
HIV gradually destroys the immune system and eventually causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes AIDS. When a person becomes infected with HIV, the virus attacks and weakens the immune system.
Is there a drug that can cure HIV?
HIV treatment involves taking medicine that reduces the amount of HIV in your body. HIV medicine is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). There is no effective cure for HIV. But with proper medical care, you can control HIV. Most people can get the virus under control within six months. Taking HIV medicine does not prevent transmission of other ...
What are the best medications for HIV?
“They will have to make their own decision, based on discussions with their provider, as to what is best for them,” he says. “Whatever option they choose, it is important for them to adhere to their medication as prescribed and have the periodic HIV ...
What drugs are used to treat HIV?
Researchers say that Merck's ( MRK +2.4%) blockbuster oncology drug Keytruda (pembrolizumab) may also have an effect against HIV. Researchers led by the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center in Seattle used Keytruda on patients with both cancer and HIV.
What is the latest treatment for HIV?
The two treatments have different goals — Cabenuva works as an HIV treatment for adults, and Apretude is a prevention medication for adolescents and adults at risk of sexually acquiring HIV. The treatments were approved by the FDA last year, with Apretude receiving approval this past December.
How long does it take to get rid of HIV?
Why is it important to take HIV medication?
What does it mean when your HIV is suppressed?
What is the amount of HIV in the blood called?
How long does it take for a mother to give her baby HIV?
What to do if substance use is interfering with your ability to keep yourself healthy?
Does HIV harm the immune system?
See more
About this website
Can HIV progress to AIDS with treatment?
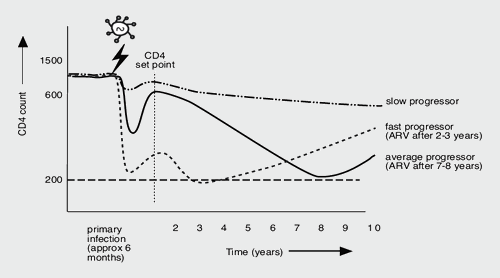
With Proper Treatment, HIV Doesn't Have to Progress to AIDS In most cases, if you take ART, HIV does not progress to AIDS. HIV attacks the immune system's CD4 cells. Over time, if these cells are destroyed, the immune system can no longer fight off infection.
Can you treat HIV before it becomes AIDS?
Not everyone who has HIV will get AIDS. But the infection will advance to AIDS, usually in 10 to 15 years, if you don't get treatment with antiretroviral drugs.
Can late stage AIDS be treated?
There is no cure for HIV, but treatment with HIV medicines (called antiretroviral therapy or ART) can slow or prevent HIV from advancing from one stage to the next. HIV medicines help people with HIV live longer, healthier lives. One of the main goals of ART is to reduce a person's viral load to an undetectable level.
How long does it take for HIV to turn into AIDS with treatment?
How long does it take to develop signs of HIV? Persons with HIV can develop signs of infection anywhere from months to years after being infected. About half of the people with HIV develop AIDS within 10 years, but the time between infection with HIV and the onset of AIDS can vary greatly. 6.
What is HIV treatment?
HIV treatment (antiretroviral therapy or ART) involves taking medicine as prescribed by a health care provider. HIV treatment reduces the amount of...
When should I start HIV treatment?
Start HIV treatment as soon as possible after diagnosis. All people with HIV should take HIV treatment, no matter how long they’ve had HIV or how h...
What if I delay HIV treatment?
If you delay treatment, HIV will continue to harm your immune system. Delaying treatment will put you at higher risk for transmitting HIV to your p...
Are there different types of HIV treatment?
There are two types of HIV treatment: pills and shots. Pills are recommended for people who are just starting HIV treatment. There are many FDA-app...
What are HIV treatment shots?
HIV treatment shots are long-acting injections used to treat people with HIV. The shots are given by your health care provider and require routine...
Can I switch my HIV treatment from pills to shots?
Talk to your health care provider about changing your HIV treatment plan. Shots may be right for you if you are an adult with HIV who has an undete...
What are the benefits of taking my HIV treatment as prescribed?
