
Initial emergent treatment remains controversial, but mainstays of therapy include drainage of the urinary bladder, often with placement of a suprapubic catheter (SPT) and primary endoscopic realignment of the urethra if possible. Immediate urethral repair is relatively contraindicated because life-threatening injuries must be corrected first.
How do you treat pain in the urethra?
Wear loose cotton underwear. Avoid harsh lotions. Clean under the foreskin of an uncircumcised penis regularly. It is never normal to have pain in the urethra. So a healthcare provider should always evaluate this symptom unless it has a clear, reversible cause, such as stinging immediately after using a new personal care product.
What is the best treatment for a prolapsed urethra?
This is commonly the favoured treatment for those unable to undergo surgery due to medical conditions or those wishing to have children in the future. Oestrogen cream – Oestrogen cream should be applied 2-3 times a day for a course of two weeks, directly to the prolapsed urethra.
What are the treatment options for urethral entrapment?
Early realignment of posterior urethral injuries is also a treatment option. This has been performed at the time of injury, using interlocking sounds or by passage of catheters from both retrograde and antegrade approaches.
How do you fix a 2 cm urethra incision?
Defects of up to 2 cm in the bulbar urethra and up to 1.5 cm in the penile urethra can be repaired primarily via a direct anastomosis over a catheter with fine absorbable suture. This is the preferred method of repair for these injuries.
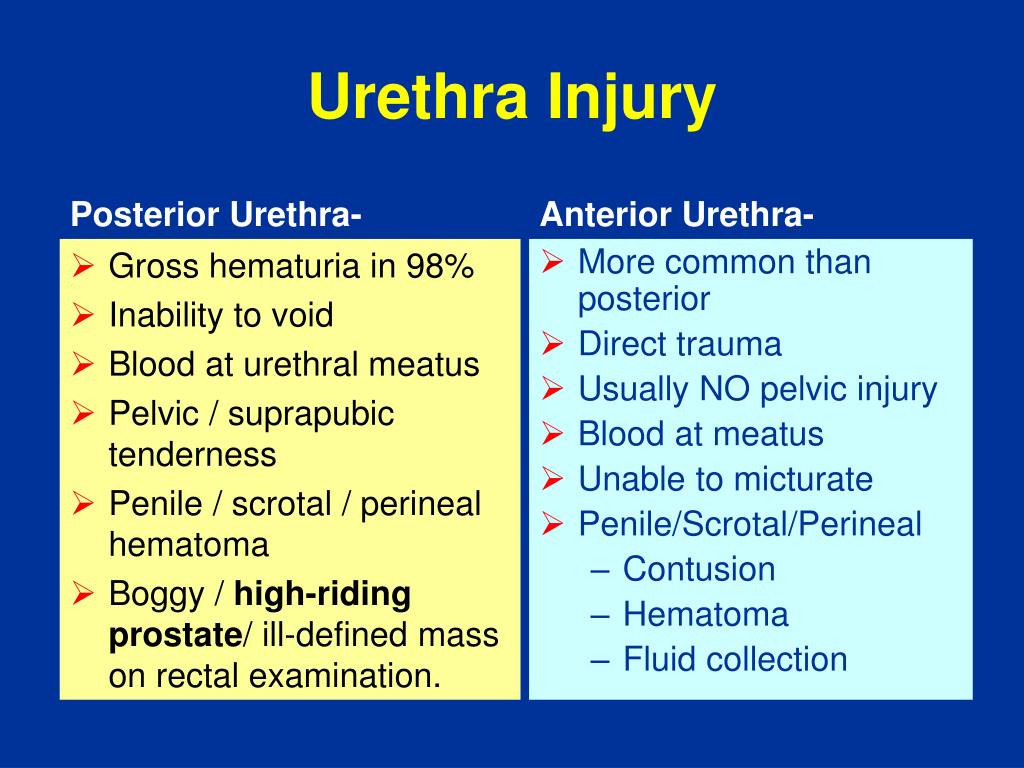
Can the urethra be repaired?
Depending on the exact location and the extent of damage, the urethra will be repaired by either replacing the tissue with tissue from another part of the body, or by taking out the damaged portion of the urethra and then reconnecting the urethral tube.
How do you treat a urethral stricture without surgery?
