If the disorder starts during pregnancy; lithium, lamotrigine or second generation antipsychotic drugs are suitable alternatives. In general, drugs used during pregnancy can also be used in the postpartum period, although some require special precautions if the mother wishes to breast-feed.
What bipolar medications are safe during pregnancy?
Aug 23, 2018 · Treatment of bipolar disorder frequently includes mainstay treatment with mood stabilizers such as sodium valproate, lithium, lamotrigine, and second-generation atypical antipsychotics. While we have robust information regarding the reproductive safety of sodium valproate, it is a teratogen with a very high risk for neural tube defects.
Is it safe to take bipolar medication during pregnancy?
Dec 24, 2014 · Lithium, quetiapine, and other selected atypical antipsychotic drugs may be considered as second-line agents; however, it is generally best to use medications that have resulted in clinical improvement and stability.243 It is also generally prudent to monitor mood-stabilizer levels, including lithium and lamotrigine, throughout pregnancy, since maternal drug …
How to manage bipolar disorder during pregnancy?
You may also consider: electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) regular exercise to naturally boost serotonin, the “feel-good” hormone talk therapy cognitive behavioral therapy support groups omega-3 fatty acids, like flax seed in addition to eating a couple of servings a week of low-mercury fish plant-based ...
What you should know about bipolar disorder and pregnancy?
Yet there is paucity of data on the acute, and maintenance treatment of major depressive episodes during pregnancy in women with BP II and BP NOS. And there are no psychopharmacological studies on the acute or maintenance treatment of bipolar postpartum depression to guide clinical decision making. Also, there is a lack of screening instruments …

What medication can you take for bipolar while pregnant?
- Lithium;
- Antiepileptic medications including carbamazepine, lamotrigine, and valproic acid; and.
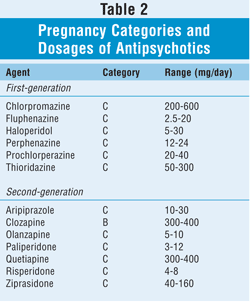
- Atypical antipsychotic medications: aripiprazole, olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone, and ziprasidone.
How is bipolar treated during pregnancy?
Which is the safest mood stabilizer during pregnancy?
Can I take mood stabilizers while pregnant?
Is trileptal safe during pregnancy?
Does pregnancy make bipolar worse?
Is latuda safe while pregnant?
Can you have a baby if you have bipolar?
What pregnancy category is latuda?
This drug should be used during pregnancy only if the benefit outweighs the risk to the fetus. US FDA pregnancy category: Not assigned.Jan 26, 2022
Is Abilify safe during pregnancy?
What is bipolar disorder?
Bipolar disorders, including bipolar I disorder, bipolar II disorder, and bipolar disorder not otherwise specified, are serious, chronic psychiatric illnesses characterized by alternating episodes of mania or hypomania and major depression, or mixtures of manic and depressive features. 1 They represent a spectrum of illnesses characterized by frequent relapses, symptom recurrences, and persisting residual symptomatology. 2 Bipolar disorders have major adverse clinical, social, and economic effects that often interfere with the patient’s ability to work and function normally in other instrumental life roles and in social relationships. 3 – 7 The annual incidence of bipolar disorders ranges from three to ten cases per 100,000 population, 8 with an estimated lifetime prevalence of 3%–7%. 9 – 11
Is postpartum depression a recurrent episode?
Several studies have identified the postpartum period as being one of high risk for first-onset and recurrent depressive, man ic, mixed, and psychotic episodes in women with bipolar disorders. 36 – 40 Large increases in rates of psychiatric hospitalization within the first few weeks postpartum have also been observed in cohorts of women with bipolar disorder diagnoses. 36, 37, 41, 42 Bipolar women have at least a one in four risk of suffering a severe recurrence following delivery, including perhaps an even higher risk if there is a family history of postpartum psychosis or a previous history of a severe postpartum bipolar mood episode. 43
Does bipolar affect the offspring?
