How long does it take for Vertigo to clear up?
Vertigo. Vertigo causes dizziness and makes you feel like you’re spinning when you’re not. This condition can occur for many reasons, but the most common cause is a problem with your …
How long will it take to recover from vertigo?
Nov 06, 2021 · Homeopathic remedies recommended mainly for the fight against vertigo are: – Bryonia 200ck (#ad): 5 granules under the tongue every 15 minutes for an hour during the crisis …
How long does vertigo last and can it return?
Mar 01, 2018 · Various medicines are used to help improve symptoms of vertigo. Drugs are typically more effective at treating vertigo that lasts a few hours to several days.

How many sessions does it take to cure vertigo?
How long is an episode of vertigo?
Can vertigo be fully cured?
What to do when vertigo will not go away?
- lie still in a quiet, dark room to reduce the spinning feeling.
- move your head carefully and slowly during daily activities.
- sit down straight away when you feel dizzy.
- turn on the lights if you get up at night.
- use a walking stick if you're at risk of falling.
- sleep with your head slightly raised on 2 or more pillows.
Is walking good for vertigo?
How long does it take for ear crystals to dissolve?
What cures vertigo fast?
- Start in a sitting position.
- Rapidly lie down toward the affected side and hold for one to two minutes.
- Turn your head quickly 45 degrees toward the ceiling and hold for two minutes.
- Sit back upright.
What is best medicine for vertigo?
What is the best exercise for vertigo?
Step 1: Sit at the end of your bed. When ready, turn your head 45 degrees to the right. Step 2: Lie down on your left side and remain still for 30 seconds until dizziness fades. Step 3: Sit up and wait 30 seconds.Nov 14, 2020
When should you worry about vertigo?
Can vertigo last for years?
Can BPPV last for months?
Is vertigo a dizziness?
Vertigo should be distinguished from other types of dizziness, such as imbalance (dysequilibrium) and lightheadedness (presyncope). Most cases of vertigo can be diagnosed clinically and managed in the primary care setting.
Can vertigo be a concurrent cause?
Because vertigo can have multiple concurrent causes (especially in older patients), a specific diagnosis can be elusive. The duration of vertiginous episodes and the presence or absence of auditory symptoms can help narrow the differential diagnosis ( Table 1). 1 Psychiatric disorders, motion sickness, serous otitis media, cerumen impaction, herpes zoster, and seizure disorders also can present with dizziness.
What causes vertigo in the central nervous system?
The most common causes of this condition are benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, acute vestibular neuronitis or labyrinthitis, Ménière’s disease, migraine, and anxiety disorders. Less common causes include vertebrobasilar ischemia and retrocochlear tumors. The distinction between peripheral and central vertigo usually can be made clinically ...
Does anxiety cause vertigo?
Vertigo associated with anxiety usually responds to a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor. Vertigo, a type of dizziness, is the illusion of motion, usually rotational motion. Associated symptoms include nausea, emesis, and diaphoresis. Vertigo should be distinguished from other types of dizziness, such as imbalance (dysequilibrium) ...
What is the name of the disease that causes vertigo, tinnitus, and roaring
Ménière’s disease (or endolympha tic hydro ps) presents with vertigo, tinnitus (low tone, roaring, or blowing quality), fluctuating low-frequency sensorineural hearing loss, and a sense of fullness in the ear. In this disorder, impaired endolymphatic filtration and excretion in the inner ear leads to distention of the endolymphatic compartment.
Is vertigo a sign of depression?
Vertigo commonly is associated with anxiety disorders (e.g., panic disorder, generalized anxiety disorder) and, less frequently, depression. 33, 34 Hyperventilation usually occurs and can result in hypocapnia with reversible cerebral vasoconstriction. Hyperventilation and hypocapnia may be accompanied by dyspnea, chest pain, palpitations, or paresthesias.
Why is motion sickness 9?
Motion sickness 9 is attributed to an incongruence in the sensory input from the vestibular, visual, and somato-sensory systems. Motion sickness occurs while riding in a car, boat, or airplane if the vestibular and somato-sensory systems sense movement, but the visual system does not.
How long does it take for vertigo to go away?
Your vertigo may go away on its own, with no specific treatment. For instance, people with BPPV often notice that their symptoms disappear within a few weeks or months. ( 3)
How long does vertigo last?
Drugs are typically more effective at treating vertigo that lasts a few hours to several days. People with Ménière's disease may benefit from taking diuretics, medicines that help your body get rid of salt and water. If your vertigo is caused by an infection, antibiotics or steroids may be given. Sometimes doctors recommend antihistamines, such as ...
