What Are the Side Effects of Radiation Therapy for Brain Cancer?
- Fatigue and mood changes. Fatigue and mood changes are among the most common side effects of radiation therapy.
- Hair loss.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Skin changes.
- Headaches.
- Fatigue and mood changes. Fatigue and mood changes are among the most common side effects of radiation therapy. ...
- Hair loss. ...
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Skin changes. ...
- Headaches. ...
- Vision changes.
- Radiation necrosis.
- Increased risk of another brain tumor.
What are the long term effects of radiation treatment?
- your skin might look darker than it was before in the treated area – as if it is suntanned
- your skin in the treatment area will always be slightly more sensitive to the sun
- your skin might feel different to touch
- your hair might grow back a different colour or texture in the treatment area
- you might have permanent hair loss within the treated area
What are the side effects of radiation therapy?
Some possible late effects are:
- fertility problems (if you had radiation therapy to the pelvis)
- heart problems (if you had radiation to the chest)
- lung problems (if you had radiation to the chest)
- changes in skin colour
- mental or emotional problems (if you had radiation to the head and neck or brain)
- osteoporosis
- second cancers
What are the long term effects of brain radiation?
- Increased, looser bowel movements
- Infertility (For patients in their childbearing years who wish to have children one day, there are options to preserve fertility prior to treatment.)
- Reduction in bladder capacity
- Vaginal dryness
What happens to the brain after radiation?
Though the risk is low, you should be aware of these possible long-term effects:
- There is a low risk of developing a second cancer in or near the radiation field. ...
- Radiation necrosis: Rarely, a mass of dead (necrotic) tissue forms at the site of the tumor. ...
- Damage to healthy brain tissue: Although rare, this side effect can cause headaches, seizures, or even death.

How long does it take to recover from brain radiation?
You may develop fatigue after 2 to 3 weeks of treatment, and it can range from mild to severe. Fatigue may last 6 weeks to 12 months after your treatment ends. There are a lot of reasons why you may develop fatigue during treatment, including: The effects of radiation on your body.
What is the success rate of radiation therapy for brain cancer?
A combination of 12 studies (n=566) with WBRT outcomes showed a median survival time of 6.0 months (95%CI: 5.9-6.2), an overall survival rate of 5.6% (95%CI: 1-24), and a 6-month survival rate of 46.5% (95%CI: 37.2-56.1).
What happens after radiation treatment for brain tumor?
Radiation to the brain can also have side effects that show up later – usually from 6 months to many years after treatment ends. These delayed effects can include serious problems such as memory loss, stroke-like symptoms, and poor brain function.
How long can you live after brain radiation?
Survival analysis The median follow-up of patients was 7 months, with a minimum of 2 months and a maximum of 34 months. At the end of the study period, 25 deaths were registered (71%). The median survival with brain metastases was 4.43 months, ranging from 0.73 months to 78.53 months.
Can radiation cure a brain tumor?
Radiation therapy uses strong beams of energy to kill brain cancer cells. It helps control the growth of some types of brain tumors. It's often used along with surgery or chemotherapy to treat brain tumors.
Can your brain heal from radiation?
Scientists have long believed that healthy brain cells, once damaged by radiation designed to kill brain tumors, cannot regenerate.
What are the worst side effects of radiotherapy?
Treatment areas and possible side effectsPart of the body being treatedPossible side effectsBrainFatigue Hair loss Memory or concentration problems Nausea and vomiting Skin changes Headache Blurry visionBreastFatigue Hair loss Skin changes Swelling (edema) Tenderness5 more rows•Jan 11, 2022
Do tumors grow back after radiation?
Normal cells close to the cancer can also become damaged by radiation, but most recover and go back to working normally. If radiotherapy doesn't kill all of the cancer cells, they will regrow at some point in the future.
What can you not do during radiation treatment?
Avoid raw vegetables and fruits, and other hard, dry foods such as chips or pretzels. It's also best to avoid salty, spicy or acidic foods if you are experiencing these symptoms. Your care team can recommend nutrient-based oral care solutions if you are experiencing mucositis or mouth sores caused by cancer treatment.
What are the final stages of a brain tumour?
These symptoms include drowsiness, headaches, cognitive and personality changes, poor communication, seizures, delirium (confusion and difficulty thinking), focal neurological symptoms, and dysphagia. Some patients may have several of these symptoms, while others may have none.
How many times can you have radiation on the brain?
Whole-brain radiation applies radiation to the entire brain in order to kill tumor cells. People undergoing whole-brain radiation usually require 10 to 15 treatments over two to three weeks. Side effects may include fatigue, nausea and hair loss.
