
Type I diabetes mellitus is caused by an autoimmune reaction to proteins in the pancreatic islets cells. Type II diabetes mellitus is caused by a combination of genetic factors related to impaired insulin secretion, insulin resistance and environmental factors such as obesity, genetics, lack of exercise, stress and aging.
Full Answer
What causes Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes?
Type 1 and type 2 have different causes, but they both involve insulin. Insulin is a type of hormone. The pancreas produces it to regulate the way blood sugar becomes energy. In this type, scientists believe that the immune system mistakenly attacks the pancreatic beta cells, which produce insulin.
What are the treatment options for type 2 diabetes?
The keys to treating Type 2 diabetes are eating healthy, staying physically active, and maintaining a healthy body weight. Healthy nutrition: Eat a variety of vegetables and fruits, whole grains, fat-free or low-fat dairy foods, and lean proteins.
How is type 1 and Type 2 diabetes diagnosed?
The primary test used to diagnose both type 1 and type 2 diabetes is known as the A1C, or glycated hemoglobin, test. This blood test determines your average blood sugar level for the past 2 to 3 months. Your doctor may draw your blood or give you a small finger prick.
Can type 2 diabetes be prevented?
Many people with Type 2 diabetes have a family history of diabetes, but with healthy lifestyle changes, it can be prevented or slowed down. Type 1 diabetes affects fewer than 5% of people with diabetes.
What is the treatment for type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Type 1 is managed by taking insulin to control your blood sugar. You can manage type 2 diabetes in more ways than type 1. These include through medication, exercise and diet. People with type 2 can also be prescribed insulin.
What is the cause of type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease. It occurs when the insulin-producing islet cells in the pancreas are completely destroyed, so the body can't produce any insulin. In type 2 diabetes, the islet cells are still working. However, the body is resistant to insulin.
What is the cause of type 1 diabetes?
What Causes Type 1 Diabetes? Type 1 diabetes is thought to be caused by an autoimmune reaction (the body attacks itself by mistake). This reaction destroys the cells in the pancreas that make insulin, called beta cells. This process can go on for months or years before any symptoms appear.
What are the causes of type 2 diabetes?
Risk Factors for Type 2 DiabetesHigh blood pressure.High blood triglyceride (fat) levels. ... Low "good" cholesterol level. ... Gestational diabetes or giving birth to a baby weighing more than 9 pounds.Prediabetes. ... Heart disease.High-fat and carbohydrate diet. ... High alcohol intake.More items...•
What is the treatment of diabetes?
Treatment for type 1 diabetes involves insulin injections or the use of an insulin pump, frequent blood sugar checks, and carbohydrate counting. Treatment of type 2 diabetes primarily involves lifestyle changes, monitoring of your blood sugar, along with diabetes medications, insulin or both.
What causes diabetes?
Doctors don't know exactly what causes type 1 diabetes. For some reason, the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Genes may play a role in some people. It's also possible that a virus sets off the immune system attack.
What are the causes and prevention of diabetes?
While the causes of diabetes differ from body to body, some of the most common factors that can lead to diabetes are obesity, unhealthy diet, alcohol consumption, and an inactive lifestyle. Age plays a crucial role too, more often than not. Diabetes can also be inherited genetically.
What is the difference between type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is caused by the body's immune system damaging the pancreas and, therefore, no insulin can be manufactured by the body. In Type 1 diabetes, the body fails to make insulin. In Type 2 diabetes, the body either develops a resistance to insulin or not enough insulin is produced to lower the blood sugars.
How is type 2 diabetes prevented?
11 Ways to Prevent Type 2 DiabetesReduce your total carb intake. ... Exercise regularly. ... Drink water as your primary beverage. ... Try to lose excess weight. ... Quit smoking. ... Reduce your portion sizes. ... Cut back on sedentary behaviors. ... Follow a high fiber diet.More items...
What causes Type 3 Diabetes?
What causes type 3c diabetes? Type 3c can happen when the pancreas stops producing enough insulin for the body. And we all need insulin to live. It allows the glucose (or sugar) in our blood to enter our cells and fuel our bodies.
Why trust us
Dr. Kevin Hwang has been treating patients with acute and chronic medical problems since 2005 as a board-certified internal medicine physician. He also conducts research and teaches medical students and residents at UTHealth McGovern Medical School in Houston.
Do you have diabetes?
Do you have diabetes? If not, you may know somebody who does. Or maybe you’re worried about your blood sugar tests and think you might have diabetes? This guide is for you.
Testing for diabetes
There are several different blood tests for diabetes according to the American Diabetes Association. These tests are used to diagnose diabetes and monitor how diabetes is responding to treatment. The same blood tests are used for Type 1 diabetes and Type 2 diabetes. The tests will not tell you which type of diabetes you have.
