The Enhanced Surface Water Treatment Rule (ESWTR) is one of the first Rules to be developed under the 1996 Amendments to the Safe Drinking Water Act. The ESWTR was promulgated in November 1998 and applies to systems using surface water (or ground water under the direct influence of surface water) serving 10,000 or more persons.
What is the Long Term 2 enhanced surface water treatment rule?
Dec 01, 2021 · The Long Term 2 Enhanced Surface Water Treatment Rule addresses the health effects associated with Cryptosporidium in surface water used as a drinking water supply. …
What are the surface water treatment rules?
Feb 03, 2022 · Long Term 1 Enhanced Surface Water Treatment Rule Documents. The Long Term 1 Enhanced Surface Water Treatment Rule (LT1ESWTR) builds on the requirements of the …
What is included in surface water treatment?
May 28, 2021 · The Interim Enhanced Surface Water Treatment Rule (IESWTR) builds on the requirements of the Surface Water Treatment Rule. IESWTR specifies treatment requirements …
What are the rules for disinfection in water systems?
Feb 02, 2022 · Guidance Manual for Compliance with the Interim Enhanced Surface Water Treatment Rule: Turbidity Provisions (PDF) (144 pp, 2980 MB, About PDF) EPA 815-R-20-004, …

Which of the following processes is required by the Surface Water Treatment Rule?
Requires most water systems to filter and disinfect water from surface water sources or GWUDI.Mar 30, 2021
What is the purpose of the Surface Water Treatment Rule?
What are the methods used in surface water treatment?
What are the four steps in treating surface water?
What does the Long Term 2 Enhanced Surface Water Treatment Rule do?
Why is chlorine added to water?
What are the 7 methods of water treatment?
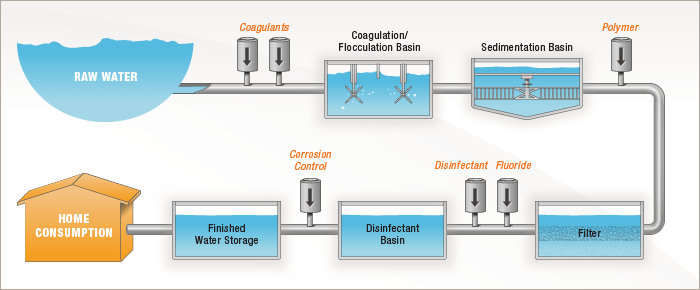
- Coagulation / Flocculation. Coagulation is adding liquid aluminum sulfate or alum and/or polymer to raw or untreated water. ...
- Sedimentation. When water and flocs undergo the treatment process, they go into sedimentation basins. ...
- Filtration. ...
- Disinfection. ...
- Sludge Drying. ...
- Fluoridation. ...
- pH Correction.
What are the 7 stages of water treatment?
What are the 5 stages of water treatment?
What are the safety rules in water purification?
What is screening and straining in water treatment?
What are the three main stages of water treatment?
What is the EPA 815-R-99-014?
Alternative Disinfectants and Oxidants Guidance Manual (PDF) (328 pp, 17000 K, About PDF) EPA 815-R-99-014, April 1999 This manual provieds technical data and engineering information on disinfectants and oxidants that are not as widely used as chlorine.
What is the IESWTR?
The Interim Enhanced Surface Water Treatment Rule (IESWTR) builds on the requirements of the Surface Water Treatment Rule. IESWTR specifies treatment requirements to address Cryptosporidium and other microbial contaminants in public water systems serving 10,000 or more persons.
What is MRDLG in water treatment?
Maximum residual disinfectant level goal (MRDLG) — the maximum level of a disinfectant added for water treatment at which no known or anticipated adverse effect pm the health of persons would occur, and which allows an adequate margin of safety. MRDLGs are nonenforceable health goals and do not reflect the benefit of the addition of the chemical for control of waterborne microbial contaminants.
What is enhanced coagulation?
Enhanced coagulation — the addition of sufficient coagulant for improved removal of disinfection byproduct precursors by conventional filtration treatment.
What is the EPA website?
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’ s (EPA’s) website provides links to the original rule language as well as the most recent guidance documents and other information for the SWTRs and Stage 1 and Stage 2 DBPRs (
What does MCL mean in water?
Maximum contaminant level (MCL) — the maximum permissible level of a contaminant in water which is delivered to any user of a public water system.
What is the purpose of the Surface Water Treatment Rules?
The purpose of the Surface Water Treatment Rules (SWTRs) is to reduce illnesses caused by pathogens in drinking water. The disease-causing pathogens include Legionella , Giardia lamblia, and Cryptosporidium.
What is surface water treatment?
The Surface Water Treatment Rules were established to protect against these pathogens. To protect public health, drinking water from lakes, rivers streams and some other sources needs to be treated. This treatment includes disinfection and, in most cases, filtration.
What is the purpose of the microbial protection provision?
Provides provisions to ensure that systems maintain microbial protection as they take steps to reduce the formation of disinfection byproducts
Why do we need to review backwash water recycling?
Requires public water systems (PWSs) to review their backwash water recycling practices to ensure that they do not compromise microbial control
What are the health risks of drinking water?
If consumed, these pathogens can cause gastrointestinal illness (e.g., diarrhea, vomiting, cramps) and other health risks. These illnesses may be severe and sometimes fatal for people with weakened immune systems. Cryptosporidium is a significant concern in drinking water because it is resistant to chlorine and other disinfectants.
Does watershed protection require filtration?
Requires that watershed protection programs address Cryptosporidium for system that are not required to provide filtration