Type I hypersensitivity
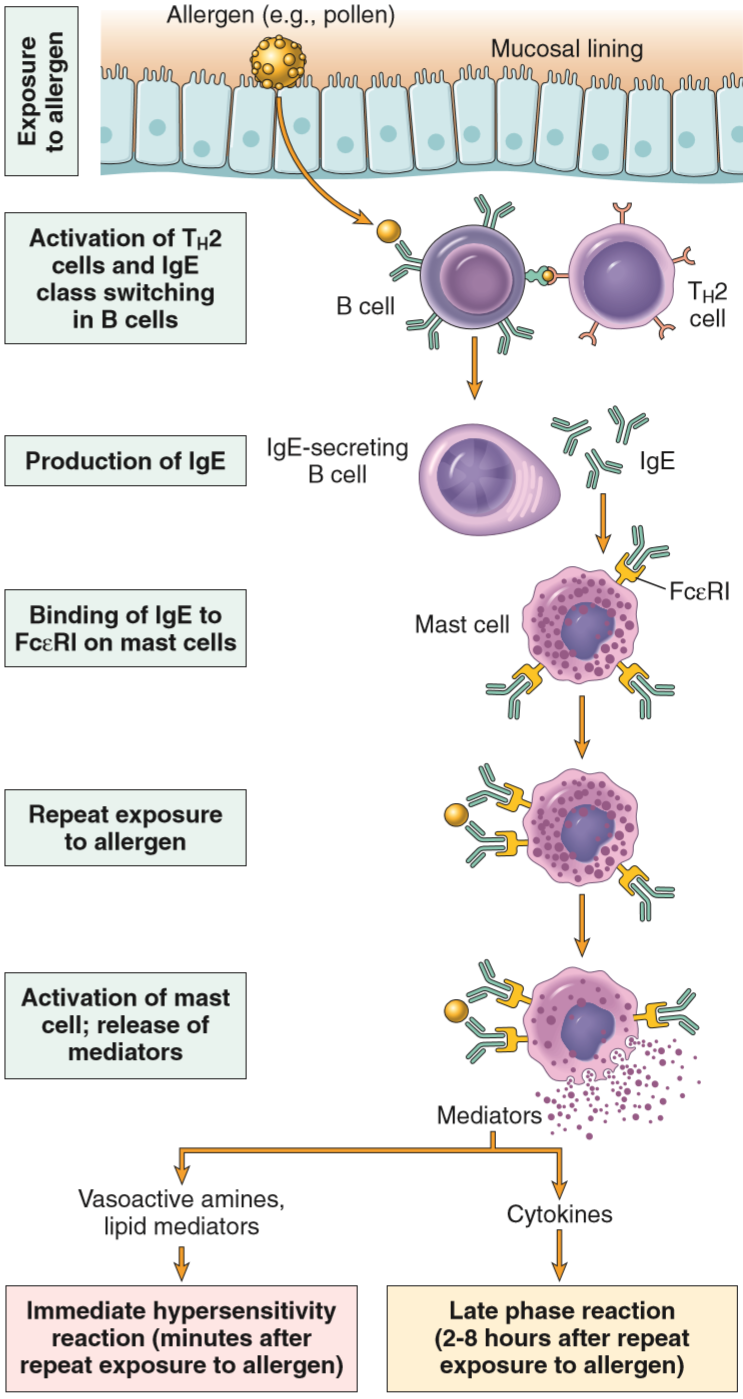
Type I hypersensitivity is an allergic reaction provoked by re-exposure to a specific type of antigen referred to as an allergen. Type I is distinct from type II, type III and type IV hypersensitivities.
Histamine receptor
The histamine receptors are a class of G protein–coupled receptors with histamine as their endogenous ligand.
Full Answer
What are the 4 types of hypersensitivity reactions?
Antihistamines are used for the treatment of type I hypersensitivity. These medications block histamine receptors on cell membrane surfaces. Treatment for anaphylactic symptoms is injection with epinephrine, a potent neurotransmitter and hormone that effectively halts the immune response. IgG blockers are also used to treat type I hypersensitivity.
Why is epinephrine used to stop allergic reactions?
Treatment of hypersensitivity and reactive skin disorders depends on the cause if it can be identified. Stopping a drug or avoiding exposure to a known irritant may be all that is needed. Bacterial infections are treated with antibiotics, and viral …
What are the four types of allergic reactions?
