Is insulin the preferred treatment for A1c?
• Insulin can be added to metformin (first-line therapy) if the A1C target is not achieved after 3 months. • Due to the progressive nature of T2D, many patients eventually require and benefit from insulin therapy. American Diabetes Association.
What is the normal range for A1c level?
What's a Normal Hemoglobin A1c Test? For people without diabetes, the normal range for the hemoglobin A1c level is between 4% and 5.6%. Hemoglobin A1c levels between 5.7% and 6.4% mean you have...
How to lower your A1C?
Tips for lowering A1C level
- Make a food plan. Eating the right foods is essential to lowering your A1C, so you want to make a plan and stick to it.
- Measure portion sizes. It’s important to choose not just the right foods to lower your A1C but also the right amount. ...
- Track carbs. ...
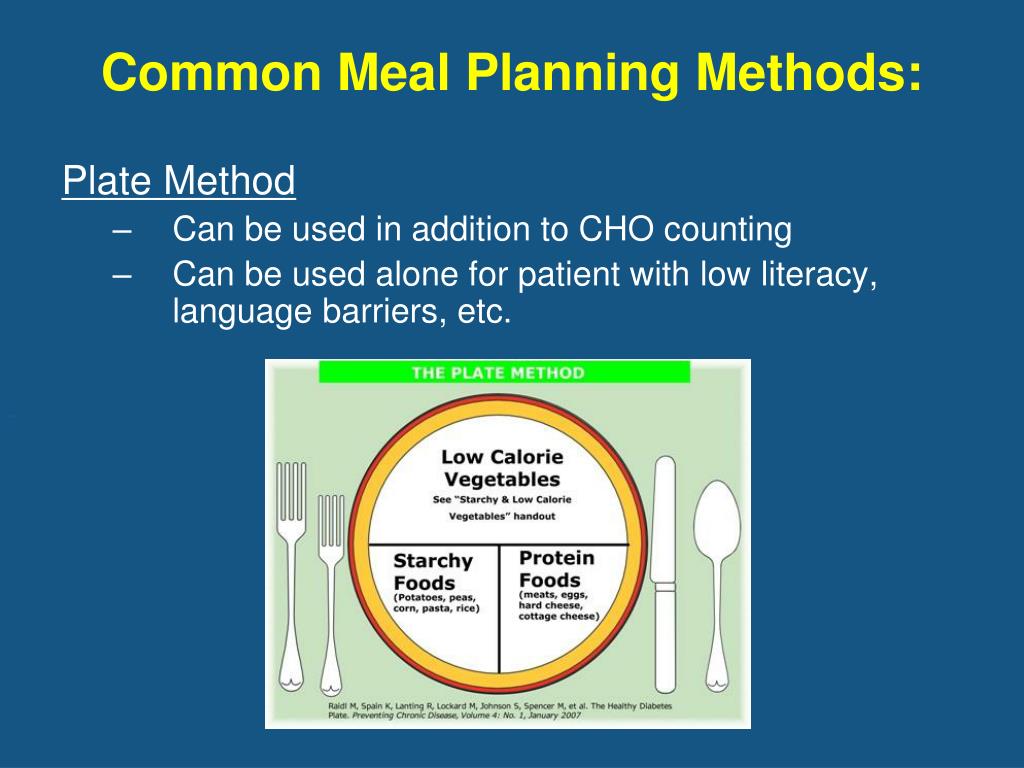
- Plate method. ...
- Have a realistic weight loss goal. ...
- Exercise plan. ...
- Take medications. ...
- Supplements and vitamins. ...
What A1c level is considered diabetic?
What A1C goal should I have?
- limited life expectancy
- long-standing diabetes and trouble reaching a lower goal
- severe hypoglycemia or inability to sense hypoglycemia (also called hypoglycemia unawareness)
- advanced diabetes complications such as chronic kidney disease, nerve problems, or cardiovascular disease
.2.gif)
What is the goal of A1C?
Your A1C Goal The A1C test, also called a hemoglobin A1c test (HbA1c), is a common blood test used to gauge your average blood sugar level over the past two to three months. Specifically, the test measures the amount of sugar attached to the protein hemoglobin in your red blood cells.
What is the A1C of type 2 diabetes?
If type 2 diabetes patients can't reach that goal with a healthy lifestyle and oral medications , they may need to start giving themselves insulin shots.
What is insulin resistance?
Patients with insulin resistance are often diagnosed with the metabolic syndrome, which predisposes them to both type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. When food is ingested, insulin is secreted by the beta cells into the bloodstream.
What does A1C 6.5 mean?
