Treatment processes
- Thickening. A sewage sludge thickener. Thickening is often the first step in a sludge treatment process. Sludge from...
- Sidestream treatment technologies. Sludge treatment technologies that are used for thickening or dewatering of sludge...
- Composting. Composting is an aerobic process of mixing sewage sludge with agricultural byproduct sources of...
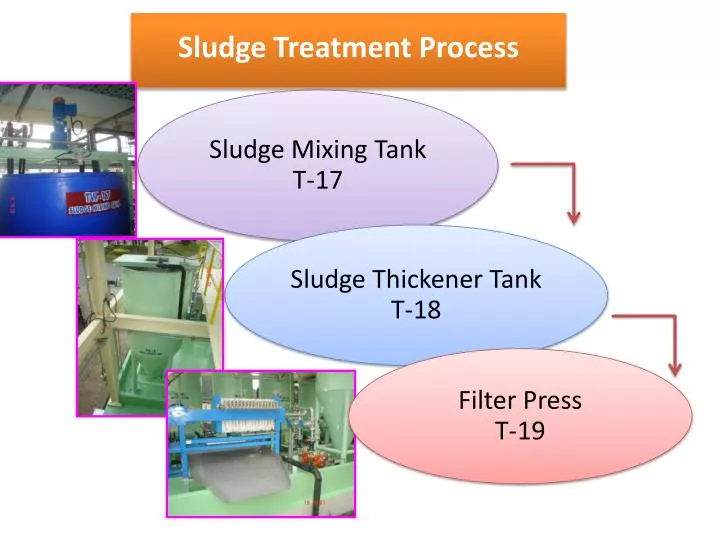
- Step 1 – Sludge Thickening. The first step in the sewage sludge treatment plan is called thickening. ...
- Step 2 – Sludge Digestion. After amassing all the solids from the sewage sludge begins the sludge digestion process. ...
- Step 3 – Dewatering. ...
- Step 4 – Disposal.
What are the methods of treatment of sludge?
Jul 23, 2019 · The sludge treatment methods mainly include sanitary landfill, land use, incineration, sludge drying, fertilizer production, lime addition and other methods.
What is sludge in sewage treatment plant?
Oct 28, 2019 · At present, the commonly used sludge treatment schemes include: concentration, sludge conditioning, anaerobic digestion, dehydration, composting and other treatment technologies. As for aerobic digestion, wet oxidation, disinfection, thermal drying, incineration, low temperature pyrolysis, etc. stage. Industrial sludge type and characteristics
What technologies are used to treat faecal sludge?
Mechanical Treatment Options • The technologies used to treat wastewater sludges are also applicable for Faecal Sludge namely: 1.Belt Filter Press 2.Frame Filter Press 3.Screw Press 4.Centrifuge • Advantages of mechanical treatment options …
What is sludge conditioning and how does it work?
Treatment processes Thickening. A sewage sludge thickener. Thickening is often the first step in a sludge treatment process. Sludge from... Sidestream treatment technologies. Sludge treatment technologies that are used for thickening or dewatering …

What methods are used to treat sludge?
Many sludges are treated using a variety of digestion techniques, the purpose of which is to reduce the amount of organic matter and the number of disease-causing microorganisms present in the solids. The most common treatment options include anaerobic digestion, aerobic digestion, and composting.
What are the 4 steps of wastewater treatment?
Treatment StepsStep 1: Screening and Pumping. ... Step 2: Grit Removal. ... Step 3: Primary Settling. ... Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge. ... Step 5: Secondary Settling. ... Step 8: Oxygen Uptake. ... Sludge Treatment.
What is sludge treatment process?
Sludge from municipalities (often called sewage sludge) is a byproduct of wastewater treatment. It is normally a mix of organic matter from human waste, food waste particles, microorganisms, trace chemicals and inorganic solids from products and medicine we use, together with water bound to these materials.
What are the different types of sludge?