What is the success rate of radiation therapy?
“In fact, based on the literature reviewed, it appears that external-beam radiation therapy is a superior treatment in some cases. “When patients are treated with modern external-beam radiation therapy, the overall cure rate was 93.3% with a metastasis-free survival rate at 5 years of 96.9%.
How does radiation affect cancer?
The radiation used to destroy cancer cells can also hurt normal cells in the area that is radiated . Side effects from radiation treatment can vary, depending on the area of the body being treated. Side effects are caused by the cumulative effect of radiation on the cells. This means they develop over time and most patients do not experience any side effects until a few weeks into their treatment. Side effects may be unpleasant, but there are treatments to help deal with them. Most side effects are temporary, disappearing bit by bit after therapy is complete.
What are the side effects of radiosurgery?
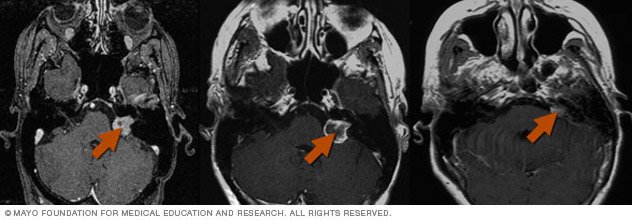
Side effects of radiosurgery are usually related to sending high doses of radiation to particular areas of the skull. For instance, if you are treated for an acoustic neuroma (a tumor involving the nerve that controls hearing), you might lose some hearing. Treatment for trigeminal neuralgia can lead to tingling or numbness of the face.
How often do radiation oncologists see patients?
Most side effects are temporary, disappearing bit by bit after therapy is complete. Most radiation oncologists see their patients at least once a week while the patient is receiving treatment. This visit with the healthcare team is an opportunity to ask questions, talk about any side effects, and to make a plan to manage side effects. ...
What to do after cancer treatment?
After treatment, talk with your oncology team about receiving a survivorship care plan, which can help you manage the transition to survivorship and learn about life after cancer.
How long does it take for fatigue to go away after radiation?
Talk with your radiation oncologist and health care team about what you can expect from your specific treatment. Fatigue is very common with radiation treatment and tends to begin a few weeks into therapy. Fatigue typically resolves slowly over the weeks and months following treatment.
How long does it take for side effects to show after cancer treatment?
The side effects mentioned above tend to occur during treatment, up until a few months after treatment. Long-term effects can happen months to many years after cancer treatment and the risks vary depending on the areas included in the field of radiation and the radiation techniques that were used, as these continue to develop and improve.
Can trigeminal neuralgia cause numbness?
Treatment for trigeminal neuralgia can lead to tingling or numbness of the face. Talk to your care team about potential side effects; they will be able to tell you what you might expect in your case.
How does radiotherapy affect your body?
Radiotherapy may affect one’s appetite, metabolism and eating habits. Regular intake of nourishment is important. 4. Low white blood cell count and decreased immunity. Neutropenia is the drop in white blood cell count leading to dysfunction in the immune system.
What happens if you have a low red blood cell count?
A drop in red blood cell count may lead to anemia. Symptoms include tiredness, shortness of breath and heart palpitations. In which case, an erythropoietin (EPO) helps increase the rate of red blood cell production.
Is radiation therapy safe for children?
However, these side effects disappear soon after treatment ends. Generally , radiation therapy is not advisable for children younger than 5 because of the high risk of damage to their developing brains.
Can a brain tumor cause general symptoms?
People with a brain tumor may experience either general or specific symptoms. The former is caused by… read more
Types of Radiation Therapy for Brain Tumors
There are 2 main types of therapy. You may get both types. They include:
External beam radiation therapy (EBRT)
There are several types of EBRT. The goal is to target the tumor and limit damage to nearby healthy brain cells. To limit the harm, your healthcare provider may use special types of EBRT such as:
Brachytherapy
For this treatment, the radiation is placed very close to or inside the tumor. This is done during surgery. The radiation the implants give off travels a very short distance. This helps limit the effect on nearby healthy tissue.
Brain Radiation Side Effects
Generally, side effects from radiation treatment are grouped into two categories:
Radiation necrosis
Sometimes dead brain tissue forms at the site of the radiation. This is called radiation necrosis. The mass of dead brain tissue comes from both cancer cells and healthy cells. Radiation necrosis can take anywhere from months to years to develop.
