Side effects of traditional treatment options can include permanent facial numbness or other damage. Gamma Knife is an effective, lasting, minimally invasive treatment for trigeminal neuralgia
Neuralgia
A severe pain due to damaged nerves.
What are the dangers of Gamma Knife?
- Local loss of hair in superficial lesions
- Local brain swelling in the treatment site
- Local tissue necrosis in the treatment site
What is the best painkiller for trigeminal neuralgia?
ViewMedica Error
- Clinical Trials. Patients who have tried medications and surgical options and keep experiencing debilitating pain may qualify for clinical trials to help manage trigeminal neuralgia.
- Acupuncture and Other Integrative Medicine Treatments. ...
- Caring for a Loved One with Trigeminal Neuralgia. ...
What is the most effective treatment for trigeminal neuralgia?
Trigeminal neuralgia
- Diagnosis. Pain related to trigeminal neuralgia is sudden, shock-like and brief. ...
- Treatment. Trigeminal neuralgia treatment usually starts with medications, and some people don't need any additional treatment.
- Alternative medicine. ...
- Coping and support. ...
- Preparing for your appointment. ...
What are long term side effects of Gamma Knife radiation?
What are long term side effects of gamma knife radiation? OBJECT: Several adverse effects such as brain edema, necrosis, arterial stenosis, hemorrhage after obliteration, and delayed cyst formation have been reported as early and late complications of Gamma Knife surgery (GKS) for arteriovenous malformations (AVMs).

Does Gamma Knife have side effects?
Some people experience mild headaches, a tingling sensation on the scalp, nausea or vomiting. Other side effects may include: Fatigue. Tiredness and fatigue may occur for the first few weeks after Gamma Knife radiosurgery.
What are the side effects of Gamma Knife surgery for trigeminal neuralgia?
What are the potential side effects of Gamma Knife surgery? Side effects may include tingling or numbness in the face (in up to 20-30% of patients), but this is usually mild if it does occur. Will I have pain when I wake up? Patients are not put to sleep for this procedure as it causes minimal pain and discomfort.
What are long term side effects of Gamma Knife radiation for trigeminal neuralgia?
Although it is generally safe and well tolerated by most patients, adverse effects have been reported. Potential ocular complications include “dry eye” and “corneal numbness.”5,6 We describe a case of vision loss that occurred 9 months after gamma knife radiosurgery for TN.
What are the long term side effects of Gamma Knife surgery?
Object: Several adverse effects such as brain edema, necrosis, arterial stenosis, hemorrhage after obliteration, and delayed cyst formation have been reported as early and late complications of Gamma Knife surgery (GKS) for arteriovenous malformations (AVMs).
What can go wrong with Gamma Knife?
Complications arising from Gamma Knife Radiosurgery are rare, but call your Rocky Mountain Gamma Knife Center doctor if you have: Pain at the points where the head frame was attached that does not improve or gets worse. A fever of 100.5 or greater. Severe headache or any headache that does not improve within 48 hours.
Can trigeminal neuralgia come back after Gamma Knife surgery?
Research indicates that as many as 96 percent of trigeminal neuralgia patients treated with Gamma Knife radiosurgery experience pain relief within a few weeks of the procedure. If pain recurs, the procedure can be repeated.
How long can you live after Gamma Knife?
Survival. The median survival (to death or to the last office visit) for the entire cohort of 677 patients was 12 months (mean, 14.6 mos). Of the 44 patients who lived for > 4 years after radiosurgery, the median survival was 68 months (mean, 68.6 mos; range, 48–156 mos).
How long does it take to recover from Gamma Knife surgery?
After the procedure, a patient will typically spend 3-5 days recovering in the hospital before being released to return home. Brain tumor recovery following traditional surgery can be relatively lengthy, including activity and work restrictions ranging from 4-8 weeks.
How many times can you have Gamma Knife surgery?
Gamma Knife can be, and often is, repeated if a doctor determines that multiple sessions are necessary. Sometimes the area to be treated is very large or deep within other structures, and it will take more than a single session to adequately treat the area.
What is the success rate of Gamma Knife for trigeminal neuralgia?
Effective short-term outcomes have been well documented for trigeminal neuralgia (TN) patients treated with Gamma Knife radiosurgery (GKRS) with reported success rates of 70–90 % with median follow-up intervals of 19–75 months.
How safe is Gamma Knife radiation?
Gamma Knife radiosurgery is safe, accurate and reliable. Since it was first introduced in 1965, more than 350,000 Gamma Knife procedures have been performed worldwide with a very high cure rate for many conditions.
What are the side effects of gamma knife?
Rocky Mountain Gamma Knife Center patients go home the same day as their Gamma Knife treatment. The most commonly reported side effects are mild and short-lived. They usually clear up within a few days of the procedure and can include: 1 Fatigue 2 Headache 3 Nausea 4 Mild swelling of the forehead and eyelids 5 Temporary numbness of the scalp
What is gamma knife?
