Medication
These include: Maintain a healthy weight. Eat a balanced diet. Stay physically active. Quit using tobacco products (if you use them). Manage any health conditions that can contribute to this problem, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol and...
Procedures
Claudication is often first treated by making lifestyle changes. This can reduce your risk factors for peripheral artery disease (PAD). Medicine and surgery may be needed in some cases. Treatment may include: Stopping smoking Exercising, such …
Nutrition
Treatment for claudication usually focuses on the reduction of risk factors associated with atherosclerosis: Smoking cessation Walking, usually 30 minutes a day Medication and lifestyle changes aimed at reducing cholesterol, blood pressure and blood-sugar levels Medication, such as aspirin, to prevent heart attack and stroke
What is neurogenic claudication and how is it treated?
How is claudication treated? With the information obtained from your diagnostic tests, your physician will be able to determine the best treatment plan and course of action to take for your particular situation. Whatever you and your doctor decide will be explained to you in full detail. This can include: Cessation of smoking Exercise Diet
How to cure claudication?
Sep 16, 2020 · Medications that help thin the blood can be used to help prevent symptoms of claudication, but they do not treat the underlying cause. Medications include: aspirin, clopidogrel ( Plavix ), ticlopidine (Ticlid), and dipyridamole (Permole, Persantine, Aggrenox ). Exercise is recommended for patients with claudication symptoms.
Is there a cure for claudication pain?
Diagnosis. A full physical exam and detailed interview will help a physician determine the type of pain and its origin. Certain symptoms can help a physician distinguish neurogenic claudication from vascular claudication–for example, the pain of vascular claudication is often relieved simply by rest, while pain due to neurogenic claudication is best relieved by bending forward or sitting …
Is claudication life threatening?
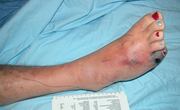
What is the best treatment for claudication?
Exercise is an important part of claudication treatment....Recommended walking programs include:Walking until you feel moderate pain or as far as you can.Resting to relieve pain.Walking again.Repeating the walk-rest-walk cycle for 30 to 45 minutes.Walking three or more days a week.Mar 2, 2022
Can claudication go away?
You usually feel these symptoms in your legs, from your feet up to your buttocks. It gets better or goes away when you stop moving.Oct 28, 2021
What is the drug of choice for claudication?
The US FDA has approved two drugs for the management of intermittent claudication: pentoxifylline and cilostazol.
Does walking help claudication?
Walking and other exercises benefit patients with peripheral arterial disease (PAD), including those with intermittent claudication. Exercise programs, which may be home-based, increase walking time and distance. Exercise has National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Level 1 evidence of efficacy.
Does aspirin help claudication?
21 (HealthDay News) -- Aspirin works as well as Plavix in patients with blocked leg arteries, a new European study finds. People with the condition, called peripheral artery disease, often suffer from intermittent claudication, which is pain while walking because of decreased blood supply to the legs.Feb 21, 2022
How serious is claudication?
Claudication is generally considered a warning of significant atherosclerosis, indicating an increased risk of heart attack or stroke. Other complications of peripheral artery disease due to atherosclerosis include: Skin lesions that don't heal.Mar 2, 2022
Which drugs improve claudication?
Pentoxifyl- line, the only approved claudication drug in the United States, has modest efficacy in improving treadmill exercise performance. Other drugs shown to be of some benefit in patients with claudication include propionyl-L-carnitine, cilostazol and possibly prostaglandin derivatives.
What is the treatment for blocked arteries in the legs?
Angioplasty is a procedure to open narrowed or blocked blood vessels that supply blood to your legs. Fatty deposits can build up inside the arteries and block blood flow. A stent is a small, metal mesh tube that keeps the artery open.Jan 28, 2021
Do support stockings help claudication?
Many patients inquire if compression stockings are a viable treatment for claudication. They are not. Compression stockings may actually worsen the condition by impeding blood flow.
How long does claudication take to heal?
Many people notice some improvement in their pain as the collateral circulation develops. This normally happens within six to eight weeks of the start of the claudication symptoms.
What are the stages of claudication?
Classification SchemesStage 0AsymptomaticStage 1Mild claudicationStage 2Moderate claudicationStage 3Severe claudicationStage 4Rest pain2 more rows
Can blood thinners help claudication?
Anticoagulants, such as heparin or warfarin, are drugs that prevent clotting and may help people with intermittent claudication.May 7, 2014
Why does claudication hurt when walking?
Claudication is pain in your thigh, calf, or buttocks that happens when you walk. It can make you limp. It may be a symptom of peripheral artery disease (PAD). This is when narrowed or blocked arteries reduce the blood flow to your legs. At first, claudication pain occurs when you walk a certain distance and goes away when you rest.