Risk of future cancer
Radiation can damage the DNA in healthy cells. As a result, you have a small risk of a second brain cancer after brain radiation. This second cancer usually occurs many years later. Talk to your radiation oncologist about the risks and benefits of radiation therapy.
The Radiation Team
Treatment planning for radiation therapy includes mapping to pinpoint the exact location of the brain tumor using X-rays or other images.
Is the risk/benefit ratio acceptable for treating malignant tumors?
While the risk:benefit ratio is considered acceptable for treating malignant tumors, risks of long-term complications of radiotherapy need thorough assessment in adults treated for benign tumors. Many previously reported delayed complications of radiotherapy can be attributed to inappropriate treatment or to the sensitivity ...
Is radiation therapy safe for brain tumors?
The long-term side effects of radiation therapy for benign brain tumors in adults. Radiation therapy plays an integral part in managing intracranial tumors. While the risk:benefit ratio is considered acceptable for treating malignant tumors, risks of long-term complications of radiotherapy need thorough assessment in adults treated ...
How does radiation affect the brain?
Effects on brain function. Radiation can cause changes in the brain tissue. Blood vessels may slowly become scarred and blocked, reducing the blood supply to some areas of the brain. This can have an effect on your brain function. Symptoms of this include: problems thinking clearly.
How long does it take for a brain tumor to heal after radiation?
This is called radiation necrosis. Radiation necrosis usually happens 1 to 3 years after the treatment finishes. It is more common in people who have had a high dose of radiation to a small area of the brain (radiosurgery). Most people don't have symptoms and do not need treatment.
Why does radiotherapy cause headaches?
This can be frightening because you might think the radiotherapy isn't working. Increased pressure in the brain might cause: headaches. feeling sick.
How long does it take for side effects to go away after radiotherapy?
Most side effects gradually go away in the weeks or months after treatment. But some can continue, or start some months or years later. Long term side effects won't happen to everyone. It's important to remember that the benefits of the radiotherapy usually far outweigh the risks.
Can radiotherapy cause hair loss?
Radiotherapy to the brain can cause hair loss or thinning. If you are having treatment to a particular part of the head, your hair usually falls out in that area. You might also have some hair loss on the opposite side of the head, where the radiotherapy beams pass through. This area is called the exit site.
Can you get a brain tumor after radiation?
In very rare cases, you may develop another brain tumour many years after you were first treated. This is because, although radiation kills cancer cells, it is also a risk factor for developing them. Unfortunately, tumours caused by previous radiotherapy tend not to respond very well to treatment.
Do you need to have steroids for brain cancer?
Most people don't have symptoms and do not need treatment. A small number of people might develop symptoms that depend on the area of the brain affected. If this is the case, you may have treatment with steroids or an operation to remove the affected area.
How long do side effects last after radiation treatment?
Early side effects happen during or shortly after treatment. These side effects tend to be short-term, mild, and treatable. They’re usually gone within a few weeks after treatment ends. The most common early side effects are fatigue (feeling tired) and skin changes. Other early side effects usually are related to the area being treated, such as hair loss and mouth problems when radiation treatment is given to this area.
How long does it take for radiation to cause side effects?
Late side effects can take months or even years to develop. They can occur in any normal tissue in the body that has received radiation. The risk of late side effects depends on the area treated as well as the radiation dose that was used. Careful treatment planning can help avoid serious long-term side effects.
How long does it take for radiation to show up in the brain?
Radiation to the brain can also have side effects that show up later – usually from 6 months to many years after treatment ends. These delayed effects can include serious problems such as memory loss, stroke-like symptoms, and poor brain function.
What is the most common drug used for radiation therapy?
The one most commonly used today is amifostine. This drug may be used in people with head and neck cancer to reduce the mouth problems caused by radiation therapy. Not all doctors agree on how these drugs should be used in radiation therapy. These drugs have their own side effects, too, so be sure you understand what to look for.
How long does radiation side effects last?
Remember that the type of radiation side effects you might have depends on the prescribed dose and schedule. Most side effects go away within a few months of ending treatment. Some side effects may continue after treatment ends because it takes time for the healthy cells to recover from radiation. Side effects might limit your ability ...
What is the best treatment for radiation?
One way to reduce side effects is by using radioprotective drugs, but these are only used for certain types of radiation given to certain parts of the body. These drugs are given before radiation treatment to protect certain normal tissues in the treatment area. The one most commonly used today is amifostine. This drug may be used in people with head and neck cancer to reduce the mouth problems caused by radiation therapy.
What are the side effects of brachytherapy?