The hemoglobin A1C test
Sometimes known simply as A1C, this test measures how high your blood glucose has been for the past 2 to 3 months. You don’t need special preparation for this test, so it can be done even on a full stomach.
Other causes of diabetes
Although more than 95% of people with diabetes have Type 2 or Type 1, there are some other rare causes of diabetes:
Keep in mind
Some people, especially young adults, can have features of both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. In fact, a recent study published in The Lancet, suggested that diabetes is a group of many very different diseases that have all been given the same name because they all share the same blood test abnormality: high blood glucose.
What is the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes both occur when the body cannot properly store and use glucose, which is essential for energy. Sugar, or glucose, collects in the blood and does not reach the cells that need it, which can lead to serious complications. Type 1 diabetes usually appears first in children and adolescents, but it can occur in older people, ...
Why do people with type 1 diabetes need insulin?
A person with type 1 diabetes will need to use supplemental insulin from the time they receive the diagnosis and for the rest of their life.
What type of diabetes is found in pregnancy?
Another type is gestational diabetes . This occurs in pregnancy and typically resolves after childbirth, but some people then develop type 2 diabetes later in life. This article will look at the differences and similarities between type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
How long does it take for a person with type 2 diabetes to show symptoms?
Symptoms may take years to appear. People may use medications, diet, and exercise from the early stages to reduce the risk or slow the disease. In the early stages, a person with type 2 diabetes does not need supplemental insulin.
What does it mean when your body stops producing enough insulin?
In type 2 diabetes, the body’s cells start to resist the effects of insulin. In time, the body stops producing enough insulin, so it can no longer use glucose effectively. This means glucose cannot enter the cells. Instead, it builds up in the blood.
What are the complications of diabetes?
Both types of diabetes can lead to complications, such as cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, vision loss, neurological conditions, and damage to blood vessels and organs. of them do not know they have it.
Why does the immune system attack the pancreatic beta cells?
The immune system attacks the pancreatic beta cells so that they can no longer produce insulin. There is no way to prevent type 1 diabetes, and it is often hereditary. Around 5 percent. of people with diabetes have type 1, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Why is type 1 diabetes the same as type 2 diabetes?
Basically, type 1 diabetes occurs because the pancreas cannot produce enough insulin; in contrast, type 2 diabetes happens due to insulin resistance. The symptoms of type 1 and type 2 diabetes are similar, with only a few differences, such as when and how fast they develop. Treatment for type 1 diabetes requires insulin, ...
What are the two types of diabetes?
Diabetes comes in two main types - type 1 and type 2. Both are indicative of high blood sugar but differ in how this happens. Read on to find out the differences and how to identify the condition.
What is the risk of developing type 2 diabetes?
Age: Unlike type 1 diabetes which commonly appears at a younger age, the risk of type 2 diabetes increases with age. Ethnicity: People of certain descents, including Blacks, Pacific Islanders, Hispanics, Native Americans, and Asians are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes. Besides these risk factors, certain medical conditions also predispose ...
Why is diabetes called juvenile diabetes?
This is why some people call type 1 diabetes “juvenile diabetes” as people tend to develop it when they are young. Geography. The incidence of type 1 diabetes is higher in areas further from the equator.
How long does it take for diabetes to show up?
On the other hand, symptoms of type 2 diabetes usually do not show up until individuals are in their 40s or older. Additionally, the signs and symptoms typically develop slowly in years.
What happens when the immune system attacks the pancreas?
In type 1 diabetes, the immune system attacks the cells in the pancreas which are responsible for producing insulin. As a result, the body has little to no insulin.
Why is my risk of diabetes higher?
Besides the possibility of an autoimmune condition, your risk of developing type 1 diabetes may be higher due to the following risk factors: Genetics: The presence of variants of genes HLA-DQA1, HLA-DQB1, and HLA-DRB1 may increase the risk of type 1 diabetes. These genes affect our immune system.
How to reduce risk of diabetes type 2?
If you have prediabetes, losing a small amount of weight if you’re overweight and getting regular physical activity can lower your risk for developing type 2 diabetes. A lifestyle change program offered through the CDC-led National Diabetes Prevention Program can help you make those changes—and make them stick.
What are the factors that increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes?
Diabetes Factors. If you have type 2 diabetes, your body doesn’t use insulin well and can’t keep blood sugar at normal levels. We don’t know exactly why this happens, but we do know factors that may increase a person’s risk of developing type 2 diabetes. You may be at risk if you: Have prediabetes. Are overweight.
How much does a type 2 diabetes test lower your risk?