Types of SludgeDrinking Water Sludge. This is the sludge obtained from drinking water treatment plants or tanks. ... Faecal Sludge. It is the sludge collected from pit latrines, onsite sanitation systems or septic tanks. ... Industrial Wastewater Sludge. ... Sewage Sludge.
What are the 3 types of sewage treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment. In some applications, more advanced treatment is required, known as quaternary water treatment.Dec 6, 2018
What are the 3 stages of sewage treatment PDF?
Wastewater is treated in 3 phases: primary (solid removal), secondary (bacterial decomposition), and tertiary (extra filtration).Jan 3, 2021
What are the main steps in sewage treatment?
The Wastewater Treatment ProcessStage One — Bar Screening. ... Stage Two — Screening. ... Stage Three — Primary Clarifier. ... Stage Four — Aeration. ... Stage Five — Secondary Clarifier. ... Stage Six — Chlorination (Disinfection) ... Stage Seven — Water Analysis & Testing. ... Stage Eight — Effluent Disposal.May 3, 2021
What is sludge example?
Sludge definition Sludge is a substance that is between solid and liquid form. An example of sludge is a mass of mud formed in a river bed after a flood. An example of sludge is the treated material from a sewage plant.
What is sludge in wastewater treatment class 7?
Sludge is the collected solid waste from the wastewater during the treatment in water treatment plant. Sludge is decomposed in a separate tank by the anaerobic bacteria. Activated sludge is used as manure.Sep 25, 2019
How many types of sludge are present?
Explanation: There are two types of sludge present, primary and secondary sludge. Primary sludge includes settleable solids removed during primary treatment in primary clarifiers.
What type of waste is sludge?
Sewage sludge is the residual, semi-solid material that is produced as a by-product during sewage treatment of industrial or municipal wastewater.
Which is the first step in the sludge treatment process?
Explanation: Thickening is often the first step in a sludge treatment process. Primary or secondary clarifier sludge may be stirred (often after addition of clarifying agents) to form larger, more rapidly settling aggregates. 9. What is the percentage of thickness that can be achieved for primary sludge?
4 Objectives of Fecal Sludge Treatment
A sanitation system deals with human excreta from the time it is generated until it is used or disposed of safely. The fourth component of a non-sewered sanitation system addresses treating fecal sludge to reduce the health and environmental risks.
What Are the Objectives of Treatment?
The type and level of treatment will depend on the final goal for the fecal sludge. There are four main treatment objectives: (1) pathogen inactivation, (2) dewatering, (3) stabilization, and (4) nutrient management.
What is sludge treatment?
The sludge treatment generally includes landfill, fertilizer, power generation, heating, etc. method. So let’s talk about the specifics of the sludge treatment methods, and what are the different treatment methods.
How to treat sludge in China?
There are three traditional sludge treatment methods: incineration, landfill and resource utilization. Many countries use incineration technology, but the investment is huge, which is easy to cause air pollution; landfill is used in China, but it needs to occupy a large amount of land, and it will cause secondary pollution of the environment. Domestic and other large and medium-sized cities in China have few land regeneration resources. This method has been adopted for a long time. Chen Liqiao said that the prospect of treating sludge with microorganisms is broad. Through the on-site test and practical application of the sewage treatment plant, the economic benefit of about 150 yuan can be obtained for each ton of sludge treated. In addition, the use of microbial aerobic fermentation can also eliminate the foul odor of the sludge, effectively control the secondary pollution of the sludge, and the environmental benefits are also significant.
What is sludge drying?
Sludge drying. Sludge drying is a treatment method that uses artificial heat source to deep dewater sludge with industrial equipment. Although the direct result of sludge drying is the decrease of sludge moisture content (dehydration), its application purpose and effect are compared with mechanical dewatering. There are big differences.
Can you incinerate sludge without drying it?