Nov 15, 2021 · Hypersensitivity reactions (HR) are immune responses that are exaggerated or inappropriate against an antigen or allergen. Coombs and Gell classified hypersensitivity reactions into four forms. Type I, type II, and type III hypersensitivity reactions are known as immediate hypersensitivity reactions …
What are the signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity?
Apr 12, 2018 · First of all, you need to identify the allergen that's causing the hypersensitivity. This is crucial so that you can avoid contact with it. Other treatment options include immunotherapy or administration of medications like cyclosporine, steroids, and more. Advertisement Causes of stimulant hypersensitivity (type V)

What is the treatment of hypersensitivity?
The treatment of immediate hypersensitivity reactions includes the management of anaphylaxis with intramuscular adrenaline (epinephrine), oxygen, intravenous (IV) antihistamine, support blood pressure with IV fluids, avoid latex gloves and equipment in patients who are allergic, and surgical procedures such as ...
What is the treatment of reaction?
Over-the-counter (OTC) antihistamines and decongestants may relieve minor symptoms of an allergic reaction. Antihistamines prevent symptoms such as hives by blocking histamine receptors so your body doesn't react to the allergens. Decongestants help clear your nose and are especially effective for seasonal allergies.
What is hypersensitivity medical term?
Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) refers to undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity. They are usually referred to as an over-reaction of the immune system and these reactions may be damaging and uncomfortable.
What is the treatment for Type 3 hypersensitivity?
Removal of the offending agent is the mainstay of treatment of type III hypersensitivity reaction. Antihistamines and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can provide symptomatic relief. Corticosteroids are used in severe cases to suppress the inflammation.Aug 22, 2021
What can epinephrine do?
This medication is used in emergencies to treat very serious allergic reactions to insect stings/bites, foods, drugs, or other substances. Epinephrine works quickly to improve breathing, stimulate the heart, raise a dropping blood pressure, reverse hives, and reduce swelling of the face, lips, and throat.
What is the medicine for allergy?
Antihistamines. Antihistamines have been used for years to treat allergy symptoms. They can be taken as pills, liquid, nasal spray, or eye drops. Over-the-counter (OTC) antihistamine eye drops can relieve red itchy eyes, while nasal sprays can be used to treat the symptoms of seasonal or year-round allergies.Nov 11, 2021
How is type 2 hypersensitivity treated?
Treatment for type 2 hypersensitivity typically involves immunosuppressants to prevent the action of unusual antibodies. Treatment options may include: systemic glucocorticoids. cyclophosphamide and cyclosporin agents.Oct 14, 2021
What are the 4 types of hypersensitivity?
The four types of hypersensitivity are:Type I: reaction mediated by IgE antibodies.Type II: cytotoxic reaction mediated by IgG or IgM antibodies.Type III: reaction mediated by immune complexes.Type IV: delayed reaction mediated by cellular response.Nov 7, 2021
What causes hypersensitivity disorder?
Hypersensitivity syndrome is caused by a complex set of interactions between a medication, your own immune system, and viruses in your body, especially herpes viruses.Jun 24, 2021
What is a Type 2 hypersensitivity reaction?
Type II hypersensitivity reaction refers to an antibody-mediated immune reaction in which antibodies (IgG or IgM) are directed against cellular or extracellular matrix antigens with the resultant cellular destruction, functional loss, or damage to tissues.Sep 20, 2021
What is the mechanism of Type 4 hypersensitivity?
Type IV hypersensitivity typically occurs at least 48 hours after exposure to an antigen. It involves activated T cells, which release cytokines and chemokines, and macrophages and cytotoxic CD8+ T cells that are attracted by these moieties.
What is a Type 1 hypersensitivity reaction?
Type I hypersensitivity (or immediate hypersensitivity) is an allergic reaction provoked by re-exposure to a specific type of antigen referred to as an allergen. Type I is distinct from type II, type III and type IV hypersensitivities. Exposure may be by ingestion, inhalation, injection, or direct contact.
What is a hypersensitivity reaction?
Hypersensitivity reactions (HR) are immune responses that are exaggerated or inappropriate against an antigen or allergen. Coombs and Gell classified hypersensitivity reactions into four forms.
What is Goodpasture syndrome?
Goodpasture Syndrome . Goodpasture syndrome is a type II hypersensitivity reaction characterized by the presence of nephritis in association with lung hemorrhage. In most patients, it is caused by cross-reactive autoantigens that are present in the basement membranes of the lung and kidney.
What is the anaphylactic response?