Previous research has also shown that the offspring of women with bipolar disorder have increased rates of neurocognitive and psychiatric impairment. In a cohort study of 117 offspring (ages 4–18 years) of 88 parents with bipolar disorder (high-risk youth) and 171 offspring of parents without a major affective disorder (control youth), high-risk youth had significantly increased rates of affective, anxiety, and disruptive behavioral disorders, memory and attention disturbances, and impaired social functioning than control youth. 33 These findings have been confirmed in other cohort studies of young offspring of parents with bipolar disorder. 34, 35
Is bipolar disorder a risk factor for pregnancy?
A diagnosis of bipolar disorder has been associated with a slight but statistically significant increase in the risk of several pregnancy complications in observational studies. For example, data from an Australian psychiatric case registry (1980–1992) were used to compare rates of pregnancy, delivery, and neonatal complications among 3,174 deliveries to women with diagnosed schizophrenia, major depression, and bipolar disorder (1,301 births among 763 mothers), using a control sample of 3,129 births to women without a psychiatric diagnosis. 30 Compared to control mothers, mothers with bipolar disorder were at significantly higher risk of experiencing placental abnormalities, antepartum hemorrhages, and toxicities related to alcohol, tobacco, and illicit-substance use. In a large-scale observational study using the Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database, a diagnosis of bipolar disorder was associated with significantly higher likelihood of low birth weight, preterm birth, and smallness for gestational age delivery compared with absence of a psychiatric diagnosis. 31 Combined data from three nationwide Swedish registers (including 332,137 women with two or more recorded diagnoses of bipolar disorder) showed that both treated and untreated women with bipolar disorder had higher risk of cesarean delivery and preterm delivery, while untreated women had a higher risk of delivering babies with a small head circumference and neonatal hypoglycemia compared with control women with no history of psychiatric illness. 32 Regardless of treatment status, rates of smoking, overweight, and substance abuse were significantly higher among women with a diagnosis of bipolar disorder compared with control women. In this study, drug exposures to lithium, valproate, carbamazepine, lamotrigine, or antipsychotic drugs were considered in aggregate based on filled prescriptions; the effects of individual agents were not studied.
Can bipolar be cured?
Although bipolar disorders cannot be cured, they can generally be managed in both acute exacerbations and in maintenance treatment with appropriate pharmacotherapy, including mood stabilizers, selected antipsychotic medications, or combinations of these. 12 The overarching goal of treatment is to achieve or maintain a euthymic mood state and maximize daily functioning in all important life domains. 13 However, the longitudinal course of bipolar disorders is marked by frequent relapses, particularly when effective pharmacotherapy is discontinued. 14 – 16 As such, long-term treatment with mood-stabilizing medications is typically required. 17
Does ECT affect pregnancy?
Although not recommended as a stand-alone treatment, empirically supported psychotherapy has no known risks of for bipolar disorders during pregnancy. Antenatal administration of ECT has not been consistently associated with adverse effects on pregnancy or neonatal outcome in pregnant women or neonates. 198 – 200 Sporadic cases of major malformations have been reported, with no clear pattern of malformations emerging. 198 Although data are limited, drugs that are commonly used for anesthesia (methohexital, propofol), neuromuscular blockade (succinylcholine), and prevention of clinically significant bradycardia during the stimulation phase of ECT (glycopyrrolate) are not considered major human teratogens. 201 Low rates of fetal bradycardia were reported in a systematic review of 339 cases summarizing outcomes of ECT administered during pregnancy. 199
Is lithium safe for babies?
Early retrospective studies of the reproductive safety of lithium were derived mainly from the International Register of Lithium Babies, which was initiated in the late 1960s by clinical investigators from North America, Australia, and Europe. Early studies suggested that fetal exposure to lithium was associated with as high as a 400-fold increase in the risk of congenital heart defects. 91 – 93 These included cases of Ebstein’s anomaly, a very rare congenital heart defect characterized by apical displacement of the septal and posterior leaflets of the tricuspid valve, variable malformation and/or displacement of the anterior leaflet, and an unfavorable prognosis for cases presenting during infancy. 94 The final updated summary of data from the registry included a total of 25 congenital malformations occurring among 225 births (11.1%), 18 of which were cardiovascular malformations, including six cases of Ebstein’s anomaly. 91 However, these data were insufficient to quantify rates of congenital malformation risk with in utero exposure to lithium, because registry data were based on voluntarily contributed cases.