Through the program, you can lower your risk of developing type 2 diabetes by as much as 58% (71% if you’re aged 60 years or older). Take the 1-minute test to see if you may be at risk of prediabetes.
How old do you have to be to be at risk for diabetes?
You may be at risk if you: Have prediabetes. Are overweight. Are 45 years or older. Have a parent, brother, or sister with type 2 diabetes. Are physically active for less than 150 minutes a week. Have ever had gestational diabetes (diabetes during pregnancy) or given birth to a baby who weighed more than 9 pounds.
What is BMI in health?
Body mass index (BMI) is a number calculated from a person’s weight and height. Most health professionals rely on BMI to assess whether their patients are overweight (BMI of 25 or more) or have obesity (BMI of 30 or more). All adults who are overweight should talk to their doctor about getting tested for type 2 diabetes.
What are the two types of fat?
There are two kinds of fat: 1 Fat that’s stored just under the skin. This is fat that we may be able to feel on the outside, like on our arms and legs. 2 Fat that’s stored in our stomach and surrounds important internal organs. We can’t see this hidden, or “visceral” fat from the outside.
Can you prevent type 2 diabetes?
You Can Prevent Type 2 Diabetes. Before developing type 2 diabetes, most people have prediabetes, where blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough yet to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes. People who have prediabetes are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
When does Type 2 diabetes start?
Type 2 diabetes most often develops in people over age 45, but more and more children, teens, and young adults are also developing it.
What is it called when your pancreas doesn't respond to insulin?
If you have type 2 diabetes, cells don’t respond normally to insulin; this is called insulin resistance. Your pancreas makes more insulin to try to get cells to respond. Eventually your pancreas can’t keep up, and your blood sugar rises, setting the stage for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes.
How does diabetes affect children?
Childhood obesity rates are rising, and so are the rates of type 2 diabetes in youth. More than 75% of children with type 2 diabetes have a close relative who has it, too. But it’s not always because family members are related; it can also be because they share certain habits that can increase their risk. Parents can help prevent or delay type 2 diabetes by developing a plan for the whole family: 1 Drinking more water and fewer sugary drinks 2 Eating more fruits and vegetables 3 Making favorite foods healthier 4 Making physical activity more fun
How many children with diabetes have a close relative?
More than 75% of children with type 2 diabetes have a close relative who has it, too. But it’s not always because family members are related; it can also be because they share certain habits that can increase their risk. Parents can help prevent or delay type 2 diabetes by developing a plan for the whole family:
How can parents help prevent diabetes?
Parents can help prevent or delay type 2 diabetes by developing a plan for the whole family: Drinking more water and fewer sugary drinks. Eating more fruits and vegetables. Making favorite foods healthier. Making physical activity more fun.
Who manages diabetes?
Unlike many health conditions, diabetes is managed mostly by you, with support from your health care team (including your primary care doctor, foot doctor, dentist, eye doctor, registered dietitian nutritionist, diabetes educator, and pharmacist), family, and other important people in your life. Managing diabetes can be challenging, but everything you do to improve your health is worth it!
How to check blood sugar?
Recognize the signs of high or low blood sugar and what to do about it. If needed, give yourself insulin by syringe, pen, or pump. Monitor your feet, skin, and eyes to catch problems early. Buy diabetes supplies and store them properly.
Why is Type 2 diabetes so bad?
Type 2 diabetes is primarily the result of two interrelated problems: Cells in muscle, fat and the liver become resistant to insulin. Because these cells don't interact in a normal way with insulin, they don't take in enough sugar. The pancreas is unable to produce enough insulin to manage blood sugar levels.
Which race is more likely to develop type 2 diabetes?
Although it's unclear why, people of certain races and ethnicities — including Black, Hispanic, Native American and Asian people, and Pacific Islanders — are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than white people are. Blood lipid levels.
How to prevent prediabetes from getting worse?
Getting active. Aim for 150 or more minutes a week of moderate to vigorous aerobic activity, such as a brisk walk, bicycling, running or swimming. Losing weight. Losing a modest amount of weight and keeping it off can delay the progression from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes.
Why is physical activity important for diabetes?
The less active you are, the greater your risk. Physical activity helps control your weight, uses up glucose as energy and makes your cells more sensitive to insulin. Family history. The risk of type 2 diabetes increases if your parent or sibling has type 2 diabetes. Race and ethnicity.
How long can you live with type 2 diabetes?
Signs and symptoms of type 2 diabetes often develop slowly. In fact, you can be living with type 2 diabetes for years and not know it. When signs and symptoms are present, they may include:
What happens if you have high blood sugar?
Eventually, high blood sugar levels can lead to disorders of the circulatory, nervous and immune systems. In type 2 diabetes, there are primarily two interrelated problems at work. Your pancreas does not produce enough insulin — a hormone ...