The anaphylactic response is mediated by IgE antibodies that are produced by the immune system in response to environmental proteins (allergens) such as pollens, animal danders, or dust mites.
Is anaphylaxis an IgE?
Anaphylaxis is a medical emergency as it can lead to acute, life-threatening respiratory failure. It is an IgE-mediated process. It is the most severe form of an allergic reaction, where mast cells suddenly release a large amount of histamine and later on leukotrienes.
What is the name of the disorder that causes double vision and weakness in the upper arms?
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disorder caused by antibodies to post-synaptic acetylcholine receptors that interfere with neuromuscular transmission. It is characterized by extreme muscular fatigue, double vision, bilateral ptosis, deconjugate eye movements, difficulty swallowing, and weakness in the upper arms.
Is asthma an atopic disease?
Allergic bronchial asthma is an atopic disease, characterized by bronchospasm. It may also be a chronic inflammatory disease. In its etiology, environmental factors along with a genetic background play an important role. The diagnosis is dependent on history and examination.
What is the disease that affects the skin and mucous membranes?
Pemphigus. Pemphigus causes a severe blistering disease that affects the skin and mucous membranes. The sera of patients with pemphigus have antibodies against desmoglein-1 and desmoglein-3, which are components of desmosomes, which form junctions between epidermal cells.
What is hypersensitivity intolerance?
Hypersensitivity has many names such as hypersensitivity intolerance or reaction. Though, it refers to any adverse response produced by the body's immune system. This condition is also known as the immune system's over-reaction which may cause damages to the body, uncomfortable feelings or even death.
How to treat allergic hypersensitivity?
The very first thing you should do to treat allergic hypersensitivity is to stay away from the allergens. You can do this if you know the exact cause of the reaction. This is the most crucial step in preventing future reactions and in reducing the symptoms of the condition.
Is there a cure for delayed type hypersensitivity?
The same thing goes if you're already following a treatment plan and you want to make modifications in it. As a matter of fact, there's no permanent cure for this condition. The treatment would only focus on managing its symptoms.
What are the different types of hypersensitivity?
The common types of hypersensitivity include type I, type II, type III, and type IV.
How does Type III hypersensitivity manifest itself?
Type III hypersensitivity can manifest itself in different ways. They can be either chronic or acute reactions which can occur in specific tissues or which can happen systematically. This is because self-antigens or foreign antigens can induce the condition.
What happens when the body's immune system reacts to foreign matter?
Allergic hypersensitivity or allergies happen when the body's immune system reacts to foreign matter. The allergic reaction would start when the immune system confuses a harmless substance for something harmful. When this happens, the immune system will produce antibodies which would remain in the body.
What is the interaction between antibodies and antigens?
Just like in type II hypersensitivity, there's an interaction between antigens and antibodies immune hypersensitivity. Here, the antibodies which are soluble bind to the antigens. They then form immune complexes which move through the bloodstream then settle in the different organs.
What are the different types of hypersensitivity reactions?
Hypersensitivity Reactions Key Takeaways 1 Hypersensitivity reactions are exaggerated immune responses to allergens. 2 There are four types of hypersensitivity reactions. Types I through III are mediated by antibodies, while type IV is mediated by T cell lymphocytes. 3 Type I hypersensitivities involve IgE antibodies that initially sensitize an individual to an allergen and provoke a quick inflammatory response upon subsequent exposure. Allergies and hay fever are both type I. 4 Type II hypersensitivities involve the binding of IgG and IgM antibodies to antigens on cell surfaces. This induces a cascade of events that leads to cell death. Hemolytic transfusion reactions and hemolytic disease of newborns are type II reactions. 5 Type III hypersensitivities result from the formation of antigen-antibody complexes that settle on tissues and organs. In an attempt to remove these complexes, underlying tissue is also damaged. Serum sickness and rheumatoid arthritis are examples of type III reactions. 6 Type IV hypersensitivities are regulated by T cells and are delayed reactions to antigens associated with cells. Tuberculin reactions, chronic asthma, and contact dermatitis are examples of type IV reactions.
What is hemolytic transfusion?
Hemolytic transfusion reactions involve blood transfusions with incompatible blood types. ABO blood groups are determined by the antigens on red blood cell surfaces and the antibodies present in blood plasma. A person with blood type A has A antigens on blood cells and B antibodies in blood plasma.
What is the function of IgE antibodies?
The antibodies are specific to a particular allergen and serve to detect the allergen upon subsequent exposure.
What is a hypersensitivity reaction?
