- Breaks in the skin allow bacteria to enter. ...
- Doctors diagnose cellulitis by how it looks. ...
- Antibiotics are needed. ...
- Complications are uncommon, but can be serious.
Medication
Cellulitis is a treatable condition, but antibiotic treatment is necessary to eradicate the infection and avoid complications and spread of the infection. Most cellulitis can be effectively treated with oral antibiotics at home.
Procedures
If your cellulitis is not improving after two or three days, your doctor may prescribe a different antibiotic or have you admitted for IV treatment. Is there anything I can do at home? Cellulitis requires treatment with antibiotics, which are only prescribed by a doctor.
Self-care
See a doctor if you have symptoms of cellulitis. Seek medical attention immediately if the red area of the skin spreads quickly or you develop a fever or chills. Anyone can get cellulitis, but some factors can increase the risk of getting this infection.
Nutrition
An ongoing infection may lead to bacteria entering the bloodstream, a potentially life-threatening situation. In the case of recurring cellulitis, the condition may cause chronic limb swelling and injure the lymphatic drainage system. Necrotizing fasciitis may result from infection of the fascia tissue and is a medical emergency.
Is cellulitis treatable with antibiotics?
What should I do if my cellulitis is not improving?
When should I see a doctor for cellulitis?
Is cellulitis a medical emergency?

How do you know if cellulitis is severe?
It's important to identify and treat cellulitis early because the condition can spread rapidly throughout your body. Seek emergency care if: You have a swollen, tender rash or a rash that's changing rapidly. You have a fever.
When can cellulitis be fatal?
Cellulitis can range from mild to severe. Most cases are treated effectively with antibiotics. Prompt treatment is key. If severe, or when left untreated, cellulitis can spread to your lymph nodes, bloodstream and deeper tissues, rapidly becoming life-threatening.
Why would you be hospitalized for cellulitis?
You may need to be hospitalized and receive antibiotics through your veins (intravenously) if: Signs and symptoms don't respond to oral antibiotics. Signs and symptoms are extensive. You have a high fever.
When does cellulitis turn into sepsis?
Cellulitis can cause sepsis in some people. Often incorrectly called blood poisoning, sepsis is the body's life-threatening response to infection. Sepsis and septic shock can result from an infection anywhere in the body, such as pneumonia, influenza, and urinary tract infections.
When should you go to the hospital for an infection?
“If there is fever, rapidly spreading redness, rapid heart rate, or extraordinary pain that is disproportionate to the wound or injury, that is when you tell the patient to visit the hospital,” he said.
Why is cellulitis an emergency?
Cellulitis is usually caused by staphylococci (“staph”) or streptococci (“strep”) bacteria that live on the skin or inner surface of the nose or mouth. Cellulitis emergency happens when bacteria manages to get under the skin and spread to the tissues beneath, cellulitis can develop.
What are the chances of dying from cellulitis?
Conclusions: The overall mortality rate for patients hospitalized with cellulitis is 1.1% and for patients in the United States the rate was 0.5%. This rate compares to mortality rates of low risk conditions that are often managed as outpatients or in observation units.
When does cellulitis need hospitalization?
