How to tell if you have vascular leg pain?
- Painful cramp in any one or both of the calf muscles, thighs and hips after climbing stairs, walking or any other similar type of activity
- Sores on the toes, legs or feet, which never heal
- Weakness or numbness in the legs
- Change in your legs color
- Coldness in the foot or lower leg, especially while you compare with your other leg/foot
How can I help my leg pain?
Potassium
- You can apply a gel containing 0.0125 percent capsaicin topically to reduce pain.
- Drink 2 to 3 cups of green tea daily.
- Eat 1 teaspoon of yellow mustard with a glass of water twice a day for a few days. ...
- Keep your blood pressure and cholesterol under control.
- Avoid drinking or drink only in moderation.
- Avoid smoking as well as secondhand smoke.
How do you treat leg pain?
- Preferably, unless your doctor tells you to, don't rest in bed as this could increase the discomfort.
- Nor is strenuous exercise advisable, but you can go for short walks to keep yourself active. ...
- It is important to avoid heavy lifting so as to not increase discomfort or injury.
How to relieve leg aches?
The good news is that getting another vaccination or booster can KO the lurking virus. It’s reported that 33% of folks with long COVID-19 who get another vaccination are cured of the symptoms within days. So get a booster vaccine ASAP and wear an N95 or KN95 mask. Q: I need help dealing with chronic pain.

What can I take for vascular pain?
Your doctor may prescribe daily aspirin therapy or another medication, such as clopidogrel (Plavix). Symptom-relief medications. The drug cilostazol increases blood flow to the limbs both by keeping the blood thin and by widening the blood vessels.
What medicine is good for pain in legs?
Take Over-the-Counter Medicines Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen may help ease swelling and pain. Acetaminophen might also fight pain. Some doctors say magnesium is a good mineral to add to your diet to help with painful swelling.
What is the best painkiller for PAD?
Low-Dose Aspirin This can reduce blockages in blood vessels and allow improved circulation to the feet, legs, hands, and fingers. The pain-killing effect of aspirin can also provide some relief for those individuals who routinely experience moderate to severe leg and foot pain as a result of PAD.
How can I relieve leg pain instantly?
If you have leg pain from cramps or overuse, take these steps first:Rest as much as possible.Elevate your leg.Apply ice for up to 15 minutes. ... Gently stretch and massage cramping muscles.Take over-the-counter pain medicines such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
How can I stop nerve pain in my legs?
Walk it off. Exercise releases natural painkillers called endorphins. Exercise also promotes blood flow to the nerves in the legs and feet. Researchers believe that regular exercise may create a long-lasting expansion in blood vessels in the feet, nourishing damaged nerves back to health.
What is vascular leg pain like?
Vascular pain is pain that is caused as a result of interruption of blood flow to a tissue or muscles. If you are experiencing lack of circulation, pain, or heaviness in certain areas, you might be having vascular pain. There also may be numbness, weakness, or a tingling feeling in the affected area.
What kind of doctor treats poor circulation in legs?
A vascular physician will diagnose any conditions, prescribe any medications you might need, and formulate an actionable treatment plan for managing your poor circulation. You may require medication or procedures to treat your conditions, but your doctor will also recommend lifestyle changes.
How is vascular disease treated?
How are vascular diseases treated?Lifestyle changes, such as eating a heart-healthy diet and getting more exercise.Medicines, such as blood pressure medicines, blood thinners, cholesterol medicines, and clot-dissolving drugs. ... Non-surgical procedures, such as angioplasty, stenting, and vein ablation.Surgery.
What to do if you have vascular leg pain?
If you’re diagnosed with PAD, a vascular leg pain treatment plan will help. It’s recommended that you start with significant lifestyle changes such as: In some cases, minimally invasive treatments such as angioplasty, stenting, and cryoplasty may be necessary. PAD treatment options.
What is the best medicine for leg pain?
Medication for Leg Pain Treatment. You can take some medications to help with symptoms of PAD; most of them require a prescription. Aspirin - Taking a low dose aspirin to thin out your blood is a known treatment for those at risk for heart disease. Do not take aspirin with any other blood thinners.
How to treat leg pain?
Medication for Leg Pain Treatment 1 Aspirin - Taking a low dose aspirin to thin out your blood is a known treatment for those at risk for heart disease. Do not take aspirin with any other blood thinners. 2 Antiplatelet Agents - Antiplatelet medications help prevent the blood from sticking together, which decreases your chances of developing a clot. 3 Anticoagulants - An anticoagulant will also help prevent a blood clot by thinning out the blood. This can help keep blood flowing to your extremities even if you have narrow arteries due to plaque build-up.