What is plaque made of?
Plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances in the blood. This plaque build-up can also affect your heart arteries. It can lead to chest pain or a heart attack. Blockages in the leg are most common in the thigh and behind the knee.
What are some ways to treat high blood pressure?
Treating related health problems, such as high cholesterol, high blood pressure, or high blood sugar levels. This may involve changes in diet, exercise, or medicine. Taking medicines that help prevent blood clots, such as aspirin or other medicines. Taking medicines that may improve walking distances in some cases.
Why is walking so painful?
Over time, it can become too painful to walk. It may be a symptom of peripheral artery disease (PAD). This is when narrowed or blocked arteries reduce the blood flow to your arms and legs. Risk factors are the same as those for hardened arteries (atherosclerosis). Treatment focuses first on making lifestyle changes.
What causes claudication in the legs?
What causes claudication? Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is very common, mainly in people over age 50. PAD is caused by narrowed or blocked arteries in the legs or in the body’s main artery (the aorta). This can reduce blood flow to muscles in your calf, thigh, or buttocks.
How to tell if you have claudication?
Typical symptoms of claudication include: Pain, a burning feeling, or a tired feeling in the legs and buttocks when you walk. Shiny, hairless, blotchy foot skin that may get sores. The leg is pale when raised (elevated) and red when lowered. Cold feet.
What is contrast dye?
A thin, flexible tube is put into a leg artery. A contrast dye is injected into the artery. The contrast dye makes the arteries and veins show up clearly on the X-ray.
What is claudication in the thigh?
What is claudication? Claudication refers to the pain, aching or fatigue of the muscles of the buttocks, thigh and/or calf that occurs with exertion. This pain or cramping is caused by poor circulation due to blockage of the arteries of the lower extremity. Nearly 9 million people, or 12 percent of the U.S.
How to treat claudication?
Treatment for claudication usually focuses on the reduction of risk factors associated with atherosclerosis: Smoking cessation. Walking, usually 30 minutes a day. Medication and lifestyle changes aimed at reducing cholesterol, blood pressure and blood-sugar levels.
What are the symptoms of claudication?
PAD symptoms may include: Pain in the buttocks, thigh and/or calf, occurring with walking. Tired or burning sensation in the buttocks, thigh and/or calf with walking.
What is CT angiography?
CT angiography: An advanced X-ray procedure that uses a computer to generate three-dimensional images of blood vessels. Magnetic resonance angiography (MR angiography): The patient is exposed to radiofrequency waves in a strong magnetic field.
How is a balloon inflated?
The balloon is inflated using a saline solution one or more times to expand the narrowed or occluded artery . Cutting balloon: A balloon imbedded with micro-blades is used to dilate the diseased area. The blades cut the surface of the plaque, reducing the force necessary to dilate the vessel.
What is a balloon stent?
Stents: Metal mesh tubes are expanded and left in place to provide scaffolding for an artery that has been opened using a balloon angioplasty. Balloon-expanded: A balloon is used to expand the stent. These stents are stronger, but less flexible. Self-expanding: Compressed stents are delivered to the diseased site.
What is self expanding stent?
Self-expanding: Compressed stents are delivered to the diseased site. They expand upon release and are left in place to hold open the artery. These stents are more flexible. Laser atherectomy: Small bits of plaque are vaporized by the tip of a laser probe.
Why does claudication occur?
Causes. Reduced blood flow in the arteries of the lower body or legs is the ultimate cause of claudication. A reduction in blood is usually a symptom of atherosclerotic occlusive conditions. These are conditions where fats, debris, and immune cells form a buildup called plaque that sticks to blood vessel walls.
What is claudication in exercise?
Claudication is muscular pain, cramping, or fatigue that typically occurs during exercise and goes away with rest. Claudication is primarily a symptom of conditions that reduce blood flow in the legs, especially peripheral artery disease (PAD). The term claudication comes from the Latin word for limp, which is ‘claudicare’.
How long does it take for claudication to go away?
Symptoms typically occur during muscular exercise and go away with 1–2 minutes. Trusted Source.
Where does the word "claudication" come from?
The term claudication comes from the Latin word for limp , which is ‘claudicare’. Claudication is also commonly referred to as intermittent claudication. This article provides an overview of claudication, including its symptoms, why it happens, treatments, and how to manage symptoms at home.
Can claudication affect one leg?
soft tissue damage, causing pain, tenderness, and temporary lameness. Claudication tends to only impact one leg, or one leg more than the other if both are involved. Symptoms often gradually worsen over the years, progressing back and forth between periods of improvement and flareups.