If your treatment includes brachytherapy (internal radiation implants), you might notice breast tenderness, tightness, redness, and bruising. You may also have some of the same side effects that happen with external radiation treatment.
How do steroids help with brain tumors?
Steroids reduce brain swelling from the tumor itself or from the effects of radiation therapy . Take steroids only as directed by your doctor. You dose may be changed as needed during your treatment. When your doctor decides it’s safe, you’ll be given a schedule to gradually reduce the dose of the medication.
How does radiation therapy work?
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to treat cancer. It works by damaging the cancer cells and making it hard for them to reproduce. Your body then is naturally able to get rid of these damaged cancer cells. Radiation therapy also affects normal cells.
What is the phone number for a radiation oncologist?
After 5:00 pm, during the weekend, and on holidays, call 212-639-2000. Ask for the radiation oncologist on call.
When will a radiation oncologist see you?
Your radiation oncologist and radiation nurse will see you for a scheduled visit during your treatment course to talk with you about any concerns, ask about any potential side effects you may be having, and answer your questions. This visit will be before or after your treatment on __________________. You should plan on being at your appointment about 1 extra hour on this day.
How to quit smoking after radiation?
Telling your doctor or nurse if you’re in pain. Caring for yourself at home: Quitting smoking, if you smoke. If you want to quit, call our Tobacco Treatment Program at 212-610-0507. Following your radiation therapy team’s instructions to care of your skin.
What happens to your hair during radiation?
During radiation therapy, your skin and hair in the area being treated may change. This may include your forehead, ears, and back of your neck. This is normal. Ask your nurse to point out the areas of your skin and scalp that will be affected.
Can radiation cause brain swelling?
Radiation therapy to the brain may cause brain swelling. If you had neurological symptoms before you began radiation therapy, they could return, or you could have new symptoms. These symptoms may include:
How long does it take for a person to recover from radiation?
Skin changes. Urinary and bladder changes. Healthy cells that are damaged during radiation treatment usually recover within a few months after treatment is over. But sometimes people may have side effects that do not improve. Other side effects may show up months or years after radiation therapy is over.
Does radiation make you tired?
People feel fatigue in different ways and you may feel more or less fatigue than someone else who is getting the same amount of radiation therapy to the same part of the body. Other radiation therapy side effects you may have depend on the part of the body that is treated.
Does radiation therapy cause cancer?
Radiation Therapy Side Effects. Radiation not only kills or slows the growth of cancer cells, it can also affect nearby healthy cells. Damage to healthy cells can cause side effects. Many people who get radiation therapy have fatigue. Fatigue is feeling exhausted and worn out.
What is radiation therapy for breast cancer?
Radiation Therapy for Breast Cancer. Radiation refers to high-energy rays that are directed at the breast to kill or slow the growth of cancer cells. Radiation reduces the risk of local cancer recurrence in the breast. Potential side effects include skin redness, swelling, peeling, and fatigue. It is necessary to undergo follow-up exams ...
What is the name of the tumor that starts in the brain?
Brain and spinal tumor are diseases in which cancer (malignant) cells begin to grow in the tissues of the brain. Tumors that start in the brain are called primary brain tumors. Tumors that start in the brain and spread to other organs are called primary brain tumors. Symptoms may include headaches, personality changes, dizziness, and trouble walking. Treatment depends upon the type and grade of tumor.
Is a brain tumor benign or malignant?
A brain tumor can be either non-cancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant), primary, or secondary. Common symptoms of a primary brain tumor are headaches, seizures, memory problems, personality changes, and nausea and vomiting. Causes and risk factors include age, gender, family history, and exposure to chemicals.
Acute (Short-Term) Side Effects
- The following list includes some of the most common side effects of radiation therapy for brain tumors. Remember that the treatment can affect each patient differently, and you may not experience these particular side effects. Side effects can also be different depending on your dose and treatment schedule. Talk with your radiation oncologist about what side effects you ca…
Chronic (Long-Term) Side Effects
- The side effects mentioned above tend to occur during or shortly after treatment. Long-term effects can happen months to years after treatment has ended. The risks of long-term effects vary depending on the treatment area, the total dose that is given, and the radiation techniques that were used, as these continue to develop and improve. Though the risk is low, you should be …
Stereotactic Radiosurgery (Srs) Side Effects
- Side effects of radiosurgeryare usually related to sending high doses of radiation to particular areas of the brain. For instance, if you are treated for an acoustic neuroma (a tumor involving the nerve that controls hearing), you might lose some hearing. Treatment for trigeminal neuralgia can lead to tingling or numbness of the face. Talk to your ...