What are existing wastewater treatment standards?
Existing wastewater treatment standards give the guidelines needed to perform this process. Wastewater, if not treated properly, can cause significant environmental harm through pollution of rivers, lakes, and other bodies of water, the majority of which ultimately connect with and flow into the ocean.
What percentage of people are not served by wastewater treatment plants?
There are many people living in rural areas that are not served by wastewater treatment plants. In fact, according to Environment Canada, as of 2000, only 57 percent of Canadians were served by wastewater treatment plants, compared with 74 percent of Americans, 86.5 percent of Germans, and 99 percent of Swedes.
Who sets the standards for drinking water quality?
Under the SDWA, EPA sets the standards for drinking water quality and monitors states, local authorities, and water suppliers who enforce those standards. As part of the SDWA, EPA has set maximum contaminant levels, as well as treatment requirements for over 90 different contaminants in public drinking water.
Which wastewaters are difficult to treat?
Some wastewaters are more difficult to treat than others; for example, industrial wastewater can be difficult to treat, whereas domestic wastewater is relatively easy to treat (though it is increasingly difficult to treat domestic waste, due to increased amounts of pharmaceuticals and personal care products that are found in domestic wastewater.

What is regulated in relation to the water treatment plant?
EPA regulates the discharge and treatment of wastewater under the Clean Water Act (CWA). The National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) issues permits to all wastewater dischargers and treatment facilities.
What are the 3 types of water quality standards?
A water quality standard consists of three elements: (1) the designated beneficial use or uses of a waterbody or segment of a waterbody: (2) the water quality criteria necessary to protect the use or uses of that particular waterbody; and (3) an antidegradation policy.
What kind of water is not regulated?
If you get your water from a private well, stream, pond, lake, or other body of water, your water is most likely unregulated.
What are the 6 categories of contaminants that the federal EPA sets drinking water standards for?
2,7 Microbial contaminants, lead, nitrates and nitrites, arsenic, disinfection byproducts, pesticides, and solvents are among the contaminants for which EPA has set health-based standards.
What are the different water quality standards?
There are five water quality parameters: pH, biological oxygen demand (BOD), suspended solids (SS), dissolved oxygen (DO), and total coliform bacteria. Six water use classes from AA to E were established for rivers.
Is code for drinking water standards?
Drinking Water Quality StandardsS.No.ParametersDrinking water IS 10500 : 20121OdorAgreeable2TasteAgreeable3pHNo relaxation4TDS (mg/l)200017 more rows
What are acceptable levels of contaminants in drinking water?
While secondary standards are not federally enforceable, EPA requires a special notice for exceedance of the fluoride secondary standard of 2.0 mg/L....National Secondary Drinking Water Regulations (NSDWRs)ContaminantSecondary StandardFoaming Agents0.5 mg/LIron0.3 mg/LManganese0.05 mg/L12 more rows•Feb 17, 2022
What are EPA water quality standards?
Water quality standards (WQS) are provisions of state, territorial, authorized tribal or federal law approved by EPA that describe the desired condition of a water body and the means by which that condition will be protected or achieved.
What is the EPA standard for drinking water pH?
U.S. EPA water quality criteria for pH in freshwater suggest a range of 6.5 to 9.
How many groups of standards are set by EPA for water?
six groupsEPA has set standards for over 90 contaminants organized into six groups: microorganisms, disinfectants, disinfection byproducts, inorganic chemicals, organic chemicals and radionuclides.
What are drinking water parameters?
A number of parameters such as pH, turbidity, conductivity, total suspended solids (TSS), total dissolved solids (TDS), and heavy metals such as Cu, Zn, Mg, Fe, Cd, Pb, Cr, As, Hg, and Sn were analysed for each water sample collected during winter and summer periods.
What are the 6 types of contaminants that are found in water?
But before you wander off there, I'll give you a breakdown of the six main contaminant categories here.Microorganisms. These are what you think they are. ... Disinfection Byproducts. ... Disinfectants. ... Inorganic Chemicals. ... Organic Chemicals. ... Radionuclides.
What are the rules for surface water treatment?
3 EPA's surface water treatment rules require systems using surface water or ground water under the direct influence of surface water to. Disinfect their water, and. Filter their water, or. Meet criteria for avoiding filtration so that the following contaminants are controlled at the following levels:
What is the NPDWR?
The National Primary Drinking Water Regulations (NPDWR) are legally enforceable primary standards and treatment techniques that apply to public water systems. Primary standards and treatment techniques protect public health by limiting the levels of contaminants in drinking water. Microorganisms.
What are the symptoms of nitrite in water?
Symptoms include shortness of breath and blue-baby syndrome. Runoff from fertilizer use; leaking from septic tanks, sewage; erosion of natural deposits.
What happens if you drink too much nitrate water?
