How does proflavine interact with DNA?
Proflavine contains amino groups that interact ionically with negatively charged phosphate groups on DNA, while the aromatic ring system intercalates. Arnab Mukherjee, Wilbee D. Sasikala, in Advances in Protein Chemistry and Structural Biology, 2013
Which type of mutation would increase the amount of functional protein?
A missense mutation may or may not affect protein function, depending on the nature of the amino acid substitution and whether the substitution is in a critical region of the protein. C. An up promoter mutation would increase the amount of functional protein.
Is proflavine an effective antibacterial agent against HIV?
Proflavine is also a promising candidate in HIV treatment due to its recently discovered intercalating ability into viral RNA ( DeJong, Chang, Gilson, & Marino, 2003 ). Trapaflavine, ethacridine, and acriflavine were also used as antibacterial agents ( Wainwright, 2001 ).
How to prepare proflavin-labeled tRNA fmet?
The preparation of proflavin-labeled tRNA fMet proceeds in two steps: reduction of the dihydroU base at position 20 in the D loop of tRNA by borohydride treatment followed by the attachment of proflavin at that position ( Wintermeyer and Zachau, 1974 ).
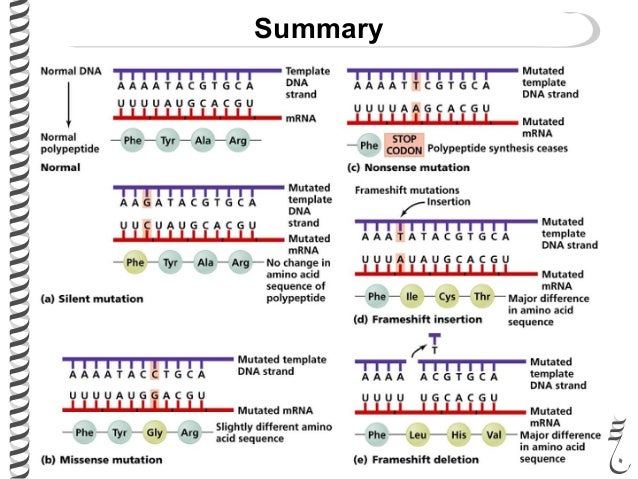
What types of mutations can intercalating agents lead to?
Intercalating agents, such as acridine, introduce atypical spacing between base pairs, resulting in DNA polymerase introducing either a deletion or an insertion, leading to a potential frameshift mutation.
What is the use of Proflavine?
The hemisulfate salt form of proflavine, an acridine-derived fluorescent contrast and disinfectant agent that can potentially be used for cellular imaging and antiseptic purposes.
Which type of mutations are commonly induced by proflavin & acridine orange?
Suppressor Mutations Mutations of the bacteriophage T4 rII genes induced by the acridine proflavin were found to be of two types, microinsertions (+) and microdeletions (−). It was discovered that some revertants of these mutants actually contained two mutations, the original rII mutation and an intragenic suppressor.
How does Proflavine interact with DNA?
Proflavine destroys microorganisms by denaturation of DNA. Due to its abundant antimicrobial properties proflavine is conventionally employed as antimicrobial agent in various forms even in developed countries. Due to its intercalating property it also affects human DNA after exposure.
What is the storage condition of proflavine?
Solutions stored at room temperature were chemically stable up to six months (94-105%). Conclusion: Proflavine solutions at concentration of 0.01% were chemically and physically stable for at least 12 months under refrigeration. The solution was chemically stable for six months when stored at room temperature.
What is the structure of proflavine?
C13H11N3Proflavine / Formula
How does proflavin lead to frameshift mutations?
Frameshift mutations were induced by proflavin in the rIIB gene of bacteriophage T4. rIIB DNA from each of 48 independent frameshifts was inserted into M13mp8 and sequenced. Two-thirds of the frameshifts (33/48) lie contiguous to one another in 10 base pairs of the rIIB sequence.
How do proflavin and acridine orange differ from other mutagenic compounds?
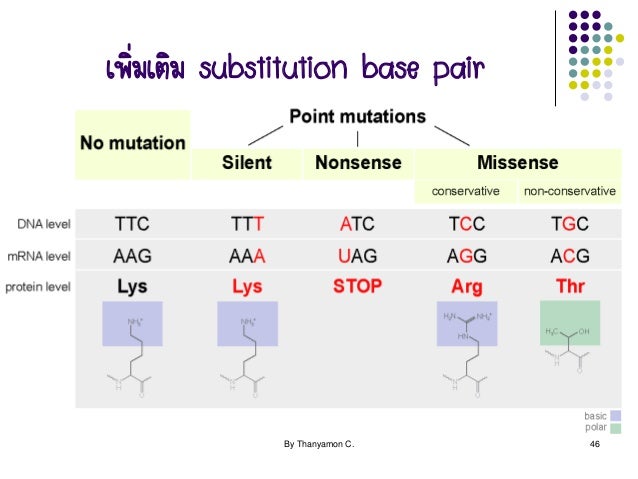
Intercalating compounds such as proflavin and acridine orange differ from other mutagenic compounds in that they distort the DNA duplex "fooling" DNA polymerase into inserting extra bases or skipping templated bases, leading to base insertions and deletions, respectively, rather than base substitutions.