HIV treatment reduces the amount of HIV in the blood (viral load). Taking your HIV medicine as prescribed will help keep your viral load low. HIV t...
Does HIV treatment cause side effects?
HIV treatment can cause side effects in some people. However, not everyone experiences side effects. The most common side effects are Nausea and vo...
What should I do if I’m thinking about having a baby?
Let your health care provider know if you or your partner is pregnant or thinking about getting pregnant. They will determine the right type of HIV...
Can I take birth control while on HIV treatment?
You can use any method of birth control to prevent pregnancy. However, some HIV treatment may make hormone-based birth control less effective. Talk...
A Third HIV Patient Now Appears To Have Been Cured of AIDS, But It's ...
Timothy Ray Brown poses for a photograph, Monday, March 4, 2019, in Seattle. Brown, also known as...[+] the "Berlin patient," was the first person to be cured of HIV infection, more than a decade ...
HIV Cure: How Soon? - WebMD
SOURCES: AIDSinfo.gov: “HIV Treatments: The Basics.” National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases: “HIV Cure.” amfAR: “The Countdown to a Cure for AIDS,” “Pathways to an HIV ...
Treatments for HIV/AIDS | Stanford Health Care
Starting treatment. Medical experts recommend that people begin treatment for HIV as soon as they know that they are infected. Treatment is especially important for pregnant women, people who have other infections (such as tuberculosis or hepatitis), and people who have symptoms of AIDS.
HIV and AIDS: Medicines to Help You | FDA
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
What is the treatment for HIV?
However, there are many medications that can control HIV and prevent complications. These medications are called antiretroviral therapy (ART). Everyone diagnosed with HIV should be started on ART, regardless of their stage of infection or complications.
What to do if you think you have HIV?
If you think you might have HIV infection, you're likely to start by seeing your family doctor. You may be referred to an infectious disease specialist — who additionally specializes in treating HIV / AIDS.
What test can help determine if you have HIV?
If you receive a diagnosis of HIV / AIDS, several tests can help your doctor determine the stage of your disease and the best treatment, including: CD4 T cell count. CD4 T cells are white blood cells that are specifically targeted and destroyed by HIV. Even if you have no symptoms, HIV infection progresses to AIDS when your CD4 T cell count dips ...
What is HIV RNA?
Viral load (HIV RNA). This test measures the amount of virus in your blood. After starting HIV treatment the goal is to have an undetectable viral load. This significantly reduces your chances of opportunistic infection and other HIV -related complications.
How long does it take to get tested for HIV?
Most rapid HIV tests, including self-tests done at home, are antibody tests. Antibody tests can take three to 12 weeks after you're exposed to become positive. Nucleic acid tests (NATs). These tests look for the actual virus in your blood (viral load). They also involve blood drawn from a vein.
What are some examples of anti-HIV drugs?
Examples include efavirenz (Sustiva), rilpivirine (Edurant) and doravirine (Pifeltro).
How to diagnose HIV?
Diagnosis. HIV can be diagnosed through blood or saliva testing. Available tests include: Antigen/antibody tests. These tests usually involve drawing blood from a vein. Antigens are substances on the HIV virus itself and are usually detectable — a positive test — in the blood within a few weeks after exposure to HIV.
How to treat HIV?
The most effective treatment for HIV is antiretroviral therapy (ART). This is a combination of several medicines that aims to control the amount of virus in your body. Antiretroviral medicines slow the rate at which the virus grows. Taking these medicines can reduce the amount of virus in your body and help you stay healthy.
Why is HIV treatment important?
Treatment is especially important for pregnant women, people who have other infections (such as tuberculosis or hepatitis), and people who have symptoms of AIDS. Research suggests that treatment of early HIV with antiretroviral medicines has long-term benefits, such as a stronger immune system.
What happens if you get HIV late?
If HIV progresses to a late stage, treatment will be started or continued to keep your immune system as healthy as possible. If you get any diseases that point to AIDS, such as Pneumocystis pneumonia or Kaposi's sarcoma, your doctor will treat them.
Why is it important to take a medicine after HIV treatment?