Symptoms include shortness of breath and blue-baby syndrome. Runoff from fertilizer use; leaking from septic tanks, sewa ge; erosion of natural deposits.
Why is turbidity important?
It is used to indicate water quality and filtration effectiveness (such as whether disease-causing organisms are present). Higher turbidity levels are often associated with higher levels of disease-causing microorganisms such as viruses, parasites and some bacteria.
What are the different levels of wastewater treatment?
There are several levels of wastewater treatment; these are primary, secondary and tertiary levels of treatment. Most municipal wastewater treatment facilities use primary and secondary levels of treatment, and some also use tertiary treatments.
What is tertiary wastewater treatment?
Tertiary (or advanced) treatment removes dissolved substances, such as colour, metals, organic chemicals and nutrients like phosphorus and nitrogen.
How to reduce pressure on septic system?
Following some water conservation practices can greatly reduce pressure on your septic system. For more information about conserving water, see the fact sheet about Water Consumption. Here are a few things that you can do to care for your septic system: 1 Do not use your drain or toilet as a garbage disposal; avoid putting dental floss, diapers, coffee grounds and paper towel down the drain, as they can clog up your septic system. 2 Spread your loads of laundry out over the week. When too much water is added to the septic tank, it does not have time to treat wastes, and you could be flooding your drainfield with wastewater. 3 Plant grass on your drainfield, but keep trees and shrubs away from it, because roots can clog the system and cause damage. 4 Do not drive on your drainfield, because this can compact the soil and damage the septic system components.
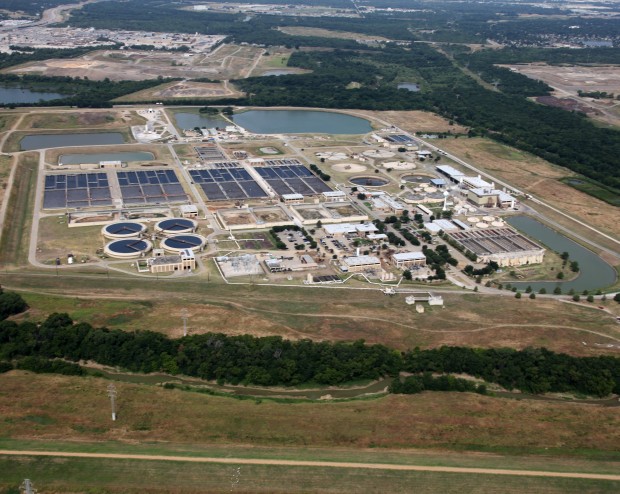
Why is oxygen important in wastewater treatment?
The oxygen helps the bacteria to digest the pollutants faster. The water is then taken to settling tanks where the sludge again settles, leaving the water 90 to 95 percent free of pollutants. The picture below shows the settling tanks in the Winnipeg Wastewater Treatment Plant.
What is the process of removing pollutants from water?
Another natural method is called rapid infiltration, which is a process where a basin is filled with wastewater, which has already gone through a pre-treatment. The ground acts as a filter and removes the pollutants from the water. This method is similar to what happens in a septic system.
What is the process of tertiary treatment?
One of the biological treatment processes is called Biological Nutrient Removal (BNR). This diagram shows the treatment steps that Saskatoon wastewater goes through. Biological Nutrient Removal Process.
What is the Canadian Environmental Protection Act?
The Canadian Environmental Protection Act governs the release of toxic substances into the environment and allows the federal government to develop regulations for the use of toxic substances. Most provincial and territorial governments have legislation regarding wastewater treatment standards and requirements.
Why are sewers not watertight?
Sanitary sewers that are not watertight due to cracks, faulty seals, and/or improper connections can receive large amounts of infiltration and inflow (I/I) during wet weather.
What is separate sanitary sewer?
Separate Sanitary Sewers. The other major type of domestic sewer design is sanitary sewers (also known as separate sanitary sewers). Sanitary sewers are installed to collect wastewater only and do not provide widespread drainage for the large amounts of runoff from precipitation events.
What is combined sewer?
Combined sewers are designed to collect both sanitary sewage and stormwater runoff in a single-pipe system. These systems were designed to convey sewage and wastewater to a treatment plant during dry weather. Under wet weather conditions, these combined sewer systems would overflow during wet weather conditions when large amounts of stormwater would enter the system. State and local authorities generally have not allowed the construction of new combined sewers since the first half of the 20th century.
What are the requirements for a NPDES permit?
NPDES permits establish discharge limits and conditions for discharges from municipal wastewater treatment facilities to waters of the United States. Resources for discharge requirements include: 1 Primer for Municipal Wastewater Treatment - Overview of municipal processes used to treat domestic wastewater before discharge to the nation's waters. 2 NPDES Permitting Framework – Framework for establishing water quality and technology-based NPDES permit limits. 3 Secondary Treatment Standards - Minimum, technology-based standards for discharges from municipal wastewater treatment facilities.