What are the side effects of a syringe?
You should tell your healthcare provider if you have any of the following before having this therapy: 1 A neck problem 2 A back condition 3 Rheumatoid arthritis 4 A detached retina in your eye 5 Blood vessel or heart problems ( 3, 4)
Can canalith repositioning cause vertigo?
Canalith repositioning is very effective for people with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) — the most common cause of vertigo. Results vary, but some studies have shown between a 50 and 90 percent success rate. ( 2) If the crystals move back into your semicircular canals, your doctor can repeat the treatment.
What is the best medication for vertigo?
If your vertigo is caused by an infection, antibiotics or steroids may be given. Sometimes doctors recommend antihistamines, such as Antivert (meclizine) , Benadryl (diphenhydramine), or Dramamine (dimenhydrinate) to help vertigo episodes. Anticholinergics, such as the Transderm Scop patch, may also help with dizziness.
Can surgery help with vertigo?
Surgery — an uncommon treatment for special cases. Surgery isn’t a common treatment for vertigo, but it’s sometimes needed. You might require a surgical procedure if your symptoms are caused by an underlying condition, such as a tumor or an injury to your brain or neck.
What are the causes of vertigo?
For instance, people with conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, multiple sclerosis (MS), Parkinson’s disease, and anemia may develop vertigo .
How long does vertigo last?
Attacks of vertigo can develop suddenly and last for a few seconds, or they may last much longer.
Can vertigo be treated?
Some cases of vertigo improve over time, without treatment. However, some people have repeated episodes for many months, or even years, such as those with Ménière's disease. There are specific treatments for some causes of vertigo. A series of simple head movements (known as the Epley manoeuvre) is used to treat BPPV.
How do you know if you have vertigo?
Other symptoms associated with vertigo may include: 1 loss of balance – which can make it difficult to stand or walk 2 feeling sick or being sick 3 dizziness
What causes vertigo in the ear?
Causes of vertigo may include: 1 benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) – where certain head movements trigger vertigo 2 migraines – severe headaches 3 labyrinthitis – an inner ear infection 4 vestibular neuronitis – inflammation of the vestibular nerve, which runs into the inner ear and sends messages to the brain that help to control balance
Is vertigo a symptom or a condition?
About vertigo. Vertigo is a symptom, rather than a condition itself. It's the sensation that you, or the environment around you, is moving or spinning. This feeling may be barely noticeable, or it may be so severe that you find it difficult to keep your balance and do everyday tasks.
What is the best treatment for vertigo?
Many people with vertigo also benefit from vestibular rehabilitation training (VRT), which is a series of exercises for people with dizziness and balance problems. Read more about treating vertigo.
What is the most common type of vertigo?
Vertigo is a symptom of several different conditions. There are two types of vertigo, known as peripheral and central, depending on the cause. Peripheral vertigo. Peripheral vertigo is the most common type, often caused by a problem with the balance mechanisms of the inner ear. The most common causes include:
How long does vertigo last?
The length of your vertigo episode will depend on what that underlying cause is. The most common causes like BPPV and migraines last for a maximum of two days, with an average of a few hours. Vertigo can be very difficult to deal with, so consider medical help if you can’t handle it on your own.
How long does vertigo last after a concussion?
While this can take time, the concussion induces vertigo that will last for a few days to a week at worst. The dizziness comes and goes frequently during this time. If it lasts for longer than a week, you should see a doctor.
Can vertigo be chronic?
Vertigo episodes may come and go and cause sudden, severe episodes of disorientation. They can also be incredibly mild, or be chronic and last for longer periods of time. There are other conditions and injuries that may cause episodes of vertigo. The length of your vertigo episode will depend on what that underlying cause is.
What are the factors that affect vertigo?
Factors that affect how long vertigo lasts. These conditions could include a change in blood flow, a head injury, a viral infection, rapid head movement, a vestibular migraine or something more serious. But how long does vertigo last?
What is the most common cause of vertigo?
BPPV is one of the most common causes of vertigo. The average episode reoccurs but usually lasts for one minute or less. Benign Paraoxysmal Positional Vertigo BP PV (or Benign Positional Vertigo) is the single most common cause of vertigo in adults and children alike.
Can migraines cause nausea?
If you live in North America, you probably know how common migraines are. These severe headaches can put you in bed for a week or more at times. Today, migraines are one of the most prevalent chronic conditions in the US and Canada, second to high blood pressure problems. Migraines are commonly accompanied by attacks of severe vertigo. This dizziness and nausea, when paired with the pain of an actual migraine, can be extremely hard to deal with. This affects the central nervous system, not the peripherals, meaning it is a little harder to treat.