What does it feel like to have claudication?
Symptoms. A person with claudication may experience pain in the hip, thigh, or buttock. At first, claudication often causes a dull, aching pain in the lower calf. The initial pain or sensation can also travel to, or develop in, other muscle groups, such as:
How many people with PAD have claudication?
Estimates suggest that between 10% and 20% of people with PAD experience claudication. Symptoms usually arise during exercise when impaired arteries cannot keep up with the increased blood flow and oxygen demands of muscle cells.
Why does claudication happen?
Claudication typically is felt while walking and subsides with rest. It is commonly referred to as "intermittent" claudication because it comes and goes with exertion and rest.
What is the pain in the legs from claudication?
Pain and cramping in the legs is the main symptom of claudication. Pain can be sharp or dull, aching or throbbing, or burning. The severity of the peripheral artery disease, the location of the plaque, and the activity of the muscles determine the severity of symptoms and the location of the pain. Calf pain is the most common location ...
How common is intermittent claudication?
Intermittent claudication is more common in men than in women. The condition affects 1% to 2% of the population under 60 years of age, increasing in incidence with age, to affect over 18% of persons over 70 years of age, according to the American Academy of Family Physicians.
Where does plaque start in the leg?
This is because the atherosclerotic plaques often begin in the arteries farthest from the heart. If the blockage or plaque formation is farther up the leg, the pain from claudication may be felt in the thigh. If the blockage is in the aorta (the main artery from the heart to the legs) then symptoms may include pain in the buttocks or groin ...
Is claudication a sign of a vascular blockage?
The underlying cause of claudication, peripheral vascular disease, does put patients at risk for other atherosclerotic diseases. A finding of claudication or peripheral artery disease should be considered a warning sign of other potential atherosclerotic blockages in the body.
Why does intermittent claudication occur?
Intermittent claudication can be due to temporary artery narrowing due to spasm of the artery (vasospasm), permanent artery narrowing due to atherosclerosis, or from the complete blockage of an artery of the leg.
What causes claudication in the body?
What causes claudication? The severity of the peripheral artery disease, the location of the plaque, and the activity of the muscles determine the severity of symptoms and the location of the pain . Several medical problems can cause claudication, but the most common is peripheral artery disease. Peripheral artery disease (PAD) ...
Make an Appointment
Our team of dedicated access representatives is here to help you make an appointment with the specialists that you need.
Symptoms
The symptoms of neurogenic claudication can include pain, tingling, or cramping in the lower back and one or both legs, hips, and buttocks. Weakness or heaviness in the legs may also occur. These symptoms are especially present when standing upright or walking and usually relieved with leaning forward or sitting down.
Diagnosis
A full physical exam and detailed interview will help a physician determine the type of pain and its origin.
Risk Factors
Neurogenic claudication is usually caused by spinal stenosis (narrowing of the spinal canal) in the lumbar spine (lower back). The narrowing of the spinal canal is generally caused by wear and tear and arthritic changes in the lower spine.
Treatments
In general, the goal of surgical treatment is to decompress (remove the pressure from) the nerve roots in the lumbar spine. If the compression results from a herniated disc, a microdiscectomy (a procedure that uses small incisions with a tiny video camera for viewing) may provide relief.

Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
- The goals of treating claudication and peripheral artery disease are to reduce pain and manage the risk factors that contribute to heart and blood vessel (cardiovascular) disease. Exercise is an important part of claudication treatment. Exercise reduces pain, increases exercise duration, im…
What Medical Tests Are Likely with This Symptom?
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
How Is This Symptom Treated?
- A healthy lifestyle can help improve treatment outcomes and lower risks associated with claudication and peripheral artery disease. Recommended lifestyle changes include the following: 1. Quit smoking.Smoking greatly increases the risk of complications of peripheral artery disease. Talk to your health care provider if you need help quitting. 2. Exercise.Follow the exercise plan re…
What Can I Do at Home to Treat This Symptom?
- Learning all you can about what's causing your claudication may help you better manage the condition. Some people also find it helpful to talk with other people who are going through similar experiences. In a support group, you may find encouragement, advice, and maybe even an exercise partner or two. Ask your health care provider if there are any support groups in your area.
How Can This Symptom Be Prevented?
- You're likely to start by seeing your health care provider. You may be referred to a doctor trained in heart diseases (cardiologist) or a blood vessel (vascular) surgeon. To make the best of your appointment time, be prepared to answer the following questions: 1. When did symptoms begin? 2. Do you have pain when you're walking or exercising, when you're at rest, or both? 3. On a scal…