Taking these medicines can reduce the amount of virus in your body and help you stay healthy. After you start treatment, it's important to take your medicines exactly as your doctor tells you. When treatment doesn't work, it is often because HIV has become resistant to the medicine.
How to keep your immune system strong?
Keep your immune system strong by eating right, quitting smoking, and learning how to avoid infection. Monitor your CD4+ (white blood cells) counts to check the effect of the virus on your immune system. See a counselor to help you handle the strong emotions and stress that can follow an HIV diagnosis.
Why do people get medicine for HIV?
Health care workers who are at risk for HIV because of an accidental stick with a needle or other exposure to body fluids should get medicine to prevent infection. Also, medicine may prevent HIV infection in a person who has been raped or was accidentally exposed to the body fluids of a person who may have HIV.
How to get rid of a foodborne infection?
Use condoms whenever you have sex. Learn how to handle food safely so you don't get a food-borne infection. Eat a healthy diet, get regular exercise, don't smoke, and don't use illegal drugs.
What is the treatment for HIV?
HIV treatment involves taking medicines that slow the progression of the virus in your body. HIV is a type of virus called a retrovirus, and the combination of drugs used to treat it is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). ART is recommended for all people living with HIV, regardless of how long they’ve had the virus or how healthy they are.
Why do you prescribe HIV?
Your health care provider may prescribe medicines to prevent certain infections. HIV treatment is most likely to be successful when you know what to expect and are committed to taking your medicines exactly as prescribed.
What is drug resistance in HIV?
What Is HIV Drug Resistance? Drug resistance can be a cause of treatment failure for people living with HIV. As HIV multiplies in the body, it sometimes mutates (changes form) and produces variations of itself. Variations of HIV that develop while a person is taking ART can lead to drug-resistant strains of HIV.
How long do HIV side effects last?
Some side effects can occur once you start a medicine and may only last a few days or weeks.
How soon can you start ART for HIV?
Treatment guidelines from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services recommend that a person living with HIV begin ART as soon as possible after diagnosis. Starting ART slows the progression of HIV and can keep you healthy for many years.
Is HIV treatment a prevention?
There is also a major prevention benefit. People living with HIV who take HIV medication daily as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of sexually transmitting HIV to their HIV-negative partners. This is called treatment as prevention.
Can HIV be drug resistant?
A person can initially be infected with drug-resistant HIV or develop drug-resistant HIV after starting HIV medicines. Drug-resistant HIV also can spread from person to person. Drug-resistance testing identifies which, if any, HIV medicines won’t be effective against your specific strain of HIV.
What happens if you leave HIV untreated?
In all but a few rare cases, if left untreated, HIV will progress to a stage of infection called AIDS. This is when the immune defenses have been compromised, and the body is less able to defend itself against potentially life-threatening infections. 2:51.
What is genetic HIV?
The genetic strain of HIV a person has been infected with (some of which may be more or less virulent than others) The general health of the individual. The place where the person lives (including healthcare access and the incidence of other diseases or infections) A person's genetics or family history.
What changes if a person receives no treatment?
A person's genetics or family history. Smoking and other personal lifestyle choices. This is, of course, if the person receives no treatment. The picture changes entirely if he or she does. 1 . Since 1996, the introduction of antiretroviral drugs has dramatically altered the natural progression of HIV infection.
How long does a virus last?
This chronic (or latent) stage of infection can last for years and even decades in some individuals until such time as the hidden viruses are reactivated (most often when the immune system is fully compromised and later-stage OI develops).
Can HIV be cured?
While HIV still cannot be cured, people newly diagnosed with HIV who get treated and stay in care can be expected to have near-normal to normal life expectancies. As with other chronic diseases, early detection is key to identifying and treating the infection as soon as possible. 2 .
What are the stages of HIV?
The three stages of HIV infection are (1) acute HIV infection, (2) chronic HIV infection, and (3) acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). There is no cure for HIV, but treatment with HIV medicines (called antiretroviral therapy or ART) can slow or prevent HIV from advancing from one stage to the next. HIV medicines help people ...
What is the second stage of HIV?