If you have a severe stricture and choose not to have surgery, you may opt for a permanent artificial tube (stent) to keep the urethra open, or a permanent catheter to drain the bladder.
Can a prolapsed urethra be repaired?
Unless another health problem is present that would require an abdominal incision, the bladder and urethra are usually repaired through an incision in the wall of the vagina. This surgery pulls together the loose or torn tissue in the area of prolapse in the bladder or urethra and strengthens the wall of the vagina.
How do you treat urethral damage?
Many cases of anterior urethral injury need to be fixed right away with surgery. Minor of these injuries can be treated with a catheter through the urethra into the bladder. This keeps urine from touching the urethra so it can mend. The catheter is often left in place for 14 to 21 days.
Is urethral stricture serious?
If left untreated, a urethral stricture can cause serious problems, including bladder and kidney damage, infections caused by the obstruction of urine flow, and poor ejaculation and infertility in men. Fortunately, strictures can be successfully treated.
Is a cystoscopy painful?
People often worry that a cystoscopy will be painful, but it does not usually hurt. Tell your doctor or nurse if you feel any pain during it. It can be a bit uncomfortable and you may feel like you need to pee during the procedure, but this will only last a few minutes.
What happens if a urethral prolapse goes untreated?
If left untreated, urethral prolapse may progress to strangulation and eventual necrosis of the protruding tissues. The fundamental anatomical defect of urethral prolapse is the separation of the longitudinal and circular-oblique smooth muscle layers [7].
Does urethral prolapse need to be treated?
Urethral prolapse usually happens to school-aged girls. Often the condition is not painful, but the swelling can cause discomfort. Urethral prolapse is treated with special creams and baths. Sometimes surgery is needed.
Can you push a urethral prolapse back in?
Milder cases can improve with noninvasive treatments like Kegel exercises and weight loss. For more severe cases, surgery can be effective. However, vaginal prolapse can sometimes come back after surgery.
Can a damaged urethra heal itself?
Rarely, urethral tears heal without surgery. Treatment helps to prevent some complications of urethral injuries.
What happens if the urethra is damaged?
If the urethra is injured, a person may develop urethra obstructions or strictures. Urethral strictures occur when the urethra is injured or scarred by an infection and then narrows. As a result, problems with the normal passage of urine and semen can develop.
How long does a damaged urethra take to heal?
This takes 3 to 6 months.
What is the treatment for ureteral obstruction?
The goal of ureteral obstruction treatment is to remove blockages, if possible, or bypass the blockage, which may help repair damage to the kidneys. Treatment might include antibiotics to clear associated infections.
What is the procedure to remove urethra obstruction?
Ureteral obstruction surgery may be performed through one of these surgical approaches: Endoscopic surgery, a minimally invasive procedure, which involves passing a lighted scope through the urethra into the bladder and other parts of the urinary tract.
What is the procedure to remove urine from the body?
Drainage procedures. A ureteral obstruction that causes severe pain might require an immediate procedure to remove urine from your body and temporarily relieve the problems caused by a blockage. Your doctor (urologist) may recommend: A ureteral stent, a hollow tube inserted inside the ureter to keep it open.
What is the purpose of a ureteral stent?
A ureteral stent, a hollow tube inserted inside the ureter to keep it open. Percutaneous nephrostomy, during which your doctor inserts a tube through your back to drain the kidney directly. A catheter, a tube inserted through the urethra to connect the bladder to an external drainage bag.
How to test for abnormal urine flow?
Voiding cystourethrogram. To test for abnormal urine flow, your doctor inserts a small tube (catheter) through the urethra, injects dye into your bladder, and takes X-rays of your kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra before and during urination. Renal nuclear scan.
What tests can you do to check if your kidneys are working properly?
Blood and urine tests. Your doctor checks samples of your blood and urine for signs of infection and the presence of creatinine, which signals that your kidneys aren't working properly. Ultrasound. An ultrasound of the area behind your abdominal organs (retroperitoneal ultrasound) allows your doctor to view the kidneys and ureters.
What tests are done after birth?
Doctors often perform another ultrasound after birth to re-evaluate the kidneys. If your doctor suspects you have an obstructed ureter, some of these tests and scans might be used to reach a diagnosis: Blood and urine tests. Your doctor checks samples of your blood and urine for signs of infection and the presence of creatinine, ...