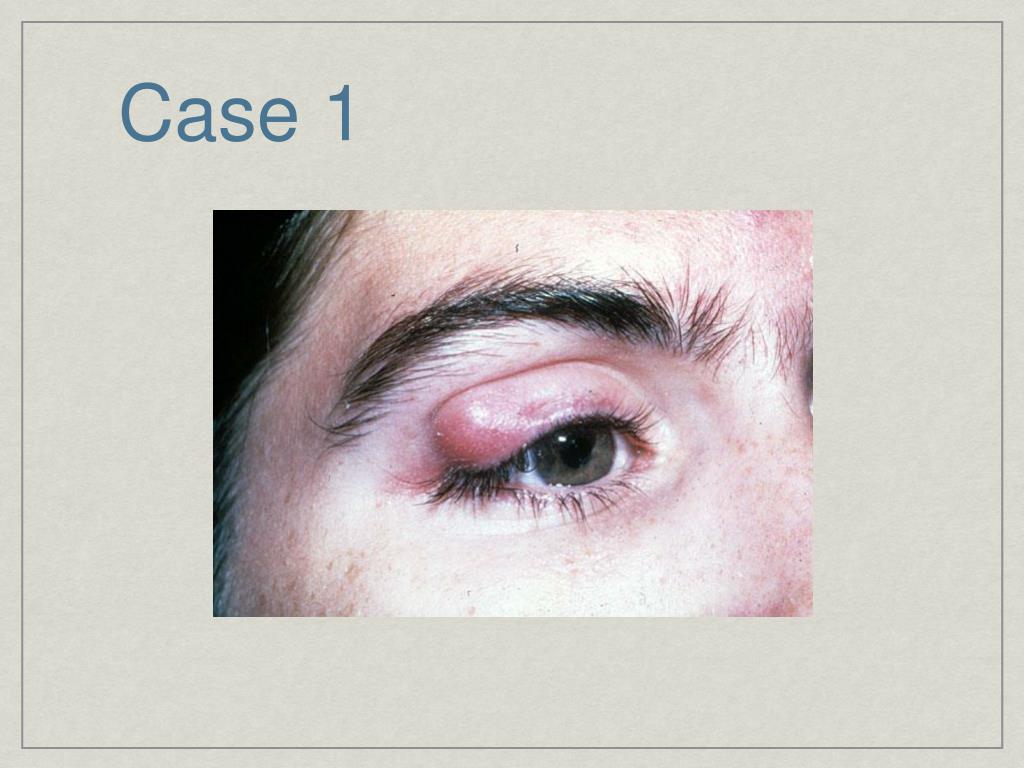
Call 999 for an ambulance or go to your nearest accident and emergency (A&E) department immediately if: your face or the area around your eye is affected. your symptoms are getting rapidly worse. you experience other symptoms in addition to the changes in your skin, such as a fever or vomiting.
Can cellulitis get worse while on antibiotics?
Cellulitis is a common infection of the skin that usually clears up with a round of oral antibiotics. Sometimes, these infections can get worse even when you are taking antibiotics. This can be a sign that you need stronger or different antibiotics to treat the infection.
What are the 5 signs of sepsis?
These can include:feeling dizzy or faint.a change in mental state – such as confusion or disorientation.diarrhoea.nausea and vomiting.slurred speech.severe muscle pain.severe breathlessness.less urine production than normal – for example, not urinating for a day.More items...•
What are the early warning signs of sepsis?
The signs and symptoms of sepsis can include a combination of any of the following:confusion or disorientation,shortness of breath,high heart rate,fever, or shivering, or feeling very cold,extreme pain or discomfort, and.clammy or sweaty skin.
What are the red flags for sepsis?
Sepsis SymptomsFever and chills.Very low body temperature.Peeing less than usual.Fast heartbeat.Nausea and vomiting.Diarrhea.Fatigue or weakness.Blotchy or discolored skin.More items...•
What are the symptoms of cellulitis?
This area spreads to surrounding tissues, resulting in the typical signs of inflammation -- redness, swelling, warmth, and pain.
How do you know if you have cellulitis?
Cellulitis has characteristic symptoms and signs. Symptoms usually begin as a small area of tenderness, swelling, and redness that spreads to adjacent skin. The involved skin may feel warm to the touch.
What is the name of the bacterial infection that causes cellulitis?
Cellulitis is a bacterial infection of the skin and tissues beneath the skin. Staphylococcus and Streptococcus are the types of bacteria that are usually responsible for cellulitis, although many types of bacteria can cause the condition.
What is cellulitis in skin?
Share Your Story. Cellulitis is a bacterial infection of the skin and tissues beneath the skin. Unlike impetigo, which is a very superficial skin infection, cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection that also involves the skin's deeper layers: the dermis and subcutaneous tissue.