What happens when your glucose levels are low?
When your glucose levels are low, such as when you haven't eaten in a while, the liver breaks down stored glycogen into glucose to keep your glucose level within a normal range. In type 2 diabetes, this process doesn't work well.
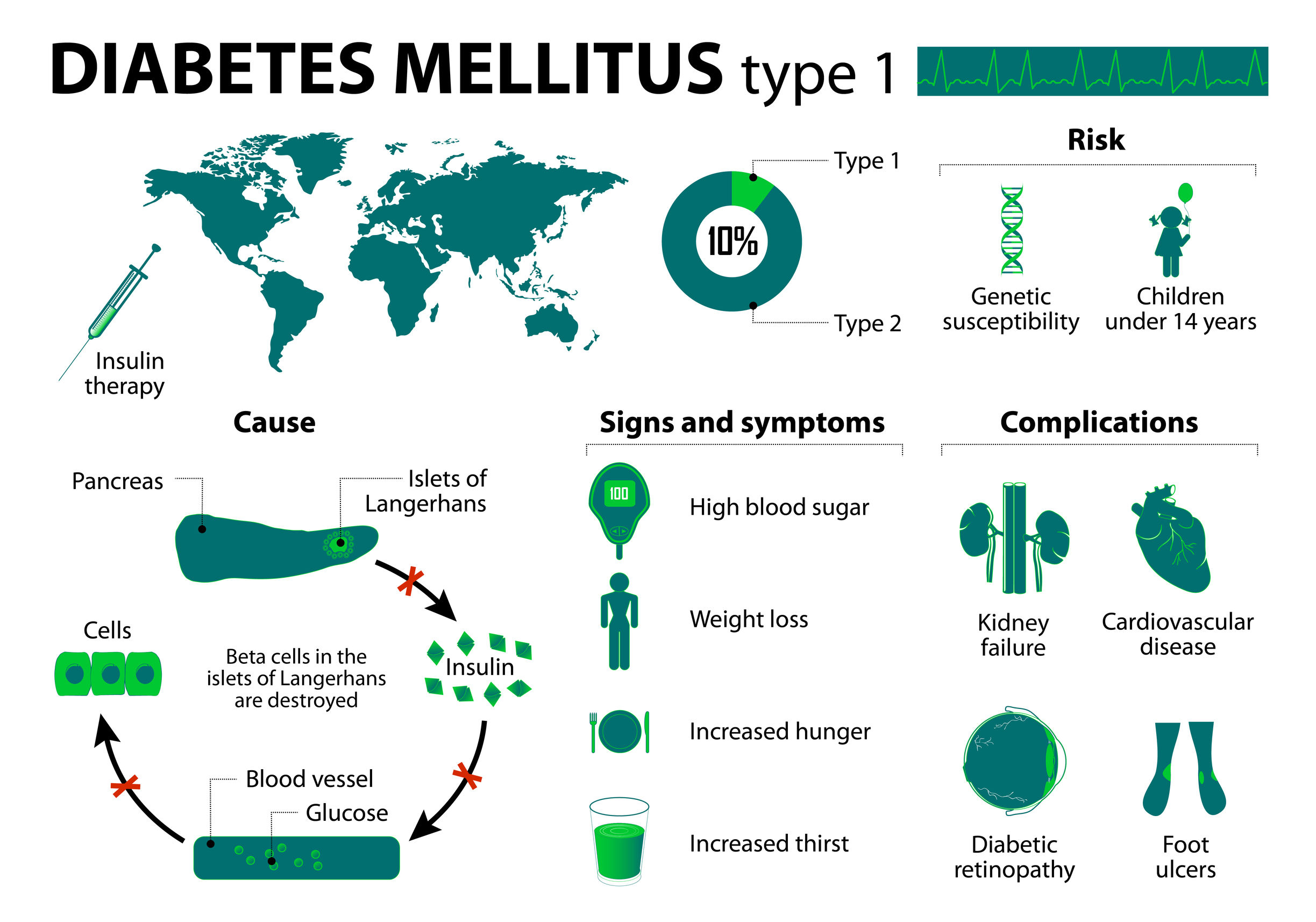
Causes and Risk Factors
Signs and Symptoms
Treatment
Lifestyle Modifications For Diabetes
How About Prevention?
The Bottom Line
- Basically, type 1 diabetes occurs because the pancreas cannot produce enough insulin; in contrast, type 2 diabetes happens due to insulin resistance. The symptoms of type 1 and type 2 diabetes are similar, with only a few differences, such as when and how fast they develop. Treatment for type 1 diabetes requires insulin, either through injections o...
Are You Worried About Diabetes?