Why does my urethra not work?
There are a few congenital (present at birth) conditions that may cause the urethra to not work properly, leading to infection and other issues. These include the urethra not being in the right place (clinically referred to as hypospadias ). This is seen in males when the opening urethra does not come out of the tip of the penis. Hypospadias is corrected surgically under general anesthesia, typically when the child is still young or even an infant.
What are the main urethra disorders?
Due to anatomical variations of the urethra, genetics, or external factors, such as suffering an injury, there are a few main urethra disorders: 8 . Urethra cancer. Urethral strictures: A narrowing of the urethra tube. Urethritis: Inflammation of the urethra caused by infection.
What causes urethral pain?
9 . In general, there can be many causes behind urethral pain, including bacteria, skin conditions, and even certain medications or food.
What is the name of the infection that causes pain in the urethra?
Urethritis : Inflammation of the urethra caused by infection. Urethral diverticulum: A pocket that forms in the urethra and can fill with urine, leading to pain or difficulty urinating. Urethritis , the most general, all-encompassing condition, is different than a UTI.
What are the parts of the urethra?
Anatomy. The male urethra is divided into three parts: the prostatic urethra, membranous urethra, and the spongy urethra. The prostatic urethra starts at the neck of the bladder and is located in the prostate. This is typically the widest part of the urethra, which then connects to the membranous urethra, found in the urogenital diaphragm.
How long is the urethra?
The urethra is a thin tube that connects to the bladder in order to empty urine out of the body. The female urethra is short, about 1.5 inches long, while the male urethra is longer at 7 to 8 inches in length as it runs length of the penis. 1 The male urethra not only carries urine out of the bladder, but it also transports semen.
How does the brain tell the bladder to release urine?
This is done when the brain tells the bladder when it’s time to squeeze and the sphincter muscle to relax, releasing urine through the urethra. 6 This same mechanism is used in males when they ejaculate and sperm is carried through the urethra.
What happens after urethral repair?
The most common problem after urethral repair is scarring in the urethra. The scars can partly block the urine flow, causing the stream to be weak. You may also have to strain to urinate. Your urologist can often fix this by widening the scarred section.
Where does the urethra go?
The anterior ("front") urethra goes from the tip of the penis through the perineum. The posterior ("back") urethra is the part deep within the body. In females, the urethra is much shorter: it runs from the bladder to just in front of the vagina. It opens outside the body.
Why is a catheter left in longer?
If the x-ray still shows leaks, the catheter is left in longer. If serious urethral trauma is seen on the x-ray, a tube is used to carry urine away from the injured area to keep it from leaking. Urine leaking inside the body can cause: The treatment of a posterior urethral injury is very complicated.
How long does a catheter stay in place for a urethral injury?
This keeps urine from touching the urethra so it can mend. The catheter is often left in place for 14 to 21 days.
What is urethral stricture?
This can occur with a sharp blow to the perineum. This type of trauma can lead to scars in the urethra (" urethral stricture "). These scars can slow or block the flow of urine from the penis.
Why do they take x-rays of the urethra?
The dye is used to be seen on an x-ray. X-rays are taken to see if any of the dye leaks out of the urethra inside your body. This would mean there’s an injury. An x-ray of the urethra is often done after a pelvic fracture, because urethral injury is common in these cases (about 1 in 10 cases).
How long does it take for a urologist to fix a pelvic fracture?
Most urologists first place a catheter in the bladder at the time of injury and wait for 3 to 6 months. This gives the body time to reabsorb the bleeding from the pelvic fracture.
How to keep urethrocele under control?
Kegel exercises – Performing daily pelvic floor exercises could be all you need to keep your urethrocele prolapse under control. Using an electronic pelvic toner such as the Kegel8 Ultra 20 Pelvic Toner will make them more beneficial.
What is it called when the urethra drops down?
If this happens to the urethra, it’s called a urethrocele prolapse .
What stage of urethrocele prolapse is it?
As with most female pelvic organ prolapses, a urethrocele prolapse can occur in varying degrees of severity: Stage 1 – The urethra begins to press down against the upper wall of the vagina and protrudes into it only to a slight degree. Symptoms can be mild or even unnoticeable.
What is a prolapse of the urethra called?