Chronic HIV Infection. The second stage of HIV infection is chronic HIV infection (also called asymptomatic HIV infection or clinical latency). During this stage, HIV continues to multiply in the body but at very low levels. People with chronic HIV infection may not have any HIV-related symptoms. Without ART, chronic HIV infection usually advances ...
How many cells does HIV have?
People with HIV are diagnosed with AIDS if they have a CD4 count of less than 200 cells/mm 3 or if they have certain opportunistic infections. Once a person is diagnosed with AIDS, they can have a high viral load and are able to transmit HIV to others very easily.
Why is AIDS the most severe stage of HIV?
AIDS is the final, most severe stage of HIV infection. Because HIV has severely damaged the immune system, the body can’t fight off opportunistic infections. (Opportunistic infections are infections and infection-related cancers that occur more frequently or are more severe in people with weakened immune systems than in people with healthy immune ...
What happens to the immune system during HIV?
The virus attacks and destroys the infection-fighting CD4 cells of the immune system. During the acute HIV infection stage, the level of HIV in the blood is very high, which greatly increases the risk of HIV transmission. A person may experience significant health benefits if they start ART during this stage. Chronic HIV Infection.
How long does it take for HIV to develop?
There are three stages of HIV infection: Acute HIV infection is the earliest stage of HIV infection, and it generally develops within 2 to 4 weeks after infection with HIV. During this time, some people have flu-like symptoms, such as fever, headache, and rash.
Can HIV be transmitted through sex?
While it is still possible to transmit HIV to others during this stage, people who take ART exactly as prescribed and maintain an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to an HIV-negative partner through sex. AIDS is the final, most severe stage of HIV infection.
How to get rid of HIV infection?
Combat stress by getting plenty of sleep each night and try stress-relieving practices like meditation or yoga. Get vaccinated. Infections like pneumonia and the flu can be devastating if you’re HIV positive. Get regular vaccinations for these and any other infections that your doctor recommends.
How long does it take for HIV to progress to AIDS?
But treatment is crucial. Without it, an HIV infection usually progresses to AIDS in a decade or so, although the figure varies, according to the CDC. And without treatment, AIDS typically leads to death in about three years. By diligently taking ART, you can manage the illness by slowing the replication of the virus ...
How does HIV affect the immune system?
HIV attacks the immune system’s CD4 cells. Over time, if these cells are destroyed, the immune system can no longer fight off infection. AIDS is diagnosed when a person gets certain infections (called opportunistic infections) or cancers, or their CD4 count is fewer than 200 cells per cubic millimeter of blood.
How to stay healthy with HIV?
How to Stay Healthy While Living With HIV. Work closely with your doctor and adhere to your medication regimen to delay the progression to AIDS. It’s also important that you maintain a healthy lifestyle and practice safer sex. If you’re HIV positive, here’s what you can do to keep your viral load as low as possible:
How long can you live with HIV without AIDS?
But treatment is crucial. Without it, an HIV infection usually progresses to AIDS in a decade or so, although the figure varies, ...
Can ART cure HIV?
By diligently taking ART, you can manage the illness by slowing the replication of the virus (when it makes copies of itself). This, in turn, can significantly delay the advancement to AIDS. But ART is not a cure for HIV or AIDS, and following the treatment regimen can’t entirely prevent the virus from replicating, weakening the immune system, ...
Can HIV be undetectable?
Often the medicines can lower the viral load so much that HIV becomes undetectable by current technology. This is a very good thing that can help in many ways, including reducing the risk that sexual partners get infected with HIV, the CDC says.
How long does it take for HIV to be under control?
Taking antiretroviral therapy reduces the amount of HIV in the blood to very low or undetectable levels. In most people using antiretroviral drugs, the virus is under control within 6 months.
How long does HIV last?
This may last for several days or weeks. Not everyone experiences these symptoms, however. If a person does not undergo testing, it is possible for HIV to progress without any indication that it is in the body. The flu-like symptoms of a stage 1 HIV infection may include: a fever. muscle or joint pain.
Why is antiretroviral therapy important?
