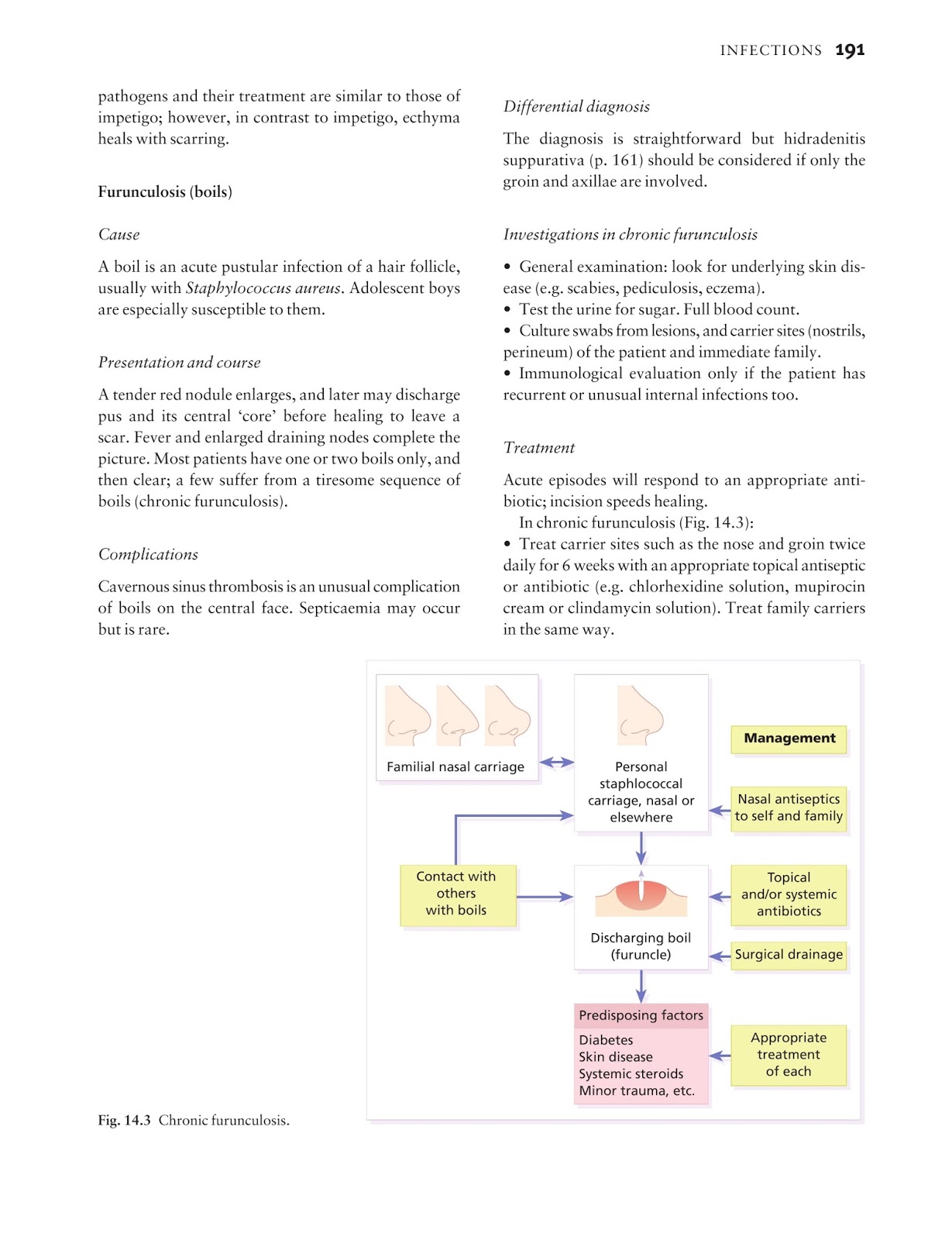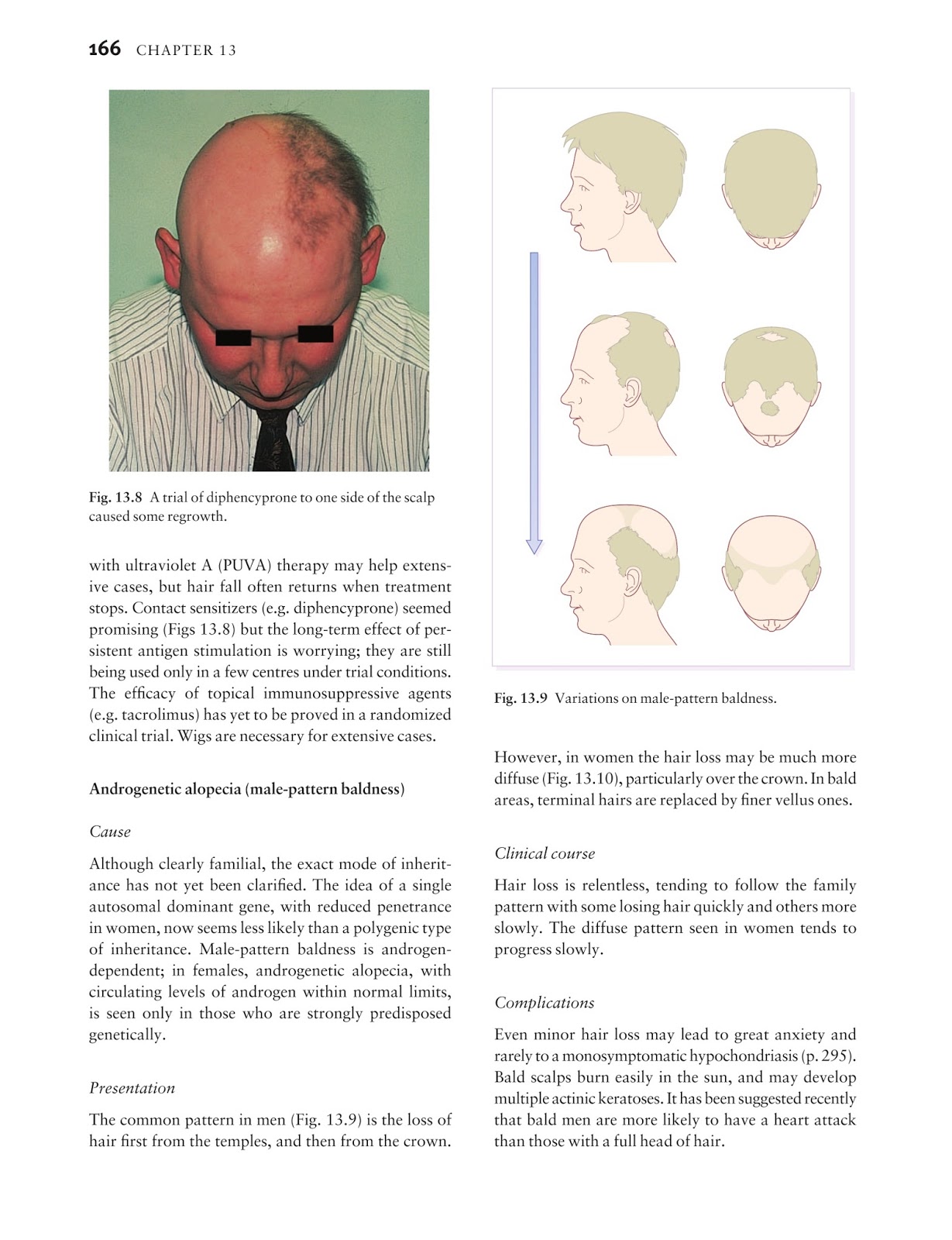
Azithromycin and ceftriaxone offer potential alternatives for penicillin-allergic women, but insufficient data on efficacy limit their use in pregnancy. Ultrasonography provides a noninvasive means to examine pregnant women for signs of fetal syphilis, and abnormal findings indicate a risk for obstetric complications and fetal treatment failure.
What is the role of penicillin allergy in syphilis during pregnancy?
For pregnant persons who report a penicillin or ß-lactam allergy, penicillin allergy is an important consideration in treating syphilis during pregnancy and the potential for group B streptococcal infection and preoperative prophylaxis if a cesarean delivery is required.
What are the treatment options for syphilis caused by penicillin allergy?
