
What are the effects of a stroke in the medulla oblongata?
MVD of the left rostral ventrolateral medulla oblongata may be an effective treatment for patients suffering from intractable severe systemic blood hypertension. This article presents a literature review. Further clinical controlled studies have to be conducted to define precise indications.
What does the medulla oblongata do for your brain?
Objective: To evaluate the effects of mechanical compression of the brain-stem in patients with vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia (VBD). Methods: In the framework of a prospective, observational study that collected clinical and laboratory data in patients with VBD, we studied 20 patients with compression of the brain-stem due to ectatic, tortuous basilar or vertebral arteries.
What are some ways to damage the medulla oblongata?
Key takeaways. Your medulla oblongata is located at the base of your brain, where the brain stem connects the brain to your spinal cord. It plays an essential role in …
Can vestibular rehabilitation improve symptoms of vertigo and unsteadiness?
Aug 04, 2020 · Vestibular rehabilitation was described in both cases and had a significant effect on symptom improvement. In the study cases, the sense of vertigo and/or unsteadiness is due to vertebral artery compression of medulla oblongata and can be an isolated symptom. Positional nystagmus is the only sign in vestibular evaluation.
How do you fix vertebrobasilar insufficiency?
A newer technique called endovascular repair is used to treat vertebrobasilar insufficiency. It involves the placement of a catheter in an artery of the groin through a small nick in the skin. A balloon is advanced to the vertebral artery where it is inflated, expanding the artery wall.
What causes Vbd?
1. Ischemic stroke. The most common clinical symptom of VBD is ischemic stroke, and is also the most common cause of VBD-related death 1.Aug 2, 2014
How is compression of the vertebral artery treated?
Mobilization and anchoring of the vertebral artery to the spinous process or the dura has been shown to be an effective treatment option for cervical myelopathy secondary compression by anomalous vertebral artery in five cases reported in the literature (19).Oct 15, 2019
What causes dolichoectasia?
Dolichoectasia is associated with hypertension, older age, and male sex; it is also reportedly associated with heritable connective tissue disorders such as Marfan syndrome and Ehlers–Danlos syndrome (2).Jun 13, 2019
What are the symptoms of vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia?
Dolichoectasia of the vertebrobasilar artery is a vascular anomaly characterized by marked elongating, widening, and tortuosity of the arteries. Although this anomaly is usually asymptomatic, it may present with ischemic symptoms or mass effect involving brainstem or cranial nerves.May 24, 2019
What is Ectatic basilar artery?
Vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia (VBD) is a condition characterized by ectasia, elongation and tortuosity of the basilar artery. It may manifest clinically by compression of the cranial nerves, ischemic symptoms or intracranial bleeding.
What happens if the vertebral artery is compressed?
The most common clinical presentation is dizziness, vertigo, imbalance, or ataxia followed by limb weakness. Cervical spinal cord compression was observed in one patient who presented with neck pain and left leg weakness.Oct 15, 2019
What are the symptoms of a blocked vertebral artery?
Vertigo, dizziness, nausea, vomiting and head or neck pain are the most common initial symptoms reported. Other common signs and symptoms include weakness, hemiparesis, ataxia, diplopia, pupillary abnormalities, speech difficulties and altered mental status.
How do you test for Vertebral artery insufficiency?
Performing the Test: Patient rotates head opposite to tested side maximally and holds position for 10 seconds. Patient returns to neutral for 10 seconds. Patient extends head for 10 seconds. Patient returns to neutral for 10 seconds.
What does Dolichoectatic mean?
The term dolichoectasia means dilated and elongated. It is used to characterize arteries that have shown a significant deterioration of their tunica intima (and occasionally the tunica media), weakening the vessel walls and causing the artery to elongate and distend.Nov 20, 2008
What is a basilar aneurysm?
Basilar trunk artery aneurysms are extremely rare lesions that account for only 2.1% of all intracranial aneurysms. They are mostly recognized in patients around the age of 60, show a slight male predominance, and are associated with high morbidity and mortality.Feb 6, 2020
What part of the brain does the basilar artery supply?
The basilar artery (BA) serves as the main conduit for blood flow through the posterior circulation. It directly supplies the brainstem and cerebellum and provides distal blood flow to the thalami and medial temporal and parietal lobes.
Where is the Medulla Oblongata located?
Your medulla oblongata is located at the base of your brain, where the brain stem connects the brain to your spinal cord. It plays an essential role in passing messages between your spinal cord and brain. It’s also essential for regulating your cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
What is bilateral medial medullary syndrome?
Bilateral medial medullary syndrome is a rare complication from a stroke. Only a fraction of 1%#N#Trusted Source#N#of people with strokes in the rear part of their brain develop this condition. Symptoms include:
What is the brain responsible for?