What to consider when having a baby with bipolar?
If you have BD and plan to have a baby, you and your doctor will consider your overall well-being along with: how well your bipolar disorder is managed. what medications you’re currently taking. the severity of your symptoms. Potential risks to your baby are also considered.
What is bipolar disorder?
Bipolar disorder (BD), previously called manic depressive disorder, is one of the most difficult mental health conditions to treat. People with BD have significant mood changes that include manic (high) and depressive (low) episodes. People with BD may be hesitant to experience major life changes, including pregnancy.
How many women have postpartum psychosis?
Postpartum psychosis is a rare, but serious condition that requires emergency treatment. It affects about 1 in 1,000 women. Symptoms include severe mania or depression that starts within two to three days after delivery. Hallucinations and delusions are also common with this type of postpartum mental illness. This can be extremely dangerous for both mother and baby.
How does pregnancy affect mental health?
Effects of pregnancy on mental health. Pregnancy involves hormonal changes that can affect your mood. Some days, you might feel on top of the world. On other days, you might feel irritable and down. BD symptoms can become more prominent during pregnancy. This is also true with other types of mental health issues.
How to naturally boost serotonin?
regular exercise to naturally boost serotonin, the “feel-good” hormone. talk therapy. cognitive behavioral therapy. support groups. omega-3 fatty acids, like flax seed in addition to eating a couple of servings a week of low-mercury fish.
Can you stop taking BD medication while pregnant?
You, your doctor, and obstetrician might decide to cease medications during pregnancy, at which time you’ll need to rely on other forms of treatment for bipolar disorder, such as self-care, and psychotherapy. Continuing BD treatment during pregnancy may decrease the risk.
Can bipolar affect a fetus?
Effects of mood disorders on fetuses. It’s not clear how bipolar disorder itself can affect fetal development. There’s a chance that BD may be passed on to your child, but this isn’t an immediate concern during pregnancy. Scientists are still investigating the genetic relationship to bipolar disorder.
What is the best medication for bipolar disorder?
Some medications used to treat Bipolar disorder are: Lithium: Lithium is a common medication used to treat Bipolar disorder. There is very little risk to the fetus when Lithium levels are monitored closely. Mothers who are on other Bipolar medications may be switched to Lithium during pregnancy. Hydration is very important when taking Lithium ...
How soon after conception can you get bipolar?
About 12 weeks after conception, there is a very good chance of a Bipolar event. Mom needs to watch her symptoms closely and write down every feeling she has from the first moments she finds out she is pregnant. This can help her to establish a pattern and possibly head off a manic or depressive episode.
What is bipolar disorder?
Bipolar disorder is a mental disorder that causes mood swings which alternate from high or manic states to low or depressive states. There are two different types of Bipolar disorder; Type I Bipolar and Type II Bipolar. Type I Bipolar is a more severe form of the disorder with worsened periods of mania and depression.
What to do if pregnancy test comes back positive?
Once the pregnancy test has come back positive, the first doctor to call is the psychiatrist to make sure any medications that mom may be taking are safe for her baby. There will be an emergency appointment to determine the best medications and treatment plans to keep both baby and mom safe.
What can a psychiatrist do to help a mom?
If a plan is established early on, the psychiatrist can place the mom-to-be on medications that are less likely to affect a baby and also help prepare her for the mental changes that will occur during the pregnancy and delivery.
Can a psychologist help with bipolar?
A psychologist may be able to discuss problems associated with Bipolar disorder that can occur during pregnancy and affect your mental health. Although the psychologist will not be able to prescribe medication, talk therapy can help to even out the emotional ups and downs associated with the disease.
Is Depakote safe for pregnancy?
Depakote: Depakote is an anti-seizure medication that is prescribed as a mood stabilizer for people with Bipolar disorder. Depakote is not safe during pregnancy. The medication can have developmental effects on the head and face of the baby. Many psychiatrists will switch the mom to another medication during pregnancy.