It occurs when the immune system is damaged to the extent that it can no longer fight off infections. Taking antiretroviral drugs keeps the immune system strong enough to prevent HIV from progressing to this stage. Without treatment, the viral load continues to increase and the CD4 cell count continues to drop.
How does antiretroviral therapy help?
Antiretroviral therapy keeps the immune system healthy and reduces the risk of transmitting the virus to virtually zero. The sooner a person receives a diagnosis, the sooner they can begin treatment. Early treatment can improve the person’s outlook and lower the risk of the virus passing on to others.
What happens to the CD4 cell count in stage 3 HIV?
Without treatment, the viral load continues to increase and the CD4 cell count continues to drop. A person will receive a diagnosis of stage 3 HIV if their CD4 cell count drops under 200 cells per cubic milliliter. . Symptoms at this stage vary greatly, as they tend to stem from specific opportunistic infections.
What is the role of CD4 T cells in HIV?
HIV targets white blood cells called CD4 T cells that help protect the body from infection. By killing these cells, HIV progressively weakens the body’s defenses against infection and illness, leading to complications that can be fatal — unless a person receives ...
What is stage 2 HIV?
Stage 2: Chronic HIV infection. After the acute stage has ended — and if the person has not received treatment — the virus remains active, reproducing at very low levels but continuing to damage immune cells. At this stage, there are usually no symptoms or very mild ones.
How to get rid of AIDS faster?
If you feel stressed, increase your sleep time, and try stress relieving practices such as breathing exercises. This is because stress lowers the level of immunity in your body, and this can increase your chances of developing AIDS faster. 6. Don’t Engage in Risky Sexual Behavior.
How to prevent AIDS?
Here are a few tips to help you take your medications in the right way and prevent an early onset of AIDS: Start taking your medication at the right time. When you start taking antiretroviral drugs, you will need to keep taking them for the entire life. So make sure you are ready to this serious commitment.
What are the entry inhibitors for HIV?
Entry inhibitors include enfuvirtide and maraviroc. These drugs delay the development of AIDS by inhibiting the entry of the HIV virus into the CD4 cells. Integrase inhibitors. Integrase inhibitors include raltegravir, elvitegravir and dolutegravir. Integrase is a protein used by the HIV virus to insert its DNA into the CD4 cells.
What are the drugs that inhibit protease?
Protease inhibitors (PIs). This class includes atazanavir, darunavir, fosamprenavir and indinavir. These drugs inhibit protease, a protein required by the HIV virus to reproduce. Entry or fusion inhibitors. Entry inhibitors include enfuvirtide and maraviroc. These drugs delay the development of AIDS by inhibiting the entry ...
How many CD4 cells are needed for HIV?
Lower amount of CD4 cells in the body makes your body more susceptible to diseases. The normal CD4 cell count ranges from between 500 and 1000. A person is considered to have AIDS when the CD4 cell count is below 200 or when you are diagnosed with ...
What is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor?
This class includes drugs like efavirenz, etravirine and nevirapine. These drugs work by disabling a protein required by the HIV virus to reproduce. Nucleoside or nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs). This class of drugs includes abacavir.
What are the side effects of HIV?
The side effects of taking HIV medications include: 1 Nausea 2 Vomiting and diarrhea 3 Heart disease 4 Loss of bones or weakening of bones 5 Loss of muscle tissues 6 Unhealthy cholesterol levels 7 High blood sugar levels
What is the first stage of HIV?
The first noticeable stage is primary HIV infection. This stage is also called acute retroviral syndrome (ARS), or acute HIV infection. Because HIV infection at this stage usually causes flu-like symptoms, it’s possible for someone in this stage to think their symptoms are due to a severe flu rather than HIV. Fever is the most common symptom.
How long does it take for AIDS to develop?
AIDS is the final stage of HIV. According to AIDSinfo, it takes at least 10 years without treatment for most people with HIV to develop AIDS. At that point, the body is susceptible to a wide range of infections and can’t effectively fight them off.
Why is it important to test for HIV if you don't have symptoms?
Even though a person has no symptoms, they still have the virus. That’s why regular HIV testing is critical to prevent transmission.