What is the most common bacteria that cause cellulitis?
The most common bacteria that cause cellulitis are beta-hemolytic streptococci (groups A, B, C, G, and F). A form of rather superficial cellulitis caused by strep is called erysipelas and is characterized by spreading hot, bright red circumscribed area on the skin with a sharp, raised border.
Where does cellulitis appear?
Sometimes cellulitis appears in areas where the skin has broken open, such as the skin near ulcers or surgical wounds. Symptoms and signs of cellulitis include. redness, pain and tenderness, swelling, enlarged lymph nodes, and. the warmth of the affected area. Cellulitis can occur anywhere in the body.
Can cellulitis cause fever?
A person with cellulitis can also develop fever and/or swollen lymph nodes in the area of the infection. Learn about cellulitis treatment options ». Illustration cross-section of the skin and where cellulitis occurs. MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staph aureus) can also cause cellulitis. Source: MedicineNet.
How is cellulitis treated?
Cellulitis is treated with antibiotics. Most cellulitis infections can be treated with antibiotics that are taken by mouth (oral antibiotics). More serious infections may need to be treated in the hospital with intravenous (IV) antibiotics, which are given directly into a vein.
How to prevent cellulitis?
Common sense and good wound care are the best ways to prevent bacterial skin infections, including cellulitis. Clean all minor injuries that break the skin with soap and water. Clean all minor cuts and injuries that break the skin (like blisters and scrapes) with soap and water.
What does it mean when your skin is red and swollen?
In general, cellulitis appears as a red, swollen, and painful area of skin that is warm and tender to the touch. The skin may look pitted, like the peel of an orange, or blisters may appear on the affected skin. Some people may also develop fever and chills. Cellulitis can appear anywhere on the body, but it is most common on the feet and legs.
What is the condition that causes redness, swelling, and pain in the infected area of the skin?
Cellulitis is a common bacterial skin infection that causes redness, swelling, and pain in the infected area of the skin. If untreated, it can spread and cause serious health problems. Good wound care and hygiene are important for preventing cellulitis.
How do you get cellulitis?
How People Get Cellulitis. Experts do not know how the bacteria get into the body for many people who get cellulitis. Sometimes the bacteria get into the body through openings in the skin, like an injury or surgical wound. In general, people cannot catch cellulitis from someone else.
What are the factors that increase the risk of cellulitis?
Other factors that increase someone’s risk for cellulitis include: Problems with the lymphatic system so it does not drain the way it should (lymphedema); the lymphatic system is a part of the body’s immune system that helps move fluid that contains infection-fighting cells throughout the body.
How do doctors diagnose cellulitis?
Doctors Diagnose Cellulitis by How It Looks. Doctors typically diagnose cellulitis by doing a physical examination and looking at the affected skin. Blood or other lab tests are usually not needed.
How to prevent cellulitis?
To help prevent cellulitis and other infections, take these precautions when you have a skin wound: Wash your wound daily with soap and water. Do this gently as part of your normal bathing. Apply a protective cream or ointment.
Why is it important to see a doctor for cellulitis?
When to see a doctor. It's important to identify and treat cellulitis early because the condition can spread rapidly throughout your body. Seek emergency care if: You have a red, swollen, tender rash or a rash that's changing rapidly. See your doctor, preferably that day, if:
What is the name of the bacterial infection that causes skin to turn red?
Cellulitis (sel-u-LIE-tis) is a common, potentially serious bacterial skin infection. The affected skin appears swollen and red and is typically painful and warm to the touch. Cellulitis usually affects the skin on the lower legs, but it can occur in the face, arms and other areas. It occurs when a crack or break in your skin allows bacteria ...
What is the most common cause of cellulitis?
Cellulitis occurs when bacteria, most commonly streptococcus and staphylococcus, enter through a crack or break in your skin. The incidence of a more serious staphylococcus infection called methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is increasing.
What is the best treatment for a wound?
