Treatment for this condition is medical marijuana, herbal supplements, and nutrition-based meals. Other methods are aromatherapy, massages, and acupuncture. Other lung cancers like mesothelioma, which affects the pleura, can cause pain. This condition can result from asbestos inhalation.
- Pain medications. Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs, such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, can help reduce pain from conditions such as costochondritis and minor chest injuries.
- Changing positions. ...
- Breathing more slowly. ...
- Cough suppressants.
How is perceived lung pain treated?
As you can probably guess, treatment of perceived lung pain is highly variable and depends on the diagnosis. For example, if a chest X-ray reveals pneumonia as the culprit behind your pain, your doctor will treat you with one or more antibiotics, rest, and fluids.
How do you get medications to treat chronic lung inflammation?
Medications to treat chronic lung inflammation, such as asthma or COPD, are available by prescription from a doctor. Once you get a prescription, you can visit your local pharmacy to buy your medication. The cost of your medication depends on if you have insurance, the particular pharmacy you visit, days’ supply, and other factors.
What is the treatment for a collapsed lung?
A collection of fluid between the swollen layers, or pleural effusion, can take place, which stops the pain however can result in a collapsed lung. Treatment concentrates on removing the underlying cause and relieving pain. If a large pleural effusion developed, it may have to be drained.
What does it mean when your lungs hurt when you inhale?
Sharp Pain in Lung When Inhaling. Pleurisy. Membranes, or pleura, surround the lungs and line the chest cavity, separating them. Pleurisy results when inflammation develops in between these two layers, the Mayo Clinic explains.
What does it mean when your lungs hurt when you inhale?
Also known as pleurisy, this is an inflammation or irritation of the lining of the lungs and chest. You likely feel a sharp pain when you breathe, cough, or sneeze. The most common causes of pleuritic chest pain are bacterial or viral infections, pulmonary embolism, and pneumothorax.
Why does it hurt when I breathe in deeply?
Pain from taking a deep breath is called pleuritic chest pain or pleurisy. 1 The names come from the membranes lining the lungs, called pleura. The term pleurisy is sometimes used to describe any sharp pain with a deep breath. But it can also be used to describe inflammation of the pleura.
What can I take for hurting lungs?
Anti-inflammatories and pain relievers: available over the counter to help with mild symptoms of lung inflammation, such as fever, body aches, and pain. Examples include acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen and naproxen.
Why does my chest hurt when I take a deep breath Covid?
Myalgia is common during acute viral infections such as COVID and, together with non-specific/non-cardiac pain, may be experienced during the COVID recovery illness. This type of pain can also be associated with trying new exercises (e.g. push ups). This type of pain is sharp and worse on breathing in.
Can pleurisy go away on it's own?
Pleurisy that's caused by bronchitis or another viral infection can resolve on its own, without treatment. Pain medication and rest can help relieve symptoms of pleurisy while the lining of your lungs heals. This can take up to two weeks in most cases. It's important to get medical care if you think you have pleurisy.
What are symptoms of pneumonia with Covid?
If your COVID-19 infection starts to cause pneumonia, you may notice things like: Rapid heartbeat. Shortness of breath or breathlessness. Rapid breathing....You may also have:Fatigue.Chills.Nausea or vomiting.Diarrhea.Belly pain.Muscle or body aches.A headache.Loss of smell or taste.More items...•
What does Covid lung pain feel like?
Even though it's generally mild for some people, the swelling and tightness that results from airway inflammation is essentially like having a sprained windpipe. Think of it like having a sprained ankle, but the effects and discomfort that come with having a sprain are felt inside of your chest.
How do you tell if your lungs are inflamed?
Lung Inflammation SymptomsFeeling tired after physical activity.A general sense of fatigue.Wheezing.Dry or productive (i.e., mucus-producing) cough.Trouble breathing.Chest discomfort or tightness.A sense of lung pain.Gasping for air.
How do you clear your lungs with COVID?