However, multiple therapies might be effective for nonpregnant persons with penicillin allergy who have primary or secondary syphilis. Doxycycline (100 mg orally 2 times/day for 14 days) ( 600, 601) and tetracycline (500 mg orally 4 times/day for 14 days) have been used for years and can be effective.
What are the treatment options for penicillin allergy during pregnancy?
Pregnant women who have a history of penicillin allergy should be desensitized and treated with penicillin G. Skin testing or oral graded penicillin dose challenge might be helpful in identifying women at risk for acute allergic reactions (see Management of Persons Who Have a History of Penicillin Allergy).
What are the treatment options for syphilis during pregnancy?
Certain evidence indicates that additional therapy is beneficial for pregnant women to prevent congenital syphilis. For women who have primary, secondary, or early latent syphilis, a second dose of benzathine penicillin G 2.4 million units IM can be administered 1 week after the initial dose ( 641 – 643 ).

How do you treat syphilis if allergic to penicillin?
However, multiple therapies might be effective for nonpregnant persons with penicillin allergy who have primary or secondary syphilis. Doxycycline (100 mg orally 2 times/day for 14 days) (600,601) and tetracycline (500 mg orally 4 times/day for 14 days) have been used for years and can be effective.
What is the best treatment for syphilis during pregnancy?
The current standard of care for the treatment of syphilis acquired during pregnancy is benzathine penicillin G, as a single intramuscular injection of 2.4 million units. Benzathine penicillin G treatment is highly effective.
Can a pregnant woman be treated for syphilis?
Syphilis can be treated effectively with penicillin. Pregnant women with diagnosed syphilis should be treated immediately. Their sex partner(s) should also receive treatment to prevent the mother from becoming re-infected and to improve the health of her partner.
What antibiotics can you take if you are allergic to penicillin and pregnancy?
The treatment during pregnancy is ideally a beta lactam (amoxicillin, penicillin or cephalosporin) with clindamycin as an alternative if the strain is susceptible (1).
When should a pregnant woman be treated for syphilis?
If you think you have syphilis, tell your provider. If you're pregnant, have syphilis and get treated for syphilis before 26 weeks of pregnancy, your baby is probably safe from the infection. Signs and symptoms of syphilis happen over time in stages.
Can I use azithromycin during pregnancy?
Azithromycin and pregnancy Azithromycin is generally thought to be OK to take during pregnancy if you have an infection that needs treatment. However, other antibiotics may be more suitable for you, depending on your type of infection.
Is doxycycline contraindicated in pregnancy?
Doxycycline is not recommended during pregnancy. It can affect tooth and bone development in your baby. Talk to your doctor about taking a different antibiotic.
Is benzathine penicillin safe in pregnancy?
The studies that included pregnant women were conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of benzathine penicillin: no serious adverse reactions were reported among the 1,244 pregnant women included.
What is the drug of choice for syphilis?
What is the treatment for syphilis? A single injection of long-acting Benzathine penicillin G can cure the early stages of syphilis. This includes primary, secondary, or early latent syphilis.
What is the safest antibiotic during pregnancy?
Here's a sampling of antibiotics generally considered safe during pregnancy:Penicillins, including amoxicillin (Amoxil, Larotid) and ampicillin.Cephalosporins, including cefaclor and cephalexin (Keflex)Clindamycin (Cleocin, Clinda-Derm, Clindagel)
Can a pregnant woman take ciprofloxacin?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), ciprofloxacin (500 mg, orally, two times a day for 60 days) is the antibiotic of choice for initial prophylactic therapy among asymptomatic pregnant women exposed to Bacillus anthracis.
Is metronidazole 500mg safe during pregnancy?
Conclusion: During pregnancy, treating bacterial vaginosis and trichomoniasis with metronidazole is effective and offers no teratogen risk. Benefit of metronidazole in the reduction of preterm birth was demonstrated for the combination of this medication with other antibiotics.
Cross-Reactivity with Cephalosporins
Penicillin and cephalosporins both contain a ß-lactam ring. This structural similarity has led to considerable confusion regarding cross-reactivity of these drugs and the risks for allergic reactions from cephalosporins among penicillin-allergic patients.