A1C levels of 6.5 percent or higher on two separate tests indicate that you have diabetes. Talk to your healthcare provider about the appropriate A1C level for you. People who have previously-diagnosed diabetes are usually encouraged by their endocrinologist to aim for personalized A1C levels below 7 percent.
How many people with diabetes take insulin?
Of adults with diabetes, only 14% use insulin, 13% use insulin and oral medication, 57% take oral medication only, and 16% control blood sugar with diet and exercise alone, according to the CDC. The point is to get blood sugar—which can be a highly toxic poison in the body—into the safe zone by any means necessary.
What are the two options for type 2 diabetes?
As recently as 1994, there were only two options for patients with type 2 diabetes: insulin and the sulfonylureas (such as glyburide and glipizide). The good news is that today, seven totally different classes of medications are available, as well as much better insulins.
What is the goal of insulin?
The goal is to mimic the pancreas The different types of insulin mimic the natural rhythm of a healthy pancreas, which produces a consistent low level of the hormone and occasional bursts of insulin to cope with postmeal boosts in blood sugar.
What is the A1C level for prediabetes?
People without diabetes usually have an A1C level of between 4.5 to 5.6 percent. A1C levels of 5.7 to 6.4 percent on two separate occasions signify prediabetes. A1C levels of 6.5 percent or higher on two separate tests indicate you have diabetes.
What is the A1C test?
The A1C test, also called a hemoglobin A1C test (HbA1c), is a common blood test. Your doctor uses it to gauge your average blood sugar level over the previous two to three months. The test measures the amount of sugar attached to the protein hemoglobin in your red blood cells. Your doctor also often uses this test to diagnose diabetes ...
How long does it take for bolus insulin to work?
You take it with meals, and it starts working quickly. Rapid-acting insulin starts working in 15 minutes or less and peaks at 30 minutes to 3 hours. It remains in your bloodstream up to 5 hours.
What does A1C 6.5 mean?
A1C levels of 6.5 percent or higher on two separate tests indicate you have diabetes. Talk to your doctor about the appropriate A1C level for you. Many people who have diabetes should aim for personalized A1C levels below 7 percent. How often you need an A1C test depends on factors like prescribed changes to your insulin treatment ...
How to control blood sugar levels with type 2 diabetes?
exercise. oral medications. But sometimes switching to insulin might be the only way to get your blood sugar levels under control.
How long does insulin work?
It peaks in 4 to 12 hours, and works for up to 24 hours. Long-acting insulin begins working within 45 minutes to 4 hours. It doesn’t peak and stays in your bloodstream for up to 24 hours after injection.
How long does insulin stay in your system?
Short-acting (or regular) insulin begins working 30 minutes after injection. It peaks in 2 to 5 hours and stays in your bloodstream for up to 12 hours.
What is the normal A1C level?
A normal A1C level is below 5.7%, a level of 5.7% to 6.4% indicates prediabetes, and a level of 6.5% or more indicates diabetes. Within the 5.7% to 6.4% prediabetes range, the higher your A1C, the greater your risk is for developing type 2 diabetes. Managing Diabetes.
How often should I get my A1C?
If you have diabetes, get an A1C test at least twice a year, more often if your medicine changes or if you have other health conditions. Talk to your doctor about how often is right for you.
Why is A1C important?
It’s one of the commonly used tests to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes, and is also the main test to help you and your health care team manage your diabetes. Higher A1C levels are linked to diabetes complications, so reaching and maintaining your individual A1C goal is really important if you have diabetes.
How often should I repeat my A1C test?
Repeat the A1C test as often as your doctor recommends, usually every 1 to 2 years. If you don’t have symptoms but your result shows you have prediabetes or diabetes, get a second test on a different day to confirm the result. If your test shows you have diabetes, ask your doctor to refer you to diabetes self-management education ...
What does A1C mean?
The A1C test measures the percentage of your red blood cells that have sugar-coated hemoglobin.
What is the goal for diabetes?
The goal for most people with diabetes is 7% or less. However, your personal goal will depend on many things such as your age and any other medical conditions. Work with your doctor to set your own individual A1C goal.
Where to get A1C blood test?
The test is done in a doctor’s office or a lab using a sample of blood from a finger stick or from your arm. You don’t need to do anything special to prepare for your A1C test. However, ask your doctor if other tests will be done at the same time and if you need to prepare for them.
What is the A1C of a diabetic?
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends an A1C of 7% or below , and the American College of Endocrinology and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists recommend an A1C of 6.5% or below. If you can't lower your A1C with diet, exercise, or other medications, you may need insulin to do the job.