What is the most common sign of PAD?
The most significant sign of PAD is leg pain . This pain is in your muscles and not your joints; it’s important to know the difference. Joint pain will often improve with activity while the muscle pain related to PAD will worsen with activity.
Why do my legs hurt?
Common Causes of Leg Pain. Leg pain can be caused by a nerve, a muscle, a bone, or even your spine issues. People rarely relate to a poor blood circulation. Let’s look a little deeper into your leg pain to try and learn more about it. These are common daily activities that may cause pain caused by a vascular problem.
What is PAD in a heart attack?
The first step is diagnosing the problem. PAD is often the sign of other even more serious underlying problems such as artery clogging around your heart and brain. These two issues can lead to heart attack and stroke, so you mustn’t wait.
What causes pain in the legs?
Pain in the feet which is worse with elevation of the legs. Poor nail and hair growth. Weakness in legs. When you experience pain in your legs, it can be either acute or chronic pain. Acute pain happens suddenly and is usually the result of something you did. A sprain or pulled muscle would be acute pain.
What is the treatment for vascular pain?
Therapies to treat vascular pain can include medications, angioplasty, or bypass surgery. Angioplasty is a procedure to reduce or eliminate blockages in blood vessels. In bypass surgery, surgeons take a segment of a healthy blood vessel from another part of the body and make a detour around the blocked blood vessel.
What is vascular pain?
Vascular Pain. If you are experiencing lack of circulation, pain, or heaviness in certain areas, you might be having vascular pain. This develops when there is interruption in blood flow to a tissue, organ or nerves.
What are the symptoms of vascular disease?
Symptoms include lack of circulation, pain, or heaviness in the area affected by vascular disease or injury. There also may be numbness, weakness, or a tingling feeling in the affected area.
What causes pain in the arteries?
Many kinds of vascular diseases or injuries have the potential to cause pain. Diseases such as the following often are culprits: Vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels) Coronary artery disease. Circulatory problems. Vascular ruptures (breakages) Constrictions. Blood vessel spasms.
Can a doctor help with pain management?
Doctors that specialize in pain management can sometimes help if the other treatments don’t work. In selected cases pain management nerve blocks and techniques such as spinal cord stimulation can reduce pain and improve circulation.
Vascular disease and leg pain: the connection
Like every other part of your body, your legs depend on a steady supply of oxygen- and nutrient-rich blood to keep them healthy. But if circulation in your legs is compromised, you can wind up with chronic aching pain, searing cramps, swelling, varicose veins, and changes in your skin.
Three treatments for vascular leg pain
Dr. Burkett tailors vascular treatments based on each patient’s unique needs, lifestyle, health history, and other factors. While leg pain caused by varicose veins or spider veins can often be treated with sclerotherapy, there are also several other approaches.
What causes blood circulation in legs?
The symptoms that develop and worse depend on the type of disease. Some comorbidities increase the chances of vascular diseases in the legs. People who are overweight, diabetic, smokers, or physically inactive are also more likely to have blood circulation issues in their legs.
How long does it take for a vascular disease to improve?
We typically see patient improvements about 1-4 weeks after initial treatment , but additional treatment is occasionally needed.
What are the different types of vascular diseases?
Types of Vascular Disease of the Legs 1 Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD). PAD is caused by a chronic narrowing or blockage in the arteries and can lead to several problems, including cramps, pain, sores, skin-color changes and ulcers. In the most severe cases, called critical limb ischemia (CLI), amputation may be needed. 2 Pelvic Congestion Syndrome (PCS). PCS is caused by the pooling of blood in your pelvis due to insufficient outflow. This typically leads to symptoms in the pelvis but can exacerbate symptoms in your lower extremities as well. 3 May-Thurner Syndome (MTS). MTS is defined by compression of the left common iliac vein by the right common iliac artery. This compression narrows the left common iliac vein and reduces the amount of blood that can be circulated out of your legs. 4 Chronic Venous Insufficiency. CVI is commonly caused by the failure or degradation of the valves in your veins. Some common symptoms of CVI include varicose veins and spider veins. 5 Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT). DVT occurs when a blood clot develops deep in a vein. This can be life-threatening if part of or the whole clot dislodges and travels to the lung. This is called a pulmonary embolism and you should seek urgent medical attention. 6 Post-Thrombotic Syndrome (PTS). PTS typically occurs as a result of a DVT or other trauma that causes damage to the valves in your veins. When your valves are damaged, blood pools because it is less efficiently circulated out of your legs.