Breathe out fully. Take a small breath in through your mouth, nose or both and hold. On top of the air already in your lungs, take another small breath. Repeat until you feel you cannot take in any more air and hold for 2 to 5 seconds.
Why does it hurt to breathe with COVID?
The most serious cases of COVID-19 involve lung infections where the virus can cause acute respiratory distress syndrome, which can be potentially fatal as it closes off air sacs and causes inflammation of the lungs, making breathing difficult.
How long does COVID chest pain last?
Some people are experiencing chest pain that lasts beyond their initial Covid-19 infection, or that starts in the weeks after they've had the virus. It's important to remember that even if you have had Covid-19 and are now are experiencing chest pain, it may not be related to the virus.
How to treat lung pain?
For example, if a chest X-ray reveals pneumonia as the culprit behind your pain, your doctor will treat you with one or more antibiotics, rest, and fluids . To ease pneumonia-related pain, your doctor may recommend ...
What causes pain in the lungs?
A pulmonary embolus is a life-threatening cause of lung pain that occurs when a blood clot in the legs (called a deep vein thrombosis) breaks off and travels to the lungs. Pain with a pulmonary embolism is sometimes very difficult to distinguish from pain due to other causes, although it is generally sharp and worsened when breathing.
Why is lung pain misnomer?
The term "lung pain" actually is a misnomer, because there are no pain receptors in the lungs, and those in the thorax (the chest cavity) provide the brain with only vague information about the precise location of pain. What may seem to be lung pain may be related to asthma or another pulmonary concern.
What is the pain in the front of the chest?
With this condition, people commonly report stinging, gnawing, or sharp areas of pain on the front of their chest. 7 The pain is reproduced when a doctor presses on them.
What is the pain of pleuritis?
The pain of pleuritis is generally increased with a deep breath and feels sharp rather than dull or achy.
What causes pain in the chest wall?
Fibromyalgia. Fibromyalgia is a central sensitivity syndrome that causes widespread musculoskeletal pain, despite the lack of visible muscle or joint injury or inflammation. Some people with fibromyalgia specifically note tenderness in the chest wall area (tender points), which can be mistaken for lung pain. 8 .
What does it feel like to have a bubble wrap in your chest?
Pneumothorax. A pneumothorax (collapsed lung) may cause pain, usually a sudden sharp chest pain, along with difficulty breathing. 5 In addition, it may be accompanied by crepitus in the chest, a sensation that feels like you have bubble wrap popping under your skin. A pneumothorax may occur for different reasons.
What are the treatments for pneumothorax?
The most common operative therapy options include laser treatment, electrocautery, thoracoscopy, open thoracotomy, and resection of pleura.
What is the space between the chest and the lung called?
The space between your lung and chest cavity is called the pleural space . You develop a pneumothorax when air builds up into this space, and this can lead to a collapsed lung. You develop this problem following an injury that leaves a hole in the pleural space. A disease like emphysema can also cause the same.
What is a PE in a pulmonary artery?
Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Pulmonary embolism is a sudden blockage of an artery in the lungs by a blood clot that traveled from other parts of your body, most commonly from your legs. A blood clot that forms in a vein can break off and travel through the circulation – it is called an embolus.
How do you know if you have pulmonary embolism?
You may also have leg pain, rapid heartbeat, fever, clammy skin, dizziness, and excessive sweating.
What are the symptoms of tension pneumothorax?
In case of tension pneumothorax, you are going to experience chest pain, hypoxia, dyspnea, and hypotension. Some patients may also have symptoms of persistent cough, dysphagia, sore throat, vomiting, and nausea. Diagnosis: Your doctor will consider your medical history and perform physical examination to make a correct diagnosis.
Can emphysema cause shortness of breath?
Symptoms: What you experience depends greatly on whether you have a partial or complete collapse. You may experience shortness of breath with acute chest pain when you have spontaneous pneumothorax.
What to do if chest pain is separated?
