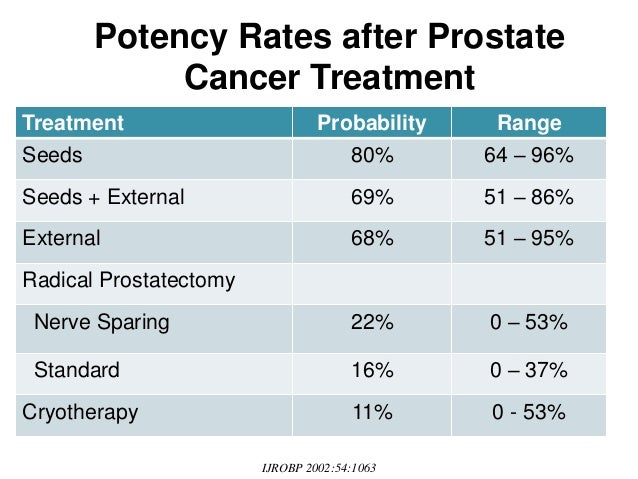
Some of the potential long-term side effects of radiation to the prostate includes:
- Erectile dysfunction can occur after radiation therapy, sometimes months after treatment ends. ...
- There is a low risk of developing a second cancer in or near the radiation field. ...
- Most men will be sterile after radiation treatment for prostate cancer. ...
What to expect after radiation treatment for prostate cancer?
May 19, 2021 · Long-Term Side Effects of Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Studies show that over time, men who have undergone this procedure, tend to develop long-term side effects. However, these radiotherapy side effects are less common and occur only when the radiation damages your body.
What are the after effects of radiation for prostate cancer?
Dec 15, 2021 · These are often called long-term side effects. Late effects can be health issues or psychological, emotional, and practical challenges. Late Effects After Radiation for Prostate Cancer. Side effects from radiation treatment are directly related to the area of the body being treated. Any area in the treatment field has a risk of being damaged, causing side effects. As …
What happens to the prostate after radiation?
Jun 21, 2019 · You might have long term side effects after having external radiotherapy for prostate cancer, such as erection problems (impotence). Tell your doctor or nurse if you have any of these problems, they can help you with them. Most side effects gradually go away in the weeks or months after treatment. But long term side effects can continue.
What are the side effects of prostate cancer treatment?
Feb 11, 2020 · In the unfavorable-risk group, external beam radiation therapy with androgen deprivation therapy was associated with low hormonal function scores six months after treatment and with low bowel function after one year.
What is the downside of radiation for prostate cancer?
Because the prostate is close to several vital structures, radiation therapy can disrupt normal urinary, bowel, and sexual functioning. Short-term Complications You may experience some temporary urinary symptoms, such as waking up in the night and needing to urinate, needing to urinate more often during the...
What are the long-term side effects of radiation?
What are the most common long-term side effects of radiation?Cataracts.Hair loss.Hearing loss.Memory loss ("It's hard to determine how much memory loss or cognitive dysfunction is related to a tumor and how much is related to radiotherapy," says Dr. Nowlan.
How long do prostate radiation side effects last?
After completing external beam radiation therapy (EBRT), urinary and bowel side effects may persist for two to six weeks, but they will improve over time. You may need to continue some medications.
Can a prostate grow back after radiation?
Prostate cancer can come back, even after you've had treatment and your doctor declared you cancer-free. Prostate cancer that returns after treatment is called recurrent prostate cancer. Prostate cancer returns for a couple of reasons: Some cancer cells were left behind after surgery or radiation therapy.May 19, 2021
Does radiation cause pain years later?
Surgery or radiation therapy to the abdominal area can cause tissue scarring, long-term pain, and intestinal problems.
Does radiation cause permanent damage?
This damage may result in permanent dry mouth or dry eyes. 16 Cataracts and dental decay may also be problems. Radiation to the abdomen and pelvic regions may affect the: Bladder.Jan 24, 2022
What should PSA be after radiation?
Recent studies have shown that for optimal results, PSA levels should be lower than 1 ng/ml, and even lower than 0.5 ng/ml. Levels that are above 1 or 2 ng/ml 12 to 18 months following completion of radiation treatments are very worrisome, because they indicate that the cancer may not have been eradicated.Mar 31, 2009
How long does it take to recover from prostate radiation?
Side effects tend to start a week or 2 after the radiotherapy begins. They gradually get worse during the treatment and for a couple of weeks after the treatment ends. But they usually begin to improve after around 2 weeks or so.
What should PSA levels be 3 months after radiation?
Patients were characterized by 3-month post-RT PSA values: <0.10 ng/mL, 0.10 to 0.49 ng/mL, and ≥0.50 ng/mL. The researchers found that a higher 3-month PSA level was strongly associated with biochemical progression-free survival (bPFS), prostate cancer-specific survival (PCSS), and overall survival (OS).May 29, 2018
Is it better to have prostate removed or radiation?
Radiation may be a better choice for men who want to avoid the side effects of surgery, such as leaking urine and erection problems. It may be a better choice for men who have other health problems that make surgery too risky. You avoid the risks of major surgery.
Does the prostate shrink after radiation?
Radiation therapy can be an effective treatment for prostate cancer. It can shrink a tumor, relieve symptoms, and delay or halt the growth of cancer cells. A therapist may target a tumor with an intense beam of radiation from an external machine, or they may implant or inject radioactive materials into the body.Oct 16, 2019
Why does PSA increase after radiation?
This is because after radiation therapy the prostate gland remains intact and can recover some function. This is also true if you received hormone therapy as part of your radiation treatment: As you recover, testosterone levels rise, and so does your PSA.Mar 11, 2009
What is a late effect?