Is vertigo permanent or semi-permanent?
Vertigo may be a permanent or semi-permanent state for some individuals. People who’ve had a stroke, head injury, or neck injury may experience long-term or chronic vertigo.
How long does vertigo last?
In case vertigo is caused while getting off a ship or a cruise (Mal de Debarquement), the symptoms last for about 24 hours. In case of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, the symptoms resolve within a week.
How to get rid of vertigo?
While experiencing vertigo, the following tips may be beneficial: 1 Avoid activities such as driving, handling machinery, exercising etc. to prevent accidents. 2 Sit down or lie down immediately for getting rest. 3 Advised to use good lighting while getting up at night for using the restroom.
How does physical therapy help with vertigo?
Physical Therapy to Help Vertigo Go Away: Vestibular rehabilitation, which is a form of physical therapy helps in management of vertigo. It promotes central nervous system compensation for inner ear issues and loss of balance.
Is vertigo a serious condition?
Vertigo is not a serious condition in itself; however, one may suffer injuries if the symptoms start while performing any task which could be dangerous. Hence, one must consult a physician as soon as the symptoms of vertigo are noticed.
What causes vertigo in the ears?
Vertigo is mainly caused by one or both of the following causes: Disturbances in certain parts of the brain or in the sensory nerves.
How long does it take for vertigo to go away?
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo may go away on its own within a few weeks or months. But, to help relieve BPPV sooner, your doctor, audiologist or physical therapist may treat you with a series of movements known as the canalith repositioning procedure.
What is the test used to diagnose vertigo?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This test uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create cross-sectional images of your head and body. Your doctor can use these images to identify and diagnose a range of conditions. MRI may be performed to rule out other possible causes of vertigo.
What is the purpose of ENG?
The purpose of these tests is to detect abnormal eye movement.
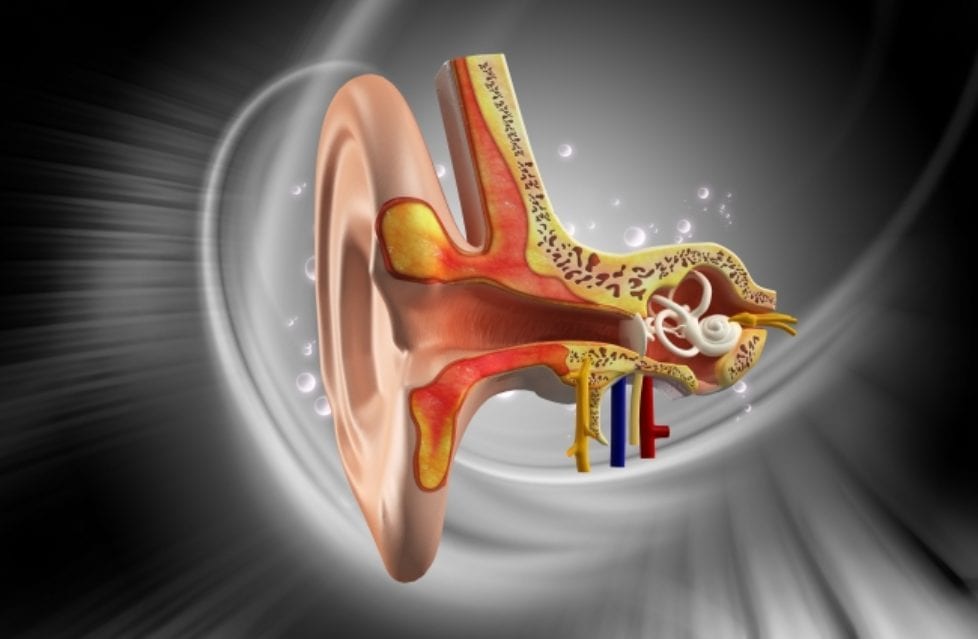
What causes vertigo in the inner ear?
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo BP PV occurs when canalith particles (otoconia) break loose and fall into the wrong part of the semicircular canals of your inner ear, causing vertigo. ...
How does canalith repositioning work?
The goal is to move particles from the fluid-filled semicircular canals of your inner ear into a tiny baglike open area (vestibule) that houses one of the otolith organs in your ear, where these particles don't cause trouble and are more easily resorbed.
How to avoid falling?
Avoid movements, such as looking up, that bring on the symptoms. Sit down immediately when you feel dizzy . Use good lighting if you get up at night. Walk with a cane for stability if you're at risk of falling.
How to get rid of BPPV?
