication for the rest of your life, your thyroid hormone levels will be normal.
What are the treatment options for hypothyroidism?
An underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) is usually treated by taking daily hormone replacement tablets called levothyroxine. Levothyroxine replaces the thyroxine hormone, which your thyroid does not make enough of. You'll initially have regular blood tests until the correct dose of levothyroxine is reached.
What are 3 symptoms of hyperthyroidism?
SymptomsUnintentional weight loss, even when your appetite and food intake stay the same or increase.Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia) — commonly more than 100 beats a minute.Irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia)Pounding of your heart (palpitations)Increased appetite.Nervousness, anxiety and irritability.More items...•
What are the dangers of hyperthyroidism?
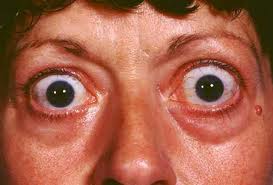
What are the complications of hyperthyroidism?an irregular heartbeat that can lead to blood clots, stroke, heart failure, and other heart-related problems.an eye disease called Graves' ophthalmopathy.thinning bones, osteoporosis link, and muscle problems.menstrual cycle and fertility issues.
What if hypothyroidism is not treated?
Over time, untreated hypothyroidism can cause a number of health problems, such as obesity, joint pain, infertility and heart disease.
What are normal TSH levels?
TSH normal values are 0.5 to 5.0 mIU/L. Pregnancy, a history of thyroid cancer, history of pituitary gland disease, and older age are some situations when TSH is optimally maintained in different range as guided by an endocrinologist. FT4 normal values are 0.7 to 1.9ng/dL.
How is high TSH treated?
Standard treatment for hypothyroidism involves daily use of the synthetic thyroid hormone levothyroxine (Levo-T, Synthroid, others). This oral medication restores adequate hormone levels, reversing the signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism. You'll likely start to feel better soon after you start treatment.
What happens when TSH is high?
High TSH levels can mean your thyroid is not making enough thyroid hormones, a condition called hypothyroidism. Low TSH levels can mean your thyroid is making too much of the hormones, a condition called hyperthyroidism. A TSH test does not explain why TSH levels are too high or too low.
What causes high TSH?
High TSH levels indicate hypothyroidism. People develop hypothyroidism when their thyroid produces low levels of hormones. When someone's thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones, the pituitary gland produces more TSH to compensate. Symptoms of hypothyroidism may include: fatigue.
What to do if you have hyperthyroidism?
If you've been diagnosed with hyperthyroidism, the most important thing is to receive the necessary medical care. After you and your doctor have decided on a course of action, there are some things you can do that will help you cope with the condition and support your body during its healing process.
How to diagnose hyperthyroidism?
Diagnosis. Hyperthyroidism is diagnosed using: Medical history and physical exam. During the exam your doctor may try to detect a slight tremor in your fingers when they're extended, overactive reflexes, eye changes and warm, moist skin. Your doctor will also examine your thyroid gland as you swallow to see if it's enlarged, ...
Why is my thyroid leaking?
The most likely cause is either Graves' disease or hyperfunctioning thyroid nodules. If you have hyperthyroidism and your radioiodine uptake is low, this indicates that the thyroxine stored in the gland is leaking into the bloodstream, which may mean you have thyroiditis. Thyroid scan.
Why is TSH important?
The amount of TSH is important because it's the hormone that signals your thyroid gland to produce more thyroxine. These tests are particularly necessary for older adults, who may not have classic symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
What test can you take to check if you have hyperthyroidism?
If blood tests indicate hyperthyroidism, your doctor may recommend one of the following tests to help determine why your thyroid is overactive: Radioiodine uptake test. For this test, you take a small, oral dose of radioactive iodine (radioiodine) to see how much will collect in your thyroid gland.
How long does it take for iodine to go away?
Symptoms usually subside within several months. Excess radioactive iodine disappears from the body in weeks to months . This treatment may cause thyroid activity to slow enough to be considered underactive (hypothyroidism), and you may eventually need to take medication every day to replace thyroxine.
What happens when you have a thyroidectomy?
In a thyroidectomy, your doctor removes most of your thyroid gland. Risks of this surgery include damage to your vocal cords and parathyroid glands — four tiny glands situated on the back of your thyroid gland that help control the level of calcium in your blood.
What is the least used treatment for hyperthyroidism?
The least-used treatment for hyperthyroidism is surgery to remove part or most of the thyroid gland. Sometimes doctors use surgery to treat people with large goiters or pregnant women who cannot take antithyroid medicines.
