
Explore
Our experience and research suggest that psychotherapy is the best treatment for self-injurious behavior. It is not uncommon for clients to have tried many different therapies, programs, and self-help strategies before coming to S.A.F.E.; and there are a few who find our program earlier in their journey to recover.
What is general treatment for self-injury?
If the person should engage in self-injury, the caretaker can continue to make the requests during the behavior; or the caretaker may direct his/her attention to stop the behavior but then present the request again until the individual complies.
What should the caretaker do if the person should engage in self-injury?
Oct 08, 2018 · Getting Help for Self-Harm TREATMENT FOR SELF-HARM. Therapy is the most common treatment for self-harm. In therapy, you may discuss any feelings of... SELF-HELP FOR SELF-INJURY. If you self-harm, there may be times when the urge to injure yourself is stronger. Although... RECOVERING FROM SELF-HARM. ...
How to deal with self-injurious behavior?
Feb 21, 2018 · • Increases monetary cost of serving a person in his or her lifetime. • Frequently results in placement in more restrictive settings • Often result in referral to specialist (for example, a BCBA-D or licensed psychologist with specific training in self-injurious behavior)
What does it mean when a person self injures?
Goal: Remain free of behaviors which would lead to arrest/violation Keep working and comply with all aspects of probation Be able to express anger in a productive manner without destroying property or personal belongings Be free of threats to self and others Comply with all aspects of probation/parole and avoid behavior that could violate
How do you write a therapy therapy goal?
- The patient's personal information, psychological history and demographics.
- A diagnosis of the current mental health problem.
- High-priority treatment goals.
- Measurable objectives.
- A timeline for treatment progress.
What are the 3 goals of family therapy?
Develop and maintain healthy boundaries. Facilitate cohesion and communication. Promote problem-solving by a better understanding of family dynamics.Jan 12, 2021
What are some treatments for NSSI?
What is a treatment plan?
What are family goals examples?
- To provide financial resources to achieve each member's personal goals.
- To maintain good health for all family members.
- To maintain a home of which you are all proud.
- To have a son or daughter join the family business.
- To enjoy leisure time as a family.
What are the basic goals of Bowen's approach?
How do I write a self harm safety plan?
- Make a list of your crisis warning signs. ...
- List your personal coping strategies. ...
- Come up with some sources of support and distraction. ...
- Make a list of people you can count on for help. ...
- List your professional sources of support. ...
- Think through ways to keep yourself safe.
Is a psychiatrist?
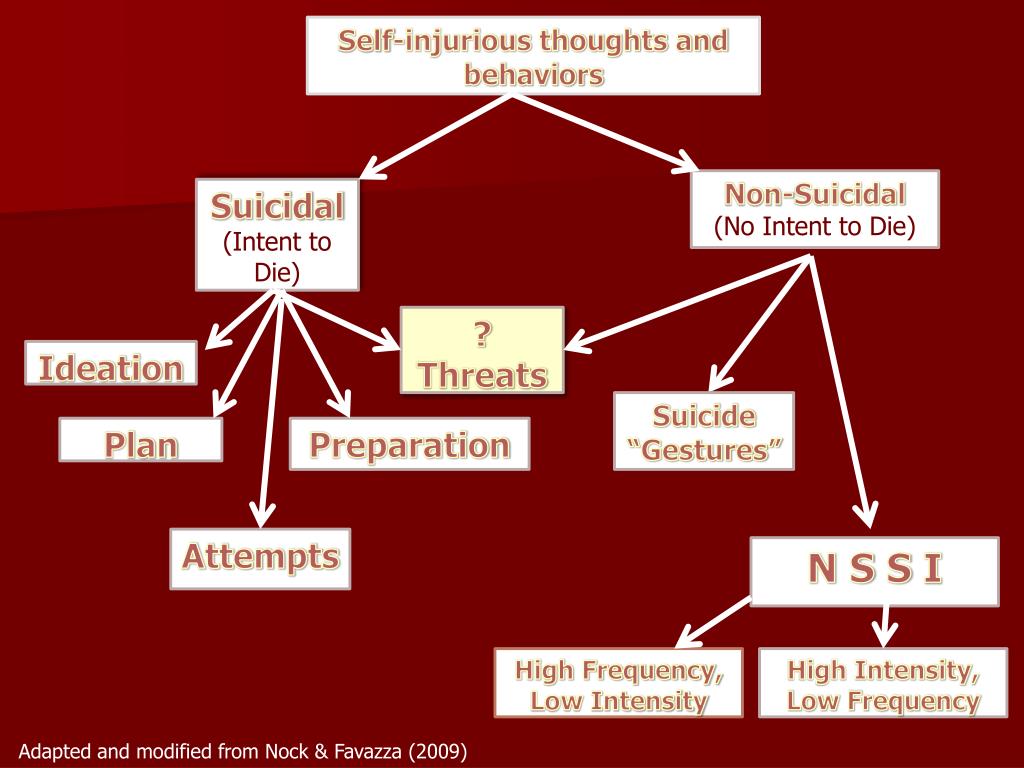
What does NSSI stand for?