Hypersensitivity Reactions. Certain human disorders are attributed to activity of the immune system. These disorders are commonly known as hypersensitivities, states of increased immune sensitivity that are mediated by antibody or cellular factors. The disorders may also involve immunodeficiencies in which failures of antibody‐mediated ...
How long does it take to die from anaphylactic shock?
In severe cases, anaphylactic shock may result in death within several minutes to an hour. To relieve the symptoms, epinephrine is administered together with a smooth muscle relaxer, a drug such as cortisone to reduce swelling, and other drugs as appropriate. Allergic reactions.
Is dust an allergen?
Foods, feathers, pollen grains, animal dander, and dust may be allergens. Animal sera, bee venoms, and wasp venoms are also allergens. The antibodies involved in anaphylaxis reactions are of the type IgE. In cytotoxic and immune complex reactions, IgG and IgM are involved. Anaphylaxis.
What is the role of the immune system in the body?
Normally the immune system plays an important role in protecting the body from microorganisms and other foreign substances. If the activity of the immune system is excessive or overreactive, a hypersensitivity reaction develops. The consequences of a hypersensitivity reaction may be injury to the body or death.
What is anaphylaxis shock?
Anaphylaxis, or type I hypersensitivity, is a whole-body, immediate hypersensitivity also known as anaphylactic shock. The allergens are introduced to the body directly to the tissues in a concentrated form (intramuscular or intravenous injection, for example).
What is an allergic reaction?
Allergic reactions (allergy) are a milder, localized form of anaphylaxis. As noted, such things as foods, pollen grains, and animal dander can induce these localized reactions. IgE, basophils, and mast cells are involved, but much less than in anaphylaxis.
What are some examples of cytotoxic reactions?
An example of a cytotoxic reaction is thrombocytopenia. In this disease, antibody molecules are elicited by certain drug molecules. The antibodies unite with antigens on the surface of thrombocytes (platelets), and with complement activation, the thrombocytes are destroyed.
What is the best treatment for pruritus?
H1- and H2-receptor blockers can be helpful in alleviating pruritus, urticaria, rhinorrhea, and other symptoms. Use albuterol nebulizers if needed. Administer a corticosteroid, which is believed to help prevent or control the late-phase reaction. Transfer the patient to the hospital for further observation and care.
What to do if you have anaphylactic reaction?
Patients should be taught what measures to take in case of a future anaphylactic reaction, i.e., immediately administer e pinephrine, call emergency services (e.g., 911), or go to the nearest emergency department (even if feeling better after the epinephrine).
What is the NAEPP?
Therapy depends on the severity of disease as well as age of patient. In 2007, the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program (NAEPP) Expert Panel from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) released guidelines on the diagnosis and management of asthma.
What is the FDA approved treatment for atopic dermatitis?
Dupilumab (Dupixent) is a monoclonal antibody antagonist which binds to the IL-4 receptor alpha antagonist. It is FDA approved for the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in patients age 6 and older whose atopic dermatitis is not well controlled on topical prescription medications. [ 80]
What is a hypersensitivity reaction?
Hypersensitivity reactions occur when the normally protective immune system responds abnormally, potentially harming the body. Various autoimmune disorders as well as#N#allergies#N#fall under the umbrella of hypersensitivity reactions, the difference being that#N#allergies#N#are immune reactions to#N#exogenous#N#substances (#N#antigens#N#or#N#allergens#N#), whereas autoimmune diseases arise from an abnormal immune response to#N#endogenous#N#substances (autoantigens). A symptomatic reaction only occurs in sensitized individuals, i.e., they must have had at least one prior asymptomatic contact with the offending#N#antigen#N#. Hypersensitivity reactions are commonly classified into four types.#N#Type I hypersensitivity#N#reactions are immediate#N#allergic reactions#N#(e.g., food and pollen#N#allergies#N#,#N#asthma#N#,#N#anaphylaxis#N#).#N#Type II hypersensitivity reactions#N#are referred to as cytotoxic, as they involve#N#antibodies#N#that are specific to particular tissues within the body and cause destruction of cells in these tissues (e.g.,#N#autoimmune hemolytic anemia#N#,#N#Goodpasture syndrome#N#).#N#Type III hypersensitivity reactions#N#are immune complex-mediated, with tissue damage caused by#N#antigen#N#-#N#antibody#N#complex deposition (e.g., many#N#vasculitides#N#and#N#glomerulonephritides#N#).#N#Type IV hypersensitivity reactions#N#(e.g.,#N#TB#N#skin tests,#N#contact dermatitis#N#) are delayed and cell-mediated and are the only hypersensitivity reaction that involves sensitized#N#T lymphocytes#N#rather than#N#antibodies#N#. Unlike true hypersensitivity reactions, which occur after sensitization,#N#nonallergic hypersensitivity#N#reactions (e.g.,#N#pseudoallergies#N#) cause#N#mast cell#N#activation and#N#histamine#N#release after initial exposure to a trigger substance (e.g., radiocontrast media).