What is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism?
Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder. With this disease, your immune system attacks the thyroid and causes it to make too much thyroid hormone.
How long does thyroiditis last?
The hypothyroidism usually lasts 12 to 18 months, but sometimes is permanent.
Why is radioactive iodine used for hypothyroidism?
Almost everyone who has radioactive iodine treatment later develops hypothyroidism because the thyroid hormone-producing cells have been destroyed. However, hypothyroidism is easier to treat and causes fewer long-term health problems than hyperthyroidism.
How much more likely is a woman to have hyperthyroidism than a man?
Women are 2 to 10 times more likely than men to develop hyperthyroidism. 2 You are more likely to have hyperthyroidism if you. have a family history of thyroid disease. have other health problems, including. pernicious anemia. NIH external link. , a condition caused by a vitamin B12 deficiency. type 1 diabetes.
What causes thyroid inflammation?
Rarely, hyperthyroidism is caused by a noncancerous tumor of the pituitary gland located at the base of the brain.
What is it called when your thyroid makes more hormones than your body needs?
Hyperthyroidism, also called overactive thyroid, is when the thyroid gland makes more thyroid hormones than your body needs. The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland in the front of your neck.
How to treat hyperthyroidism?
Traditional treatment for hyperthyroidism can include medication and surgery. If the thyroid is completely removed, technically hyperthyroidism is reversed, however, now the patient has hypothyroidism and has to be on levothyroxine (synthetic thyroid hormone) for life.
What is the most common treatment for hyperthyroidism?
Radioactive iodine is the most common treatment for hyperthyroidism. This treatment is where patients are given a pill containing actual radioactive iodine. When you take this pill the radioactive iodine is processed by your thyroid, and the thyroid dies.
What causes thyroid problems?
The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is Graves disease, an autoimmune disease where the thyrotropin receptor antibody (TRAb) causes an overproduction of thyroid hormones.
What does it mean when your thyroid is producing too much thyroxine?
While hyperthyroidism means that the thyroid is producing too much thyroxine, in hypothyroidism, the thyroid is producing too little thyroxine. Thyroxine or T4 is the inactive hormone produced by your thyroid. Hyperthyroidism can alternate with hypothyroid symptoms, which can make it confusing for patients.
What are the symptoms of hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism symptoms can include unexplained weight loss, heart palpitations, diarrhea, anxiety, insomnia, and excessive sweating. This is a condition most commonly caused by antibodies that stimulate the thyroid gland to produce too much thyroid hormone in what is called Grave’s disease. In this article we'll explore conventional treatments ...
How to help thyroid over producing hormones?
When your thyroid is over-producing hormones, your entire body can become depleted of nutrients. Testing for nutrient deficiencies can help you understand your needs. Be extremely mindful of your diet — eat nutrient-dense foods. Include lots of vegetables and pasture-raised proteins in your diet.
What vitamins are needed for hyperthyroidism?
If you are hyperthyroid, take extra precautions to get sufficient vitamin D, vitamin A , and minerals like magnesium and calcium.
How to manage hyperthyroidism?
What to eat and what to avoid. One way to manage hyperthyroidism is to have a healthy diet. If you have hyperthyroidism, your doctor might prescribe a low-iodine diet before starting medical treatment. This increases the effectiveness of the treatment.
What is the best supplement for hyperthyroidism?
L-carnitine . A natural supplement that may help treat the effects of hyperthyroidism is L-carnitine. L-carnitine is an amino acid derivative that naturally occurs in the body. It’s often found in weight loss supplements. It’s also found in foods like meat, fish, and dairy products. Learn about the benefits of L-carnitine here.
What causes a goiter in the thyroid gland?
increased sweating. diarrhea. trembling and shaking. irritability. sleep problems. Hyperthyroidism can also lead to your thyroid gland swelling. This is called a goiter. Hyperthyroidism is often treated with antithyroid drugs, which stop the overproduction of thyroid hormone.
What is it called when you have too much thyroid hormone?
Hyperthyroidism occurs when there’s too much thyroid hormone in the body. This condition is also called an overactive thyroid . It affects the thyroid gland, a gland located in the throat which is responsible for secreting a number of important hormones. Hyperthyroidism shouldn’t be confused with hypothyroidism.
What is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism?
Selenium is a mineral that naturally occurs in water, soil, and foods like nuts, fish, beef, and grains. It can also be taken as a supplement. Graves’ disease, the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, is associated with thyroid eye disease (TED), which can be treated with selenium.