It is not only difficult to directly incinerate without drying the sludge, but it is also extremely uneconomical in terms of energy consumption. The sludge treatment method with incineration as the core is one of the most thorough sludge treatment methods.
What is sludge processing?
Overview of sludge processing. Sludge is the main waste stream generated from water purification, both water for drinking and wastewater for environmental discharge. It requires processing to reduce: its volume, and so the cost of subsequent haulage and disposal, the risk it poses to public health, primarily from the pathogenic micro-organism ...
How is sludge reduced?
There are essentially two methods by which the volume of sludge is reduced: consolidation, which reduces the sludge volume by removing the water along with the associated dissolved solids, and. destruction, in which the organic carbon component of the sludge is either oxidised, ultimately to carbon dioxide, or reduced, predominantly to methane.
Does stabilization reduce sludge volume?
Stabilisation through chemical dosing (specifically lime dosing) does not reduce the sludge volume. All other methods which are termed ‘stabilisation’ either substantially reduce the water content ( thermal drying ), or else thermally or biologically degrade the organic matter ( thermochemical and digestion processes respectively). Both biological and thermochemical treatment can be carried out in the presence or absence of oxygen, and both effectively stabilise the sludge. Both treatment types also recover a useful resource in the form of either a combustible gas or thermal energy directly.
What is the difference between thickening and dewatering sludge?
Sludge consolidation processes can be categorised as either thickening or dewatering, depending on the extent of water removal. Thickened sludge retains the free-flowing liquid-like properties of sludge. Dewatered sludge (called cake) has a higher suspended solids concentration.
How is water removed from sludge?
Water is removed from sludge by: allowing the solids to settle or encouraging them to float and removing the resulting clarified supernatant water, allowing the water to drain from the solids through a porous retaining material, or else forcing the water from the sludge under pressure through the porous material,
Is sludge a resource?
Sludge as a resource. While sludge is essentially a was te product, there is increasing focus on its potential as a resource (i.e. sludge valorisation ), specifically with reference to its: nutrient content (phosphate and nitrate).
What is cake sludge?
Dewatered sludge (called cake) has a higher suspended solids concentration. The cake does not flow like a liquid and so cannot be pumped. It must instead be conveyed by a conveyor belt, Archimedean screw, or mechanical earth-moving equipment such as a front loader. Water is removed from sludge by:
What is the best treatment for sludge?
The most common treatment options include anaerobic digestion, aerobic digestion, and composting. Sludge digestion offers significant cost advantages by reducing sludge quantity by nearly 50% and providing biogas as a valuable energy source.
What is sewage sludge treatment?
Dried, anaerobically digested sludge. Sewage sludge treatment describes the processes used to manage and dispose of sewage sludge produced during sewage treatment. Sludge is mostly water with lesser amounts of solid material removed from liquid sewage.
Why is incineration less common?
Incineration of sludge is less common because of air emissions concerns and the supplemental fuel (typically natural gas or fuel oil) required to burn the low calorific value sludge and vaporize residual water.
How is energy recovered from sludge?
Energy may be recovered from sludge through methane gas production during anaerobic digestion or through incineration of dried sludge, but energy yield is often insufficient to evaporate sludge water content or to power blowers, pumps, or centrifuges required for dewatering.
Where is sewage sludge reprocessed?
In the very large metropolitan areas of southern California inland communities return sewage sludge to the sewer system of communities at lower elevations to be reprocessed at a few very large treatment plants on the Pacific coast . This reduces the required size of interceptor sewers and allows local recycling of treated wastewater while retaining the economy of a single sludge processing facility and is an example of how sewage sludge can help solve an energy crisis.
What is composting sludge?
Composting is most often applied to small-scale plants with aerobic digestion for mid-sized operations, and anaerobic digestion for the larger-scale operations.
How thick is primary sludge?
Primary sludge may be thickened to about 8 or 10 percent solids, while secondary sludge may be thickened to about 4 percent solids.