Along with being the site of conscious thought, your brain also controls most of your body’s involuntary actions. It tells your glands when to release hormones, regulates your breathing, and tells your heart how fast to beat.
Where is the medulla located?
Your medulla oblongata is located at about the same level or slightly above this hole. The top of your medulla creates the floor of the fourth ventricle of your brain. Ventricles are cavities filled with cerebral spinal fluid that help provide your brain with nutrients.
What is the function of the spinal cord?
It’s critical for relaying information between your spinal cord and brain. It also regulates your cardiovascular and respiratory systems . Four of your 12 cranial nerves. originate on this region. Your brain and spine communicate through columns of nerve fibers that run through your medulla called spinal tracts.
Does Parkinson's disease affect the heart?
before spreading to other parts of the brain. People with Parkinson’s frequently have cardiovascular dysfunction such as regulating their heart rate and blood pressure. A 2017 study, conducted on 52 patients with Parkinson’s disease, established the first link between medulla abnormalities and Parkinson’s.
Who approved the study of otolaryngology?
The Otolaryngology Department Board, King Fahad University Hospital , Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faisal University ethically approved the study on 5/1/2018 after thorough presentation by the authors. Consent to participate is not applicable.
What is a dolichoectasia?
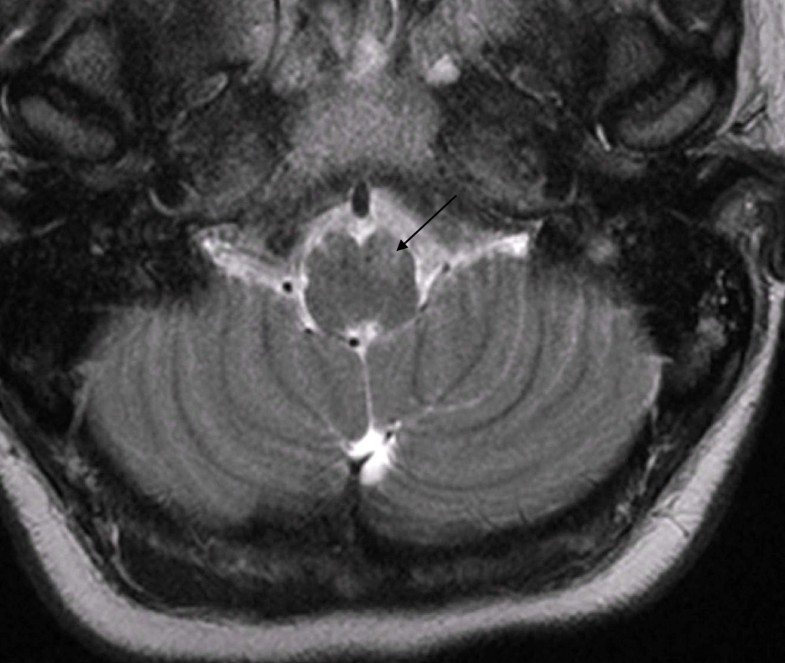
Dolichoectasia refers to an enlargement and elongation of the vertebrobasilar artery. Asymptomatic cases of dolichoectasia of vertebral and basilar arteries are not uncommon. However, there are reports suggesting that VBD can implicate in neurologic symptoms, both by compression of the brain stem and cranial nerves or by producing transient ischemic attacks [ 7 ]. According to the authors’ knowledge the isolated symptom of dizziness due to VA compression of the medulla are extremely rare in the literature (Table 1 ). Astonishingly, there were no neurological abnormalities and cranial nerve affections especially in case (1) in spite of severe compression of the medulla. Due to its gradually progressive nature, the course of brainstem compression by VBD is usually slow. Although sometimes the mass effect of VBD can be very serious, the brainstem can gradually tolerate compression without showing obvious clinical symptoms [ 8 ]. In both cases, vertigo and nystagmus are mostly attributed to compression of vestibular nuclei located in the dorsolateral aspect of the medulla; in addition to compression of cisternal component of the 8th cranial nerve in case (2). No MRI evidence of any ischemic effects or brainstem infarction in both cases.
Is medulla oblongata rare?
Medulla oblongata (MO) compressing lesions are rare in the literature . Most of the reported cases are due to tumor compressions, while it is less common to find vascular indentation [ 1 ]. Different vascular pathologies were reported such as fusiform aneurysm, a persisting trigeminal artery, a dolichoectasia of the vertebrobasilar arterial system, ...
What is open access?
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author (s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Is medulla oblongata heterogeneous?
Symptomatic medulla oblongata compressing lesions due to dilated vertebral artery are rare in the literature. The symptoms are extremely heterogeneous and not correlated to the severity of compression in many cases.