Gamma Knife is used to kill or shrink non-cancerous and metastatic tumors in the brain. It can also be used to treat other physiological conditions, such as trigeminal neuralgia. It does not involve any incisions or general anesthesia. (Read more about common Gamma Knife misconceptions .)
How long does it take for a gamma knife to clear?
The most commonly reported side effects are mild and short-lived. They usually clear up within a few days of the procedure and can include: Fatigue. Headache.
What are the side effects of radiosurgery?
Delayed side effects can include: Swelling in the brain. Hair loss near the treated area, if close to the scalp. It will regrow on its own. Radiation necrosis, which is the death of brain tissue at or near the treatment site. It can occur months or years after radiosurgery and is usually treated with steroids.
Is gamma knife radiosurgery safe?
Although uncommon, traditional brain tumor surgery can lead to bleeding, infection and adverse reactions to general anesthesia. These are not risks associated with Gamma Knife Radiosurgery. Gamma Knife Radiosurgery does have some side effects you’ll want to be aware of so you know what to expect and can alert your physician to anything out of the ordinary.
Can gamma knife radiosurgery cause headaches?
Complications arising from Gamma Knife Radiosurgery are rare, but call your Rocky Mountain Gamma Knife Center doctor if you have: Pain at the points where the head frame was attached that does not improve or gets worse. Severe headache or any headache that does not improve within 48 hours.
What is the complication of trigeminal neuralgia?
The main complication after radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia was new facial sensory symptoms caused by partial trigeminal nerve injury. Seventeen patients (7.7%) in our series developed increased facial paresthesia and/or facial numbness that lasted longer than 6 months.
What is the surgical procedure for trigeminal neuralgia?
The surgical options for trigeminal neuralgia include peripheral nerve blocks or ablation, gasserian ganglion and retrogasserian ablative (needle) procedures, craniotomy followed by microvascular decompression (MVD), and stereotactic radiosurgery (Gamma Knife®).
What causes pain in the trigeminal nerve?
The mechanism of pain production remains controversial. One theory suggests that peripheral injury or disease of the trigeminal nerve increases afferent firing in the nerve perhaps by ephaptic transmission between afferent unmyelinated axons and partially damaged myelinated axons; failure of central inhibitory mechanisms may also be involved. Blood vessel-nerve cross compression, aneurysms, chronic meningeal inflammation, tumors, or other lesions may irritate trigeminal nerve roots along the pons. Uncommonly, an area of demyelination, such as may occur with multiple sclerosis, may be the precipitant. In some cases, no vascular or other lesion is identified rendering the etiology unknown. Development of trigeminal neuralgia in a young person (<45 years) raises possibility of multiple sclerosis, which should be investigated. Thus, although trigeminal neuralgia typically is caused by a dysfunction in the peripheral nervous system (the roots or trigeminal nerve itself), a lesion within the central nervous system may rarely cause similar problems.
What are the outcomes of pain relief?
The outcome of pain relief was categorized into four results (excellent, good, fair, and poor). Complete pain relief without the use of any analgesic medication was defined as an excellent outcome. Complete pain relief with still requiring some medication was defined as a good outcome. Partial pain relief (>50% relief) was defined as a fair outcome. No or less than 50% pain relief was defined as a poor outcome. Most patients responded to radiosurgery within six months (median, two months). At the initial follow-up within six months after radiosurgery, complete pain relief without medication (excellent) was obtained in 105 patients (47.7%), and excellent and good outcomes were obtained in 139 patients (63.2%). Greater than 50% pain relief (excellent, good, and fair) was obtained in 181 patients (82.3%).
What is the most effective pharmacologic treatment?
The goal of pharmacologic therapy is to reduce pain. Carbamazepine (Tegretol) is regarded as the most effective medical treatment. Additional agents that may benefit selected patients include phenytoin (Dilantin), baclofen, gabapentin (Neurontin), Trileptol and Klonazepin.
Can trigeminal neuralgia be treated with radiosurgery?
Trigemin al neuralgia patients who experience recurrent pain during the long-term follow-up despite initial pain relief after radiosurgery can be treated with second radiosurgery procedure. The target is placed anterior to the first target so that the radiosurgical volumes at second procedure overlaps with the first one by 50%. We advocate less radiation dose (50 to 60 Gy) for second procedure, because we believe that a higher combined dose would lead to a higher risk of new facial sensory symptoms.
Do you need an MRI for trigeminal neuralgia?
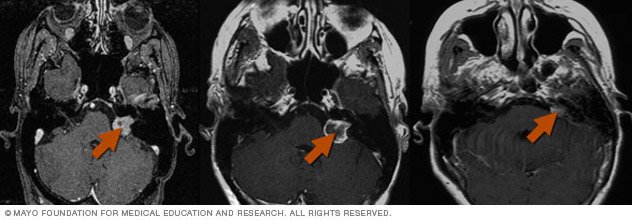
Prior to considering surgery, all trigeminal neuralgia patients should have a MRI, with close attention being paid to the posterior fossa. Imaging is performed to rule out other causes of compression of the trigeminal nerve such as mass lesions, large ectatic vessels, or other vascular malformations.