A urethrocele is a prolapse of the urethra only. If the pelvic floor muscles weaken and allow the bladder to prolapse, then this is separately called a cystocele. Often, both a urethrocele and a cystocele occur at the same time and the prolapse is then called a cystourethrocele.
What is a urethra prolapse?
What Is a Urethrocele Prolapse? The urethra is the tube that takes urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. It is part of the group of organs that make up the female pelvic area. These organs are held in place by strong pelvic floor muscles.
What is the term for the removal of the uterus and cervix?
Effects can be worsened by the general loss of muscle tone associated with ageing. Hysterectomy – A hysterectomy is the complete removal of the uterus and cervix. This surgery removes some of the strength of the pelvic area as the uterus is no longer there as support.
What does it mean when you can't hold in your urine?
discomfort or pain during sex. persistent or frequent urinary tract infections (cystitis) urinary stress incontinence – the inability to hold in urine when you cough, sneeze, laugh, exercise or lift heavy objects. urinary incontinence – a complete inability to hold in urine. a frequent need to urinate.
What should follow up be for urethral injury?
Follow-up. In all instances of urethral injury, follow-up should include assessment of the patient's voiding history, continence status, and potency. Undoubtedly, follow-up should be life-long, although in the trauma population this is often difficult to achieve.
How is urethra repair carried out?
It is often carried out via a perineal approach, and repair consists of mobilizing the urethra distally to allow a direct anastomosis after excision of the stricture. To prevent tension on the anastomosis, the distal urethra can be mobilized to the penoscrotal junction.
How long does it take for a suprapubic catheter to be removed?
Antibiotics are maintained for 2 weeks, and the catheter is removed after 4 weeks.
Why is anastomosis performed in open urethral reconstruction?
In open urethral reconstruction, careful dissection of the urethra is important. Anastomoses must be performed in a mucosa-to-mucosa fashion to ensure proper healing without further scarring. All anastomoses should be performed over a catheter for stenting purposes.
Why is excessive mobilization of the urethra avoided?
Excessive mobilization of the urethra must be avoided to prevent tethering of the penis. If a gap of more than 2 cm must be bridged, performing a flap procedure rather than placing the anastomosis under tension or tethering the penis, which causes curvature, is better.
When faced with urethral trauma, initial management decisions must be made in the context of other injuries and patient stability
Life-threatening injuries must be corrected first in any trauma algorithm. [ 12]
Should long defects be repaired emergently?
This is the preferred method of repair for these injuries. Longer defects should never be repaired emergently; they should be reconstructed at an interval following the injury to allow for resolution of other injuries and proper planning of the tissue transfers required for the repair.
Why do they take x-rays of the urethra?
The dye is used to be seen on an x-ray. X-rays are taken to see if any of the dye leaks out of the urethra inside your body. This would mean there’s an injury. An x-ray of the urethra is often done after a pelvic fracture, because urethral injury is common in these cases (about 1 in 10 cases).
Where does the urethra run?
In males, the urethra starts at the bladder and runs through the prostate gland, perineum (the space between the scrotum and the anus), and through the penis.
What causes iatrogenic injuries to the urethra?
Iatrogenic injuries to the urethra occur when difficult urethral catheterization leads to mucosal injury with subsequent scarring and stricture formation. Catheter placement is the most common cause of iatrogenic urethral trauma.
What is a blunt injury to the anterior urethra?
Blunt injury to the anterior urethra most often results from a blow to the bulbar segment such as occurs when straddling an object or from direct strikes or kicks to the perineum 9). Blunt anterior urethral trauma is sometimes observed in the penile urethra in the setting of penile fracture.
How long does a catheter stay in place for urethral injury?
This keeps urine from touching the urethra so it can mend. The catheter is often left in place for 14 to 21 days.
What is urethral injury?
Urethral injury. Urethral injury is when the urethra is hurt by force. The mechanisms of injury ranges from gunshot wounds to self-inflicted sexual misadventures. Urethral injury can first be classified based on location as either anterior or posterior urethra 1) . Posterior urethral injuries are located in the membranous and prostatic urethra.
Why is a catheter left in longer?
If the x-ray still shows leaks, the catheter is left in longer. If serious urethral trauma is seen on the x-ray, a tube is used to carry urine away from the injured area to keep it from leaking. Urine leaking inside the body can cause: The treatment of a posterior urethral injury is very complicated.
