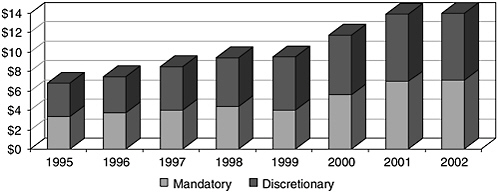
How much does the US spend on HIV/AIDS?
Of this, $7.8 billion (22% of the overall HIV budget and 53% of discretionary funding) is for domestic programs – prevention research, housing, and non-mandatory care programs (e.g., the Ryan White HIV/AIDS Program). The remainder, $6.8 billion (19% of the overall budget and 47% of the discretionary component), is for the global epidemic.
How much does it cost to treat HIV?
$501,000 lifetime cost to treat one person with HIV infection About 20% of new HIV infections occur in teens and young adults 4 in 5 people who could benefit from PrEP, a medicine to prevent HIV, aren’t getting it
What drives the US budget for HIV treatment to increase?
This growth has been driven primarily by increased spending on mandatory domestic care and treatment programs (largely through Medicaid and Medicare), as more people are living with HIV in the United States, as well as by greater investments to combat HIV in low and middle-income countries.
How is HIV/AIDS treated in the United States?
Medicaid and Medicare offer low-income HIV/AIDS patients care and treatment through government-run programs. The AIDS Drug Assistance Program [ 15] , mandated by the Ryan White Act, provides help for HIV/AIDS treatment in each state. Participating in clinical trials [ 16] might provide access to medicine at little or no cost.

How much do we spend on AIDS research?
HIV funding through USAID ($330 million) and the CDC ($128 million) is all flat in FY 2019 compared to the FY18 level. Funding for international HIV research activities at NIH is $590 million in FY 2019, an increase of $25 million above the FY 2018 level. flat compared to the FY 2018 level.
How did the US deal with the AIDS epidemic?
Furthermore, since testing became available in 1985, CDC began providing federal funds to establish an extensive system of alternate testing and counseling sites, leading to the first nationwide HIV- and AIDS-related prevention program. Today, testing—knowing one's HIV status—is a key strategy in AIDS prevention.
What is the lifetime cost to treat a baby with AIDS in the United States?
Currently, the lifetime treatment cost of an HIV infection is estimated at $379,668 (in 2010 dollars), therefore a prevention intervention is deemed cost-saving if its CE ratio is less than $379,668 per infection averted.
How much has AIDS cost the world?
The HIV epidemic has cost the global economy over half a trillion dollars so far in the 21st century. A new study to analyze the long-term cost and impact of the global HIV/AIDS epidemic revealed that over half a trillion dollars has been spent fighting the disease since the millennium began.
How much is mandatory spending on HIV?
Mandatory spending for HIV accounts for $20.3 billion, or 58%, of the total HIV budget and includes estimated spending levels for: Medicaid, Medicare, Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI), Supplemental Security Income (SSI), and the Federal Employees Health Benefits Plan (FEHB), programs which provide health coverage and cash assistance. ...
How much is HIV research budget?
Research. $2.6 billion (7% of the overall FY 2019 amount and 9% of the domestic budget) in the FY 2019 HIV budget is for domestic HIV research across multiple agencies, essentially the same as the FY 2018 level. The National Institutes of Health (NIH), which carries out almost all HIV research, receives $2.5 billion in FY 2019 for domestic HIV ...
What is the federal HIV budget?
The largest component of the federal HIV budget is health care services and treatment for people living with HIV in the U.S., which totaled $21.5 billion in FY 2019 (62% of the total HIV budget and 77% of the domestic share). This represents a 5% increase over the FY 2018 level, primarily due to increased mandatory spending for Medicaid and Medicare. 2 Medicare is the largest federal funder of HIV care and treatment, followed by Medicaid. The Ryan White HIV/AIDS Program, the largest HIV-specific discretionary grant program in the U.S. and third largest source of federal funding for HIV care (behind Medicaid and Medicare), is funded at $2.3 billion, the same as the FY18 level. Ryan White’s AIDS Drug Assistance Program (ADAP), which provides access to HIV-related medications to people with HIV, was flat funded at $900.3 million.