What is MTS in a vein?
MTS is defined by compression of the left common iliac vein by the right common iliac artery. This compression narrows the left common iliac vein and reduces the amount of blood that can be circulated out of your legs. Chronic Venous Insufficiency. CVI is commonly caused by the failure or degradation of the valves in your veins.
Why does blood pool in legs?
When your valves are damaged, blood pools because it is less efficiently circulated out of your legs.
What is the condition that causes pain and cramps?
Peripheral Artery Disease ( PAD). PAD is caused by a chronic narrowing or blockage in the arteries and can lead to several problems, including cramps, pain, sores, skin-color changes and ulcers. In the most severe cases, called critical limb ischemia (CLI), amputation may be needed. Pelvic Congestion Syndrome (PCS).
Can vascular disease be found in legs?
There are many types of vascular diseases that can occur in the legs – below are some of the common ones that can be treated at the Center for Vascular Medicine and the cause of the disease. You can generalize these diseases as failures to transport blood to or from key areas of the body. It is best to treat these diseases as early as possible ...
What is peripheral vascular disease?
Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) is a term that applies to a variety of vessel-occlusive conditions, which may develop within either the arterial or venous systems. When PVD develops, the condition is often seen concurrently with coronary artery disease, diabetes, and hypertension. 1 However, PVD may arise from vasculitides ...
What is PAD in a limb?
Usually, PAD is indicative of a condition involving the main artery that supplies blood to the legs. Lower extremity PAD, or PVD, typically is caused by atherosclerosis due to obstruction of the internal lining of a blood vessel and leads to poor skin, limb, and muscle perfusion. 5. PVD, or arteriosclerosis obliterans, ...
When was angioplasty first used for PVD?
Charles Dotter first described angioplasty for the treatment of PVD in 1964. However, this application has evolved considerably.
Why do my calves hurt after exercise?
During exercise, a buildup of lactic acid may occur because of anaerobic respiration in which the oxygen demand is not fulfilled because of arterial blockage, initiating pain. Normally, this pain would dissipate in less than 5 minutes once the patient discontinues the exercise and returns to rest, only to return again when the patient begins to move again.
Does smoking cause limb ischemia?
Smoking represents a key risk factor for critical limb ischemia (CLI). In the general population, smoking tends to increase the risk of this condition 2 to 6 fold. Smokers with CLI have a greater risk of amputation and higher rates of mortality and morbidity.
Can arterial stenosis be seen during exercise?
Nevertheless, an arterial stenosis, that is not apparent at rest, might become evident during exercise if augmented peripheral muscle demands do not match the augmented flow. It is easy to see how muscle discomfort, fatigue, and pain manifest as the primary symptoms of PAD.
What are the best ways to treat peripheral artery disease?
4 of the Most Common PAD Treatment Options. 1. Lifestyle Changes. Often, simple lifestyle changes can be the most effective peripheral artery disease treatment option. Here are a few changes you can make to reduce the symptoms from PAD.
How to reduce the risk of PAD?
Change Your Diet. Foods high in saturated fats can contribute to the development of plaque in the bloodstream and increase both the risk and the severity of PAD. Eating heart-healthy foods like fresh fruits and vegetables can dramatically reduce the effects of the disease.
What to ask your doctor about non surgical treatment?
If lifestyle changes and prescription medication treatments aren’t doing enough to ease your symptoms, it may be time to ask your doctor about some of the non-surgical treatment options that are available to you. If your doctor hasn’t discussed some of the following minimally invasive procedures, you should bring them up. Surgery isn’t always the best option, and depending on the severity of your case, you may be better off with one of these treatments and have a substantially quicker recovery time than you would typically have with surgery.
What is statins for?
Statins for High Cholesterol . Statins are prescription drugs designed specifically to lower cholesterol. These medications are often prescribed for patients with PAD. High cholesterol can contribute to the build-up of plaque in blood vessels, causing poor circulation that can directly lead to PAD in vulnerable individuals.
What to do if your PAD is not working?
You’ll want to be sure to stay in close contact with your doctor though, in the event that the medication isn’t working as it should.
How to reduce the risk of developing PAD?
Be sure to work out regularly. Cardio workouts can help lower cholesterol and blood pressure, and can reduce the risk for plaque build-up in blood vessels and help you maintain a healthy weight. This can significantly lessen your chances for developing PAD.