Which mutagen causes frameshift mutation?
ProflavinProflavin is an acridine dye that intercalates itself between base pairs of the DNA chain thereby causing loss or gain of a single nucleotide. The gene mutation alters the base sequence of the whole genetic frame from the point of mutation called frameshift mutation. So the correct answer is option is B. Proflavin.
Which heterocyclic ring is present in proflavine?
This compound belongs to the class of organic compounds known as acridines. These are organic compounds containing the acridine moiety, a linear tricyclic heterocycle which consists of two benzene rings joined by a pyridine ring.
Which ring is present in proflavine?
3,6-diaminoacridine is an aminoacridine that is acridine that is substituted by amino groups at positions 3 and 6. A slow-acting bacteriostat that is effective against many Gram-positive bacteria (but ineffective against spores), its salts were formerly used for treatment of burns and infected wounds.
What are acridine dyes?
Definition of acridine dye : any of a small class of basic dyes containing the acridine nucleus, most of them being yellow, orange, red, or brown, that are fluorescent in solution and are used chiefly for dyeing leather and mordanted cotton.
What are the inhibitors of PARG?
Several inhibitors, including proflavine, ethacridine (IC50 = 7.2 μM), ethidium bromide, ellipticine, daunomycin, and tilorone (IC 50 = 7.3 μM), were evaluated by Tavassoli et al. (1985). These inhibitors have been shown to indirectly inhibit PARG by forming a complex with PAR and blocking the binding of PARG to substrate. More recently, the second generation of DNA intercalator PARG inhibitors was developed, based on the structure of tilorone. The representative compounds, GPI16552 and GPI18214, have been tested in several in vivo studies showing anti-inflammatory effects (see Section 6.1 ).
How does intercalation affect DNA?
Intercalation has the effect of lengthening the duplex by around 3 Å per bound drug molecule, causes DNA to unwind, and prevents replication and transcription by interfering with the action of topoisomerases. The degree of unwinding depends on the structure of the intercalating molecule and the site of intercalation. The tight ternary complex formed between the intercalated drug, the DNA, and the topoisomerase is lethal to proliferating cells, so intercalators are often more toxic to cancer cells than to normal cells.
What is the purpose of tricyclic acridine chromophore?
The tricyclic acridine chromophore was originally developed ( Harrison et al., 1999) as an alternative platform to the anthraquinones, in order to circumvent the poor aqueous solubility of many amidoanthraquinone derivatives. The central ring nitrogen atom in acridines such as 3,6-diaminoacridine (proflavine) is protonated at physiological pH (Albert, 1966 ), which would aid solubility as well as increase electron deficiency through the chromophore, leading to enhanced G–quadruplex interactions. This prediction was borne out in a series of 3,6-disubstituted amidoacridines ( Figure 4–9 ), with side-chains closely similar to those established in the earlier amidoanthraquinone series. Their ability to inhibit the telomerase enzyme is approximately correlated with their antiproliferative activity and their relative quadruplex affinity relates, as with the anthraquinone derivatives, to the cationic charge and size of the end-groups on the side chains ( Read et al., 1999 ).
What are some examples of anthracycline antibiotics?
Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) and daunorubicin (Daunomycin), isolated from Streptomyces strains, are important examples of anthracycline antitumor antibiotics. Both possess an amino group on the sugar, which forms an ionic interaction with the negatively charged DNA phosphate backbone when protonated. This bond helps to hold the molecule in place allowing the planar aromatic ring system to slide into the double helix. Although doxorubicin and daunorubici n differ by only one hydroxyl group, they have different activities: daunorubicin is active only against leukemias, but doxorubicin is active against leukemias and a wide range of solid tumors ( Fig. 7.6 ).
When was photoreactivation repair discovered?
Answer: Photoreactivation repair, discovered in 1949 , is a process described in E. coli in which UV-induced DNA damage can be partially reversed if cells are briefly exposed to light in the blue range of the visible spectrum.
What is a homozygous deletion?
b) A deletion (homozygous) that removes approximately half of the rRNA genes. Answer: (a) Population of proteins: Half of the protein products of that gene will be defective, and the other half will be normal.
What is the analog of thymine?
The mutagen 5-bromouracil is an analog of thymine, which anomalously pairs with guanine. Ultraviolet light causes thymine dimers. Three human disorders—fragile X syndrome, myotonic dystrophy, and Huntington's disease-are conceptually linked by a common mode of molecular upset.
Is a new recessive mutation homozygous?
Answer: If the new mutation is dominant and passed to the next generation, it would be expressed. New recessive mutations are not normally expressed in the next generation unless, through a combination with a like mutation from the other parent, they are homozygous.