What is the largest federal funder of HIV care and treatment?
This represents a 5% increase over the FY 2018 level, primarily due to increased mandatory spending for Medicaid and Medicare. 2 Medicare is the largest federal funder of HIV care and treatment, followed by Medicaid.
How much is Ryan White HIV/AIDS?
and third largest source of federal funding for HIV care (behind Medicaid and Medicare), is funded at $2.3 billion, the same as the FY18 level. Ryan White’s AIDS Drug Assistance Program (ADAP), which provides access to HIV-related medications ...
How much money does the NIH give to HIV research?
The National Institutes of Health (NIH), which carries out almost all HIV research, receives $2.5 billion in FY 2019 for domestic HIV research activities (additional amounts used for international HIV research are attributed to the global category), the same as in FY 2018. 3. Table 1: Federal Funding for HIV/AIDS by Category, FY 2013 – FY 2019.
How much is HIV funding in 2019?
The FY 2019 budget for HIV includes $6.8 billion for the global epidemic – $5. 4 billion for bilateral programs and $1.35 billion for the U.S. contribution to the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria (Global Fund). Congress provided a slight increase in funding for global HIV activities in FY 2019 ...
How much does a private insurance cover for HIV?
Most private insurers cover the cost of HIV/AIDs treatments and medications, requiring covered members to be responsible for copays that typically range from $10-$30 per prescription.
What is the AIDS drug assistance program?
The AIDS Drug Assistance Program [ 15] , mandated by the Ryan White Act, provides help for HIV/AIDS treatment in each state. Participating in clinical trials [ 16] might provide access to medicine at little or no cost. Many manufacturers provide discounts on name-brand medications.
How much does Selzentry cost?
Another medication, Selzentry [ 8] (maraviroc), costs about $550 per month. Integrase inhibitors block a protein need for HIV to infect CD4 cells. Isentress [ 9] (raltegravir) costs about $1,100 per month. HIV/AIDS patients typically start by seeing a primary care physician if exposure to the virus is known.
What should be included in HIV/AIDS diagnostics?
Diagnostic tests [ 10] are likely to include checking CD4 count, viral load and drug resistance.
What are the diagnostic tests for HIV?
What should be included: 1 HIV/AIDS patients typically start by seeing a primary care physician if exposure to the virus is known. The doctor may refer the patient to an infectious disease specialist. Diagnostic tests [ 10] are likely to include checking CD4 count, viral load and drug resistance. 2 Medication and lifestyle changes [ 11] are the typical treatments for the chronic disease.
How does HIV/AIDS work?
The virus acts by attacking the immune system, leaving the body unable to fight off disease. There is no cure for HIV/AIDs, but it can be controlled through a combination of medications. Typical costs: Physicians are likely to prescribe one or more medications to treat HIV/AIDS [ 2] . Most private insurers cover the cost ...
How much does Truvada cost?
Another NRTI, Truvada, costs about $1,200 per month. Protease inhibitors are frequently part of an HIV/AIDS patients' medication regimen, preventing the reproduction of HIV.
How much is HIV prevention?
This amount includes approximately: $397 million for HIV prevention by health departments. $120 million for HIV surveillance. $103 million for activities to improve program effectiveness. $135 million for national, regional, local, community, and other organizations. $33 million for adolescent and school health.
What is the HIV/AIDS strategy?
HIV/AIDS prevention investments will continue to align activities with the National HIV/AIDS Strategy and promote high-impact prevention that focuses resources on effective, scalable, and sustainable prevention strategies.
What is the FY 2017 budget?
On February 9, 2016, the President released the fiscal year (FY) 2017 budget#N#pdf icon#N#[PDF – 78 KB] request to Congress. It includes approximately#N#$788 million for domestic HIV/AIDS prevention and research at CDC, which is level with the FY 2016 enacted level.#N#This amount includes approximately: 1 $397 million for HIV prevention by health departments 2 $120 million for HIV surveillance 3 $103 million for activities to improve program effectiveness 4 $135 million for national, regional, local, community, and other organizations 5 $33 million for adolescent and school health
What is Ryan White HIV?
