
Therapy
This result clearly shown that ampicilin is the most effective antibiotic to inhibit the growth of E.coli. Besides that, E.coli is a gram negative bacteria.
Self-care
coli?
- Drink clear fluids. Drink clear fluids throughout the day. ...
- Replace electrolytes. E.coli toxins cause the intestines to dump electrolytes as well as water, so drink broths and soups.
- Practice good hygiene. Remember that as long as the symptoms last, you are shedding E. ...
- Rest. Fighting infection wears out the body, so give the body plenty of bed rest. ...
Nutrition
Place the pot with the water to the heat source. Wait until the water begins to boil. According to the the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, bringing water to rolling boil for one minute is very effective in killing E. coli. Turn off the heat source and let the water cool down before drinking it.
What is the most effective antibiotic against E coli?
One strain, E. coli O157:H7, produces a powerful toxin (poison), and can cause severe illness, kidney failure and even death. The symptoms of E. coli O157:H7 are diarrhea or bloody diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea, and malaise.
What antibiotics are used to treat E coli?
Does boiling water get rid of E coli?
How dangerous is ecoli in the sputum?
See more
What is the best treatment for E. coli?
Antibiotics can be an effective treatment for E. coli infections that reside outside of the digestive system, like urinary tract infections. But there is no specific drug treatment recommended for a STEC infection. Antibiotics should not be used to treat an E.
How can E. coli outbreaks be prevented?
Thoroughly wash hands, counters, cutting boards, and utensils after they touch raw meat. Avoid raw milk, unpasteurized dairy products, and unpasteurized juices (such as fresh apple cider). Don't swallow water when swimming and when playing in lakes, ponds, streams, swimming pools, and backyard “kiddie” pools.
Can E. coli be treated without antibiotics?
Symptoms usually last 5 to 10 days. People with mild symptoms usually recover on their own without treatment. Antibiotics are not helpful for treating E. coli O157 infections, and may even increase the likelihood of developing HUS.
What is the source and control for E. coli?
Avoid cross contamination i.e. spreading bacteria from a raw food item to a ready-to-eat or cooked food item, by for example, using separate cutting boards for raw meat and cooked meat or fresh vegetables and wash the cutting board with soap in between the handling of raw and ready-to-eat food.
What antibiotic treats E. coli?
Which medications in the drug class Antibiotics are used in the treatment of Escherichia coli (E coli) Infections?Antibiotics. ... Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim, Bactrim DS, Septra DS, Sulfatrim) ... Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) ... Levofloxacin (Levaquin) ... Amoxicillin (Moxatag) ... Aztreonam (Azactam)More items...
What happens if E. coli goes untreated?
They develop symptoms that last longer (at least a week) and, if not treated promptly, the infection may lead to disability or death. Later or late symptoms of E. coli infections may include: Hemorrhagic diarrhea (large amounts of blood in the stools)
Can probiotics help E. coli?
The most effective single-strain probiotics against E. coli strains were Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 and Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938. The most effective multi-strain probiotics contained lactobacilli, bifidobacteria and enterococci strains, thus proving that most effective probiotics against E.
How to get rid of E. coli in urine?
Drinking water (especially after intercourse) helps dilute urine and spur more frequent urination, which flushes E. coli from the urinary tract. Avoid diaphragms or spermicides. These can contribute to bacterial growth and kill the good bacteria that work to protects against UTIs.
Where is E. coli high risk?
Preventing E. coli–Related Traveler’s Diarrhea. Many areas of Central and South America, Mexico, Africa, the Middle East, and most of Asia are considered high-risk destinations for traveler's diarrhea. (There is some risk when traveling to Eastern Europe and a few Caribbean islands as well.)
What is the name of the bacteria that causes diarrhea?
Usually, traveler’s diarrhea occurs when an individual ventures to a developing country and is then exposed to bacteria (most often a strain of E . coli dubbed enterotoxigenic E. coli, or ETEC) via food or water to which their body has little to no familiarity.
How to stop vomiting from a syringe?
These include apple and pear juices, caffeine, alcohol, spicy food, dairy, fatty foods, and high-fiber foods. Gradually add bland food into your diet. Start with items like soda crackers, toast, eggs, and rice.