What tests are used to diagnose PAD?
The first step in treating PAD is to consult with your physician, who will perform a few diagnostic tests that may include ultrasound imaging, an Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) test, Pulse Volume Recording (PVR) exam, ...
Leg Pain and Aching: Peripheral Artery Disease Could Be the Cause
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a common, yet serious, health condition. PAD can cause a range of symptoms, including leg pain, cramping, weakness, and fatigue. It is also a progressive disease: when left untreated, it can place you at risk for heart attack, stroke, and limb amputation.
How Does PAD Cause Leg Pain?
Peripheral artery disease can develop when plaque builds up in the arteries that lead to your legs. This type of plaque buildup, known as atherosclerosis, causes the arteries to narrow or, in severe cases, become completely blocked.
Diagnosing Peripheral Artery Disease
If you suffer from leg pain, we recommend contacting your doctor or a vascular specialist for a full medical evaluation. They can order medical tests to accurately determine whether your leg pain is caused by PAD or a different health condition.
How To Treat Pain and Aching in the Legs Caused by PAD
The good news is that leg pain caused by PAD can be treated. At USA Vascular Centers, we offer a range of minimally invasive, outpatient PAD treatments that include angioplasty, stent placement, and atherectomy. We can also help identify beneficial lifestyle changes and prescribe medications intended to encourage blood flow to your legs.
Schedule a Consultation With USA Vascular Today
There is no need to suffer from sore legs due to PAD any longer. Our vascular specialists are available to help alleviate your leg pain and other PAD symptoms. We believe that vascular treatment can help you regain mobility and return to normal daily activities.
What is the procedure to restore blood flow to the legs?
A variety of minimally invasive procedures can help with this task. One common procedure for PAD is angioplasty .
Why do my legs hurt?
Tracing the cause of leg pain can follow many paths. If your leg hurts, you may assume that you have a minor sprain or a pulled muscle. You might also believe that your pain is due to arthritis or a normal sign of aging. But did you know that leg pain is often the first symptom of peripheral artery disease (PAD)? PAD is a potentially serious vascular condition that can have a significant impact on your health. Read on to learn more about vascular leg pain and what steps to take if you think you might have PAD.
What is peripheral artery disease?
Peripheral artery disease is a vascular disorder that affects blood flow to your extremities, most commonly to the legs. The condition is caused by atherosclerosis, the accumulation of plaque material on the inside walls of arteries. (i) Atherosclerosis can prevent your limbs from receiving the oxygenated blood they need.
Why do my legs hurt when I lay down?
If this occurs, you might experience leg pain even when you’re resting or lying down. Leg pain at night can be a sign that your vascular disease is getting worse. (ii) Leg pain caused by an injury often gets better with time but the pain caused by PAD is often progressive and gets worse without treatment.
Why does my lower leg hurt?
Tendinitis. Herniated disk. Many people also experience lower leg pain due to less serious vascular conditions like varicose veins. (vi) A vascular specialist can evaluate your symptoms and determine if a vascular condition is causing your leg pain.
What are the symptoms of PAD?
The most common symptom of a vascular issue is claudication, or leg pain that’s worse with exercise caused by an obstruction in the arteries.
Does pain from a PAD get worse?
Leg pain caused by an injury often gets better with time but the pain caused by PAD is often progressive and gets worse without treatment. (iv) Never overlook any kind of long-term pain. Chronic pain or injuries that don’t seem to heal on their own should be evaluated by a doctor.
How to treat a swollen leg?
Use the R.I.C.E. Method 1 Rest. If movement is painful at first, rest your legs and stay off them as much as you can until you’re able to move without pain. 2 Ice. Keep an ice pack on your legs for about 20 minutes every hour over the first 3 days after symptoms start. Avoid using heat, as it may make swelling worse. 3 Compression. Wrap an elastic bandage around your legs or wear compression stockings, which use pressure to keep swelling down. 4 Elevation. Keep your legs raised above the level of your heart for 30 minutes, three or four times per day, so that gravity can help move fluids out and toward the rest of your body.
What to do if your leg is swollen?
When to See Your Doctor. Sometimes, the best thing to do is to get medical help or have a specialist check your leg pain and swelling. In general, if your symptoms start severely, suddenly, more often than usual, or for no clear reason, they may be signs of something more serious.
How to stop swelling in legs after a symtom?