What essential oils can help with hyperthyroidism?
Lavender and sandalwood essential oils can, for example, reduce feelings of anxiety and help you feel calm. This might help you fight nervousness and sleeplessness, both symptoms of hyperthyroidism. Beyond that, there isn’t enough research out there to suggest that essential oils could help treat hyperthyroidism.
Is hyperthyroidism the same as hypothyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism shouldn’t be confused with hypothyroidism. While hyperthyroidism describes an overactive thyroid, hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland underperforms. The symptoms and treatment of hypothyroidism are very different than for hyperthyroidism.
What is the best treatment for hyperthyroidism?
Because of this, and unless you can reverse your hyperthyroidism naturally, you will be forced to choose one (or both) of the following options: #2. Thyroid surgery (Thyroidectomy). Thyroid surgery is considered more of a 'final' or 'complete' solution for hyperthyroidism as it completely eliminates the problem.
What to do if you have had your thyroid removed?
If you have had your thyroid removed then you will be required to take thyroid medication for the rest of your life . #3. Radioactive iodine ablation (RAI). Another option that is often used in place of surgical removal of the thyroid gland is known as radioactive iodine ablation or RAI .
How to slow down thyroid?
This is typically accomplished one of 3 ways (and sometimes a combination are used). #1. Anti-thyroid medication. The first step is almost always to start taking something called anti-thyroid medication.
How to heal a thyroid?
Diet. The first natural therapy that you should look at is your diet . The foods that you put into your mouth have a profound effect on your body and your thyroid. The foods you eat can either reduce inflammation or cause inflammation. They can either upset your stomach or help heal your gut.
Is hyperthyroidism a treatable condition?
Yes, Hyperthyroidism is Treatable. Hyperthyroidism is a treatable condition. But there is a difference between treating a condition and calling it a day and thriving with whatever treatment you are taking. And it is the difference here that you really need to pay close attention to. If you use the standard therapies for hyperthyroidism then you ...
Is there a difference between Hashimoto's and hypothyroidism?
There is no difference between you and someone who has Hashimoto's or hypothyroidism because in both situations the thyroid gland is NOT producing enough thyroid hormone . But this is confusing for many patients with hyperthyroidism who tend to hold on to their original diagnosis for the rest of their lives.
Can hyperthyroidism be treated?
And it is the difference here that you really need to pay close attention to. If you use the standard therapies for hyperthyroidism then you will treat your condition but you may not thrive. You may not have the energy you used to, you may gain weight, you may suffer from depression, and the list goes on and on.
What tests are done to determine if you have hyperparathyroidism?
These tests include: Bone mineral density test. This test is done to see if you have developed osteoporosis.
What does it mean when your calcium level is low?
If a very low calcium level is found in the urine, this may mean it's a condition that doesn't need treatment. Imaging tests of kidneys. Your doctor may order an X-ray or other imaging tests of your abdomen to determine if you have kidney stones or other kidney abnormalities.
How many glands can a surgeon remove?
A surgeon will remove only those glands that are enlarged or have a tumor. If all four glands are affected, a surgeon will likely remove only three glands and perhaps a portion of the fourth — leaving some functioning parathyroid tissue.
Does hormone replacement therapy cause breast cancer?
This treatment doesn't address the underlying problems with the parathyroid glands. Prolonged use of hormone replacement therapy can increase the risk of blood clots and breast cancer. Work with your doctor to evaluate the risks and benefits to help you decide what's best for you.
Can you treat calcium if your kidneys are working?
Your doctor may recommend no treatment and regular monitoring if: Your calcium levels are only slightly elevated. Your kidneys are working normally, and you have no kidney stones. Your bone density is normal or only slightly below normal. You have no other symptoms that may improve with treatment.
Can hyperparathyroidism be diagnosed by blood test?
Blood tests. If blood test results show you have high calcium levels in your blood, your doctor will likely repeat the test to confirm the results after you haven't eaten for a period of time. Many conditions can raise calcium levels. But your doctor can diagnose hyperparathyroidism if blood tests show you also have high levels ...
Drugs used to treat Hyperthyroidism
The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Hyperthyroidism is diagnosed using: 1. Medical history and physical exam.During the exam your doctor may try to detect a slight tremor in your fingers when they're extended, overactive reflexes, eye changes and warm, moist skin. Your doctor will also examine your thyroid gland as you swallow to see if it's enlarged, bumpy or tender and check your pulse to see if it's rapid or irregul…