A late effect is a side effect related to a cancer diagnosis or treatment that happens months to years after treatment. Some side effects that you develop during treatment can last for months to years after treatment is completed (for example, fatigue or neuropathy). These are often called long term side effects.
Late Effects After Radiation for Prostate Cancer
Side effects from radiation treatment are directly related to the area of the body being treated. Any area in the treatment field has a risk of being damaged, causing side effects. As radiation techniques have improved over the years, the risk of late effects has decreased.
Managing Late Effects
If you experience any concerning or persistent symptoms, contact your care team. Some side effects require specialized care from healthcare providers experienced in working with cancer survivors. Interdisciplinary survivorship clinics are available at many cancer treatment sites.
How long does it take for side effects from radiation to go away?
Tell your doctor or nurse if you have any of these problems, they can help you with them. Most side effects gradually go away in the weeks or months after treatment.
How many men leak urine after 6 years?
Nearly 15 men out of every 100 (15%) have some problem with leaking urine after 6 years. But it is more likely if you have previously had a trans urethral resection of the prostate (TUR or TURP).
Why is it so hard to pass urine?
This is due to the treatment causing a narrowing of the tube from the bladder to the penis (the urethra). The narrowing is called a urethral stricture. Tell your doctor if you find it harder to pass urine.
How old do you have to be to get impotence?
your age (impot ence is less likely if you are under 65) whether you have other health conditions. whether you had erection problems before the treatment. if you have hormone therapy before or after the radiotherapy. whether you have internal radiotherapy as well as external radiotherapy. Tell your doctor or specialist nurse ...
Can B12 cause numbness?
A B12 deficiency can be a cause of anaemia. This can lead to a feeling of weakness, constipation or diarrhoea and numbness and tingling. It’s important that you go to your doctor if you’re experiencing these symptoms so that they can help you. Talk to your doctor or specialist nurse if you have side effects.
Can radiotherapy cause pain?
The bones can become weaker. This is called avascular necrosis. Damage to the bones can cause pain and sometimes makes it hard to walk or climb stairs.
What are the long term effects of radiation?
These may include proctitis (rectal inflammation), cystitis (bladder inflammation), urinary or rectal bleeding, narrowing of the rectum or urethra, chronic diarrhea or urinary frequency or urgency, or development of an ulcer in the rectum.
How to know if you have a urinary tract infection?
You may experience some temporary urinary symptoms, such as waking up in the night and needing to urinate, needing to urinate more often during the day, or urgency – needing to urinate right now, and not being able to hold it in for a long time. Tell your doctor; there are medications that can help reduce acute symptoms. You may also experience some rectal problems, including the need to have a bowel movement more often than usual, or loose stools. Diarrhea is rare, but if needed, there are medications that can help. Your doctor may also suggest that you try a low-fiber diet for a while.
What are the treatments for prostate cancer?
The 1,386 men with favorable-risk prostate cancer received one of these treatments: 1 active surveillance, in which they received treatment only if their cancer worsened over time 2 nerve-sparing prostatectomy, in which surgeons remove the prostate but attempt to protect adjacent nerves in an effort to preserve sexual function 3 external beam radiation therapy, in which daily doses of radiation attack cancer cells 4 low-dose-rate brachytherapy, in which radioactive “seeds” are planted in an attempt to combat the cancer.
What is the procedure to remove prostate?
nerve-sparing prostatectomy, in which surgeons remove the prostate but attempt to protect adjacent nerves in an effort to preserve sexual function. external beam radiation therapy, in which daily doses of radiation attack cancer cells. low-dose-rate brachytherapy, in which radioactive “seeds” are planted in an attempt to combat the cancer.
What is low dose brachytherapy?
low-dose-rate brachytherapy, in which radioactive “seeds” are planted in an attempt to combat the cancer. The 619 men with unfavorable-risk prostate cancer received one of two treatments: prostatectomy, which is the surgical removal of the prostate.
What is external beam radiation therapy?
external beam radiation therapy with androgen deprivation therapy, in which radiation is paired with medications to lower levels of male hormones, which can stimulate prostate cancer growth. The men who received surgery saw an immediate, steep drop-off in their erectile function compared with men who received other types of treatment.
Does prostatectomy cause incontinence?
Looking at urinary function, the study authors found that after five years, receiving a prostatectomy was associated with worse incontinence compared with receiving other forms of treatment, regardless of the cancer risk group.
How many men were diagnosed with prostate cancer in 1994?
The study followed 3,533 men with prostate cancer, diagnosed in 1994 and 1995, who underwent either surgery or definitive radiation therapy within a year of their diagnosis.
Does radiation cause prostate cancer?
Localized prostate cancer treatment with surgery or radiation results in similar long-term side effects, such as erectile dysfunction and urinary incontinence. Men treated for their localized prostate cancer have been found to have similar long-term side effects regardless of treatment type, a new study says.
Short-Term Complications
- You may experience some temporary urinary symptoms, such as waking up in the night and needing to urinate, needing to urinate more often during the day, or urgency – needing to urinate right now, and not being able to hold it in for a long time. Tell your doctor; there are medications that can help reduce acute symptoms. You may also experience some rectal problems, includin…
Long-Term Complications
- The risk of long-term problems after radiation therapy is very low, less than 5 percent. These may include proctitis (rectal inflammation), cystitis (bladder inflammation), urinary or rectal bleeding, narrowing of the rectum or urethra, chronic diarrhea or urinary frequency or urgency, or development of an ulcer in the rectum. All of these can be managed.
Erectile Dysfunction
- Similar to surgery, damage to blood vessels and nerves after radiation therapy can result in decreased erectile function over time. In general, radiation therapy has less of an impact on erectile function in the first 5 to 10 years after treatment compared with surgery, and approximately 60-85% of men who have baseline erectile function before treatment will keep ere…