If the chest pain is separated (no other symptom) then you may be able to simply call your medical care physician and schedule an appointment soon. Since some of the causes can be life threatening, you shouldn’t wait to obtain medical attention if you feel ill or have any of these disconcerting symptoms.
Why does my lung collapse?
Other causes include autoimmune diseases such as Lupus, injury to the chest, broken ribs, open heart surgery and tuberculosis. A collection of fluid between the swollen layers, or pleural effusion, can take place, which stops the pain however can result in a collapsed lung.
Why does pleurisy hurt?
Membranes, or pleura, surround the lungs and line the chest cavity, separating them. Pleurisy results when inflammation develops in between these two layers, the Mayo Clinic explains. Swelling causes the layers to rub against each other, producing the characteristic sharp pain of pleurisy that happens during breathing. An underlying medical condition, such as the flu, pneumonia or other infection, can cause pleurisy (find out how long does pleurisy last ). Other causes include autoimmune diseases such as Lupus, injury to the chest, broken ribs, open heart surgery and tuberculosis. A collection of fluid between the swollen layers, or pleural effusion, can take place, which stops the pain however can result in a collapsed lung. Treatment concentrates on removing the underlying cause and relieving pain. If a large pleural effusion developed, it may have to be drained.
What causes a pleural collapse?
The collapse can be partial or total, and results when injury or disease, such as emphysema, causes a hole in the pleural area, which then fills with air. A spontaneous pneumothorax can likewise happen, and has no known cause. Symptoms depend on the degree of the collapse, and include shortness of breath, a stabbing pain when breathing, pain in the shoulder or abdomen and a dry, hacking cough. Shock, cardiac arrest and death can result, states the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute.
What is pleuritic pain?
Pleuritic chest pain happens when there is swelling of the pleura (the connective tissue lining of the lung and inside chest wall). The pain is typically referred to as sharp, and increases with deep breathing.
What is a PE in the lungs?
Pulmonary embolism, or PE, is an unexpected obstruction of an artery in the lungs by a blood clot that took a trip from elsewhere in the body, many frequently the legs. A blood clot that forms in a vein and then breaks off and travels through the flow is called an embolus, the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute describes. A PE is a deadly condition. It can cause low oxygen levels in the blood which can harm organs, completely damage part of a lung and cause death if several clots, or a big clot, causes the issue. Symptoms consist of a sharp, stabbing pain in the chest during breathing, shortness of breath and a quick heart rate.
Can pleurisy be idiopathic?
The cause can be idiopathic (unknown), secondary to an infection, autoimmune disease, or potentially a lung embolism. Separated pleurisy that is idiopathic and not due to a harmful illness (such as a lung embolism) can be treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen.
Can I buy medication over the counter?
Yes, some medications to help manage mild symptoms are available over the counter. These include acetaminophen, NSAIDs, common cough and cold products, soothing teas, and more. Be sure to speak with a doctor before taking any OTC products, including supplements, herbs, or vitamins.
How effective are medications?
Medications to treat causes of lung inflammation are effective depending on your specific condition and how soon you receive treatment. For types of chronic lung inflammation, it’s important to take your medication regularly.
Is lung inflammation contagious?
Yes, some causes of lung inflammation are contagious. Infectious causes of lung inflammation from bacteria (pneumonia, tuberculosis) or viruses (influenza, COVID-19) are contagious. Other forms caused by autoimmune or genetic causes of lung inflammation aren’t contagious.
What is the best medicine for pleurisy?
For the pain and inflammation that pleurisy causes, a doctor will recommend nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen. Learn more about pleurisy here.
What is the best treatment for bacterial pneumonia?
For bacterial pneumonia, which is the most common form, antibiotics may help treat the symptoms. Antiviral medications, rest, and a high intake of fluids may help treat pneumonia resulting from a virus. Antifungal medications may help treat fungal types of pneumonia.
What does chest trauma feel like?