How to know when you need insulin?
How to Know When You'll Need Insulin. Injecting insulin above and to the side of the belly button can result in more consistent results. Injecting insulin above and to the side of the belly button can result in more consistent results. (ISTOCKPHOTO)
What is the body's resistance to insulin?
In type 2 diabetes the body is resistant to insulin. The beta cells in the pancreas churn out insulin as fast as they can to overcome this insulin resistance. This Herculean task can eventually exhaust the beta cells and diminish their ability to produce insulin, potentially resulting in them being unable to produce any insulin at all.
What is the goal of insulin?
The goal is to mimic the pancreas. The different types of insulin mimic the natural rhythm of a healthy pancreas, which produces a consistent low level of the hormone and occasional bursts of insulin to cope with postmeal boosts in blood sugar.
Can you lower your A1C with insulin?
If you can't lower your A1C with diet, exercise, or other medications, you may need insulin to do the job. There are exceptions, of course. Someone who otherwise seems to be a good candidate for insulin may not be able to manage such a regimen if he or she has limited vision and dexterity and no family support.
Does insulin mean you have failed?
Needing Insulin Doesn't Mean You've Failed to Control Diabetes. Why Insulin Use Isn't Always Permanent. If you do need insulin in the short- or long-term, your doctor may prescribe one of four different types. These vary by how quickly or slowly they reach the bloodstream (the onset), the amount of time they work at maximum strength ...
Do you need insulin if you have diabetes?
• How long you have had diabetes. • Your blood glucose level. • What other medicines you take. • Your overall health. As diabetes progresses, you may be more likely to need insulin. In type 2 diabetes the body is resistant to insulin.
Treatment Delays and Barriers
Patient and clinician factors contribute to delays in adding insulin to treatment regimens or in transitioning from oral antidiabetic agents (OADs) to insulin.
Advanced Basal Insulin Analogs and Fixed-Ratio Combinations
Advanced insulin analogs and pre-filled pen delivery devices are helping to overcome some of the barriers to insulin initiation and titration experienced by some patients and PCPs.
Current Guidelines for Insulin Initiation and Titration
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends initiation of basal insulin at 10 units/day or 0.1–0.2 units/kg/day, adjusted by 10–15% or 2–4 units once or twice weekly to reach a target fasting plasma glucose (FPG) in patients whose A1C remains uncontrolled after >3 months of triple combination therapy, whose A1C is >10%, whose blood glucose is >300 mg/dL, or who are symptomatic of hyperglycemia ( 37 ).
Insulin Titration Algorithms
A number of titration algorithms have been evaluated that aim to simplify insulin titration and enable patient empowerment through self-titration to effectively participate in the management of their disease ( 4, 39 – 42 ), the details of which are summarized in Table 1.
When Too Much Insulin Has Little Effect on Glycemic Target
Current use of basal insulin has been shaped by treat-to-target trials that have emphasized systematically titrating the insulin dose without limit until an FPG of 100–130 mg/dL is reached ( 50 ). “Overbasalization” is said to occur when FPG is uncontrolled despite uptitration of basal insulin and the A1C target remains unmet ( 51 ).
Managing Insulin Regimens in the Primary Care Setting
It is important to gain an understanding of a patient’s background and lifestyle before initiating insulin to ensure that the treatment regimen takes into account the patient’s needs and preferences as well as clinical characteristics ( 37, 56, 57 ).
Conclusion
Multiple insulin algorithms have been developed to help PCPs with insulin initiation and titration and to enable patient self-management.
When is insulin taken?
The usual treatment schedule is: The long acting insulin is typically taken at bedtime and/or morning. Nutritional insulin is taken before each meal, based on how many carbohydrates are in the meal, ...
What is correctional insulin?
Correctional insulin corrects high blood glucose before meals. Similar to nutritional insulin. Similar to nutritional insulin. Most patients with type 1 diabetes are treated with “intensive” or “basal-bolus” insulin therapy, which requires four injections a day. This method allows a great deal of flexibility with regards to the types ...
Can you produce insulin on your own?
Type 1 diabetes completely damages the pancreas, an organ responsible for making insulin. For that reason, persons with type 1 diabetes cannot produce any insulin on their own. Every patient with type 1 diabetes depends on injections of insulin so that glucose can be used as energy in the body.
Is insulin taken before or after a meal?
Nutritional insulin is taken before each meal, based on how many carbohydrates are in the meal, in addition to correctional insulin which is based on the blood glucose reading before the meal. Meeting with a dietitian can help patients learn carbohydrate counting, with specific dosing recommendations from the health care provider.