What causes sewage overflows?
In addition, sewage overflows can be caused by other problems such as blockages, equipment failures, broken pipes, or vandalism. Resources for overflows and peak flows at treatment plants include: Combined Sewer Overflows (CSOs) Sanitary Sewer Overflows (SSOs)
Why is sewage important?
The collection and treatment of domestic sewage and wastewater is vital to public health and clean water. It is among the most important factors responsible for the general level of good health enjoyed in the United States. Sewers collect sewage and wastewater from homes, businesses, and industries and deliver it to wastewater treatment facilities ...
Can combined sewers overflow?
Under wet weather conditions, these combined sewer systems would overflow during wet weather conditions when large amounts of stormwater would enter the system. State and local authorities generally have not allowed the construction of new combined sewers since the first half of the 20th century.
What is the Clean Water Act?
The Clean Water Act: Regulates pollution in U.S. waterways. Gives the EPA authority to implement pollution control programs. Sets water quality standards for contaminants in surface waters, such as rivers, lakes, wetlands and/or oceans. Makes it unlawful to pollute U.S. waterways without a proper permit.
When was the Clean Water Act passed?
The original law, the Federal Water Pollution Control Act, was passed by Congress in 1948. That law was amended, reorganized and expanded and became known as the Clean Water Act. Some additional amendments have been made to the CWA since its creation. In 1981, revisions streamlined the municipal construction grants process; in 1987, ...
What is a stormwater inspection?
Stormwater inspections at industrial facilities and construction sites are designed to evaluate compliance with NPDES permits for stormwater discharge. The CWA, and its implementing regulations, requires certain industrial facilities, construction sites, and municipal separate storm sewer systems (MS4) to:
What is the EPA's NPDES?
Under the Clean Water Act’s National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES), the EPA regulates discharges of pollutants from municipal and industrial collection systems and treatment plants, and stormwater discharges from industrial facilities and municipalities.
What is a pretreatment permit?
National and Local Pretreatment Standards - Requirements for industrial facilities to pre-treat wastewater discharged to public water treatment facilities. Dredge or Fill Discharge Permit Program - A permit program, administered by the Army Corps of Engineers, for regulating dredge or fill material in U.S. waterways.
Which states have EPA enforcement authority?
The EPA has direct implementation responsibilities in four unauthorized US states—Idaho, New Hampshire, Massachusetts and New Mexico— as well as the District of Columbia and most U.S. territories.
Who has authority to enforce the CWA?
Authority to enforce the CWA is given to the EPA in accordance with sections 308, 309 and 309 (b) of the Act. Most state governments are able to perform many of the permitting, administrative and enforcement activities related to the program.
Meat & Poultry Rule
Effluent Guidelines are national regulatory standards for wastewater discharged to surface waters and municipal sewage treatment plants. EPA issues these regulations for industrial categories, based on the performance of treatment and control technologies.
Pollutants, Analytical Methods, Research
Pollutant discharges regulated by Effluent Guidelines must be measured with approved analytical methods.
Where is the EPA drinking water plant?
EPA and Indian Health Service inspect a drinking water plant on the Yavapai Apache Nation reservation in Arizona. During inspections of drinking water treatment plants, inspectors must climb to the top of the storage tank to check the condition of the tank.
How to minimize stormwater pollution?
Construction sites are required to minimize stormwater pollution by stabilizing exposed dirt and placing filters around storm drains to catch dirt and other debris. (Cont) Two sand bags were not sufficient to keep dirt and other debris from entering this storm drain.
What is the EPA's NPDES program?
Wastewater Management. Under the CWA's National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) program, EPA regulates discharges of pollutants from municipal and industrial wastewater treatment plants, sewer collection systems, and stormwater discharges from industrial facilities and municipalities. Learn more about the NPDES program .
What is the impact of stormwater discharges on the environment?
Uncontrolled stormwater discharges can pose significant threats to public health and the environment.
How does the EPA protect human health?
EPA safeguards human health by enforcing the requirements of the SDWA to ensure that the nation's public drinking water supply and its sources (rivers, lakes, reservoirs, springs, and ground water wells) are protected. Learn more about drinking water.
What is wetlands discharge?
Learn more about oil spill prevention and preparedness regulations . Wetlands - Discharges of Dredge and Fill Material. EPA ensures that dredged or fill material is not discharged into wetlands and other waters of the United States except as authorized by a permit issued by the United States Army Corps of Engineers.
What is the EPA using to clean up an oil spill?
EPA field personnel using booms and absorbent pads to clean up an oil spill in the Pacific Northwest. EPA inspectors preparing to measure discharge flow during an inspection of a NPDES-permitted wastewater treatment plant in Georgia.