What happens if you have a stroke of the Medulla Oblongata?
A stroke of the medulla oblongata interferes with vital nerve messages and can result in a number of serious problems, such as paralysis on one or both sides of the body, double vision and coordination problems. 1
Where is the Medulla oblongata located?
Location. The medulla oblongata, also known simply as the medulla, is located at the back and the lower region of the brain, connected to the spinal cord. The area where the medulla oblongata is located is commonly known as the brainstem. The brainstem is composed of three sections: the upper part is called the midbrain, ...
What causes a headache on one side of the body?
Severe headaches that start suddenly and get worse when you change positions, bend, strain, or cough. Among the unique features of a medullary stroke is that it causes numbness and sensory problems on one side of the body, and weakness on the opposite side.
Can a medulla oblongata be diagnosed?
A stroke in the medulla oblongata can be more difficult to diagnose than other strokes due to vague symptoms, such as dizziness, balance problems, and headaches. Usually, a neurologist can identify a medullary stroke during a physical examination, but if the symptoms are mild, then it might not be very apparent in the early stages.
Is a medullary stroke difficult to diagnose?
Medullary strokes and other brainstem strokes are among the most difficult to recognize and diagnose . This can delay your treatment, which may be frustrating for you and your loved ones. The outcome of a medullary stroke can vary- as it is a small region of the brain with many vital functions.
What are the functions of the sphincter?
In addition to connecting sensory and motor messages, it is responsible for many vital involuntary functions including regulating blood pressure, adjusting your heart function, pacing your rate of breathing and coordinating swallowing. Encyclopaedia Britannica / UIG / Getty Images.
What is the upper part of the brain called?
The brainstem is composed of three sections: the upper part is called the midbrain, the middle part is the pons, and the lower part of the brainstem is the medulla. The medulla is located above the spinal cord and below the pons.
What is the function of the Medulla Oblongata?
The medulla oblongata carries signals from the brain to the rest of the body for essential life functions like breathing, circulation, swallowing, and digestion. Making up a tail-like structure at the base of the brain, the medulla oblongata connects the brain to the spinal cord, and includes a number of specialized structures and functions.
Where is the Medulla Oblongata located?
These three collaborating structures are located in front of the cerebellum at the base of the brain and connect to the spinal cord. 1
Which organ is the most complex?
Your Brain Is the Most Complex Organ of Your Body.
Can you test for damage to the medulla?
Detecting damage to the medulla and other parts of the brain stem can be difficult, as people who have injuries here may not be able to fully participate in an examination. The following are a few examples of tests that may be done to determine the level of function in the brainstem.
What is the function of the brainstem?
The brainstem controls the autonomic nervous system, or the functions that the body performs without thought like breathing, maintaining blood pressure and temperature, circulating blood, and digesting.
Can a medulla be damaged?
In cases where the medulla is damaged, the critical functions controlled there may be interrupted, resulting in severe disability or brain death. Without the function of the medulla and the other two areas of the brain stem, survival is not possible. 1

Location
Stroke of The Medulla
- A stroke of the medulla oblongata interferes with vital nerve messages and can result in a number of serious problems, such as paralysis on one or both sides of the body, double vision and coordination problems.1 A stroke involving the medulla can also interfere with your body's normal breathing and heart function. Some people with a medullary stroke may require the use o…
Symptoms of Medullary Stroke
- Stroke symptoms can be hard to recognize. Stroke of the brainstem and medulla may initially cause vague symptoms, such as headaches and dizziness.3 But the symptoms can worsen and the stroke may progress rapidly. Some of the symptoms of a medullary stroke include:4 1. Severe headaches that start suddenly and get worse when you change positions, bend, strain, o…
Risk Factors
- Risk factors for medulla oblongata stroke are the same as the risk factors for strokes in other areas of the brain, including:5 1. High blood pressure 2. Atrial fibrillation and another heart disease 3. Diabetes 4. Blood disorders 5. A family history of stroke 6. Elevated cholesterol and triglycerides 7. Age 8. Ethnicity 9. Illegal drug use 10. Smoking 11. Physical inactivity 12. Hormo…
Diagnosis
- A stroke in the medulla oblongata can be more difficult to diagnose than other strokes due to vague symptoms, such as dizziness, balance problems, and headaches. Usually, a neurologist can identify a medullary stroke during a physical examination, but if the symptoms are mild, then it might not be very apparent in the early stages. Diagnostic testing includes imaging studies suc…
Recovery
- If you have had a medullary stroke, your recovery depends on the size of your stroke and how quickly you were treated, as well as your own rate of healing. Strokes of the medulla oblongata do not affect the language or thinking areas of the brain, and this can make it easier for you to participate more fully in your rehabilitation therapy.6