What is the first step in sludge treatment?
Thickening. Thickening is usually the first step in sludge treatment because it is impractical to handle thin sludge, a slurry of solids suspended in water. Thickening is usually accomplished in a tank called a gravity thickener. A thickener can reduce the total volume of sludge to less than half the original volume.
What is sludge in sewage treatment?
The residue that accumulates in sewage treatment plants is called sludge (or biosolids). Sewage sludge is the solid, semisolid, or slurry residual material that is produced as a by-product of wastewater treatment processes . This residue is commonly classified as primary and secondary sludge. Primary sludge is generated from chemical precipitation, sedimentation, and other primary processes, whereas secondary sludge is the activated waste biomass resulting from biological treatments. Some sewage plants also receive septage or septic tank solids from household on-site wastewater treatment systems. Quite often the sludges are combined together for further treatment and disposal.
How does a thickener work?
A thickener can reduce the total volume of sludge to less than half the original volume. An alternative to gravity thickening is dissolved-air flotation. In this method, air bubbles carry the solids to the surface, where a layer of thickened sludge forms.
What is secondary sludge?
Primary sludge is generated from chemical precipitation, sedimentation, and other primary processes, whereas secondary sludge is the activated waste biomass resulting from biological treatments. Some sewage plants also receive septage or septic tank solids from household on-site ...
What is sludge digestion?
Sludge digestion is a biological process in which organic solids are decomposed into stable substances. Digestion reduces the total mass of solids, destroys pathogens, and makes it easier to dewater or dry the sludge. Digested sludge is inoffensive, having the appearance and characteristics of a rich potting soil.
Is methane a fuel?
Methane is combustible and is used as a fuel to heat the first digestion tank as well as to generate electricity for the plant. Anaerobic digestion is very sensitive to temperature, acidity, and other factors. It requires careful monitoring and control.
What is robust LCI?
A robust LCI is the groundwork for a reliable eLCA. With regards to waste treatment, the waste composition, treatment paths and technological equipment must initially be compiled. The difficulty lies in the stark variability of (i) conceivable treatment paths, (ii) the technological design of the components and (iii) the composition of the sewage sludge. Therefore, a treatment path was clearly defined for each scenario and uncertainty ranges were applied to parameters to cover deviations in the technological setup and the chemical composition.
Who is the research project Metabolon?
This work was carried out in cooperation with the Teaching and Research Centre:metabolon, a consortium of the TH Köln and BAV. The research project is financially supported by the European Commission and the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) under the slogan “Investing in our future”
Is sewage sludge sustainable?
Against the background of amended regulations, sustainable sewage sludge treatment is of increased interest. An environmentally compatible solution for the post-treatment of the digested sludge should be the main focus of plant operators and legislators. This study assessed treatment paths that are partly not yet implemented in the industrial scale or lack market maturity. The proposed options should be considered as prospective approaches that may be applied in the next years or decades.
Is phosphorous recovery mandatory in Germany?
Due to the amendment of the sewage sludge ordinance, both a thermal post-treatment and a phosphorous recovery from sewage sludge will become mandatory for large-scale wastewater treatment plants in Germany. This study analyzed four prospective treatment paths for sewage sludge by means of life cycle assessment.

Overview of Sludge Processing
Sludge Processing Methods
- There are essentially two methods by which the volume of sludge is reduced: 1. consolidation, which reduces the sludge volume by removing the water along with the associated dissolved solids, and 2. destruction, in which the organic carbon component of the sludge is either oxidised, ultimately to carbon dioxide, or reduced, predominantly to methane.
Sludge as A Resource
- While sludge is essentially a waste product, there is increasing focus on its potential as a resource (i.e. sludge valorisation), specifically with reference to its: 1. latent energy (or calorific content, which can be used to quantify its potential for methane and/or hydrogen production), and 2. nutrient content (phosphate and nitrate). There is also significant interest in, and increasing i…