Validating Penicillin or Another ß-Lactam Antibiotic Allergy
Evaluating a patient who reports a penicillin or another ß-lactam antibiotic allergy involves three steps: 1) obtaining a thorough medical history, including previous exposures to penicillin or other ß-lactam antibiotics ( 658 ); 2) performing a skin test evaluation by using the penicillin major and minor determinants; and 3) among those who have a negative penicillin skin test, performing an observed oral challenge with 250 mg amoxicillin before proceeding directly to treatment with the indicated ß-lactam therapy ( 667, 675 )..
Skin Testing for Penicillin Allergy
Skin testing for penicillin allergy should be performed if any indication exists that the symptoms were secondary to an IgE-mediated hypersensitivity. Testing is also indicated as a potential diagnostic procedure to definitively rule out penicillin allergy and document a negative allergy status in the medical record (i.e., delabeling).
Can you take penicillin for syphilis?
Combinations of some penicillin preparations (e.g., Bicillin C-R, a combination of benzathine penicillin and procaine penicillin) are not appropriate treatments for syphilis, as these combinations provide inadequate doses of penicillin.
Is there a cure for syphilis?
What is the treatment for syphilis? There are no home remedies or over-the-counter drugs that will cure syphilis, but syphilis is easy to cure in its early stages.
Does penicillin kill syphilis?
Treatment will kill the syphilis bacterium and prevent further damage, but it will not repair damage already done. Selection of the appropriate penicillin preparation is important to properly treat and cure syphilis.
Can syphilis be cured?
Syphilis can be cured with the right antibiotics. However, treatment will not undo any damage that the infection has already caused. If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device. Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendations.
Is penicillin G effective for syphilis?
How would you approach the work-up and treatment of a pregnant woman with a history of penicillin allergy who has syphilis? Penicillin G continues to be the only known effective antimicrobial for preventing maternal transmission to the fetus and treating fetal infection.
Can penicillin be used for syphilis?
No proven alternatives to penicillin are available for treatment of syphilis during pregnancy as the alternatives are not safe for the fetus, do not cross the placental barrier or are not efficacious.
Nontreponemal Tests and Traditional Algorithm
False-positive nontreponemal test results can be associated with multiple medical conditions and factors unrelated to syphilis, including other infections (e.g., HIV), autoimmune conditions, vaccinations, injecting drug use, pregnancy, and older age ( 566, 569 ).
Treponemal Tests and Reverse Sequence Algorithm
The majority of patients who have reactive treponemal tests will have reactive tests for the remainder of their lives, regardless of adequate treatment or disease activity. However, 15%–25% of patients treated during the primary stage revert to being serologically nonreactive after 2–3 years ( 570 ).
Cerebrospinal Fluid Evaluation
Further testing with CSF evaluation is warranted for persons with clinical signs of neurosyphilis (e.g., cranial nerve dysfunction, meningitis, stroke, acute or chronic altered mental status, or loss of vibration sense).
Special Considerations
Parenteral penicillin G is the only therapy with documented efficacy for syphilis during pregnancy. Pregnant women with syphilis at any stage who report penicillin allergy should be desensitized and treated with penicillin (see Management of Persons Who Have a History of Penicillin Allergy).
Management of Sex Partners
Sexual transmission of T. pallidum is thought to occur only when mucocutaneous syphilitic lesions are present. Such manifestations are uncommon after the first year of infection.
Treatment
Parenteral penicillin G has been used effectively for achieving clinical resolution (i.e., the healing of lesions and prevention of sexual transmission) and for preventing late sequelae. However, no comparative trials have been conducted to guide selection of an optimal penicillin regimen.
Other Management Considerations
All persons who have primary and secondary syphilis should be tested for HIV at the time of diagnosis and treatment. Those persons whose HIV test results are negative should be offered HIV PrEP.
Follow-Up
Clinical and serologic evaluation should be performed at 6 and 12 months after treatment; more frequent evaluation might be prudent if opportunity for follow-up is uncertain or if repeat infection is a clinical concern. Serologic response (i.e., titer) should be compared with the titer at the time of treatment.
Special Considerations
Data to support use of alternatives to penicillin in treating primary and secondary syphilis are limited. However, multiple therapies might be effective for nonpregnant persons with penicillin allergy who have primary or secondary syphilis.