Trusted Source. of people who experience physical trauma have chest trauma, with the severity ranging from a rib fracture to injury of the heart. Chest trauma can lead to sharp pain when breathing in. Other symptoms of chest trauma may include: shortness of breath. pain that radiates to the neck or back.
What causes a person to have chest pain when breathing in?
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that causes inflammation of the air sacs, which fill up with fluid or pus. Pneumonia occurs as a result of. Trusted Source. bacterial, viral, or fungal infection. The severity of the condition depends on a person’s age and overall health. People with pneumonia often experience chest pain when breathing in.
What is the pain in the back of the chest?
Costochondritis is an inflammation of the cartilage, a tissue that connects the breastbone and ribs. The chest pain that costochondritis causes can range from mild to severe. People with costochondritis often. Trusted Source. experience chest pain, which may radiate to the back.
What are the symptoms of pleurisy?
Symptoms of pleurisy include: sharp pain in the chest that worsens during breathing. pain that radiates to the shoulders and back. shortness of breath.
What is the inflammation of the pleura?
Pleurisy. Pleurisy is an inflammation of the pleura, a tissue that lines the chest cavity and covers the outside surface of the lungs. Pleurisy often results from viral or bacterial infection, with viral pleurisy being among the most common causes. People with pleurisy tend to experience sharp pain, particularly in the chest, when inhaling.
What is the term for a collapse of the lung?
Pneumothorax is a collapse of part or all of a lung which can trigger severe chest pain and shortness of breath. Pneumothorax is a common complication of emphysema and other lungs diseases. Pulmonary embolism is a potentially life-threatening condition in which a clot in a vein will break off and travel to the lungs.
What does it mean when you take a deep breath?
If you are having pain with breathing, whether normal breathing or when taking a deep breath, you’re likely feeling worried. Doctors describe the kind of pain that occurs with taking a deep breath as either pleuritic chest pain or pleurisy. 1 The name is derived from the membranes lining the lungs known as pleura .
What is the cause of pleuritic pain?
Pneumonia is an infection in the lungs that may be bacterial, viral, or fungal. Viral infections can often cause pleuritic pain. 1 These include the Coxsackie virus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), influenza, parainfluenza, the novel coronavirus (COVID-19), mumps, adenovirus, cytomegalovirus (CMV), and the Epstein Barr virus (EBV).
Why does my pleura hurt?
Lung-Related Causes. While the lungs themselves do not have pain receptors, medical conditions involving the lungs can cause pain in several ways, including those that cause irritation of the pleura. Some of these include: Pneumonia is an infection in the lungs that may be bacterial, viral, or fungal. Viral infections can often cause pleuritic ...
What is pleurisy pain?
The term pleurisy is sometimes used to describe any sharp pain that occurs with a deep breath, but can also be used to describe inflammation of the pleura. Pleuritic pain may be triggered by any number of disorders, diseases, or injuries involving the lungs, pleura, or associated tissues or organs, including: ...
What causes pleural effusion?
Pleural effusion is the accumulation of fluid between the layers of the pleura and may be caused by any number of diseases, including lung disease, heart disease, and autoimmune disorders (like rheumatoid arthritis).
What is the pain of a pleuritic?
Wheezing. Pain spreading the back or shoulder. Fever and/or body chills. Pleuritic pain may occur only with breathing or be omnipresent but worsen while taking a breath. Pleuritic pain tends to be sudden, sharp, stabbing, and intense.
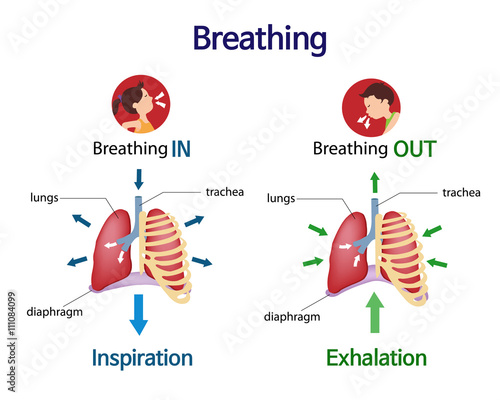
How many times do you inhale and exhale?