What is a smart treatment plan?
The treatment plan addresses problems identified in the client assessment, defines and measures interventions in their care and provides a measure for client's progress in treatment.
What is the treatment planning process?
What is self injury treatment?
Self-injury treatments involving psychiatric medication, on the other hand, are used in more specialized cases, particularly where the individual has a co-occurring disorder, like depression or bipolar disorder. These are typically prescribed by psychiatrists.
What is general treatment?
General treatment includes treatments that are not centered specifically on the self-harming behavior. Psychotherapy, for example, may explore many aspects of a person's life in an attempt to curb or stop self-injury behavior.
How does cognitive behavioral therapy work?
Cognitive behavioral therapy would work to identify that thought pattern, challenge it and replace it with one that is more realistic and positive. Another treatment that works to eliminate self-harm is dialectical behavior therapy (DBT). 2 Dialectical behavior therapy is typically used in those that have a personality disorder along ...
What is the act of deliberately injuring oneself?
Self-harm is the act of deliberately injuring oneself, most often through cutting. The behavior is also called non-suicidal self-injury, or NSSI. It is generally often a sign of intense anxiety or distress. A person might harm themselves to numb emotional pain.
Why do people use NSSI?
They may use NSSI to remind themselves they are alive. All forms of self-harm use physical pain to address emotional problems. Yet the relief self-harm offers some individuals is only temporary. It does not help a person work through the issues that created the impulse.
Can you cut your wrist?
Non-suicidal cutting is rarely done on the wrist due to the risk of piercing a blood vessel. 21-44% of cases involve hitting one’s head or throwing oneself against a wall. 15-35% of people who self-harm burn their skin, often with a lit match or cigarette.
What is self embedding?
Self-embedding is an extreme form of self-harm in which a person inserts objects into their skin, such as staples or needles. They may leave the object there permanently or for a set period. A person may engage in multiple types of self-harm in the same time frame.
Does shame cause anxiety?
Shame in turn can lead to more anxiety, restarting the cycle. Self-harm might follow a course similar to that of an alcohol or drug addiction, complete with secret stashes and rituals. They may wish to stop the behavior but feel unable to do so.
What are the most common forms of SIB?
The most common forms of SIB are hand-biting, head-banging, and self-scratching. The methods and intentions behind these behaviors often differ from NSSI behaviors like cutting. Before the age of four, United Cerebral Palsy estimates up to 20% of children engage in head-banging behaviors during tantrums.
Why do people engage in self injury?
Some individuals engage in self-injury to avoid or escape an ‘aversive’ social encounter (Carr et al., 1976; Edelson et al., 1983). The individual may engage in self-injury just prior to the social interaction; and thus, he/she may avoid the social interaction before it begins. Alternatively, the individual may engage in self-injury to escape (or terminate) a social encounter that has already begun. For example, a caretaker may ask a client to do something (e.g., to leave the play area); and if the person does not want to comply, he or she may then engage in self-injury. As a consequence, the caretaker’s initial request is dropped or forgotten, and the caretaker’s attention is then directed at stopping the behavior.
What are some examples of self-injurious behavior?
The most common forms of these behaviors include: head-banging, hand-biting, and excessive self-rubbing and scratching.
Is self injury a symptom of autism?
Strictly speaking, self-injury is not a symptom of autism. However, certain symptoms, situations, and comorbidities related to ASD can lead some people with autism to engage in self-injurious behavior. Treating underlying disorders
What are the symptoms of a seizure?
Behaviors often associated with seizure activity include: headbanging, slapping ears and/or head, hand-biting, chin hitting, scratching face or arms, and, in some cases, knee-to-face contact. Since this behavior is involuntary, some of these individuals seek some form of self-restraint (e.g., having their arms tied down). Seizures may begin, or are more noticeable, when the child reaches puberty, possibly due to hormonal changes in the body.
Can stress cause a seizure?
Since seizure-induced, self-injurious behaviors are involuntary, one may not observe a relationship between the person’s behavior and his/her environment. However, since stress can trigger a seizure, there may be a relationship between stressors in the environment and self-injury.
Does self injury increase or decrease arousal?
Researchers have suggested that self-injury may increase or decrease one’s arousal level. The under-arousal theory states that some individuals function at a low level of arousal and engage in self-injury to increase their arousal level (Edelson, 1984; Baumeister & Rollings, 1976).