For most surface wounds, an over-the-counter ointment (Vaseline, Polysporin, others) provides adequate protection. Cover your wound with a bandage. Change bandages at least daily. Watch for signs of infection. Redness, pain and drainage all signal possible infection and the need for medical evaluation.
How does a scaby skin infection spread?
It occurs when a crack or break in your skin allows bacteria to enter. Left untreated, the infection can spread to your lymph nodes and bloodstream and rapidly become life-threatening. It isn't usually spread from person to person.
How to treat cellulitis?
Treatment for Cellulitis. Your doctor will prescribe antibiotics to control the growth and spread of the infection. The choice of drug will depend upon the type of bacteria responsible for the infection. 1. Antibiotics.
How many people seek emergency care for cellulitis?
Moreover, cellulitis is reported to be one of the top causes of visits to the emergency room. More than 200 people per 100,000 seek emergency help at the hospital for cellulitis every year.
What is the infection of the deep skin layers and subdermal tissue?
Cellulitis is an infection of the deep skin layers and subdermal tissue with symptoms of redness, swelling, warmth, pain, and in severe cases, blisters, pustules, and necrotic (dead) tissue. Advertisements.
How many cases of cellulitis in 2006?
Cellulitis most commonly affects middle-aged men and older adults. In 2006, nearly 2,500 cases per 100,000 patients were diagnosed with cellulitis in the United States. (1) A considerable mortality rate is attributed to cellulitis, which underlines just how dangerous it can be.
Where does cellulitis occur?
Cellulitis can occur anywhere on the body, but it mostly affects the exposed areas of the skin, such as the face, neck, and limbs. Children most often get cellulitis on the head, face, or neck, whereas adults usually get it on the extremities.
Can cellulitis cause nerve damage?
Uncomplicated cases of cellulitis do not usually lead to nerve damage. Untreated infections that spread to deep tissues or necrotizing fasciitis can cause permanent nerve damage due to the severity of the infection and increased likelihood of the need for surgical debridement (removal of dead tissue).
Can cellulitis be fatal?
Accurate diagnosis and prompt treatment are key. Cellulitis can be fatal if not treated appropriately and can spread to deep tissues and eventually to the lymph system, bloodstream, and organs.
How to heal cellulitis at home?
Covering your wound. Properly covering the affected skin will help it heal and prevent irritation.
How long does it take for cellulitis to go away?
With antibiotic treatment, the symptoms of cellulitis should begin to disappear within 48 hours, but it’s very important to continue taking your antibiotics until all the pills are gone. Otherwise, it may come back, and the second course of antibiotics may not be as effective as the first.
What is cellulitis on legs?
What is cellulitis? Cellulitis is a type of bacterial infection that can quickly become serious. It affects your skin, causing inflammation, redness, and pain. This type of infection occurs when bacteria enters your body through broken skin. It can affect any part of the body, but it’s most common on the lower legs.
How long does it take for antibiotics to work on cellulitis?
Sometimes oral antibiotics don’t work as well as they should. If your cellulitis is not improving after two or three days, your doctor may prescribe a different antibiotic or have you admitted for IV treatment.
What is it called when you have a deep infection of the fascia?
An infection of the fascia, a deep layer of tissue surrounding your muscles and organs, is known as necrotizing fasciitis, or flesh-eating disease. People with necrotizing fasciitis usually need multiple surgeries to remove dead tissue, often entire limbs.
How do you know if you have cellulitis?
Cellulitis tends to progress quickly, so early identification is key. At first, you might just feel some pain and tenderness. But over the course of a few hours, you may start to notice: skin that’s warm to the touch. blistering. skin dimpling. growing area of redness.
What is the best treatment for athlete's foot?
A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory, like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or naproxen (Aleve), can help reduce pain and inflammation. Treating any underlying conditions. Treat any underlying conditions, such as athlete’s foot or eczema, that caused the wound that got infected. Taking all your antibiotics.
What is the best treatment for cellulitis?