Every minute we inhale and exhale anywhere between 12 to 20 times and this respiration rate varies by age and level of physical activity.
Why does my breathing hurt?
Ask a Doctor Online Now! Infections are also among the more common causes of painful breathing. Bronchitis, pneumonia, pleuritis, tuberculosis (pulmonary TB), psittacosis and other viral, bacterial and fungal lung diseases often present with pain when breathing.
What muscles are involved in respiration?
The main respiratory muscle is the diaphragm which is a large muscle sheet that sits below the lungs. The intercostal muscles between the ribs are the other important respiratory muscles. The diaphragm also separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity. When it contracts, it flattens and the negative pressure around the lungs causes it to expand. In fact the entire chest wall an expand to some extent. The lung tissue is highly elastic to inflate in this way. When the diaphragm relaxes, the lungs recoil and air is pushed out. Sometimes accessory muscles of respiration on the chest wall and neck also aid with inspiration and expiration.
What is flail chest?
A flail chest is where a portion of the ribcage breaks away from the rest of the chest wall. It is more likely to occur from motor vehicle collisions. Some bone and joint conditions may cause painful breathing despite there not being a fracture.
What causes a chest wall to hurt?
A blow to the chest, soreness of the muscles and sometimes even very tight clothing are common causes of chest wall injury. These injuries can also lead to broken bones like a fractured rib which causes intense pain. Trauma may also extend to the tissue of the airways and lungs.
Where does pain come from when breathing?
Most causes of pain during breathing arises from the airways, lungs, other organs of the chest cavity of chest wall.
How does air travel through the lungs?
In the lungs, oxygen from the air is absorbed and carbon dioxide from the bloodstream is then passed out. The air then travels back out through the way it came. In order for this to happen, the respiratory muscles have to expand and contract the chest cavity around the lungs. It is important to understand how air flows through the airways and lungs, as well as the structures involved in this process to have a better understanding of where pain may be arising.
Why does smoking cause shortness of breath?
Shortness of breath. Injury to your respiratory tract decreases oxygen delivery to your blood. Smoke inhalation can interfere with your blood’s ability to carry oxygen. Rapid breathing can result from an attempt to compensate for the damage done to the body.
What happens when you breathe in smoke?
Inhaling harmful smoke can inflame your lungs and airway, causing them to swell and block oxygen. This can lead to acute respiratory distress syndrome and respiratory failure.
What to do if you have smoke inhalation?
If you or someone else has been in a fire and exposed to smoke or showing signs of smoke inhalation, such as trouble breathing, singed nostril hair, or burns, call 911 for immediate medical care.
What does it mean when you have soot in your throat?
Soot in the nose or throat. Soot in your nostrils or throat are an indicator of smoke inhalation and the extent of the smoke inhalation. Swollen nostrils and nasal passages are also a sign of inhalation.
What is the purpose of blood tests?
A series of blood tests, including a complete blood count and metabolic panel , are used to check red and white blood cell counts, platelet counts, as well as the chemistry and function of many organs that’re sensitive to changes in oxygen levels. Carboxyhemoglobin and methemoglobin levels are also checked in those who’ve inhaled smoke to look for carbon monoxide poisoning.
How does smoke affect oxygen?
There are two ways that smoke can deprive you of oxygen. Combustion uses up the oxygen near a fire, leaving you without oxygen to breathe. Smoke also contains products, such as carbon dioxide, that cause harm by further limiting the amount of oxygen in the air.
What is the best treatment for smoke inhalation?
Medication. Certain medications may be used to treat the symptoms of smoke inhalation. Bronchodilators may be given to relax lung muscles and widen airways. Antibiotics may be given to treat or prevent an infection. Other medications may be given to treat any chemical poisoning.