Does E. coli require antibiotics?
coli infections caused by Shiga toxin–producing E. coli, or STEC — which spurs an estimated 265,000 foodborne infections each year in the United States — does not require antibiotic treatment. ( 1)
Does hand sanitizer prevent E. coli?
While opting for a hand sanitizer may seem like a smart choice when no running water is close by, know that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved any products claiming to prevent E. coli infection. ( 9) It’s also very important to follow certain food preparation and cooking rules.
Can pregnant women get E. coli?
Preventing Intestinal E. coli Infection and Its Complications. While preventive measures are the same for everyone, know that pregnant women, newborns, children, the elderly, and individuals who have a compromised immune system have a higher risk of contracting a foodborne E. coli illness.
What is the treatment for E. coli?
coli is the cause of a different type of infection such as a urinary tract infection, blood infection, or respiratory infection, your treatment will likely include antibiotics. Because these types of infection with E. coli are less common, your healthcare provider should be closely involved in managing your care and determining ...
How to prevent E. coli outbreak?
E. coli outbreaks can occur anywhere and affect anyone. Using good hand hygiene and food preparation habits can reduce the risk of spreading the bacteria and making others sick. Although E. coli can be serious and many people worry about contracting this infection, most of the time it resolves on its own within a few days and doesn't require additional treatment. If you have symptoms that concern you, it's always best to check with your healthcare provider to figure out what is best for you.
What is the most serious E. coli infection?
One of the more serious complications from an E. coli infection is hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS). 2 This occurs when kidney function diminishes following a GI illness. It occurs in 5% to 10% of people who have STEC infections. 1
What are the symptoms of E. coli?
The most common type of E. coli that causes illness is Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC). 1 The common symptoms of gastrointestinal (GI) disease caused by STEC are: 1 Diarrhea (may be bloody) 2 Stomach cramps 3 Vomiting 4 Occasional low-grade fever (usually not over 101 Fahrenheit)
How is E. coli spread?
E. coli is spread through the fecal-oral route, meaning tiny particles of fecal matter that contain E. coli are ingested by a person—usually through food or water—and they then become ill. Although it sounds disgusting, it is quite common and it is how most foodborne illnesses are spread. 4 .
What is the incubation period of E. coli?
The incubation period is defined as the time between exposure to the germs and the onset of symptoms. Shiga toxin-producing E. coli is to blame for many foodborne illness outbreaks. The bacteria may live in the intestinal tracts of animals and is then spread to foods that humans eat (such as leafy vegetables) when manure is used as fertilizer ...
Where does E. coli live?
Most pathogenic (illness-causing) E. coli live in the gastrointestinal tracts of animals such as cattle, goats, deer, and elk. They do not make the animals sick but when they are spread into the environment through the feces of these animals, they can contaminate the food we eat, causing a variety of symptoms.
How is STEC transmitted?
It is transmitted to humans primarily through consumption of contaminated foods, such as raw or undercooked ground meat products, raw milk, and contaminated raw vegetables and sprouts. STEC produces toxins, known as Shiga-toxins because of their similarity to the toxins produced by Shigella dysenteriae.
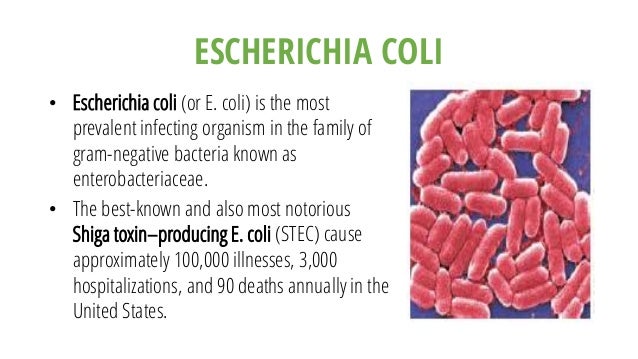
Is E. coli a bacterium?
Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a bacterium that is commonly found in the gut of humans and warm-blooded animals. Most strains of E. coli are harmless. Some strains however, such as Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC), can cause severe foodborne disease. It is transmitted to humans primarily through consumption of contaminated foods, such as raw or undercooked ground meat products, raw milk, and contaminated raw vegetables and sprouts.
How to get rid of E. coli in feces?
Make sure that you don’t use the same bathroom as other family members. If you must, always clean bathroom surfaces with disinfectant after use. Wash your hands regularly throughout the day, especially after using the restroom. Finally, do not prepare food for other people or touch any utensils other people may use for eating.
What causes death from E. coli?
Death caused by E. coli infections is usually due to hemolytic uremic syndrome. The Shiga toxin is absorbed by the intestines and enters the bloodstream. There, the toxin kills off red blood cells, causing anemia, and platelets, the blood cells responsible for clotting.
What is E. coli?
Enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC) invades intestinal cells and causes watery diarrhea and fever. Enteroinvasive E. coli is a rare form of E. coli that does not produce toxins. Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) are bacteria that both attach to the intestinal lining and invade intestinal cells.
How long does E. coli last?
An infection with E. coli usually produces symptoms in about three days following the exposure to the bacteria. Symptoms can last for five to ten days. E. coli that produce Shiga or Shiga-like toxins will usually cause watery diarrhea for two or three days followed by bloody diarrhea for another seven days.
How many Escherichia coli infections are spread from person to person?
Person-to-person contact. Although animals are the main source of Escherichia coli infections, anywhere from 10% to 15% of infections are spread from person to person. The most common cause of person-to-person spread is poor hygiene.
What is the nastiest E. coli bug?
Still, the nastiest E. coli bugs are the strains found in the colon that can cause serious and even fatal intestinal infections. When the news covers stories about E. coli outbreaks sending people to the hospital, or resulting in death, it’s these more infectious E. coli strains they’re reporting on.
How is E. coli spread?
The infectious strains of E. coli normally live in animals but are spread to humans through the ingestion of animal feces in contaminated food or water.
What is the Department of Agriculture's plan to prevent E. coli outbreaks?
In an effort to help prevent such a large outbreak from happening again, the Department of Agriculture implemented new regulations a few years later, which were designed to help prevent contaminated meat and poultry in processing plants from reaching the public. E. coli Outbreaks in the United States.
How long does it take to get E. coli?
Up to 22 days can pass from the time that the first individual falls ill from a potential E. coli outbreak to the time the public becomes aware of it. Here’s why: 1 Time lag for symptoms to develop For example, it can take up to three days after consumption of food contaminated with E. coli O157 for a person to fall ill. 2 Delay in calling the doctor The time between experiencing the first symptoms of E. coli illness until a person seeks medical care is typically one to five days. 3 Time to diagnosis It can take one to three days to get lab results from a provided stool sample. 4 Shipping samples It can take up to seven days for a laboratory sample to arrive at a state public health department where DNA fingerprinting takes place. 5 DNA fingerprinting The start-to-finish process of DNA fingerprinting can take two to four days. ( 12)
How many people have been affected by E. coli in Canada?
There were also 22 people affected in Canada. To help prevent any additional cases of E. coli infections, the CDC advised the public to refrain from buying and consuming all romaine lettuce and to discard any romaine in their homes.
How long does it take for E. coli to show symptoms?
Delay in calling the doctor The time between experiencing the first symptoms of E. coli illness until a person seeks medical care is typically one to five days.
How many E. coli outbreaks have there been in the US?
In the United States, there have been at least two E. coli outbreaks each year since 2009. (1) But only about 20 percent of E. coli cases occur as part of a recognized outbreak.
What is a foodborne disease outbreak?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), two or more individuals need to have become ill through contact with the same contaminated beverage or food, like raw or undercooked hamburger, spinach, or romaine, for the event to be called a foodborne disease outbreak. ( 1)
When was E. coli first discovered?
Scientists first recognized E. coli O157 as a pathogen in 1982. But the public had little awareness of the bacteria until 1993, when undercooked hamburgers from the Jack in the Box fast-food chain gave E. coli O157 to more than 700 people across multiple states.
How long does it take for E. coli to go away?