Why is arousal high?
High arousal levels may be a result of an internal, physiological dysfunction and/or may be triggered by a very stimulating environment. A reduction in arousal may be positively reinforcing, and thus, the client may engage in self-injury more often when encountering arousal-producing stimuli (Romanczyk, 1986).
How to help someone who is self injured?
Therapy can help people who self-injure develop other coping mechanisms to address their emotional pain. Social support can also contribute to recovery. If you or a loved one is in crisis, you can call the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 1-800-273-8255.
What is the purpose of a therapist?
A therapist might work with you to identify the source of your emotional pain, such as childhood trauma. You and your therapist can then develop strategies to manage and reduce that emotional pain.
Why is treatment important?
It is also important to create an aftercare plan to support your new, healthier behaviors.
How to vent your feelings?
If you self-injure to express your feelings, then your therapist may recommend other ways to vent your emotions, such as: Writing down what you are feeling, then ripping the paper up. Blowing off steam through exercise or punching a pillow. Listening to music that expresses the pain or emotion you feel.
Do scars go away after therapy?
Even after therapy has treated your emotional wounds, you may still have physical scars on your body. Your scars are nothing to be ashamed of – they are signs that you survived incredible pain. Some people wear their scars openly, while others prefer to hide or reduce them.
Why do people have semicolon tattoos?
Tattoos are an increasingly popular way to disguise one’s scars. Many people who have survived suicide or self-harm have marked their journey with a semicolon specifically. The semicolon tattoo often represents the choice to continue one’s life rather than end it.
How to cope with stress in therapy?
Make a new same-age friend. Spend two hours playing with peers each week. Stress. Goal: Be able to cope with routine life stressors and take things in stride. Assess personal risk traits and resiliency traits and discuss the role each plays in coping with daily stresses during the time between therapy sessions.
What is the goal of a therapist?
Goal: Be able to cope with routine life stressors and take things in stride. Assess personal risk traits and resiliency traits and discuss the role each plays in coping with daily stresses during the time between therapy sessions. Learn two ways to manage frustration in a positive manner.
What is re-frame in a situation?
Re-framing a situation is where you try to turn a situation which you first see as negative as a positive or different. This can help you feel less affected by a difficult situation. It can help you to see situations from a
How to breathe deep?
If you learn how to do deep breathing it can be really helpful. Sit straight on a chair and put one hand gently on your chest and one hand gently on your stomach. Slowly breathe in, feeling the air expanding your lungs. Your stomach should move outwards as the air fills you. Hold the breath for a moment, then breathe out as deeply as possible. This can help to calm you down in situations when you feel panicked. You can get free guided breathing exercises online such as on YouTube.
What is affirmation in writing?
Affirmations are phrases you say to yourself. It should be something good about you or something that you want to achieve. You should repeat these a few times during theday. Slowly they will start to be part of your natural way of thinking. They can be ones you made up or famous quotes you believe in.

What Is self-harm?
Warning Signs of Self-Harm
- For example, a person might tend to magnify the negative of a situation rather than seeing it as it truly is. Cognitive behavioral therapy would work to identify that thought pattern, challenge it and replace it with one that is more realistic and positive.
Why Do People self-harm?
The Course of Self-Harm
Self-Harm and Suicide
- People who self-harm often try to hide their behavior from others. Yet even careful individuals often leave traces of their actions. Here are some warning signs that someone may be injuring themself: 1. Suspicious injuries: The person may have frequent cuts or bruises which they blame on “accidents.” 2. Stash of tools: A person may have a collection of sharp items that seem to ha…
Statistics on Self-Harm
- Many people use self-harm as a coping mechanism for emotional overwhelm. Self-injury may serve different goals at different times. People who self-injure may be trying to: All forms of self-harm use physical pain to address emotional problems. Yet the relief self-harm offers some individuals is only temporary. It does not help a person work through the issues that created the …
Psychological Issues Associated with Self-Harm
- Self-injury often follows a cycle. Often a person feels anxiety, followed by the impulse to self-harm. They may try to resist the impulse, only to feel even more tension. The person will likely engage in the self-harm to release the tension. They may feel shame around engaging in NSSI or the scars caused by the behavior. Shame in turn can lead to m...
Self-Injurious Behaviors
- Self-harm behaviors are not the same as suicidal behaviors. NSSI is generally an attempt to cope with life, not end it. Individuals may feel emotionally numb and use the pain of the self-injury to remind themselves they are alive. However, chronic self-harm can put a person at risk of becoming suicidal in the future. Over time, an individual may habituate, or become used to the p…