Different antibiotics are used depending on the severity of the infection. Mild cases of cellulitis are treated with oral antibiotics such as dicloxacillin and cephalexin. Severe cases of cellulitis are treated with intravenous antibiotics ...
How long does it take for cellulitis to heal?
Many people will notice fever and chills dissipating 1 to 2 days after starting antibiotics. Warmth and swelling may recede within a few days although do not be surprised if the symptoms last a few weeks.
How to treat cellulitis on the arm?
Elevating the limb helps decrease swelling and encourages faster healing. Keep the affected area clean and dry. It is okay to bathe, just be very gentle with the skin patting it dry. Do not rub the area. It may irritate the skin. Do not use antibiotic cream or ointment on the affected area.
What is cellulitis in the body?
Cellulitis is a bacterial infection deep within the skin. It is more likely in cases where people have: Skin conditions like athlete's foot, shingles, or eczema. Diabetes or other immune system problems. Pressure sores, lymphedema, puncture injuries, insect bites, animal bites, or surgical incisions.
Why do you need an MRI for cellulitis?
A doctor may be more likely to order an MRI if any of the following are present: Inadequate circulation in the lower legs. Immune system dysfunction. Diabetes.
What conditions mimic cellulitis?
Conditions that mimic cellulitis include: Contact dermatitis: This is a rash that may develop after coming into contact with an irritating substance. Stasis dermatitis: This is a type of swelling that occurs due to inadequate circulation, usually in the lower leg.
What are the signs of a severe infection?
These include: The presence of an animal bite. The presence of a serious condition like diabetes or cancer. The presence of fever or other potential signs of systemic infection. The presence of a severe skin infection. Inadequate response to the first antibiotic prescribed.
What to do if you suspect cellulitis?
If you suspect a Cellulitis Emergency you should go and see your doctor as soon as possible to avoid potential complications. Keep an eye on the suspected area from day to day, and if you notice any worsening or spreading of the signs or symptoms, seek medical care.
How to protect against cellulitis?
For instance, taking care when using knives or other sharp instruments, and not going barefoot in hazardous areas such as on the beach or in the forest.Cellulitis is also easily spread from skin to skin contact or by touching infected surfaces.
What is cellulitis emergency?
Cellulitis is a skin disease. Cellulitis Emergency happens when bacteria manages to get under the skin and spread to the tissues beneath, cellulitis can develop. The bacteria responsible are Streptococcus or Staphylococcus. In most cases, Cellulitis Emergency is not a serious, life-threatening condition and as a bacterial skin infection, ...
What is the emergency diagnosis for cellulitis?
Cellulitis Emergency Diagnosis is normally a simple matter for your doctor, based on a physical exam and your medical history. Occasionally the doctor may request some blood work if he or she suspects infection has passed into the bloodstream, or to check your white blood cell count. If a foreign object is suspected, ...
What causes cellulitis to get worse?
Pain gets worse. Vomiting or nausea. High fevers or chills. Certain pre-existing medical conditions can also increase the seriousness of cellulitis, so if you have any of the following you should also seek urgent medical care: Diabetes. Liver conditions such as cirrhosis or hepatitis. Kidney disease.
Can cellulitis cause eye infections?
In addition, certain areas of the body are more sensitive than others, for instance in or around the eyes. Children with facial cellulitis can sometimes develop brain or eye infections. These are potentially dangerous so should always be treated as an emergency.
Can a bite on the skin cause cellulitis?
Insect bites puncture the skin and can put you at risk. Cellulitis can sometimes result from surgical wounds. Foreign objects becoming embedded in or under the skin (such as glass, metal or ceramics) can lead to cellulitis.

Overview
Symptoms
Causes
Risk Factors
Specialist to consult
Complications
Prevention
- Cellulitis usually occurs on one side of the body. Its signs and symptoms may include: 1. An irritated area of skin that tends to expand 2. Swelling 3. Tenderness 4. Pain 5. Warmth 6. Fever 7. Chills 8. Spots 9. Blisters 10. Skin dimpling