How many times does bipolar affect pregnancy?
Bipolar symptoms throughout 40% of the pregnancy -- or more than four times that of women who continued their bipolar medications
How long does it take for bipolar to recur?
A 50% risk of recurrence within just two weeks, if they stopped suddenly.
What are the risks of untreated bipolar disorder?
Heart defects. Developmental delay or neurobehavioral problems. However, you must weigh these risks against the risks of untreated bipolar disorder. Untreated depression, for example, has been linked in some studies with low birth weight, or possible negative effects on developing brain structures in the baby.
What is the best treatment for mania?
Antipsychotic medications. Antipsychotic medications can be used during acute treatment of mania, especially to manage delusions or hallucinations. Some medicines in this family also have become standard first-line treatments for acute bipolar depression. Examples of newer antipsychotics include:
How much does lithium reduce relapse rate?
And when lithium is continued after childbirth, it can reduce the rate of relapse from 50% to 10%. To reduce its risks to you and your child: Drink plenty of water and maintain normal salt intake to prevent lithium toxicity. Have your lithium levels checked regularly.
How to prevent premature contractions?
Encourage you to eat well and drink plenty of water to help prevent premature contractions.
Do you have bipolar and want to get pregnant?
Do you have bipolar disorder and want to become pregnant or are pregnant already? Perhaps you have bipolar disorder and do not want a pregnancy. Be sure to talk with both your obstetrician and psychiatrist about the risks and benefits of bipolar medications and forms of birth control. For some women, a contraceptive injection that is only needed every few months is best.
How much chance of passing bipolar disorder to child?
The chance of passing bipolar disorder to your child is 10% if one parent has bipolar disorder but goes up to 40% if it’s both parents.
What is reproductive psychiatry?
A reproductive psychiatrist will see you through preconception, pregnancy, postpartum, and lactation, providing full-service mental health support, and can also care for women with infertility and those who experience a miscarriage.
How many women get pregnant after stopping birth control?
It’s impossible to know exactly when you may become pregnant—in fact, 1 in 5 women get pregnant within a month of stopping birth control. So, keep using contraception until you have a real plan in place. If you are pregnant now—please talk to your doctor right away—don’t stop taking medication without speaking with your healthcare providers.
Can bipolar disorder cause mood swings?
Bipolar disorder comes with its own unique challenges that include mood swings as a result of hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy.”. Below, Dr. Momodu shares 5 tips and pro-active steps to take if you have bipolar and want to have a baby.
Can you have children with bipolar?
Momodu, MD, MPH, MBA, Chairman, Department of Psychiatry at AtlantiCare Regional Medical Center, who shared some key insights with us. “The decision to have children while suffering from bipolar disorder should not be taken lightly. Bipolar disorder comes with its own unique challenges that include mood swings as a result of hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy.”
Can you take mood stabilizers while pregnant?
As a result, some people choose not to take mood-stabilizing medications while pregnant. But here’s the downside: not taking medications during pregnancy could lead to a relapse of your condition. And even on medication, there is an increase in relapse during pregnancy and the postpartum period.
Can you relapse after delivery?
After delivery, taking care of a newborn could be stressful and could increase the chance of a relapse. Even with medication, you have an increased risk of relapse during the postpartum period, according to the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Can you take lithium while pregnant?
There are limited data to recommend discontinuing lithium, lamotrigine, or carbamazepine during pregnancy. Valproic acid is not recommended during pregnancy due to increased odds of neural tube defects associated with its use.
Is bipolar disorder a pregnancy disorder?
Bipo lar Disorder in Pregnancy: A Review of Pregnancy Outcomes. The knowledge of benefits and risks of bipolar disorder and its treatment can help women and health care providers make individualized decisions.
Can a prenatal care provider discuss the evidence about safety of medications used to treat bipolar disorder with women in collaboration
Prenatal care providers can discuss the evidence about safety of medications used to treat bipolar disorder with women in collaboration with their mental health care providers. In addition, women being treated for bipolar disorder require close monitoring for depressive and manic/hypomanic episodes that impact pregnancy outcomes.