What is cytotoxic reaction?
asthma. , anaphylaxis. ). Type II hypersensitivity reactions. are referred to as cytotoxic, as they involve. antibodies. that are specific to particular tissues within the body and cause destruction of cells in these tissues (e.g., autoimmune hemolytic anemia.
What is the difference between hypersensitivity and allergy?
Allergy: an abnormal immunological response to an otherwise harmless environmental stimulus (e.g., food, pollen, animal dander)
Why do children have sensory overload?
In children who do not have a related condition, sensory overload may simply occur because the brain is still developing. Parents and caregivers should learn to recognize both the triggers and the signs and symptoms of sensory overload in children.
What is sensory overload?
Summary. Sensory overload is the overstimulation of one or more of the body’s five senses, which are touch, sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Sensory overload can affect anyone, but it commonly occurs in those with autism, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), sensory processing disorder, and certain other conditions.
Does autism have sensory input?
Autistic people commonly perceive sensory input differently. According to Autism Speaks, in 2013, the American Psychiatric Association added sensitivity to sensory input to the list of diagnostic criteria for autism.
Can ADHD cause sensory overload?
In people with ADHD, sensory inputs compete for attention in the brain, which may trigger sensory overload. Understood.org, a nonprofit organization, suggest that certain types of sensory information, such as the texture of food or sensation of clothing, are more likely to cause sensory overload in those with ADHD.
Is sensory overload a disorder?
As sensory overload is not an official disorder, it is not possible to get a formal diagnosis. However, many doctors and healthcare professionals recognize sensory overload, especially in autistic people and those who have ADHD and other related conditions.
Is there a treatment for sensory overload?
There is no specific treatment for sensory overload. Generally, the aim is to help people with frequent episodes of sensory overload to be able to plan for them and manage their reactions. Occupational therapy may be helpful for children who experience sensory overload.
Can sensory overload be a problem?
Sensory overload can happen to anyone, but it is more common in autistic people and people with ADHD, PTSD, and certain other conditions. It causes feelings of discomfort and being overwhelmed. Moving away from sources of sensory input, such as loud sounds or strong smells, can reduce these feelings.
How to tell if you are sensitive to a syringe?
Signs of sensitive skin come from the breakdown of your skin’s protective barrier. This can be caused by the environment, dehydration, or an underlying condition. Signs include: 1 Rough, flaky patches 2 Wrinkled, rough texture 3 Redness 4 Swelling 5 Open sores or yellow crust over the skin 6 Peeling skin
Why does my skin itch when I pull weed?
When your skin touches an allergen, such as pollen when pulling weeds, your body tries to protect itself by releasing T-cells. 2 This process can lead to redness and itching.
What does it mean when your skin is sensitive?
Sensitive skin is a common condition and means your skin is more prone to reactions such as redness and itching. Most people who have sensitive skin notice occasional or frequent itching, burning and stinging of patches of skin. Sensitive skin is very treatable and may require a visit to the dermatologist. While uncommon, sensitive skin can ...
How long should I shower in the winter?
Make sure to limit hot baths or showers to five minutes, as the hot water could further irritate sensitive skin. When you towel off, gently pat your skin dry, as opposed to rubbing it. Apply sunscreen any time you’ll be spending time outdoors, even in the winter.
Who is Dr. Leah Ansell?
Leah Ansell, MD, is a board-certified dermatologist and an assistant professor of dermatology at Columbia University. Sensitive skin is a common condition and means your skin is more prone to reactions such as redness and itching.
Can dry winter air cause skin sensitivity?
It turns out the dry winter air may be enough to cause your skin sensitivity. According to the American Academy of Dermatology Association, excessively dry skin can put you at risk for developing another skin condition due to the irritation and itching. 5
Why do I have pimples on my face?
Acne is a skin condition that causes pimples on the skin. It is the most common reason for seeing a dermatologist. There are plenty of myths for what causes it, but acne is triggered when your skin pores are clogged. 4 . Acne.