Use good lighting if you get up at night. Walk with a cane for stability if you're at risk of falling. Work closely with your doctor to manage your symptoms effectively. BPPV may recur even after successful therapy. Although there's no cure, the condition can be managed with physical therapy and home treatments.
What is the most prescribed anti-vertigo drug?
The most prescribed anti-vertigo drug is betahistine. 25 26 It is estimated that more than 130 million patients have taken betahistine since its launch in 1968. 27 This is surprising, since betahistine has no FDA approval in the US due to insufficient efficacy 28 and is only registered for the relatively rare Ménière’s disease in other countries. 26 29 30 This discrepancy can be explained by excessive off-label use. A Canadian observational study (50 823 patients) found off-label prescribing in 91.5% of all betahistine prescriptions. 30 Off-label prescriptions are considered “ill founded” when prescribing is not advised by clinical practice guidelines or pharmacotherapeutic handbooks. A Dutch observational study (319 843 participants) found that 26.4% of all betahistine prescriptions were ill founded off-label. 26
Is betahistine good for vertigo?
There is no place for betahistine or any other anti-vertigo drugs in the treatment of chronic vertigo: stop all anti-vertigo drugs that the patient is using for acute vertigo (see box 1 for indications) and offer vestibular rehabilitation to all patients with chronic vertigo.
What is vestibular rehabilitation?
Vestibular rehabilitation is a form of exercise therapy designed to optimise the process of vestibular compensation that is disrupted in patients with chronic vertigo. Patients with chronic vertigo who do not respond to disease-specific ...
What is the most common type of dizziness?
Currently patients are generally treated in general practice with betahistine (off-label use), while stronger evidence exists for the effectiveness of vestibular rehabilitation. Vertigo is the most common type of dizziness. 1 Each year around 1 in 20 people in the general population experiences vertigo.
What is the most important barrier to general practitioners using vestibular rehabilitation?
The most important barrier to general practitioners using vestibular rehabilitation is that they do not know how to perform the treatment. Most patients surveyed prefer exercise based treatment over anti-vertigo drugs.
Overview
Pathophysiology
Diagnosis
Treatment
Mechanism of action
- Vertigo is the illusion of motion, usually rotational motion. As patients age, vertigo becomes an increasingly common presenting complaint. The most common causes of this condition are benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, acute vestibular neuronitis or labyrinthitis, Ménières disease, migraine, and anxiety disorders. Less common causes include vertebrobasilar ischemi…
Adverse effects
- Vertigo results from acute unilateral vestibular lesions that can be peripheral (labyrinth or vestibular nerve) or central (brainstem or cerebellum). In contrast, tumors and ototoxic medications produce slowly progressive unilateral or bilateral lesions. Lesions that progress slowly or processes that affect both vestibular apparatuses equally usually do not result in verti…
Benefits
- Because vertigo can have multiple concurrent causes (especially in older patients), a specific diagnosis can be elusive. The duration of vertiginous episodes and the presence or absence of auditory symptoms can help narrow the differential diagnosis (Table 1).1 Psychiatric disorders, motion sickness, serous otitis media, cerumen impaction, herpes zoster, and seizure disorders a…
Contraindications
- Medications are most useful for treating acute vertigo that lasts a few hours to several days (Table 3).6,7 They have limited benefit in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, because the vertiginous episodes usually last less than one minute. Vertigo lasting more than a few days is suggestive of permanent vestibular injury (e.g., stro...
Prognosis
- Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vestibular system.6 Benzodiazepines enhance the action of GABA in the central nervous system (CNS) and are effective in relieving vertigo and anxiety.
Clinical significance
- Older patients are at particular risk for side effects of vestibular suppressant medications (e.g., sedation, increased risk of falls, urinary retention). These patients also are more likely to experience drug interactions (i.e., additive effects with other CNS depressants).
Symptoms
- The vertigo improves with head rotation maneuvers that displace free-moving calcium deposits back to the vestibule. Maneuvers include the canalith repositioning procedure or Epley maneuver15 and the modified Epley maneuver16 (Figure 2). The modified Epley maneuver can be performed at home.
Signs and symptoms
- Patients may need to remain upright for 24 hours after canalith repositioning to prevent calcium deposits from returning to the semicircular canals, although this measure is not universally recommended. Contraindications to canalith repositioning procedures include severe carotid stenosis, unstable heart disease, and severe neck disease, such as cervical spondylosis with my…
Mechanism
- One study21 on the long-term effects of canalith repositioning procedures in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo reported a recurrence rate of about 15 percent per year. Another study22 reported recurrence rates of 20 percent at 20 months and 37 percent at 60 months.