
Coagulation water treatment process
- Coagulants. Coagulants are the chemicals that are used to removes tiny particles in water. ...
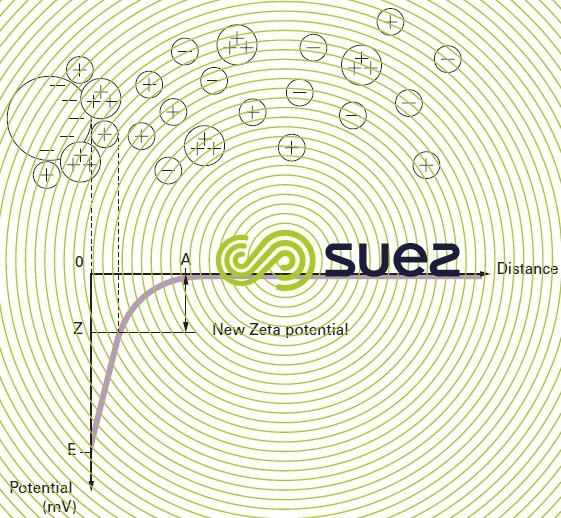
- Coagulation Mechanism. The colloidal particles carry electrical charges; normally negative charge. ...
- Factors affecting coagulation water treatment. ...
- Coagulation jar test. ...
- Conclusion. ...
What is coagulation for water treatment?
Oct 15, 2021 · What Are the Most Common Types of Coagulants? Aluminum Sulfate. Aluminum sulfate is available in several forms, including ground, kibbled or block. When added to naturally alkaline water (which ... Ferric Sulfate. Ferric Chloride. Sodium Aluminate.
What are flocculants and coagulants for wastewater treatment?
Coagulants are a category of products used to reduce water turbidity — in other words, to clarify water. They add cationic charges to neutralize the negative charges surrounding soluble particles, rendering them insoluble. Different coagulants have been used to clarify water for many years.
Is coagulant and flocculant are same?
Coagulants for Waste Water Treatment. Coagulation for waste water treatment plays a vital role in the process, allowing for solids removal and dewatering, water clarification, lime softening, and sludge thickening. With the help of other specialized chemicals and mechanical filtration methods, coagulants help companies maintain a consistent and reliable source of clean water …
What is the process of water treatment?
May 19, 2021 · Ferrous sulfate; a commonly used water coagulant. Image via Wikimedia. Water coagulants are critical to an effective water treatment process. But, with so many options now available on the market, what is the best agent for your coagulation water treatment? There are many advantages and disadvantages to electrocoagulation or coagulation processes. …
Why are coagulants used in water treatment?
In water treatment, coagulants are used to remove a wide variety of hazardous materials from water, ranging from organic matter and pathogens, to inorganics and toxic materials, like arsenic, chemical phosphorous and fluoride.
What is coagulation in water treatment process?
Coagulation is the chemical water treatment process used to remove solids from water, by manipulating electrostatic charges of particles suspended in water. This process introduces small, highly charged molecules into water to destabilize the charges on particles, colloids, or oily materials in suspension.6 days ago
What are examples of coagulants?
Examples of primary coagulants are metallic salts, such as aluminum sulfate (referred to as alum), ferric sulfate, and ferric chloride. Cationic polymers may also be used as primary coagulants.
What is the function of coagulant?
3 Coagulants. Coagulants and flocculation processes are used to remove colloidal impurities: suspended particles such as bacteria, clay, silts, and organic matter from the contaminated water. This produces large flock aggregates that can be removed from the water in subsequent clarification/filtration processes.
What are coagulants?
Coagulants are a substance which cause particles in a liquid to curdle and clot together. Particles stay suspended in water rather than settling because they carry surface electrical charges that mutually repel each other.Jan 4, 2016
What is coagulant and coagulation?
Coagulation treatment neutralizes the negative electrical charge on particles, which destabilizes the forces keeping colloids apart. Water treatment coagulants are comprised of positively charged molecules that, when added to the water and mixed, accomplish this charge neutralization.
What are natural coagulants?
They are mainly composed of polymers of natural origin extracted from plants, algae or animals. Among these are polysaccharides and water soluble substances that act as coagulation and / or flocculation agents.
What is the most commonly used coagulant?
Iron and aluminium salts are the most widely used coagulants but salts of other metals such as titanium and zirconium have been found to be highly effective as well.
What is coagulant made of?
The most common coagulants are salts of aluminum or trivalent iron, with aluminum being more commonly used.
What Coagulants Are Used In Water Treatment?
In order to use coagulation in your water treatment, you have to apply coagulants to chemically initiate the process. These specialty chemicals should be formulated to meet your specific water quality application based on a particle analysis of your dissolved/suspended solids.
Coagulant Applications
Control Alkalinity and pH Changes: Our pond, pH control, and caustic chemicals allow you to easily comply with water quality standards in situations that require implementing chemical stability and neutralization of bases and acids.