The Ryan White HIV/AIDS Program is a federally funded program that provides services and support for those living with HIV. Its AIDS Drug Assistance Program provides medications to those with limited or no health coverage.
What factors affect the cost of a medication?
Several other factors can also affect the cost of a medication, including: what pharmacy discounts are available. whether a person has prescription drug insurance. the availability of generic versions of medications. what prescription assistance programs are available. where a person lives.
What is a PAP program?
Prescription assistance programs . A variety of prescription assistance programs (PAPs) are available to people taking HIV medications. These programs provide discounts or funds to help cover the cost of HIV treatment. Each PAP maintains its own requirements for participants, such as proof of need for the medication.
What is Medicaid insurance?
Medicaid is a state and federal partnership that provides insurance coverage to low-income individuals, seniors, those with disabilities, and others who qualify. While coverage varies from state to state, Medicaid is an important source of coverage for many individuals living with HIV.
Can HIV be treated without financial assistance?
And learning the costs of HIV treatment without financial assistance can be disheartening, especially for those who are newly diagnosed. However, services are available to help people obtain medications, and many of them will cover a large portion of the cost. With a little work, people with HIV can typically obtain the treatment they need.
Can HIV save money?
A person living with HIV may be able to save a significant amount of money if they understand a few things about cost. These things include how HIV drugs are covered by insurance and the resources that are available to help manage the often high costs associated with lifelong therapies.
Is HIV a generic drug?
Generic drugs. Many HIV medications are new. That means pharmaceutical companies still maintain the rights to the medication’s patent, and as a result, a generic option isn’t available. Generic medications are often less expensive than brand-name drugs.
How many people were diagnosed with HIV in 2017?
In 2017, CDC funded approximately 3 million HIV tests in 61 jurisdictions in the United States, Puerto Rico, and the Virgin Islands. Through this program: 11,843 people were newly diagnosed with HIV—nearly one-third of all new HIV diagnoses in the U.S. that year.
How many people are unaware of HIV?
1 in 7 people are unaware of their HIV infection. 4 in 5 people who could benefit from PrEP, a medicine to prevent HIV, aren’t getting it. Knowing one’s HIV status is the first step in getting care and treatment—and in protecting others.
When did the first AIDS cases start?
When analyzing federal funding by the US government for HIV both home and abroad since the first AIDS cases were identified in 1981 , “you notice a very dramatic, steep rise at different points, and generally a rise over time,” said Jen Kates, vice president, director of global health and HIV policy, Kaiser Family Foundation.
How much was the FY18 budget cut?
The FY18 budget request includes a $1.2 billion cut. In regard to philanthropic funding, in 2016, the United States saw $680 million in disbursements from 392 funders in 15 different countries going to 3600 grantees worldwide in just over 7000 grants. Funding in 2016 reached almost $680 million ...
What are the factors that contribute to the increase in spending?
While the political well plays a role, there are 2 factors that really account for the rise in spending: the increasing number of people living with HIV in the US, which has led to increasing expenditures on care and treatment; the other is the increasing recognition of the importance of combatting the global epidemic.
What are the top five disease-based spending categories?
The top five disease-based spending categories (ill-defined conditions, circulatory, musculoskeletal, respiratory, and endocrine ) account for half of all medical services spending by disease category. Ill-defined conditions each represent about 13% of overall health spending by disease while circulatory, musculoskeletal, respiratory, and endocrine conditions represent 12%, 10%, 8%, and 7% respectively.
What was the growth rate of ill-defined conditions in 2012?
The number of treated cases grew fastest for ill-defined conditions and endocrine disorders, each at an average annual growth rate of 4.4% from 2000-2012. (Because the spending changes above adjust for treatment cost, they primarily represent changes in the number of cases over the time period.)

Domestic HIV/AIDS Prevention and Research FY 2016
Health Departments HIV Prevention Programs FY 2015
Division of HIV Prevention Funding (DHP) Allocations FY 2014
HIV Funding at CDC FY 2013