What Is Trigeminal Neuralgia?
Trigeminal neuralgia — also known as tic douloureux — is a neurological condition that affects your trigeminal nerve. This is the fifth cranial nerve and is responsible for much of the sensation you feel in your cheeks, jaw, upper lip and upper teeth. When you are suffering from trigeminal neuralgia, the nerve is essentially misfiring, sending jolts of pain into your face. These sensations have often been likened to the pain that accompanies an intense electric shock.
How long do you stay in the hospital after trigeminal neuralgia surgery?
Following surgery, you can expect to stay in the hospital for 1-2 days. During this time you’ll be observed, and your post-operative pain medications for surgical site pain adjusted. You may notice relief from your trigeminal neuralgia symptoms right away. When you’re ready to go home, you will need to have someone drive you.
What is the type of neuropathy that can be triggered by sounds?
Much like Type 1, this form of trigeminal neuralgia can be triggered by sounds, touch or other normal activities
Why is trigeminal neuralgia misdiagnosed?
Because of this nerve’s location, trigeminal neuralgia is often misdiagnosed as dental pain. It’s sometimes only discovered when dental interventions have failed to relieve the symptoms.
What exam is needed for trigeminal neuralgia?
You will be given a physical exam that will include a neurological exam. This can help determine whether or not your trigeminal neuralgia is being caused by nerve compression.
Can trigeminal neuralgia affect both sides of the face?
In the vast majority of trigeminal neuralgia cases, only one side of the face is affected. In more rare instances it occur s on both sides of the face.
Does rhizotomy wear off?
The only notable risk or side effect from percutaneous rhizotomy is some facial numbness. If you experience this, there is a good chance it will wear off over time.
What is the incidence of trigeminal nerve dysfunction after GKS?
Conclusions: The incidence of trigeminal nerve dysfunction after GKS for TN was 49%. The severity of the dysfunction improved in one-third of the afflicted patients, even in those with severe dysesthesia at long-term follow-up. A strong relationship between TN and good pain control was identified.
Is gamma knife surgery effective?
Object: Gamma Knife surgery (GKS) is an effective treatment option for intractable trigeminal neuralgia (TN). The incidence of trigeminal nerve dysfunction, such as facial numbness or dysesthesia, has been reported to be higher than previously published, and the degree and prognosis of trigeminal nerve dysfunction has not been well evaluated. The authors evaluated the incidence, timing, degree, and outcome of trigeminal nerve dysfunction after GKS for TN.
Who Is a Candidate for Gamma Knife Treatment for Trigeminal Neuralgia?
Most trigeminal neuralgia patients are good candidates, as no general anesthesia is required. Gamma Knife treatment for trigeminal neuralgia also is a good option for patients who want a nonsurgical treatment with little to no recovery time or side effects. The procedure also is particularly appropriate for patients who want to minimize risk of facial numbness or cannot tolerate general anesthesia.
How much pain relief does gamma knife give?
Approximately 80 to 96 percent of trigeminal neuralgia patients reported adequate pain relief after Gamma Knife treatment, and still five years later. For patients who did not get adequate pain relief and repeated the procedure, 89 percent reported adequate pain relief. Success rates for patients with multiple sclerosis also were high compared to other treatments, providing relief to more than half of all patients.
What Is Gamma Knife Treatment?
Sometimes referred to as stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), Gamma Knife is a noninvasive method for treating trigeminal neuralgia. It is the delivery of a single, high dose of irradiation to a small and critically located target through the skull. Gamma Knife treatment for trigeminal neuralgia is preferred for its extreme accuracy, efficiency, and outstanding therapeutic response. Because there is no incision, the recovery time, potential for infection, and bleeding risk are all substantially reduced, making it the best option for patients with many types of brain disorders. In addition, Gamma Knife’s precise delivery means that only the targeted area of the brain receives radiation, while surrounding healthy tissue remains intact.
How long does it take for gamma knife to heal?
Research indicates that as many as 96 percent of trigeminal neuralgia patients treated with Gamma Knife radiosurgery experience pain relief within a few weeks of the procedure. If pain recurs, the procedure can be repeated.
What is gamma knife radiosurgery?
In Gamma Knife radiosurgery, a neurosurgeon uses computer imagery to direct a precisely focused beam of high-dose radiation to the root of the trigeminal nerve. This causes a lesion to form on the nerve, which eventually disrupts the transmission of pain signals to the brain. Pain relief occurs gradually.
How long does gamma knife pain last?
Gamma Knife treatment provides effective pain relief for 80 to 96 percent of trigeminal neuralgia patients, even five years after the procedure. It also can be repeated.
What is a gamma knife?
Sometimes referred to as stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), Gamma Knife is a noninvasive method for treating trigeminal neuralgia. It is the delivery of a single, high dose of irradiation to a small and critically located target through the skull. Gamma Knife treatment for trigeminal neuralgia is preferred for its extreme accuracy, efficiency, ...