What is a coagulant in water treatment?
Water treatment coagulants are comprised of positively charged molecules that, when added to the water and mixed, accomplish this charge neutralization. Inorganic, organic, or a combination of both coagulant types are typically used to treat water for suspended solids removal. When an inorganic coagulant is added to water containing ...
What is the most widely used class of organic coagulation chemicals?
Polyamine and PolyDADMAC. These are the most widely used classes of organic coagulation chemicals. They function by charge neutralization alone, so there is no advantage to the sweep-floc mechanism. Polyamines will generally treat higher turbidity raw water (approximately >20 NTU) effectively.
What are some examples of flocculants?
Examples of ChemTreat flocculants include low-, medium-, and high-molecular weight polymers.
Is aluminum sulfate a chemical?
It is manufactured as a liquid, and the crystalline form is dehydrated from the liquid. Alum is one of the most commonly used water treatment chemicals in the world.
Is aluminum chloride the same as alum?
Generally, aluminum chloride works similarly to alum, but is usually more expensive, hazardous, and corrosive. Because of this, it is normally a distant second choice to alum. ChemTreat has aluminum chloride available as a liquid.
What is a sweep floc?
This sweep-floc precipitate readily adsorbs organic materials such as oil and grease. The precipitate generally dewaters to low moisture concentration, making this choice of coagulant particularly well-suited to unit operations that generate hazardous sludge, such as DGF and IGF units in oil refineries. This self-precipitating chemistry is generally significantly more expensive to use than inorganic coagulant chemistry, but it can be economical when sludge removal and disposal costs are factored in.
Is ferric chloride a coagulant?
Ferric chloride is generally the least expensive inorganic coagulant, because it is generated as a waste material from steel-making operations (waste “pickle liquor”). However, it is by far the most corrosive and hazardous inorganic coagulant, and its use is limited to facilities equipped to handle it safely.
What is the process of removing solids from water?
Wastewater coagulation. Coagulation is the chemical water treatment process used to remove solids from water, by manipulating electrostatic charges of particles suspended in water. This process introduces small, highly charged molecules into water to destabilize the charges on particles, colloids, or oily materials in suspension.
Is there a coagulant for wastewater treatment?
There are many coagulants available for wastewater treatment, for a deep dive check out. Below is an introduction to the coagulants representing the variety of different formulations and charge densities.
What is a 10 mm particle?
Particles over 100μm are generally considered “settleable solids” and readily settle out of suspension. Particles sized 10-100μm are generally considered “turbidity” and are often addressed in a wastewater treatment system with coagulation. Particles smaller than 10μm are “colloidal particles”, which are almost always treated with coagulation ...
What is a jar test?
Jar testing is an essential tool for comparing products, optimizing performance, estimating treatment costs, and planning operations.
What are some examples of coagulants?
Particles in water carry an electrostatic charge on their surface. Common examples include clay, silica, iron, paints, and even oil.
What are some examples of suspended particles?
Common examples include clay, silica, iron, paints, and even oil. These small, suspended particles are stabilized in suspension & difficult to remove via mechanical methods. A suspension of solids in water typically contains a variety of particles sizes. A lab analysis of “particle size distribution” will help define the size ...
What is a colloidal particle?
Particles smaller than 10μm are “colloidal particles”, which are almost always treated with coagulation because it is quite expensive to remove small particles using only mechanical water treatment like filtration. Colloidal particles are further classified as hydrophobic and hydrophilic colloids.
Why are polymers important in wastewater treatment?
As you can tell, polymers play an important role in wastewater treatment. Besides separating solids from liquids, they also help thicken sludge and dewater contaminated material for easier handling and disposal. Removing the water content from a waste sludge can change the waste properties from liquid to solid waste.
What is wash water?
The wash water picks up dirt, clay, and silt during the washing process. To reuse or safely discharge this wash water, the solids need to be separated from the water. This opens in a new window. Many aggregate producers use settling ponds to hold the wastewater and allow sedimentation.
What is a cationic polymer?
Cationic polymers have a positive charge and are often used to settle organic solids such as animal waste or vegetation. Cationic polymers are used in dredging, municipal wastewater treatment plants, food processing, agricultural and dairy applications.
What are polymers used for?
However, they don’t just make products. Specific polymers are widely used in wastewater treatment to remove suspended solids and/or contaminants from the water. They’re used regularly in municipal, industrial, and stormwater treatment systems, but many consumers aren’t aware of their importance. Polymers are nothing short of incredible.
What industries use polymers?
Industries That Use Polymers to Treat Wastewater. Almost any industry that needs to remove solids from their wastewater stream can use polymers in their treatment process. For instance, aggregate producers use water to wash the sand, gravel, or other aggregates they produce.
What is the next step in a chemical reaction?
The next chemical reaction is called flocculation, which helps create even larger flocs or macro-flocs. In this step, chemical products called flocculants help bring together the coagulated particles to form longer and larger particle chains.