What is the pain in the urethra?
He specializes in male infertility. Pain in the urethra (the tube that passes from the bladder to the outside of the body) can be very uncomfortable. While the pain is often burning in quality (depending on the cause), it can sometimes be severe to the point where the thought of urinating is excruciating.
Why does my urethra hurt?
In both men and women, common causes of urethral pain include sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) such as chlamydia, local irritation from soaps or spermicides, and urinary tract infections (UTIs). In men, prostatitis isn't an uncommon cause, whereas in women, vaginal dryness due to menopause can be an issue.
What STD causes urethral pain?
Mycoplasma genitalium: Now the third most common STD in the United States, this infection can cause urethral pain but is often asymptomatic. In women, it is often associated with bacterial vaginosis. Trichomoniasis: Trichomoniasis is an STD caused by a parasite that can cause urethral pain in both men and women.
What is the most common cause of urethritis?
Gonorrhea: Gonorrhea is caused by the bacteria Neisseria gonorrheae, and was, at one time, the most common cause of urethritis. It can cause pain in the urethra, penile discharge in men and vaginal discharge in women (often greenish-yellow), and pelvic pain, among other symptoms.
What tests are done for STDs?
Diagnostic tests may include tests for common STDs, a urinalysis, and further blood tests and imaging studies for the less common causes. The treatment will depend on the specific cause, with treatment of partners of importance in the case STDs. Urethra pain in women and men.
What causes nerve compression in the urethra?
Lumbar disc disease, spinal stenosis, or cysts on the spinal cord may cause nerve compression. 11 When this involves the nerves that travel to the urethra, pain may feel like it is coming from the urethra. Other conditions that may cause pain include Crohn's disease (especially with fistulas), and endometriosis .
Can menopausal women have urethral atrophy?
In women who are menopausal, vaginal atrophy can lead to urethral pain along with vaginal pain and dryness. 8 When severe, urethral prolapse may occur. Atrophy of the urethra and vagina can also increase the risk of urinary tract infections.
How to check urethra?
The urethra is visually examined by spreading the urinary meatus with two gloved fingers to check for redness, discharge, and other abnormalities. Next, a dry cotton swab is inserted into the urethra and rotated once to obtain a sample of cells. You will also be asked to submit a urine sample.
What are the symptoms of urethra?
Common symptoms include: 1 . Urethral discharge. Itching or tingling of the penis or urethra. Pain or burning during urination ( dysuria ) Swelling and tenderness of the penis.
What is the condition in which the urethra (the tube through which urine exits the body) becomes
Learn about our Medical Review Board. Jamin Brahmbhatt, MD. Updated on March 17, 2021. Urethritis is a condition in which the urethra (the tube through which urine exits the body) becomes inflamed and irritated.
Is urethritis a disease?
Urethritis is not a disease unto itself but rather a symptom of an infection or other specific or non-specific causes. Many of the symptoms of urethritis in men are the same as in women. However, some can be more overt, such as a visible discharge or pain during urination.
Can HIV be detected in the urethra?
Even people on HIV therapy with undetectable viral loads can have detectable viral loads in the urethra due to viral shedding. 2 . Treating urethritis is even more imperative in men with HIV as it reduces their infectivity and the risk of sexual transmission. 3 Surprising Ways That STDs Increase HIV Risk.
Can antibiotics cause urethritis?
A variety of drugs may be prescribed based on the underlying cause of urethritis. Antibiotics are typically used if a bacterial infection is diagnosed. Even if the cause cannot be definitively identified, antibiotics may be prescribed if there is either urethral discharge or inflammation.
Can urethritis cause HIV?
If left untreated, urethritis can increase a man's risk of getting or passing HIV. This is because inflammation draws immune cells to the site of infection in a phenomenon known as viral shedding. This, in turn, attracts HIV to the site of inflammation as it targets the very immune cells (called CD4 T-cells) meant to defend the body against infection.

Symptoms
Diagnosis
- The goal of ureteral obstruction treatment is to remove blockages, if possible, or bypass the blockage, which may help repair damage to the kidneys. Treatment might include antibiotics to clear associated infections.
Causes
Complications
Treatment
A Word from Verywell