Most cases of intestinal E. coli infection can be treated at home. Symptoms generally resolve within a few days to a week.
How long does E. coli last?
Symptoms can last anywhere from a few days to more than a week. Symptoms of a severe E. coli infection may include: bloody urine. decreased urine output. pale skin. bruising. dehydration. Call your doctor if you experience any of these severe symptoms. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
What is the name of the bacteria that live in the intestines?
E. coli is a type of bacteria that normally live in the intestines of people and animals. However, some types of E. coli, particularly E. coli O157:H7, can cause intestinal infection. E. coli O157:H7 and other strains that cause intestinal sickness are called Shiga toxin–producing E. coli (STEC) after the toxin that they produce.
How long does it take for diarrhea to get better?
You should see your doctor if: You have diarrhea that isn’t getting better after four days, or two days for an infant or child. You have a fever with diarrhea.
What are the symptoms of intestinal infection?
Symptoms of intestinal infection include diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever. More severe cases can lead to bloody diarrhea, dehydration, or even kidney failure. People with weakened immune systems, pregnant women, young children, and older adults are at increased risk for developing these complications.
How long does it take for E. coli to show symptoms?
coli. This is known as the incubation period. Once symptoms appear, they usually last around 5 to 10 days.
What are the risk factors for E. coli?
While anyone can experience an E. coli infection, some people are more at risk than others. Some risk factors include: Age: Older adults and young children are more likely to experience serious complications from E. coli.
How long does it take for E. coli to recover?
Healthy adults usually recover from infection with E. coli O157:H7 within a week. Young children and older adults have a greater risk of developing a life-threatening form of kidney failure.
What are the risk factors for E. coli?
coli can affect anyone who is exposed to the bacteria. But some people are more likely to develop problems than are others. Risk factors include: Age. Young children and older adults are at higher risk of experiencing illness caused by E. coli and more-serious complications from the infection.
What is the E. coli strain O157?
The E. coli O157:H7 strain belongs to a group of E. coli that produces a powerful toxin that damages the lining of the small intestine. This can cause bloody diarrhea. You develop an E. coli infection when you ingest this strain of bacteria.
Where does E. coli live?
Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria normally live in the intestines of healthy people and animals. Most types of E. coli are harmless or cause relatively brief diarrhea. But a few strains, such as E. coli O157:H7, can cause severe stomach cramps, bloody diarrhea and vomiting. You may be exposed to E. coli from contaminated water or food — ...
Can you get E. coli from a pool?
No vaccine or medication can protect you from E. coli -based illness, though researchers are investigating potential vaccines. To reduce your chance of being exposed to E. coli, avoid swallowing water from lakes or pools, wash your hands often, avoid risky foods, and watch out for cross-contamination.
Does washing produce remove E. coli?
Washing produce may not get rid of all E. coli — especially in leafy greens, which provide many places for the bacteria to attach themselves to. Careful rinsing can remove dirt and reduce the amount of bacteria that may be clinging to the produce.
Can E. coli cause a weakened immune system?
People who have weakened immune systems — from AIDS or from drugs to treat cancer or prevent the rejection of organ transplants — are more likely to become ill from ingesting E. coli. Eating certain types of food.
What to do if you touch raw meat?
Thoroughly wash hands, counters, cutting boards, and utensils after they touch raw meat. Avoid raw milk, unpasteurized dairy products, and unpasteurized juices (such as fresh apple cider). Don’t swallow water when swimming and when playing in lakes, ponds, streams, swimming pools, and backyard “kiddie” pools.
Is E. coli a disease?
Most E. coli are harmless and are actually an important part of a healthy human intestinal tract. However, some E. coli can cause diarrhea, urinary tract infections, respiratory illness, bloodstream infections, and other illnesses.

Overview
Symptoms
Sources and Transmission
Prevention
Specialist to consult
Who Response
- To diagnose illness caused by E. coli infection, your doctor sends a sample of your stool to a laboratory to test for the presence of E. coli bacteria. The bacteria may be cultured to confirm the diagnosis and identify specific toxins, such as those produced by E. coliO157:H7.