How long does it take for HIV symptoms to show?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Trusted Source. , primary HIV symptoms may show up two to four weeks after initial exposure. Symptoms can continue for up to several weeks. However, some people may exhibit the symptoms only for a few days.
How long can you live with HIV?
Without treatments, the CDC estimates the average survival rate to be three years once AIDS is diagnosed. Depending on the severity of their condition, a person’s outlook may be significantly shorter. The key to living with HIV is to continue seeing a healthcare provider for regular treatments.
Does HIV appear overnight?
However, unlike what may occur with infections by other types of viruses, HIV symptoms don’t suddenly appear and peak overnight.
Can HIV be severe?
There can be long periods when the virus is present but symptoms are minimal. In more advanced stages of chronic HIV, symptoms can be much more severe than they are in ARS. People with advanced, chronic HIV can experience episodes of: coughing or breathing difficulties.
How long does it take to get rid of HIV?
There is no effective cure for HIV. But with proper medical care, you can control HIV. Most people can get the virus under control within six months. Taking HIV medicine does not prevent transmission ...
Why is it important to take HIV medication?
Taking HIV medication consistently, as prescribed, helps prevent drug resistance. Drug resistance develops when people with HIV are inconsistent with taking their HIV medication as prescribed. The virus can change (mutate) and will no longer respond to certain HIV medication. If you develop drug resistance, it will limit your options ...
What does it mean when your HIV is suppressed?
Viral suppression is defined as having less than 200 copies of HIV per milliliter of blood. HIV medicine can make the viral load so low that a test can’t detect it (called an undetectable viral load ). If your viral load goes down after starting HIV treatment, that means treatment is working.
What is the amount of HIV in the blood called?
The amount of HIV in the blood is called viral load . Taking your HIV medicine as prescribed will help keep your viral load low and your CD4 cell count high. HIV medicine can make the viral load very low (called viral suppression ). Viral suppression is defined as having less than 200 copies of HIV per milliliter of blood.
How long does it take for a mother to give her baby HIV?
If a mother with HIV takes HIV medicine as prescribed throughout pregnancy, labor, and delivery and gives HIV medicine to her baby for 4 to 6 weeks after birth, the risk of transmitting HIV to her baby can be 1% or less.
What to do if substance use is interfering with your ability to keep yourself healthy?
If substance use is interfering with your ability to keep yourself healthy, it may be time to quit or better manage it. If you need help finding substance use disorder treatment or mental health services, use SAMHSA’s Treatment Locator. external icon. .
Does HIV harm the immune system?
HIV will continue to harm your immune system. This will put you at higher risk for developing AIDS. Learn more about AIDS and opportunistic infections. This will put you at higher risk for transmitting HIV to your sexual and injection partners.

Diagnosis
Treatment
- Currently, there's no cure for HIV/AIDS. Once you have the infection, your body can't get rid of it. However, there are many medications that can control HIV and prevent complications. These medications are called antiretroviral therapy (ART). Everyone diagnosed with HIV should be started on ART, regardless of their stage of infection or complicati...
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Along with receiving medical treatment, it's essential to take an active role in your own care. The following suggestions may help you stay healthy longer: 1. Eat healthy foods.Make sure you get enough nourishment. Fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein help keep you strong, give you more energy and support your immune system. 2. Avoid raw meat, eggs and mo…
Alternative Medicine
- People who are infected with HIV sometimes try dietary supplements that claim to boost the immune system or counteract side effects of anti-HIVdrugs. However, there is no scientific evidence that any nutritional supplement improves immunity, and many may interfere with other medications you're taking. Always check with your doctor before taking any supplements or alter…
Coping and Support
- Receiving a diagnosis of any life-threatening illness is devastating. The emotional, social and financial consequences of HIV/AIDScan make coping with this illness especially difficult — not only for you but also for those closest to you. But today, there are many services and resources available to people with HIV. Most HIV/AIDSclinics have social workers, counselors or nurses wh…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- If you think you might have HIV infection, you're likely to start by seeing your family doctor. You may be referred to an infectious disease specialist — who additionally specializes in treating HIV/AIDS.