Avoid using heat, as it may make swelling worse. Compression. Wrap an elastic bandage around your legs or wear compression stockings, which use pressure to keep swelling down. Elevation.
How to help swelling in legs?
These tips will help with leg pain and swelling whenever you have to lie down or stay seated for long periods of time, such as when you’re sleeping, traveling, or working at a desk: Don’t wear tight clothing, especially around your thighs. Wear compression stockings that are approved by your doctor.
How to stop swelling in the back of the leg?
Get up and stretch as often you can during the day. Focus on extending your knees as well as flexing your ankles to help with blood circulation. This may help pump extra fluid away from your legs and back toward your heart.
How to get fluid out of your legs?
Try Massage. If you can’t visit a massage therapist and don’t have any tools, you can still do massage on your own at home. Rub or stroke your legs upward, in the direction of your heart. Make sure the pressure is firm but not painful. This can help move excess fluid out of that area.
What are the symptoms of a swollen leg?
Have swelling in only one leg, especially if the skin is cool or pale. Have leg pain, swelling, warmth, or redness that keeps getting worse. Have symptoms that don't get better after a few days of home treatment.

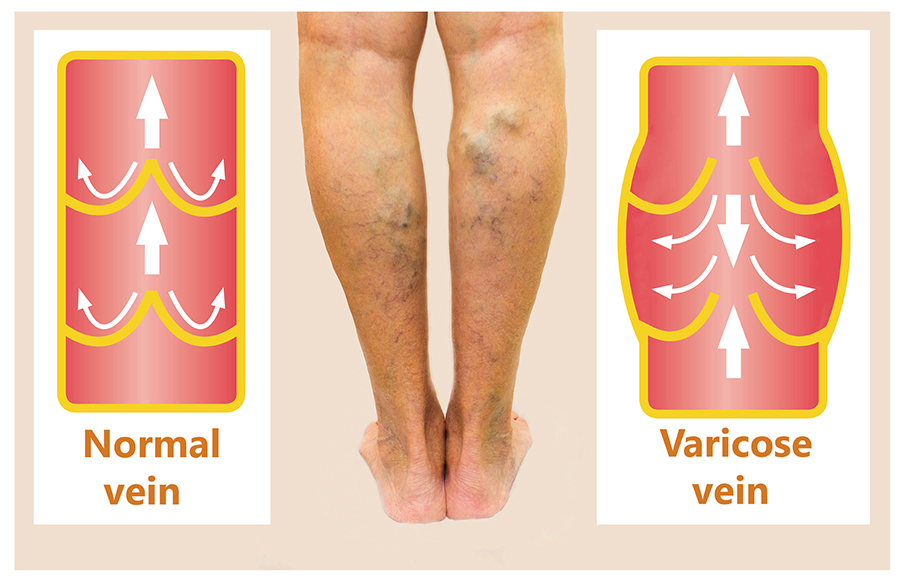
Types of Vascular Disease of The Legs
Arterial Versus Venous Vascular Diseases
- Rest the affected leg or reduce level of activity
- Apply an ice pack
- Slightly elevate your leg whenever you sit or lie down
- Try over- the- counter topical pain relievers or mild oral pain relievers
- Pain during or after walking
- Swelling in both legs
- Pain worsens over time
- Symptoms don't improve after a few days of home treatment
- Painful varicose veins
See a doctor immediately if you notice:
- Leg injury with a deep cut or exposed bone
- Sudden, severe pain
- Inability to walk or put weight on the leg
- Pain, swelling, redness or warmth in the calf region
- Signs of severe illness (for example, confusion, fever, or collapse)
- Popping or grinding sound at the time of a leg injury
- Sudden swelling, blistering, or black spots
- Weakness or numbness of the affected leg
- Signs of infection, such as redness, warmth or tenderness, or a fever greater than 100 F (37.8 C)
Treatment Options
Prognosis After Treatment
- There are many types of vascular diseases that can occur in the legs – below are some of the common ones that can be treated at the Center for Vascular Medicineand the cause of the disease. You can generalize these diseases as failures to transport blood to or from key areas of the body. It is best to treat these diseases as early as possible to avoid future complications. 1. …
What to Expect from CVM?
- Your vascular system is responsible for ensuring the proper transport of oxygen, and other nutrients to all parts of your body. This Lsystem is typically broken down into two main groups: 1. Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from your heart. 2. Veins carry this blood back to the heart so it can be recirculated. There are many diseases that can affect this system and, while most a…